集合框架
集合和数组的区别
- 数组的长度是固定的,集合的长度是可变的
- 数组中存储的是同一类型的元素,可以存储基本数据类型的值;集合存储的都是对象,而且对象的类型可以不一致
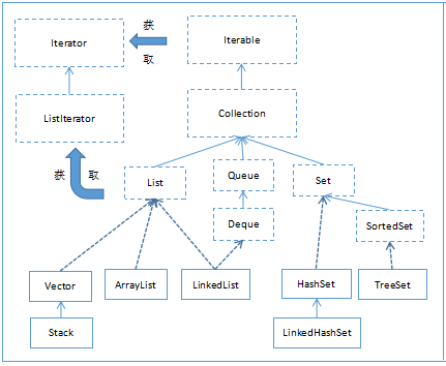
Collection集合体系
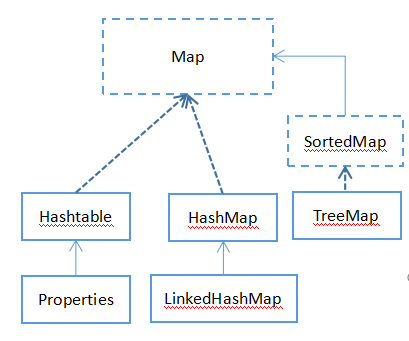
Map集合体系
Collection常用功能
添加元素
- add(E obj)
- addAll(Collection<? extends E> other)
删除元素
- boolean remove(Object obj)
- boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll)
判断元素
- boolean isEmpty()
- boolean contains(Object obj)
查询
- int size()
- Object[] toArray()
Iterator迭代器
public class IteratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用多态方式 创建对象
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();
// 添加元素到集合
coll.add("串串星人");
coll.add("吐槽星人");
coll.add("汪星人");
//遍历
//使用迭代器 遍历 每个集合对象都有自己的迭代器
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator();
// 泛型指的是 迭代出 元素的数据类型
while(it.hasNext()){ //判断是否有迭代元素
String s = it.next();//获取迭代出的元素
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}使用Iterator迭代器删除元素
既然Collection已经有remove(xx)方法了,为什么Iterator迭代器还要提供删除方法呢?
因为Collection的remove方法,无法根据条件删除
@Test public void test02(){ Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>(); coll.add("陈琦"); coll.add("李晨"); coll.add("邓超"); coll.add("黄晓明"); //删除名字有三个字的 //coll.remove(o)//无法编写 Iterator<String> iterator = coll.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ String element = iterator.next(); if(element.length()==3){ //coll.remove(element);//错误的 iterator.remove(); } } System.out.println(coll); }
增强for
JDK1.5以后出来的一个高级循环,专门用来遍历数组和集合
只能用来遍历元素,不能再遍历过程中进行增删操作
public class NBForDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {3,5,6,87}; //使用增强for遍历数组 for(int a : arr){//a代表数组中的每个元素 System.out.println(a); } } }public class NBFor { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>(); coll.add("小河神"); coll.add("老河神"); coll.add("神婆"); //使用增强for遍历 for(String s :coll){//接收变量s代表 代表被遍历到的集合元素 System.out.println(s); } } }
快速失败机制
- 使用foreach或Iterator遍历集合时,如果集合发生了修改,就会抛 ConcurrentModificationException异常
快速机制的实现
- 在ArrayList等集合类中都有一个modCount变量。它用来记录集合的结构被修改的次数。
- 当我们给集合添加和删除操作时,会导致modCount++。
- 然后当我们用Iterator迭代器遍历集合时,创建集合迭代器的对象时,用一个变量记录当前集合的modCount。例如:
int expectedModCount = modCount;,并且在迭代器每次next()迭代元素时,都要检查expectedModCount != modCount,如果不相等了,那么说明你调用了Iterator迭代器以外的Collection的add,remove等方法,修改了集合的结构,使得modCount++,值变了,就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException
List集合
List接口的特点
- 元素有序,可以重复
List接口中常用方法
- 添加元素
- void add(int index, E ele)
- 获取元素
- E get(int index)
- List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
- 获取元素索引
- int indexOf(Object obj)
- int lastIndexOf(Object obj)
- 删除和替换元素
- E remove(int index)
- E set(int index, E ele)
List的实现类
ArrayList集合
- 数组结构,元素增删慢,查找快
- 日常开发中多用来查询数据、遍历数据
- 线程不安全
LinkedList集合
- 链表结构,方便元素添加、删除
- 双向列表
ListIterator
继承了Iterator接口,提供了专门操作List的方法
public static void main(String[] args) { List<Student> c = new ArrayList<>(); c.add(new Student(1,"张三")); c.add(new Student(2,"李四")); c.add(new Student(3,"王五")); c.add(new Student(4,"赵六")); c.add(new Student(5,"钱七")); //从指定位置往前遍历 ListIterator<Student> listIterator = c.listIterator(c.size()); while(listIterator.hasPrevious()){ Student previous = listIterator.previous(); System.out.println(previous); } }
ArrayList源码分析
JDK1.8
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;//初始化为空数组
}
public boolean add(E e) {
//查看当前数组是否够多存一个元素
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//存入新元素到[size]位置,然后size自增1
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//如果当前数组还是空数组
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//那么minCapacity取DEFAULT_CAPACITY与minCapacity的最大值
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
//查看是否需要扩容
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;//修改次数加1
// 如果需要的最小容量 比 当前数组的长度 大,即当前数组不够存,就扩容
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;//当前数组容量
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);//新数组容量是旧数组容量的1.5倍
//看旧数组的1.5倍是否够
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//看旧数组的1.5倍是否超过最大数组限制
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
//复制一个新数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}Set集合
- set集合不允许包含相同元素
- 支持使用foreach和Iterator遍历
HashSet
- 底层是HashMap
TreeSet
底层是TreeMap,基于红黑树实现
把一个对象添加到TreeSet时,该对象的类必须实现Comparable接口
对于TreeSet而言,判断两个对象相等的唯一标准是:两个对象通过compareTo方法比较返回值是0
@Test public void test1(){ TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<>(); set.add("zhangsan"); //String它实现了java.lang.Comparable接口 set.add("lisi"); set.add("wangwu"); set.add("zhangsan"); System.out.println("元素个数:" + set.size()); for (String str : set) { System.out.println(str); } }如果没有实现Comparable接口,则要单独指定Comparator比较器
@Test public void test3(){ TreeSet<Student> set = new TreeSet(new Comparator<Student>(){ @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return o1.getId() - o2.getId(); } }); set.add(new Student(3,"张三")); set.add(new Student(1,"李四")); set.add(new Student(2,"王五")); set.add(new Student(3,"张三风")); System.out.println("元素个数:" + set.size()); for (Student stu : set) { System.out.println(stu); } }

