Map集合概述
- 元素成对存在,由键值对组成
- 值可以重复,键不能重复
- 每个键只能对应一个值,可以是单个值,也可以是一个数组或集合
Map常用方法
添加
- V put(K key,V value)
- 若指定的键(key)在集合中存在,则返回值为集合中键对应的值(该值为替换前的值),并把指定键所对应的值,替换成指定的新值
删除
- void clear()
- V remove(Object key)
查询
- V get(Object key)
- boolean containsKey(Object key)
- boolean containsValue(Object value)
- boolean isEmpty()
元视图操作方法
- Set
keySet() - Collection
values() - Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
其他方法
- int size()
Map集合的遍历
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("许仙", "白娘子");
map.put("董永", "七仙女");
map.put("牛郎", "织女");
map.put("许仙", "小青");
System.out.println("所有的key:");
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key);
}
System.out.println("所有的value:");
Collection<String> values = map.values();
for (String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println("所有的映射关系");
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String,String> entry : entrySet) {
// System.out.println(entry);
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"->"+entry.getValue());
}
}
}Map的实现类
HashMap 和 Hashtable
- 都是哈希表
- 作用键的对象必须实现hashCode方法和equals方法
- Hashtable是线程安全的,HashMap是线程不安全的
TreeMap
基于红黑树实现
package com.atguigu.map; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeMap; import org.junit.Test; public class TestTreeMap { @Test public void test1() { TreeMap<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(); map.put("Jack", 11000); map.put("Alice", 12000); map.put("zhangsan", 13000); map.put("baitao", 14000); map.put("Lucy", 15000); //String实现了Comparable接口,默认按照Unicode编码值排序 Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) { System.out.println(entry); } } @Test public void test2() { //指定定制比较器Comparator,按照Unicode编码值排序,但是忽略大小写 TreeMap<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2); } }); map.put("Jack", 11000); map.put("Alice", 12000); map.put("zhangsan", 13000); map.put("baitao", 14000); map.put("Lucy", 15000); Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) { System.out.println(entry); } } }
Properties
Hashtable的子类,可以保存在流中或从流中加载
public static void main(String[] args) { Properties properties = System.getProperties(); String p2 = properties.getProperty("file.encoding");//当前源文件字符编码 System.out.println(p2); }
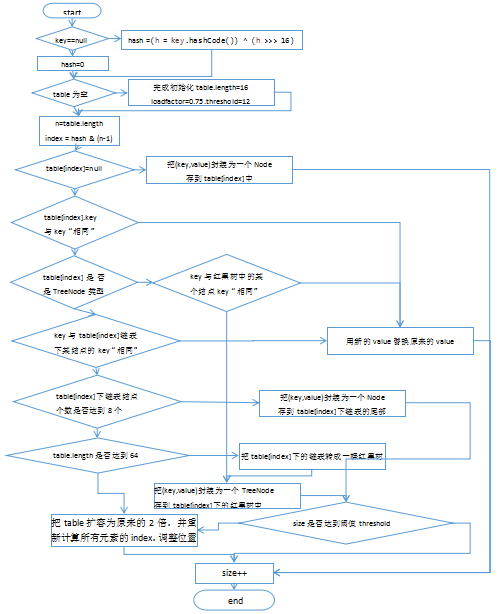
HashMap源码分析
JDK1.8
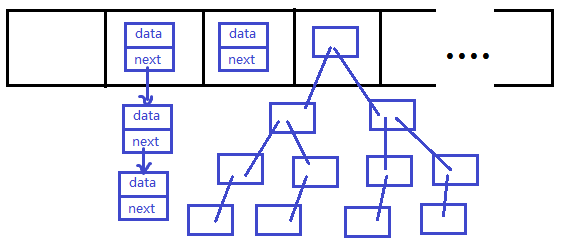

put方法源码分析
关于映射关系的key是否可以修改
- 如果已经put到Map中的映射关系,再修改key的属性,而这个属性又参与hashcode值的计算,那么会导致匹配不上原来的hash值
- 所以实际开发中,经常选用String,Integer等作为key,因为它们都是不可变对象
集合框架
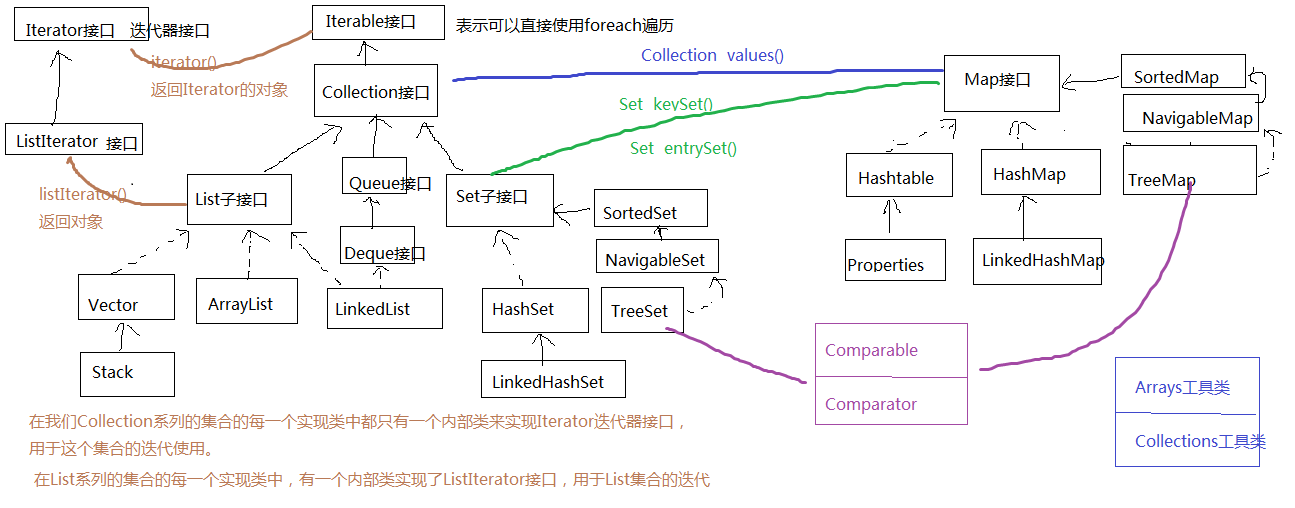
Collections工具类
- 参考数组的工具类:Arrays
- public static void shuffle(List<?> list) List 集合元素进行随机排序,类似洗牌
- public static void reverse(List<?> list)反转指定列表List中元素的顺序
- public static int frequency(Collection<?> c,Object o)返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数

