IDEA常用快捷键
万能提示:Alt + 回车
使用xx块环绕:Ctrl + Alt + T
向下插入一行: Shift + 回车
向上插入一行:Ctrl + Alt + 回车
复制行:Ctrl + D
删除行:Ctrl + Y
单行注释:Ctrl + /
多行注释:Ctrl + Shift + /
搜索: Ctrl + n
类的定义
public class Person {
//成员变量
String name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
boolean isMarried;
public void walk(){
System.out.println("人走路...");
}
public String display(){
return "名字是:" + name + ",年龄是:" + age + ",Married:" + isMarried;
}
}对象的创建
class Student{ //一个文件中只能有一个public类
}
public class TestStudent{
//Java程序的入口
public static void main(String[] args){
//对象名中存储的是对象的地址
System.out.println(new Student());//Student@7852e922
Student stu = new Student();
System.out.println(stu);//Student@4e25154f
int[] arr = new int[5];
System.out.println(arr);//[I@70dea4e
}
}成员变量
成员变量的分类
- 成员变量分为实例变量和类变量
- 实例变量也叫对象属性,是属于某个对象的,通过对象来调用
- 类变量是属于整个类的,用static修饰,通过类名直接调用
实例变量的内存图
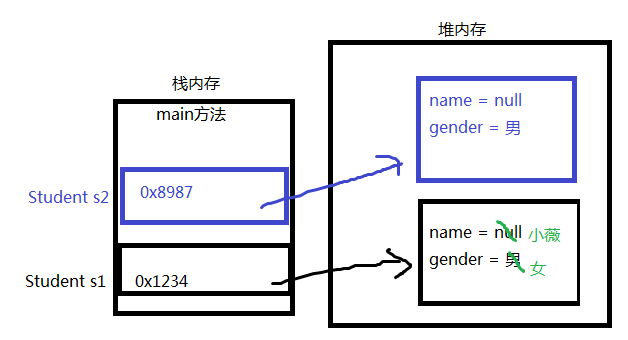
class Student{
String name;
char gender = '男';//显式赋值
}
class TestStudent{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println("姓名:" + s1.name);//null
System.out.println("性别:" + s1.gender);//男
s1.name = "小薇";
s1.gender = '女';
System.out.println("姓名:" + s1.name);//小薇
System.out.println("性别:" + s1.gender);//女
Student s2 = new Student();
System.out.println("姓名:" + s2.name);//null
System.out.println("性别:" + s2.gender);//男
}
}
实例变量和局部变量的区别
- 定义的位置不同
- 实例变量:类中,方法外
- 局部变量:方法中或者方法声明上
- 作用范围不一样
- 实例变量:类中
- 局部变量:当前方法的作用域中
- 初始化值不同
- 实例变量:有默认值
- 局部变量:没有默认值,必须先定义,赋值,后使用
- 在内存中的位置不同
- 实例变量:堆内存
- 局部变量:栈内存
- 生命周期不同
- 实例变量:随着对象的创建而存在,对象的小时而消失
- 局部变量:随着方法的调用而存在,方法调用完即消失
成员变量的练习
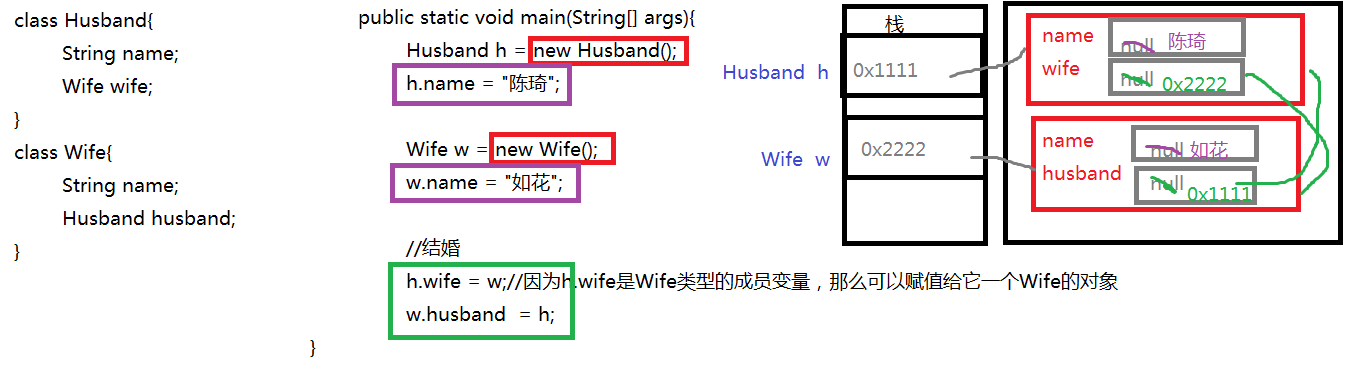
public class Field_Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建丈夫对象
Husband husband = new Husband();
//创建妻子对象
Wife wife = new Wife();
//指定属性
husband.name = "邓超";
wife.name = "孙俪";
husband.wife = wife;
wife.husband = husband;
System.out.println("丈夫:" + husband.name + ",他妻子是:" + husband.wife.name);
System.out.println("妻子:" + wife.name + ",他丈夫是:" + wife.husband.name);
}
}
class Husband{
String name;
Wife wife;
}
class Wife{
String name;
Husband husband;
}
成员方法
形参
- 方法定义时的参数
实参
- 方法调用时的参数
class Count {
/*
定义计算两个整数和的方法
返回值类型,计算结果是int
参数:不确定数据求和,定义int参数.参数又称为形式参数
*/
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
/*
定义计算两个整数差的方法
返回值类型,计算结果是int
参数:不确定数据求差,定义int参数.参数又称为形式参数
*/
public int getSubtract(int a, int b){
return getSum(a,-b);//直接返回getSum(a,-b)方法调用的结果作为getSubtract(a,b)的结果
}
}
public class Method_Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象
Count c = new Count();
// 通过单独调用方式调用方法
c.getSum(3,4);
// 通过输出调用方式调用方法
System.out.println(c.getSum(3,4));
// 通过赋值调用方式调用方法
int sum = c.getSum(3,4);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}成员方法的练习
打印任意行列数的矩形
public class Method_Exer5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
PrintUtil pu = new PrintUtil();
//调用printRectangle方法
pu.printRectangle(5, 10, "&");
}
}
class PrintUtil{
public void printRectangle(int line, int column, String sign){
for (int i = 0; i < line; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++) {
System.out.print(sign);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}声明圆类
public class Method_Exer6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
Circle c = new Circle();
c.radius = 1.2;
System.out.println(c.getInfo());
}
}
class Circle{
double radius;
public double getArea(){
return 3.14 * radius * radius;
}
public double getPerimeter(){
return 2 * 3.14 * radius;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "半径:" + radius + ",面积:" + getArea() + ",周长:" + getPerimeter();
}
}方法调用内存分析
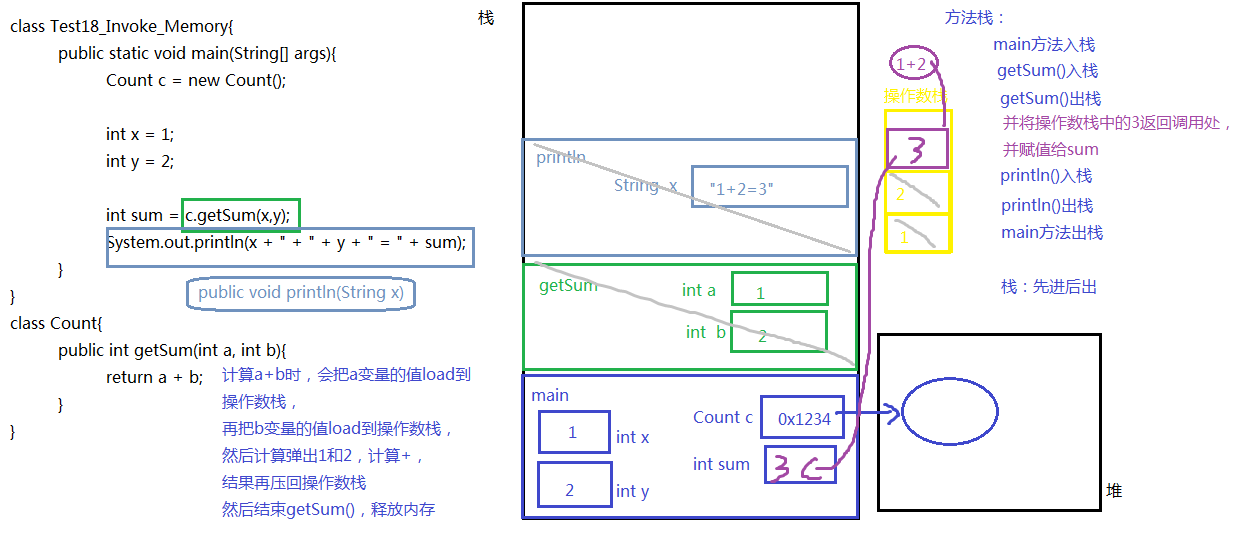
class Test18_Invoke_Memory{
public static void main(String[] args){
Count c = new Count();
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
int sum = c.getSum(x,y);
System.out.println(x + " + " + y + " = " + sum);
}
}
class Count{
public int getSum(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
}