 结构体定义形式:
结构体定义形式:
struct 结构体名
{
成员列表(可以是基本数据类型、指针、数组或其他结构类型);
}struct是结构体关键字,struct+结构体名 是结构体类型,stu是通过上面的结构体类型定义的结构体变量。
下面程序要求输出结构体中成员a的数据,不能填入横线处的内容是:
 上述代码struct S a, * p = &a中,a是结构体变量,p是结构体指针, * 和struct S 组合成结构体指针类型,p指向a。
a.a = 99中,第一个a是结构体变量a,第二个a是结构体成员a。
打印结构体成员a的值时,可以使用a.a。
如果使用 * p.a时,“.”优先级高于“*”,应写成( * p).a。
p是结构体指针,可以使用p->a写法。
上述代码struct S a, * p = &a中,a是结构体变量,p是结构体指针, * 和struct S 组合成结构体指针类型,p指向a。
a.a = 99中,第一个a是结构体变量a,第二个a是结构体成员a。
打印结构体成员a的值时,可以使用a.a。
如果使用 * p.a时,“.”优先级高于“*”,应写成( * p).a。
p是结构体指针,可以使用p->a写法。
计算程序输出结果
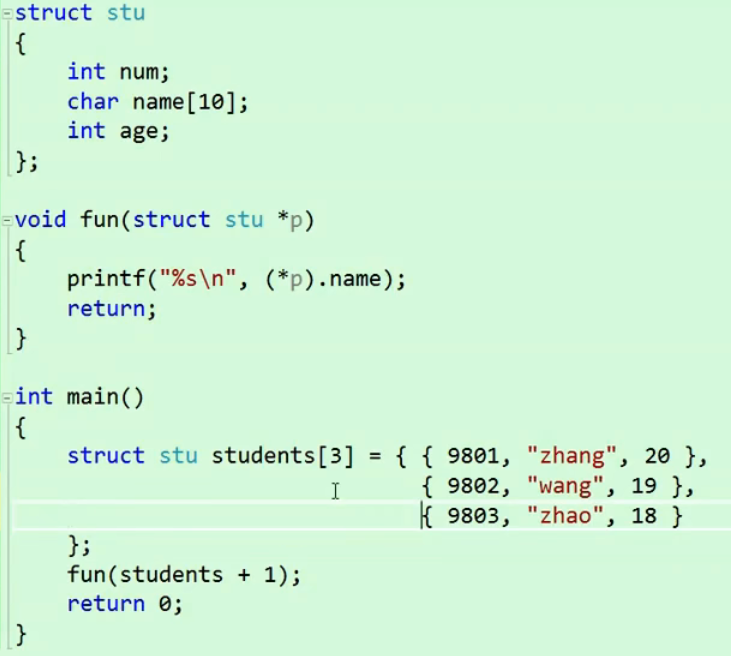 上述代码中,students分别初始化成主函数中列出的3个元素。
fun(students + 1)中,数组名students表示首元素地址,即结构体“zhang”的地址,+1后指向了第二个元素结构体“wang”的地址,传入fun函数中,fun函数使用指针p接收。( * p).name打印该结构体中name变量即{ 9802 , "wang" ,19}中的“wang”。
上述代码中,students分别初始化成主函数中列出的3个元素。
fun(students + 1)中,数组名students表示首元素地址,即结构体“zhang”的地址,+1后指向了第二个元素结构体“wang”的地址,传入fun函数中,fun函数使用指针p接收。( * p).name打印该结构体中name变量即{ 9802 , "wang" ,19}中的“wang”。

int main()
{
int empty = 0; //空瓶
int money = 20; //钱数
int total = 0; //总数
empty = money / 1;
total = empty;
while (empty >= 2)
{
total +=empty / 2;
empty = empty % 2 + empty / 2;
}
printf("%d", total); //39
return 0;
}
