2021.1.27 更新
已更新新版本博客,更新内容与原文章相比有点多,因此新开了一篇博客,请戳这里。
1 背景
开发一个App与后台数据库交互,基于MySQL+原生JDBC+Tomcat,没有使用DBUtils或JDBC框架,纯粹底层JDBC实现。
这几天踩了很多坑,说得夸张点真是踩到没有知觉,希望能帮助读者少踩坑...
2 开发环境
Windows10- 服务器
CentOS 7 Android Studio 3.5.1IntelliJ IDEA 2019.02MySQL 8.0.17Tomcat 9.0.26
3 准备环境
主要是安装MySQL与Tomcat,已经安装的可以略过。
3.1 安装MySQL
这个是目前比较新的MySQL版本。
服务器系统是CentOS。
其他系统安装看这里:
CentOS使用yum安装即可。
3.1.1 下载并安装MySQL
sudo yum localinstall https://repo.mysql.com//mysql80-community-release-el7-1.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install mysql-community-server
3.1.2 启动服务并查看初始化密码
sudo service mysqld start
sudo grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
3.1.3 修改密码
首先使用root登录:
mysql -u root -p
输入上一步看到的密码,接着使用alter修改密码:
alter mysql.user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'password';
注意新版本的MySQL不能使用太弱的密码,比如:
 出现这种提示的话则说明密码太弱了,请使用一个更高强度的密码。
出现这种提示的话则说明密码太弱了,请使用一个更高强度的密码。
3.1.4 允许外部访问
use mysql;
update user set host='%' where user='root';
这个可以根据自己的需要去修改,host='%'表明允许所有的ip登录,也可以设置特定的ip,若使用host='%'的话建议新建一个用户配置相应的权限。
3.1.5 配置防火墙(可选)
一般来说需要在对应的云厂商的防火墙配置中开启响应端口,如图:
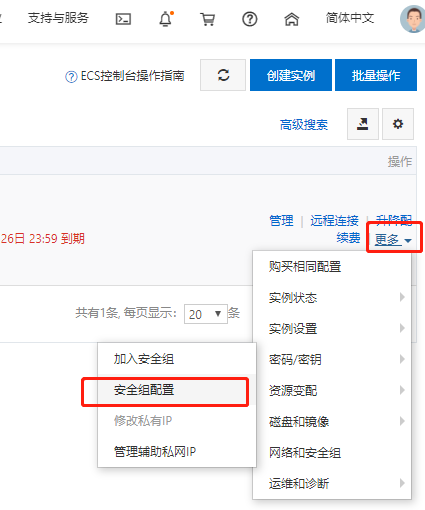
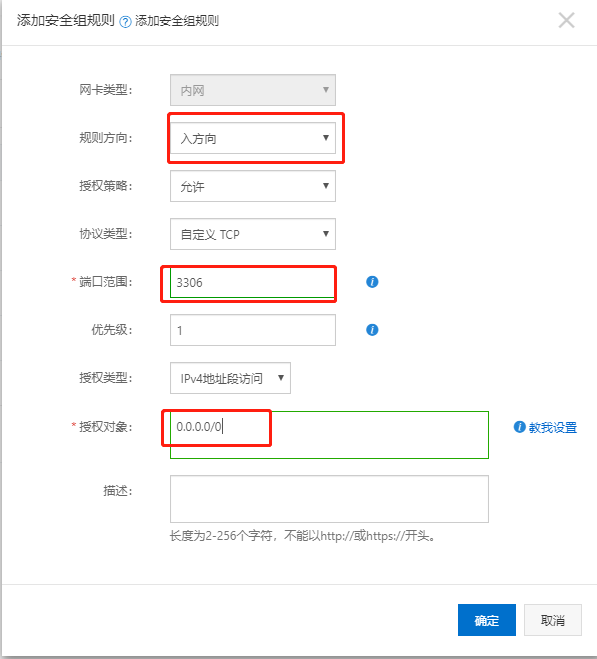
其中授权对象可以根据自己的需要更改,0.0.0.0/0表示允许所有的ip。
3.2 安装Tomcat
3.2.1 下载并上传到服务器
先去官网下载,下载后上传文件到服务器:
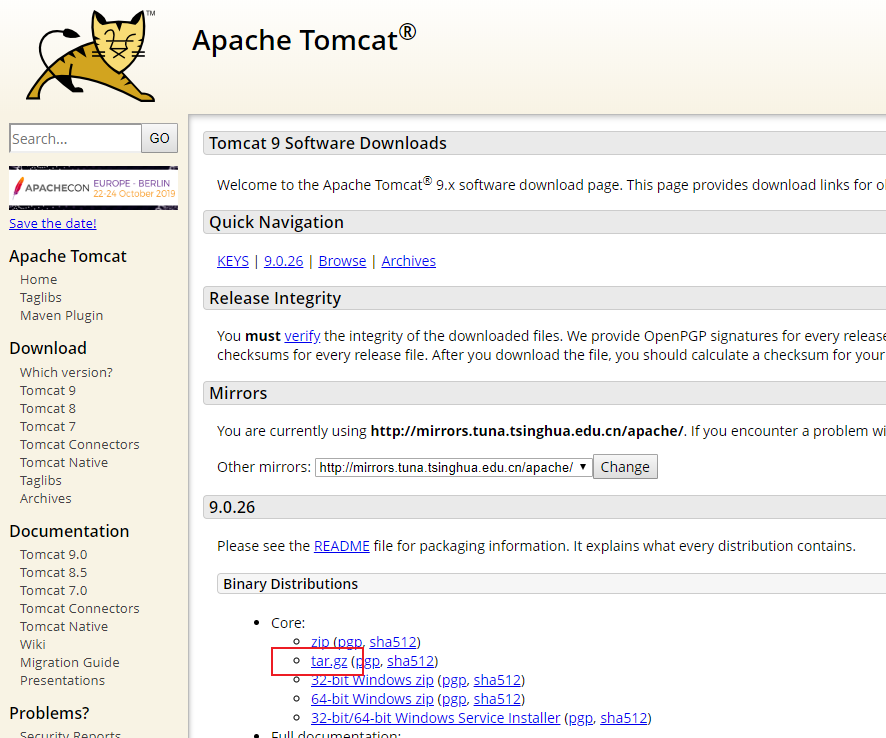
笔者使用的是scp命令,使用不熟练的可以戳这里看看:
scp apache-tomcat-xxxx.tar.gz username@xx.xx.xx.xx:/
改成自己的用户名和ip。
3.2.2 解压
ssh连接到服务器,接着移动到/usr/local并解压:
mkdir /usr/local/tomcat
mv apache-tomcat-xxxx.tar.gz /usr/local/tomcat
tar -xzvf apache-tomcat-xxx.tar.gz
3.2.3 修改默认端口(可选)
修改conf/server.xml文件,一般只需修改
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" connectionTimeout="20000" redirectPort="8443" />
中的8080端口,修改这个端口即可。
需要的话自行更改。
3.2.4 启动
运行bin目录下的startup.sh:
cd bin
./startup.sh
3.2.5 测试
浏览器输入:
服务器IP:端口
若出现:
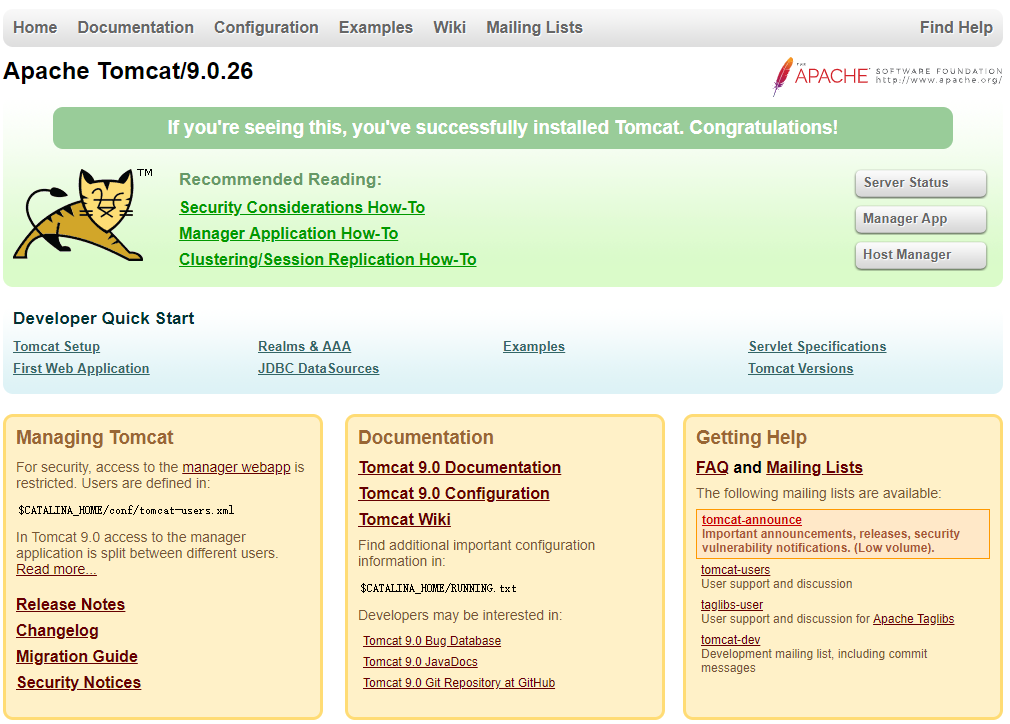
则表示成功。
3.2.6 开机启动(可选)
建议配置开机启动,修改/etc/rc.local文件,添加:
sh /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
这个根据自己的Tomcat安装路径修改,指定bin下的startup.sh。
4 建库建表
创建用户表,这里简化操作就不创建新用户不授权了。
这是一个在本地用root登录的示例,请根据实际情况创建并授权用户。
4.1 用户表
CREATE DATABASE userinfo;
USE userinfo;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name CHAR(30) NULL,
password CHAR(30) NULL
);
4.2 导入
mysql -u root -p < user.sql
这样准备工作就做好了,下面正式开始进行敲代码阶段。
5 后端部分
5.1 创建项目
选择Web Application: 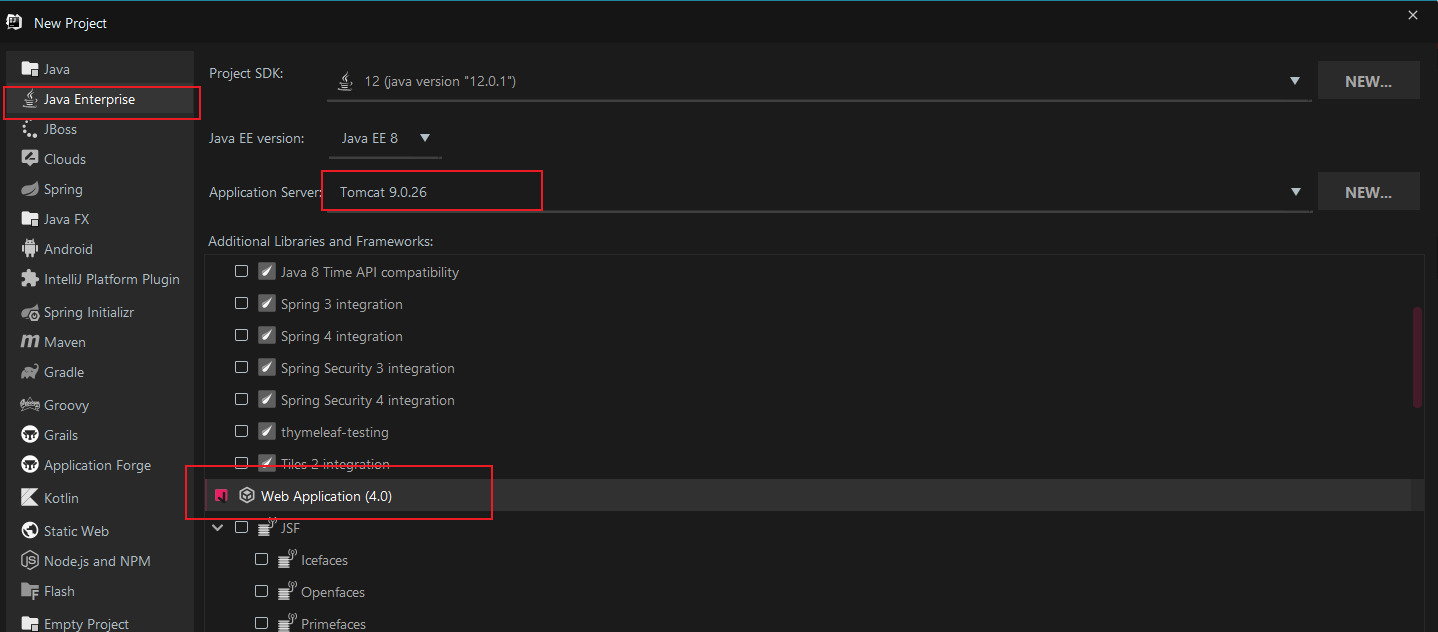
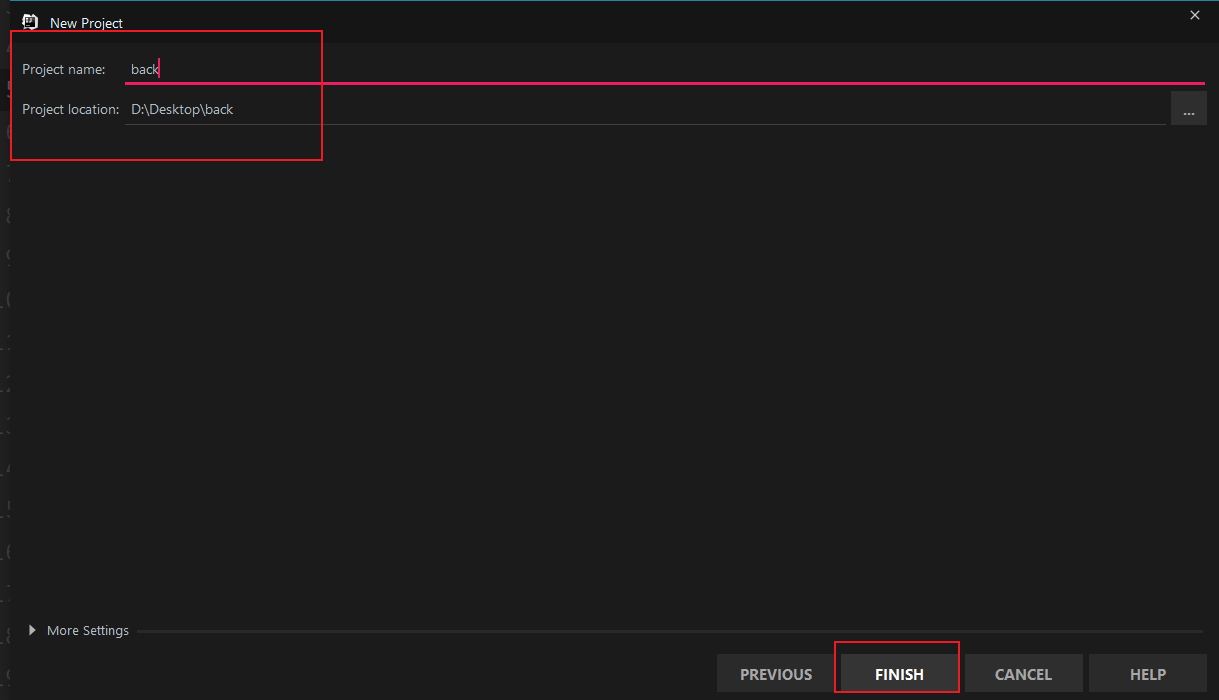
5.2 添加依赖库
创建一个叫lib的目录: 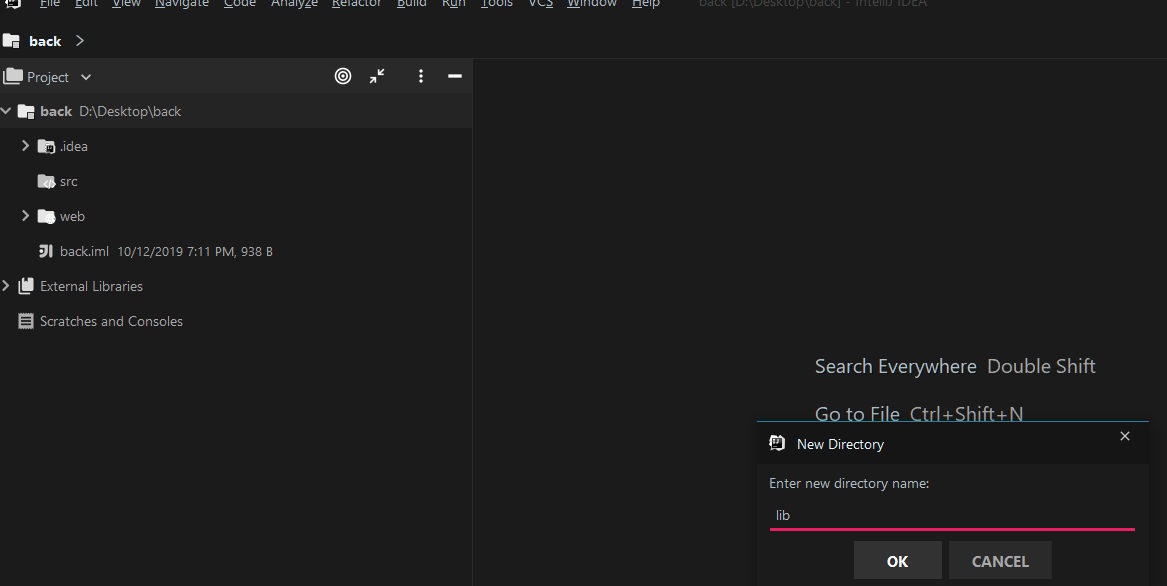
添加两个JAR包(文末提供下载链接):
mysql-connector-java-8.0.17.jarjavax.servlet-api-4.0.1.jar
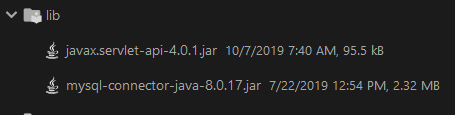
打开Project Structure:
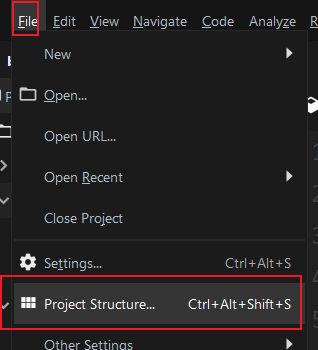
Modules --> + --> JARs or directories:
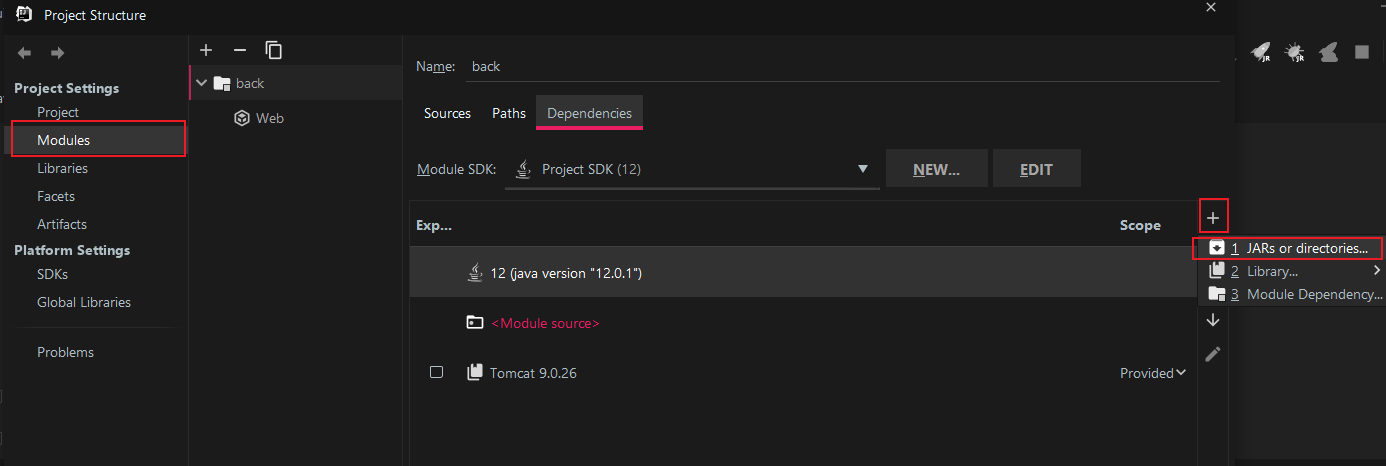
选择刚才新建的lib下的两个JAR包:
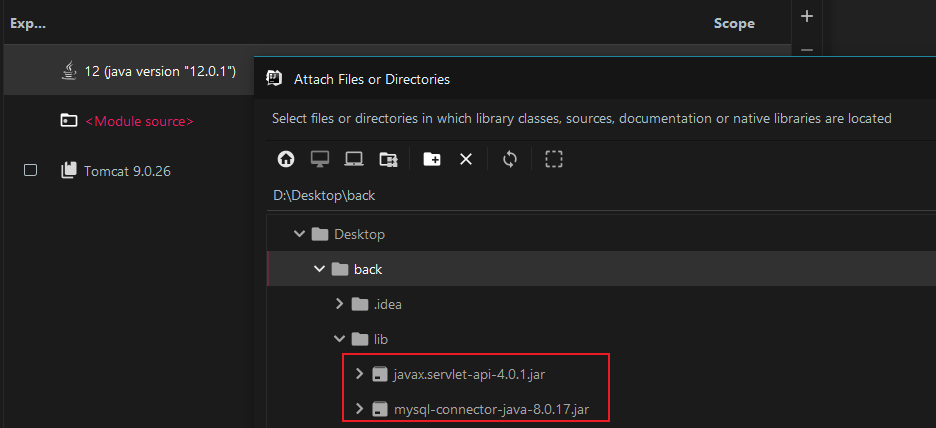
勾选并apply:
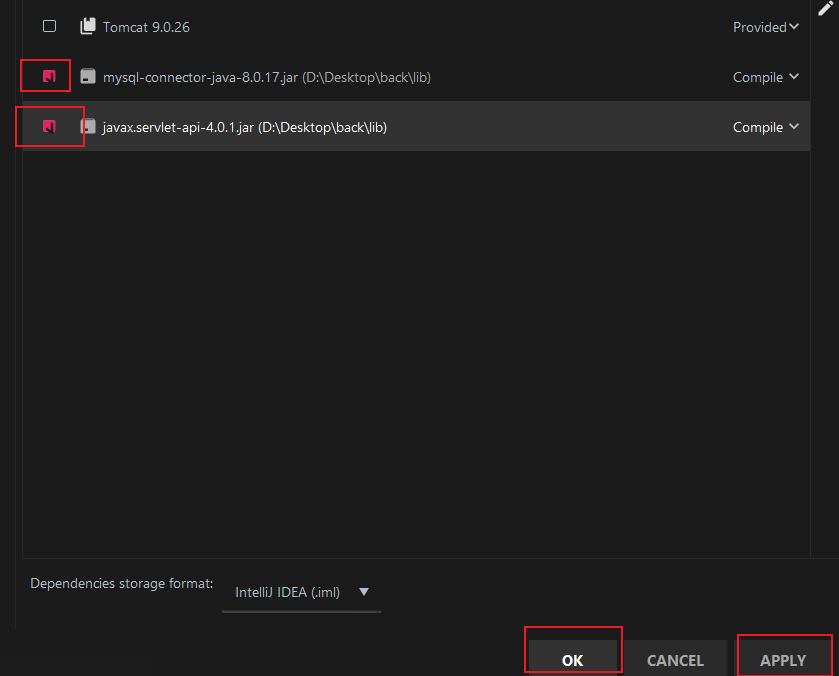
5.3 创建包与类
总共4个包:
com.servlet:用于处理来自前端的请求,包含SignUp.java、SignIn.javacom.util:主要功能是数据库连接,包含DBUtils.javacom.entity:实体类,包含User.javacom.dao:操作用户类的类,包含UserDao.java
5.4 DBUtils
连接数据库的类,纯粹的底层JDBC实现,注意驱动版本。
public class DBUtils {
private static Connection connection = null;
public static Connection getConnection()
{
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/数据库名字";
String usename = "账号";
String password = "密码";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,usename,password);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
return connection;
}
public static void closeConnection()
{
if(connection != null)
{
try {
connection.close();
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
主要就是获取连接与关闭连接两个函数。
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/数据库名字";
String usename = "账号";
String password = "密码";
这几行根据自己的用户名,密码,服务器ip和库名修改。
注意,MySQL 8.0以上使用的注册驱动的语句是:
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
旧版的是:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
5.5 User
User类比较简单,就是就三个字段与Getter+Setter。
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
//三个Getter与三个Setter
//...
}
5.6 UserDao
public class UserDao {
public boolean query(User user)
{
Connection connection = DBUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user where name = ? and password = ?";
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,user.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2,user.getPassword());
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
return resultSet.next();
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
finally {
DBUtils.closeConnection();
}
}
public boolean add(User user)
{
Connection connection = DBUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into user(name,password) values(?,?)";
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,user.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2,user.getPassword());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return preparedStatement.getUpdateCount() != 0;
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
finally {
DBUtils.closeConnection();
}
}
}
主要就是查询与添加操作,查询操作中存在该用户就返回true,否则返回false。
添加操作中使用executeUpdate()与getUpdateCount() != 0。
注意不能直接使用
return preparedStatement.execute();
去代替
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return preparedStatement.getUpdateCount() != 0;
咋一看好像没有什么问题,那天晚上笔者测试的时候问题可大了,Android那边显示注册失败,但是数据库这边的却insert进去了。。。
啊这。。。
好吧,还是函数的问题。
- 一般来说
select使用executeQuery(),executeQuery()返回ResultSet,表示结果集,保存了select语句的执行结果,配合next()使用 delete,insert,update使用executeUpdate(),executeUpdate()返回的是一个整数,表示受影响的行数,即delete,insert,update修改的行数,对于drop,create操作返回0create,drop使用execute(),execute()的返回值是这样的,如果第一个结果是ResultSet对象,则返回true,如果第一个结果是更新计数或者没有结果则返回false
所以在这个例子中
return preparedStatement.execute();
肯定返回false,所以才会数据库这边insert进去,但前端显示注册失败(这个问题笔者找了是真的久。。。)
5.7 SignIn+SignUp
servlet包中:
SingIn类用于处理登录,调用JDBC查看数据库是否有对应的用户SignUp类用于处理注册,把User添加到数据库中
SignIn.java如下:
@WebServlet("/SignIn")
public class SingIn extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException,ServletException
{
this.doPost(httpServletRequest,httpServletResponse);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException, ServletException
{
httpServletRequest.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setContentType("text/plain;charset=utf-8");//设置相应类型为html,编码为utf-8
String name = httpServletRequest.getParameter("name");
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("password");
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setPassword(password);
if(!userDao.query(user))//若查询失败
{
httpServletResponse.sendError(204,"query failed.");//设置204错误码与出错信息
}
}
}
首先是@WebServlet注解,表示这是一个名字叫SignIn的Servlet,可用于实现Servlet与URL的映射,如果不在这里添加这个注解,则需要在WEB-INF目录下的web.xml添加一个<servlet-mapping>。
@WebServlet("/SignIn")
接着设置响应类型与编码:
httpServletResponse.setContentType("text/plain;charset=utf-8");//设置相应类型为html,编码为utf-8
HttpServletRequest.getParameter(String name)方法表示根据name获取相应的参数:
String name = httpServletRequest.getParameter("name");
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("password");
下面是SignUp.java:
@WebServlet("/SignUp")
public class SignUp extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException,ServletException
{
this.doPost(httpServletRequest,httpServletResponse);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException,ServletException
{
httpServletRequest.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");//设定编码防止中文乱码
httpServletResponse.setContentType("text/plain;charset=utf-8");//设置相应类型为html,编码为utf-8
String name = httpServletRequest.getParameter("name");//根据name获取参数
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("password");//根据password获取参数
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setPassword(password);
if(!userDao.add(user)) //若添加失败
{
httpServletResponse.sendError(204,"add failed.");//设置204错误码与出错信息
}
}
}
5.8 添加Servlet到web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SignIn</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.servlet.SingIn</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SignUp</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.servlet.SignUp</servlet-class>
</servlet>
</web-app>
要把刚才创建的Servlet添加进web.xml,在<servlet>中添加子元素<servlet-name>与<servlet-class>:
<servlet-name>是Servlet的名字,建议与类名一致<servlet-class>是Servlet类的位置
如果在Servlet类中没有添加@WebServlet("/xxxx")注解,则需要在web.xml中添加:
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SignIn</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/SignIn</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
其中<servlet-name>与<servlet>中的子元素<servlet-name>中的值一致,<url-pattern>是访问的路径。
5.9 Hello.html测试文件
最后添加一个叫Hello.html的测试文件。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Welcome</title>
</head>
<body>
Hello web.
</body>
</html>
6 打包发布
笔者用的IDEA,Eclipse的打包请看这里。
6.1 Project Structure->Artifacts->Web Application:Archive
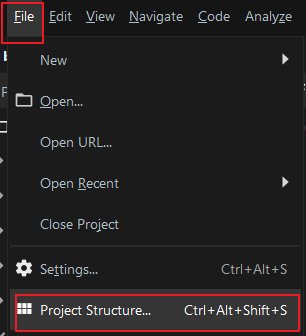
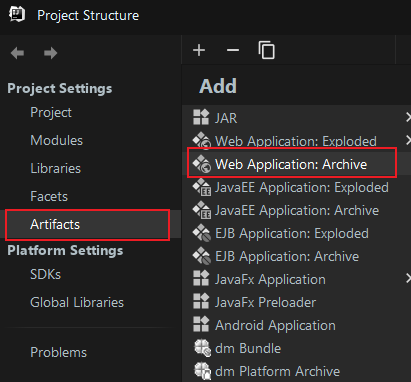
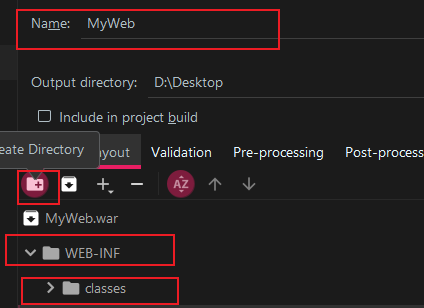
6.2 创建目录并添加模块
修改名字,并创建WEB-INF目录与子目录classes:
选中classes,添加Module Output,选择自己的web项目:
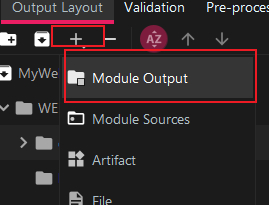
6.3 添加依赖库与其他文件
添加JAR包,选中lib目录后添加JAR包文件:
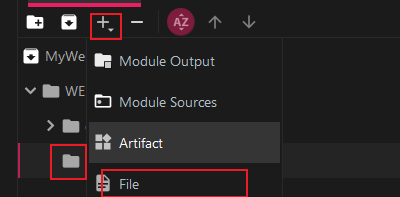
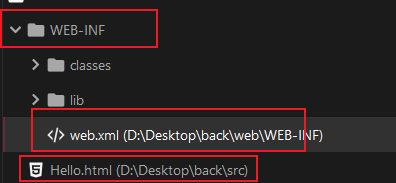
接着添加Hello.html与web.xml,web.xml需要在WEB-INF目录里,Hello.html在WEB-INF外面:
6.4 打包
Build->Build Artifacts: 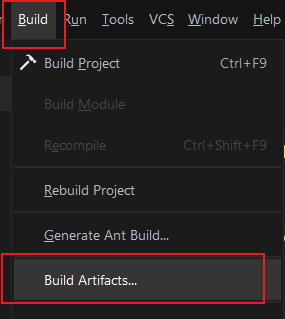
6.5 上传测试
打包好的WAR文件上传到服务器Tomcat的webapps目录下:
scp ***.war username@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps
注意改成自己的webapps目录。
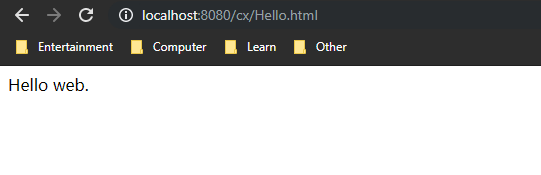
Tomcat启动后,在浏览器输入
服务器IP:端口/项目/Hello.html
笔者为了方便就在本地测试了:
7 Android端
7.1 新建工程
7.2 MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button signin = (Button) findViewById(R.id.signin);
signin.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String name = ((EditText) findViewById(R.id.etname)).getText().toString();
String password = ((EditText) findViewById(R.id.etpassword)).getText().toString();
if (UserService.signIn(name, password))
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "登录成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
else {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "登录失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
});
Button signup = (Button) findViewById(R.id.signup);
signup.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String name = ((EditText) findViewById(R.id.etname)).getText().toString();
String password = ((EditText) findViewById(R.id.etpassword)).getText().toString();
if (UserService.signUp(name, password))
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "注册成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
else {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "注册失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
});
}
}
两个简单的Button绑定事件,然后设置两个Toast提示信息。
7.3 UserService.java
public class UserService {
public static boolean signIn(String name, String password) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread("http://本机内网IP:8080/cx/SignIn",name,password);
try
{
myThread.start();
myThread.join();
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return myThread.getResult();
}
public static boolean signUp(String name, String password) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread("http://本机内网IP:8080/cx/SignUp",name,password);
try
{
myThread.start();
myThread.join();
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return myThread.getResult();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread
{
private String path;
private String name;
private String password;
private boolean result = false;
public MyThread(String path,String name,String password)
{
this.path = path;
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public void run()
{
try {
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
httpURLConnection.setConnectTimeout(8000);//设置连接超时时间
httpURLConnection.setReadTimeout(8000);//设置读取超时时间
httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("POST");//设置请求方法,post
String data = "name=" + URLEncoder.encode(name, "utf-8") + "&password=" + URLEncoder.encode(password, "utf-8");//设置数据
httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");//设置响应类型
httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", data.length() + "");//设置内容长度
httpURLConnection.setDoOutput(true);//允许输出
OutputStream outputStream = httpURLConnection.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(data.getBytes("utf-8"));//写入数据
result = (httpURLConnection.getResponseCode() == 200);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public boolean getResult()
{
return result;
}
}
MyThread myThread = new MyThread("http://内网IP:8080/cx/SignUp",name,password);
MyThread myThread = new MyThread("http://内网IP:8080/cx/SignIn",name,password);
这两行换成自己的ip,内网ip的话可以用ipconfig或ifconfig查看,修改了默认端口的话也把端口一起改了。
路径的话就是:
端口/web项目名/Servlet名
web项目名是再打成WAR包时设置的,Servlet名在web.xml中的<servlet>的子元素<servlet-name>设置,与源码中的@WebServlet()注解一致。
另外一个要注意的就是线程问题,需要新开一个线程进行HTTP的连接。
7.4 activity_main.xml
前端页面部分很简单,就两个按钮,用于验证功能。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="用户名"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:id="@+id/etname"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="密码"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:id="@+id/etpassword"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="注册"
android:id="@+id/signup"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="登录"
android:id="@+id/signin"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
8 测试
8.1 注册测试
随便输入用户名与密码:
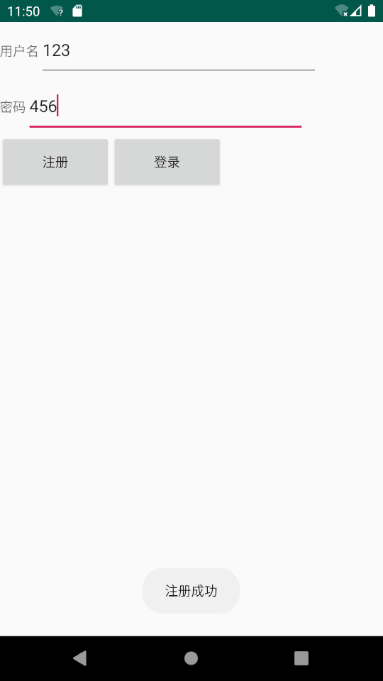
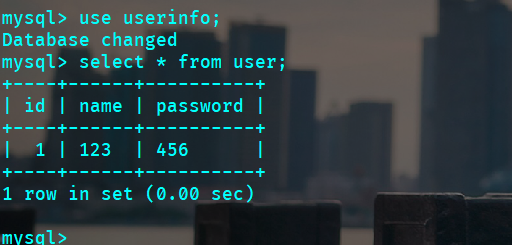
查看数据库:
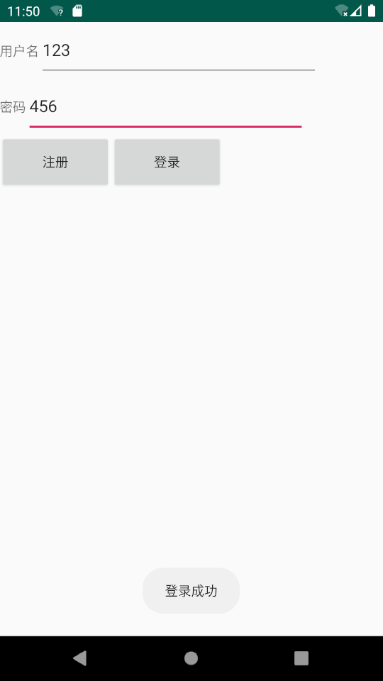
8.2 登录测试
9 注意事项
9.1 数据库用户名与密码
数据库的用户名和密码一定要设置正确,要不然会像下图一样抛出异常:
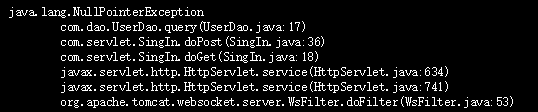
在加载驱动错误时也可能会出现这个错误,因此要确保打成WAR包时lib目录正确且JAR包版本正确。
还有就是由于这个是JDBC的底层实现,注意手写的SQL语句不能错。
千万千万别像笔者这样:

9.2 网络权限问题
需要在AndroidManifest.xml添加网络权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
9.3 安全组/防火墙问题
因为如果是现在的云服务器一般都使用安全组而不是直接使用防火墙配置安全设置,所以如果没法访问请到云服务器上面对应的安全组配置中开放端口,默认是8080端口,一般是允许所有ip通过,源ip配置为0.0.0.0/0,比如:

如果设置了安全组通过了,还是不能访问,可能是服务器防火墙的问题,可以查看iptables(CentOS8使用firewalld)是否开启:
systemctl status iptables
开启的话可以选择关闭:
systemctl stop iptables
若不关闭,可以添加端口规则,修改/etc/sysconfig/iptables:
vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
添加
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
-A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
重启iptables:
systemctl restart iptables
9.4 HTTP注意事项
由于从Android P开始,默认要求使用加密连接,也就是要使用HTTPS,所以会禁止使用HTTP连接。
使用HTTP连接时会出现以下异常:
W/System.err: java.io.IOException: Cleartext HTTP traffic to **** not permitted
java.net.UnknownServiceException: CLEARTEXT communication ** not permitted by network security policy
两种解决办法:
- 使用
HTTPS - 修改默认的
AndroidManifest.xml使其允许HTTP连接
在res下新建一个文件夹xml,创建一个叫network_security_config.xml的文件,文件内容如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<network-security-config>
<base-config cleartextTrafficPermitted="true" />
</network-security-config>
然后在AndroidMainfest.xml中加入:
<application
android:networkSecurityConfig="@xml/network_security_config"
/>
即可。
如果上面的方法不行,可以试一下直接在AndroidManifest.xml直接加入一句:
<application
android:usesCleartextTraffic="true"
/>
9.5 线程问题
从Android 4.0开始,联网不能在主线程操作,万一网络不好就会卡死,所以有关联网的操作都需要新开一个线程,不能在主线程操作。
9.6 AVD问题
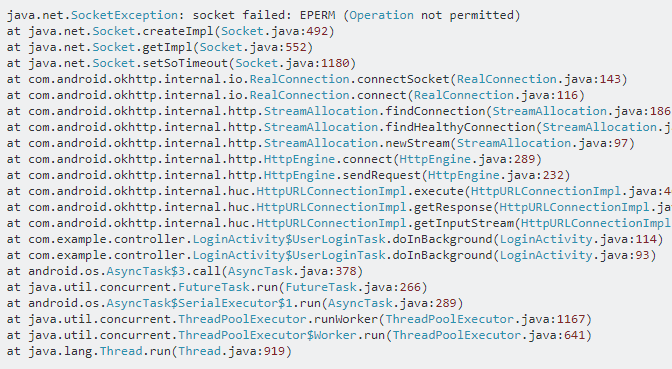
这个问题笔者找了很久,HTTP连接没问题,服务器没问题,数据库没问题,前端代码没问题,然后去了StackOverflow,发现是AVD的问题。。。
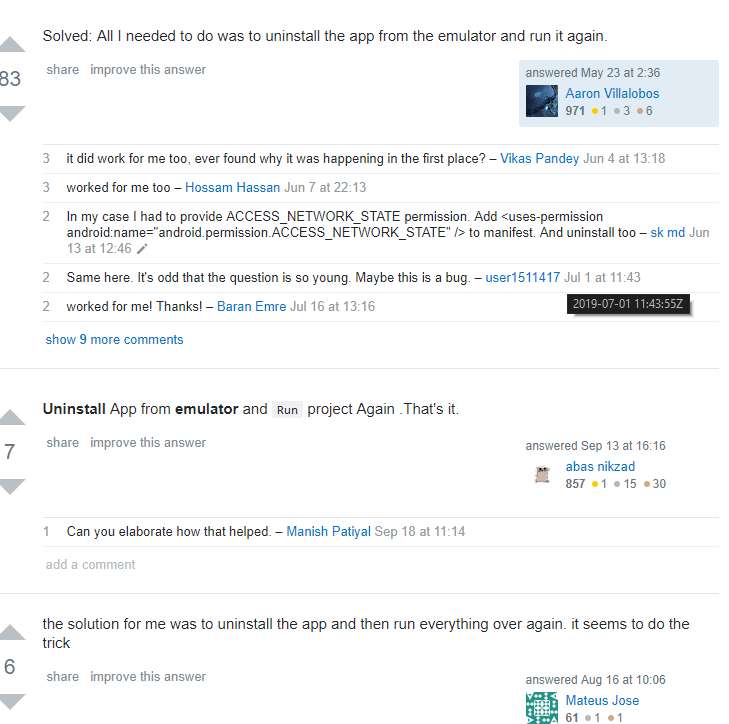
简单来说就是卸载了APP再重启AVD,居然成功了。。。
9.8 404
根据评论反映(这里同时感谢评论的各位)会出现404问题,出现404的主要原因就是访问路径的不正确,这里分三种情况进行说明。
9.8.1 本地IDEA中访问
IDEA运行项目后,可以使用postman进行测试,访问路径:
http://localhost:8080/SignIn
即可,因为此时还没有打包,所以不需要加上打包的项目名。
9.8.2 本地Tomcat访问
打包后会有一个叫xxx.war的打包文件,比如叫demo.war,那么使用postman测试的路径就要变为
http://localhost:8080/demo/SignIn
因为Tomcat会自动把demo.war解包,运行Tomcat后会在webapps下会有一个叫demo的文件夹,里面就是打包后的文件,此时的路径需要以demo为基准,因此SignIn前需要加上demo。
9.8.3 部署到服务器的Tomcat
部署到服务器后与本地Tomcat是基本一样的,只是把对应的locahost改成对应的域名或者公网ip即可,比如:
http://www.example.com:8080/demo/SignIn
http://111.111.111.111:8080/demo/SignIn
10 源码与JAR包
10.1 JAR包
- MySQL 8.0.17驱动(注意这个要与自己的
MySQL版本对应) - java-servlet-api-4.0.1
其他版本可以来这里搜索下载.
10.2 源码
11 最后
首先感谢读者能看到末尾,笔者也确实花了不少时间写这篇文章,但是,总会有不对或让读者疑惑的地方,希望读者有疑问或者其他什么问题可以私信笔者或在评论中指出,感激不尽。
12 参考网站
1、CSDN-Android 通过Web服务器与Mysql数据库交互
4、CSDN-PreparedStatement的executeQuery、executeUpdate和execute
5、CSDN-preparedstatement execute()操作成功!但是返回false















