大家好,我是Python进阶者,今天给大家分享一个网页结构解析模块beautifulsoup。
前言
beautifulsoup(以下简称bs),是一款网页结构解析模块,它支持传统的Xpath,css selector 语法,可以说很强大了,下面我们就来着重介绍下它的用法。
安装
bs 可以使用pip 或者easy_install安装,方便快捷。
pip install Beautifulsoup4 基本用法
一般就是先由requests 获取到网页源码后然后对页面进行解析,如图:
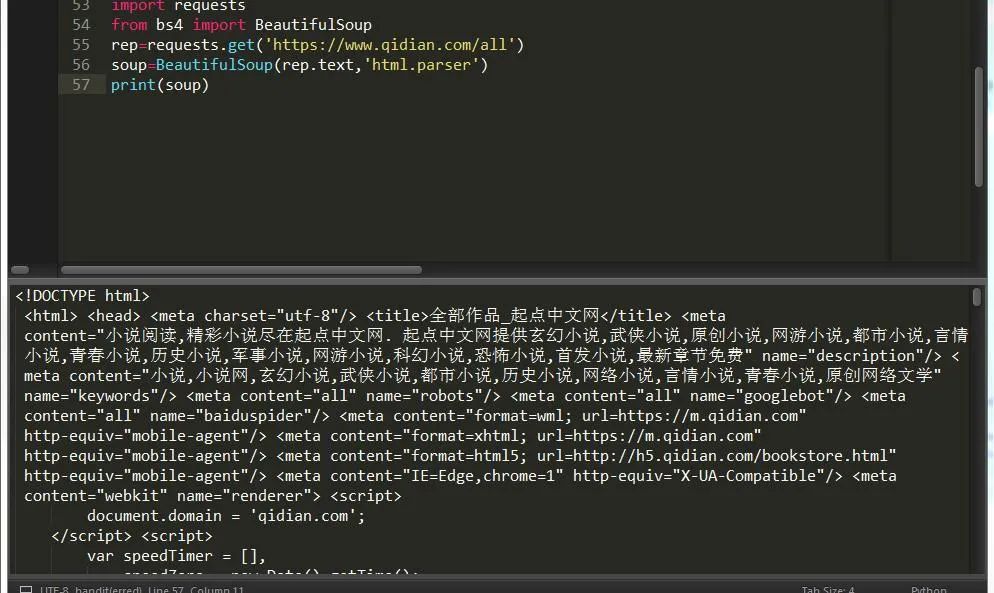
这样就基本上拿到了页面的源码了。
1.根据标签直接获取元素,如下图:
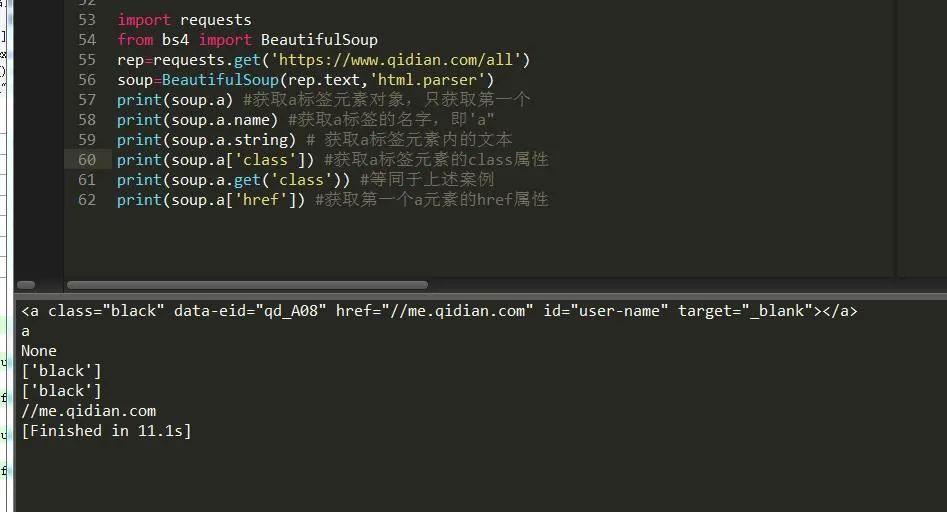
2.根据find,find_all方法查找
前者返回一个结果,后者返回所有结果
find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
name :要查找的标签名(字符串、正则、方法、True)
attrs: 标签的属性
recursive: 递归
text: 查找文本
**kwargs :其它 键值参数因为class是关键字,所以要写成class_="value", 等同于attrs={"class":"value"}
这里的参数适用于find find_all两种方法。
只不过find_all 还有其他参数,比如限制查找返回数量 的limit方法,标签内容string方法。
3.根据select方法查找
| soup.select('div') | 所有名为 的元素 |
|---|---|
| soup.select('#aa') | 所有 id 属性名为aa的元素 |
| soup.select('.oo') | 所有class 属性名为oo的元素 |
| soup.select('div p') | 所有在 元素之内的 元素 |
| soup.select('div >p') | 所有直接在 元素之内的 元素,中间没有其他元素 |
| soup.select('input[name]') | 所有名为,并有一个 name 属性,其值无所谓的元素 |
| soup.select('input[type="button"]') | 所有名为,并有一个 type 属性,其值为 button 的元素 |
soup.select('a')[0].get_text() # 获取首个a元素的文本
soup.select('a')[0].attrs['href'] # 获取首个a元素的链接地址
4.关系节点名
find_parents()返回所有祖先节点的列表,find_parent()返回直接父节点
print(soup.title.find_parent())
print(soup.title.find_parent().find_all('link')[1])
print(soup.title.find_parents())
find_next_siblings()返回后面所有兄弟节点的列表,find_next_sibling()返回后面第一个兄弟节点
print(soup.title.find_next_sibling())
print(soup.title.find_next_siblings())
find_previous_siblings()返回前面所有兄弟节点的列表,find_previous_sibling()返回前面第一个兄弟节点
print(soup.title.find_previous_sibling())
print(soup.title.find_previous_siblings())
find_all_next()返回节点后所有符合条件的节点的列表, find_next()返回节点后第一个符合条件的节点
print(soup.title.find_next('link'))
print(soup.title.find_all_next('link'))
find_all_previous()返回节点前所有符合条件的节点, find_previous()返回节点前第一个符合条件的节点
print(soup.title.find_previous('link'))
print(soup.title.find_all_previous('link'))5.对象种类
tag(标签) navigablestring(标签内字符串) beautifulsoup(对象) comment(备注)
rep=requests.get('https://book.qidian.com/info/1014243481#Catalog',timeout=3)
soup=BeautifulSoup(rep.text,'html.parser')
print(soup.name) #beautifulsoup 对象
tr=soup.div
print(type(tr),tr) #tag对象 标签
print(tr.get_attribute_list('class')) #获取属性对应列表
print(tr.a.string) #navigablestring 对象,获取标签内文字,可使用str()方法将她转换为unicode字符串
print(soup.a.string.replace_with('fdf')) #替换navigablestringcomment 即为提取的注释内容,一般被!--xxxxxxx--! 包裹的内容就是了
三、使用案例
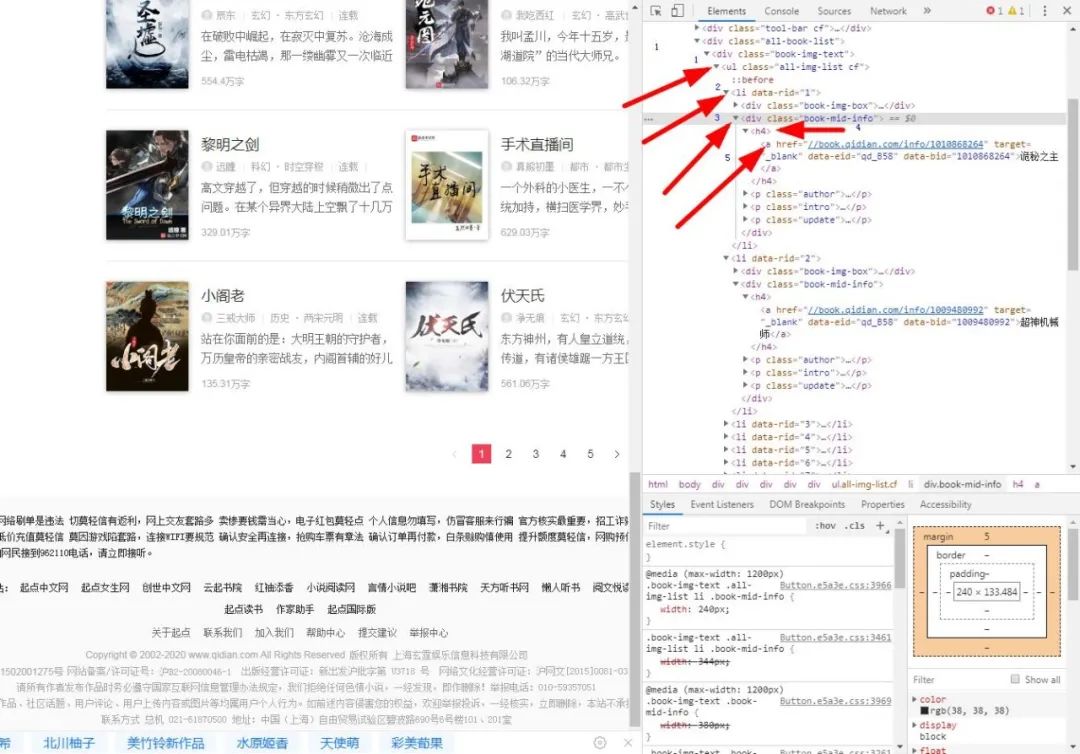
爬取起点小说主页第一页所有小说名字和链接,如图:
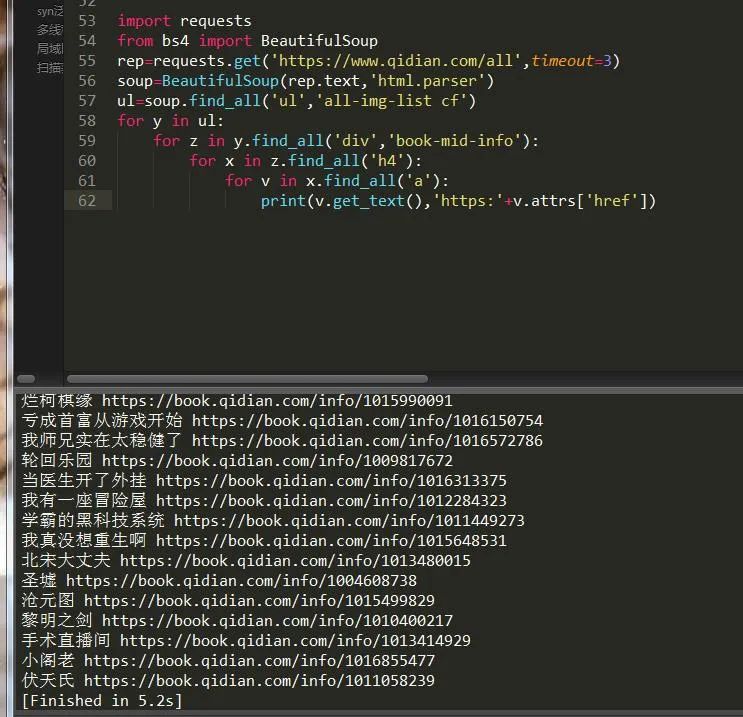
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
rep=requests.get('https://www.qidian.com/all',timeout=3)
soup=BeautifulSoup(rep.text,'html.parser')
#按照步骤一步一步来爬取
ul=soup.find_all('ul','all-img-list cf')
for y in ul:
for z in y.find_all('div','book-mid-info'):
for x in z.find_all('h4'):
for v in x.find_all('a'):
print(v.get_text(),'https:'+v.attrs['href']) #获取a标签的内容和href属性值最后就可以得出正确结果,如图:
关于bs大致就这么多,大家学会了吗??
总结
今天就讲这么多,关于BS的强大之处,远不止于此,本文只是介绍了它的安装和基本用法,并通过一个案例来帮助大家加深理解,希望大家好好利用,在爬虫路上可以事倍功半!
**-----**------**-----**---**** End **-----**--------**-----**-****

往期精彩文章推荐:
欢迎各位大佬点击链接加入群聊【helloworld开发者社区】:https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=mBlk6nzX进群交流IT技术热点。
本文转自 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jOfka8WJL4T6QEOWYdaV-A,如有侵权,请联系删除。