双向链表及其Java实现
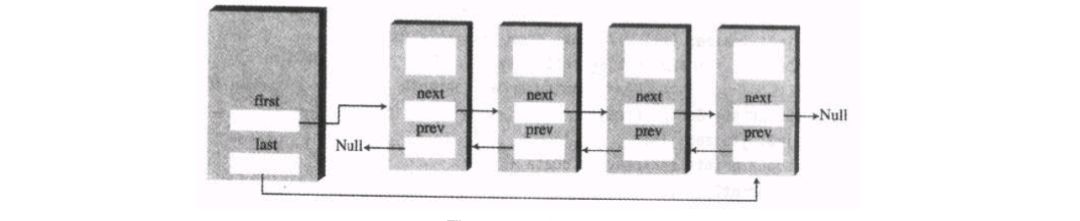
双向链表(双链表)是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。
具体的数据结构如图所示:
1.定义双向链表节点类
class Node{
public int data;//数据域
public Node next;//后继指针域
public Node previous;//前驱指针域
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.previous = null;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Node getPrevious() {
return previous;
}
public void setPrevious(Node previous) {
this.previous = previous;
}
}2.添加新节点
2.1在头部添加
public class NodeDemo2 {
private static Node head;//链表头
private static Node tail;//链表尾
private static int length;//链表长
public void addHead(int value) {
Node newNode=new Node(value);
if(length==0) {
//将链表的头部与尾部都设置为当前节点
head=newNode;
tail=newNode;
length++;
}else {
//将原链表头部的上一节点设置为当前节点
head.previous=newNode;
//将当前节点的下一个节点设置为原链表头的节点
newNode.next=head;
//将链表的头部设置为当前节点
head=newNode;
//链表长度加1
length++;
}
}
public void printNode(){
// 判断链表是否为空
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 因为头节点不能动,需要一个辅助变量来遍历
Node temp = head;
while (true) {
// 判断是否到链表最后
if(temp == null)
break;
// 输出节点的信息
System.out.println(temp.getData());
// 将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
NodeDemo2 n=new NodeDemo2();
for (int i = 1; i <5 ; i++) {
n.addHead(i);
}
n.printNode();
}
}
输出:
4
3
2
12.2在尾部添加
public void printNode(){
// 判断链表是否为空
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 因为头节点不能动,需要一个辅助变量来遍历
Node temp = head;
while (true) {
// 判断是否到链表最后
if(temp == null)
break;
// 输出节点的信息
System.out.println(temp.getData());
// 将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}
部分重复代码省略!
输出:
1
2
3
43.删除节点
3.1删除指定项数据节点
public void delete(int value)throws RuntimeException{
Node temp = head;//辅助节点,从头节点开始
while(temp.data!= value){//遍历寻找value值所在的节点
temp = temp.next;
if(temp == null){ //不存在该节点
throw new RuntimeException("Node is not exists");
}
}
if(temp == head){ // 如果该节点为头节点
head = temp.next; //该节点的下一节点设为头节点
}else {
temp.previous.next = temp.next;//前面节点的后继指向当前节点的后一个节点
}
if(temp == tail){ // 如果当前节点是尾节点
tail = temp.previous; // 尾节点的前驱前移
}else {
temp.next.previous = temp.previous; //后面节点的前驱指向当前节点的前一个节点
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
NodeDemo2 n=new NodeDemo2();
for (int i = 1; i <5 ; i++) {
n.addTail(i);
}
System.out.println("---------删除前---------");
n.printNode();
n.delete(2);
System.out.println("---------删除后---------");
n.printNode();
}
输出:
---------删除前---------
1
2
3
4
---------删除后---------
1
3
43.2删除指定位置节点
public Node getNode(int index){
if ((length == 0 )&& (index > length - 1)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", length: " + length);
}
Node result = head;
int n = 0;
while (n < index) {
result = result.next;
n++;
}
return result;
}
//删除结点
public void remove(int index) {
//删除的当前节点是头节点
if (index == 0) {
head = head.next;
head.previous = null;
//删除的当前节点是尾节点
} else if (index == length - 1) {
tail = tail.previous;
tail.next = null;
} else if (index >= length) {
System.out.println("超出链表长度");
System.exit(0);
} else {
Node del = null;
// 获取删除节点的前一个节点
Node prev = getNode(index - 1);
// 获取将要被删除的节点
del = prev.next;
// 让被删除节点的next指向被删除节点的下一个节点
prev.next = del.next;
// 让被删除节点的下一个节点的prev指向prev节点
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.previous = prev;
}
// 将被删除节点的prev、next引用赋为null
del.previous = null;
del.next = null;
}
length--;
}4.查找某个节点的索引
public int getIndex(int value){
if (length == 0 ) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "length: " + length);
}
Node result = head;
int n = 0;
while (result.data != value) {
result = result.next;
n++;
}
return n;
}
