前言
本文的内容主要包含3部分:声明并渲染变量,包括条件渲染;通过class和style定义样式并动态绑定;事件的绑定,包含了事件传参。三部分均具有动态绑定的特性。
一、模板语法及数据绑定
1.声明和渲染变量
在使用变量前,需要先声明,一般在data块中进行声明,如hello uniapp项目中index.vue中定义的title变量如下:
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello'
}
},可以在script语言块的data块中定义多个变量,并且在template语言块的视图中用{{}}调用变量,并且可以绑定多种类型的变量,包括基本数据类型、数组等。
先测试基础数据调用,index.vue如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view class="red">
hello-{{name}}
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley'
}
},
onLoad() {
console.log('index onload')
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
显示:

可以看到,定义的title和name变量渲染到了视图中。
需要注意,声明的变量都是响应式的,即视图中渲染的结果与变量本身是绑定的,会同步变化,index.vue如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view class="red">
hello-{{name}}-{{age}}
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley',
age: 18
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this;
setTimeout(function(){
_self.age = 20
}, 3000);
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
显示:
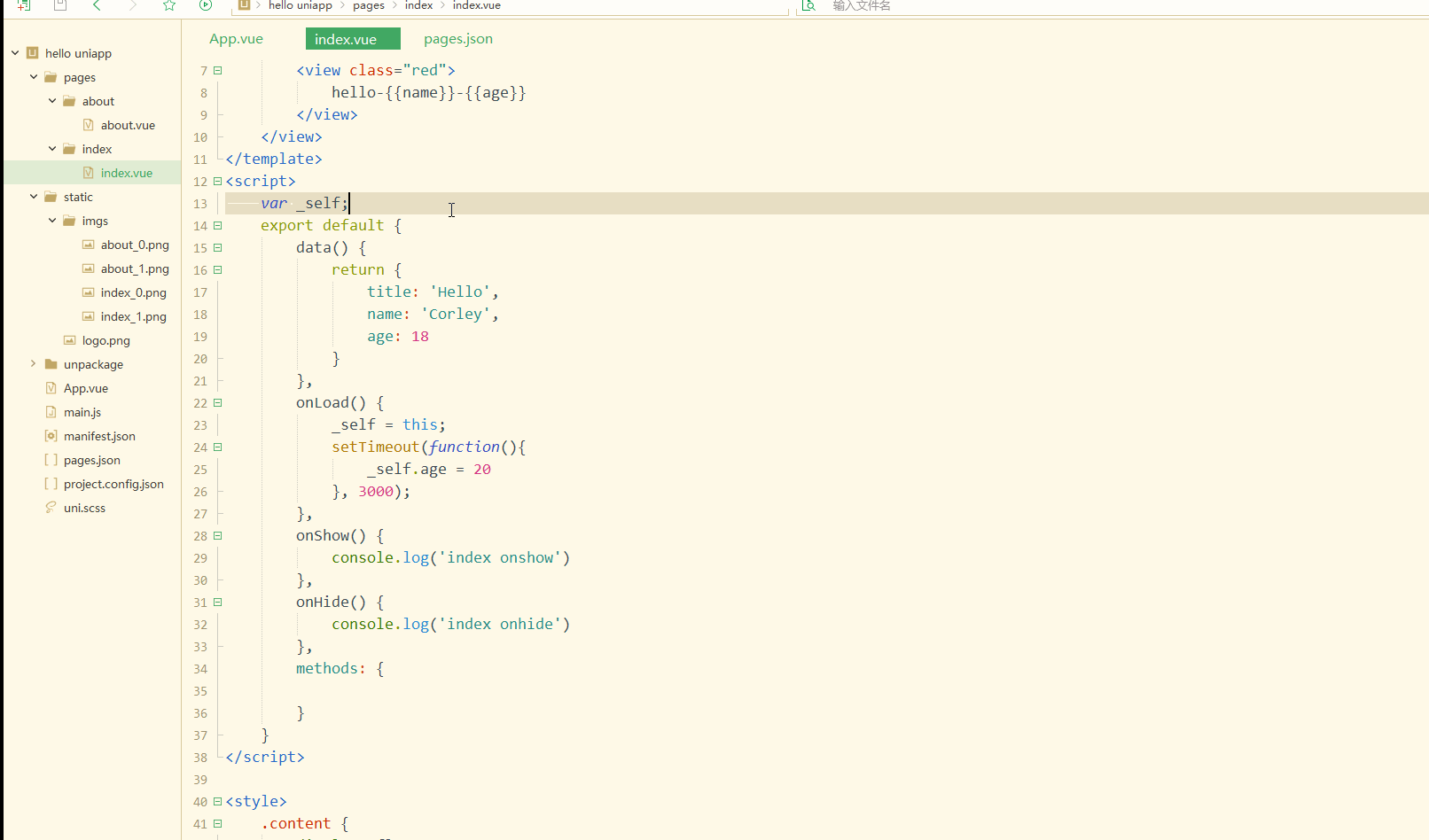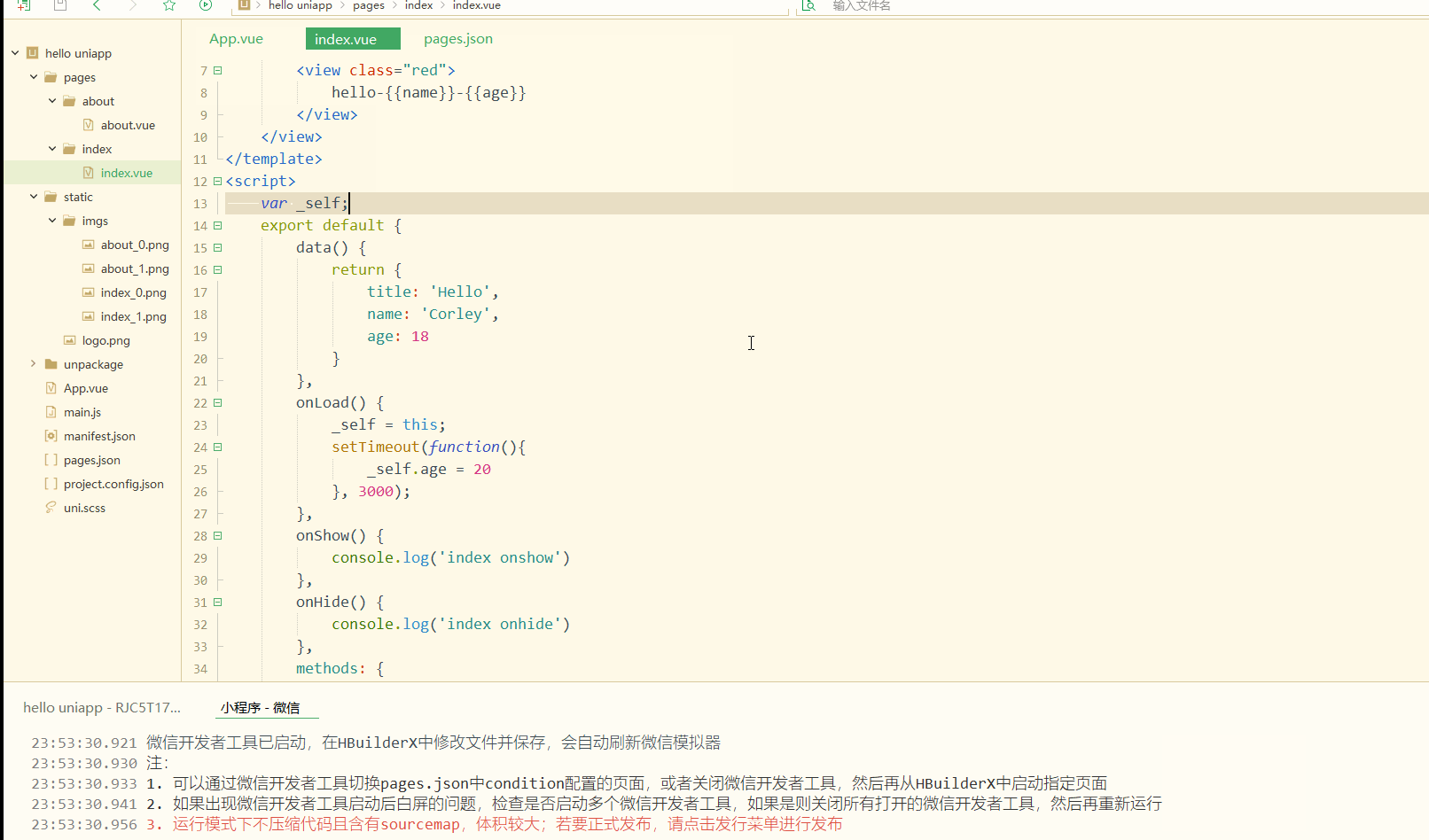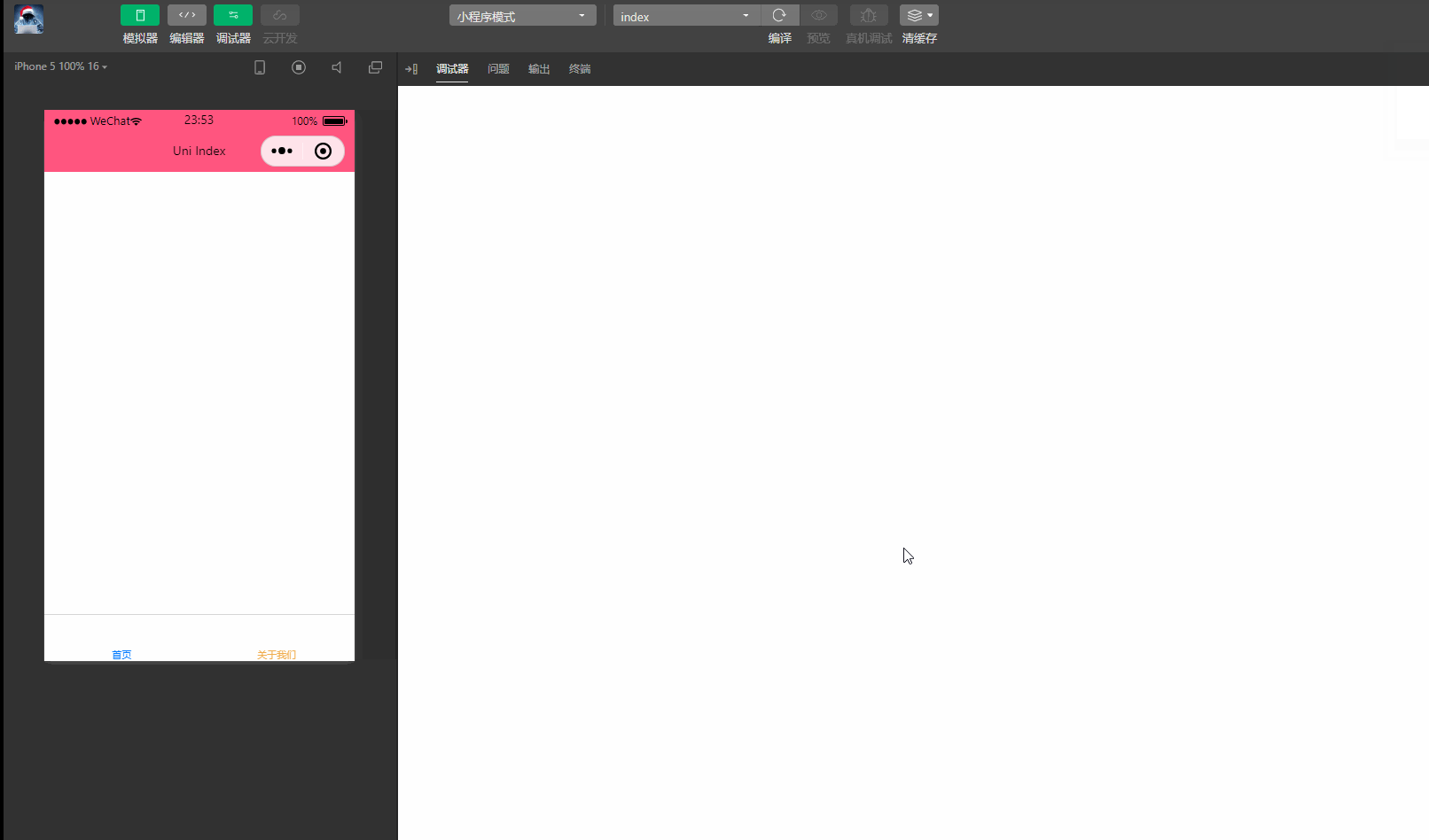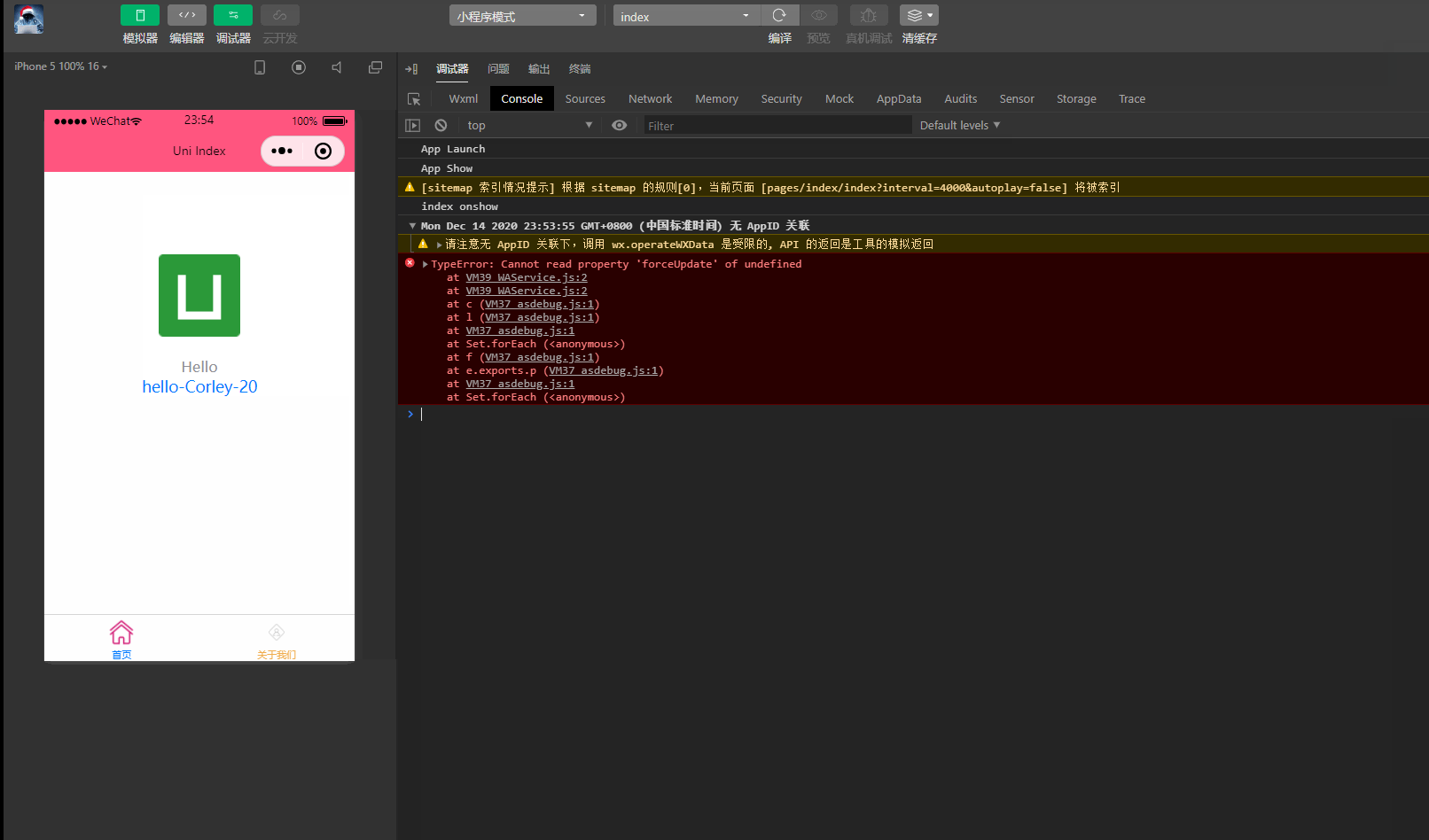
可以看到,在进入onLoad阶段后,渲染的age变量也发生变化,变为20。
还可以对数组进行数据绑定,可以获取数组的单个元素及其属性,如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view class="red">
{{students[0]}}<br>
{{students[0].name}}
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley',
age: 18,
students: [{
name: "张三",
age: 18
},
{
name: "李四",
age: 20
}
]
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this;
setTimeout(function() {
_self.age = 20
}, 3000);
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
显示:

也可以使用循环来遍历数组,即使用v-for进行遍历。
index.vue如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view v-for="(item, index) in students">
{{index}} - {{item.name}} : {{item.age}}
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley',
age: 18,
students: [{
name: "张三",
age: 18
},
{
name: "李四",
age: 20
}
]
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this;
setTimeout(function() {
_self.age = 20
}, 3000);
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
显示:
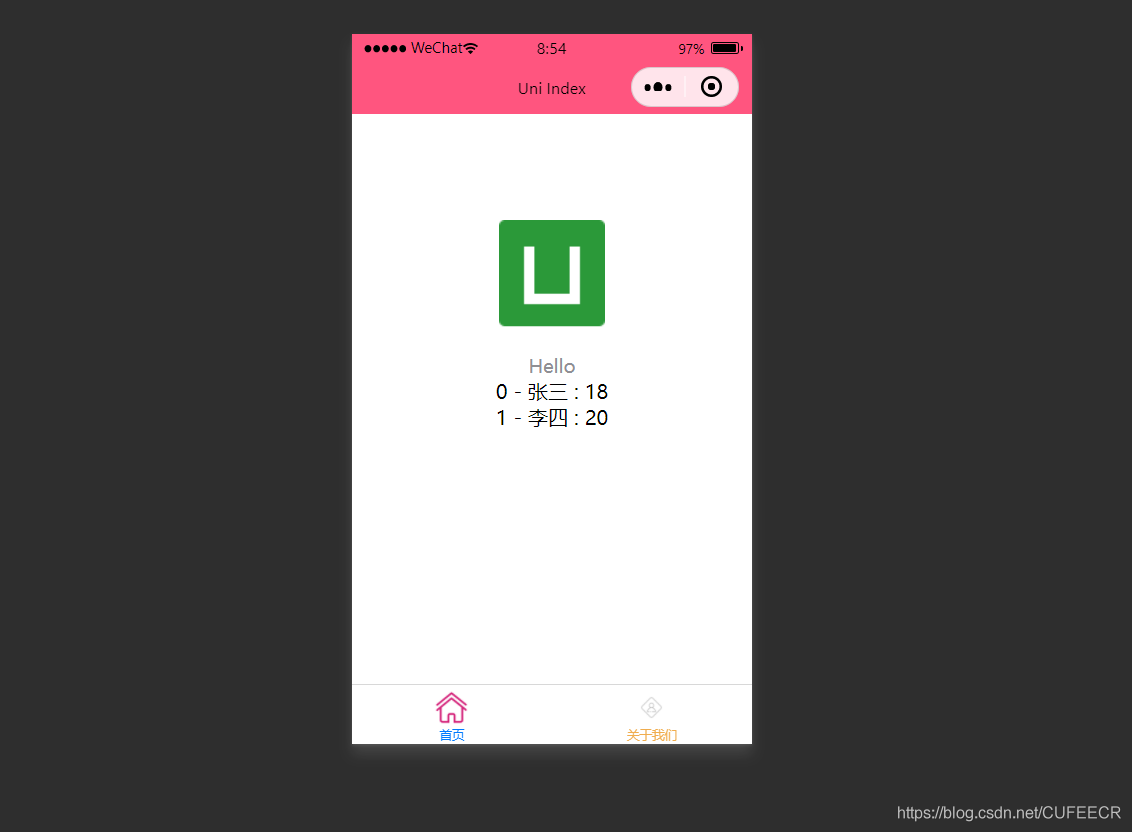
显然,此时遍历出了数组中的所有元素。
2.条件渲染
条件渲染是指满足某个条件才渲染某个元素,使用v-if。
如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view v-if="show1">
show1...
</view>
<view v-if="show2">
show2...
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley',
age: 18,
show1: true,
show2: false
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this;
setTimeout(function() {
_self.age = 20
}, 3000);
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
显示:

此时根据v-if中传的值判断是否渲染。
:hidden属性用来定义是否隐藏某个元素,如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view :hidden="show1">
show1...
</view>
<view :hidden="show2">
show2...
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley',
age: 18,
show1: true,
show2: false
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this;
setTimeout(function() {
_self.age = 20
}, 3000);
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
</style>
显示:

可以看到,v-if和:hidden的效果相反,但是原理上还是有一定区别:
v-if是根据条件决定是否渲染,:hidden会渲染但根据条件决定是否展示,可以根据具体需要进行选择。
二、class和style绑定
前面已经提到过,可以在template语言块的某个标签中通过style属性直接定义样式,也可以在style语言块中通过选择器定义样式,再在template语言块中使用。
为节约性能,可以将Class与Style的表达式通过compiler硬编码到uni-app中,通过条件判断来决定是否显示某个样式。
1.class语法
class支持的语法方式如下:
<!-- 1 -->
<view class="static" v-bind:class="{ active: isActive, 'text-danger': hasError }">111</view>
<!-- 2 -->
<view class="static" v-bind:class="[isActive ? activeClass : '', errorClass]">222</view>
<!-- 3 -->
<view class="static" v-bind:class="[{ active: isActive }, errorClass]">333</view>
<!-- 4 -->
<view :class="{ active: isActive }">444</view>
<!-- 5 -->
<view class="static" :class="[activeClass, errorClass]">555</view>其中,前3种为完整形式,后2种为简写形式;
isActive ? activeClass : ''为三元运算符。
index.vue如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view :class="{'red' : isRed}">
class bind 2...
</view>
<view :class="[isBlue ? 'blue' : 'red']">
class bind 3...
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley',
age: 18,
isRed: true,
isBlue: true
}
},
onLoad() {
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
.blue {
color: #007AFF;
}
</style>
显示:
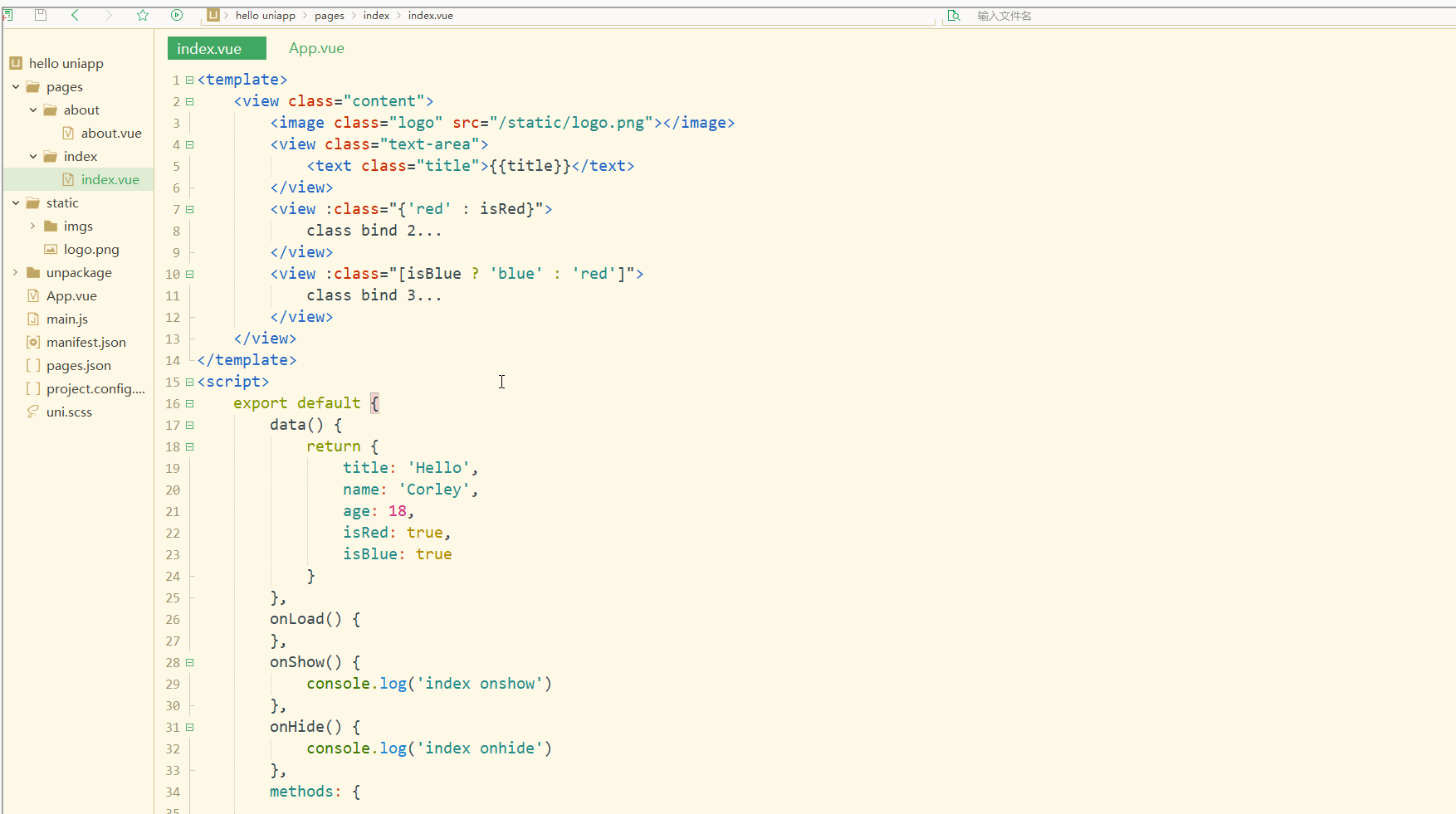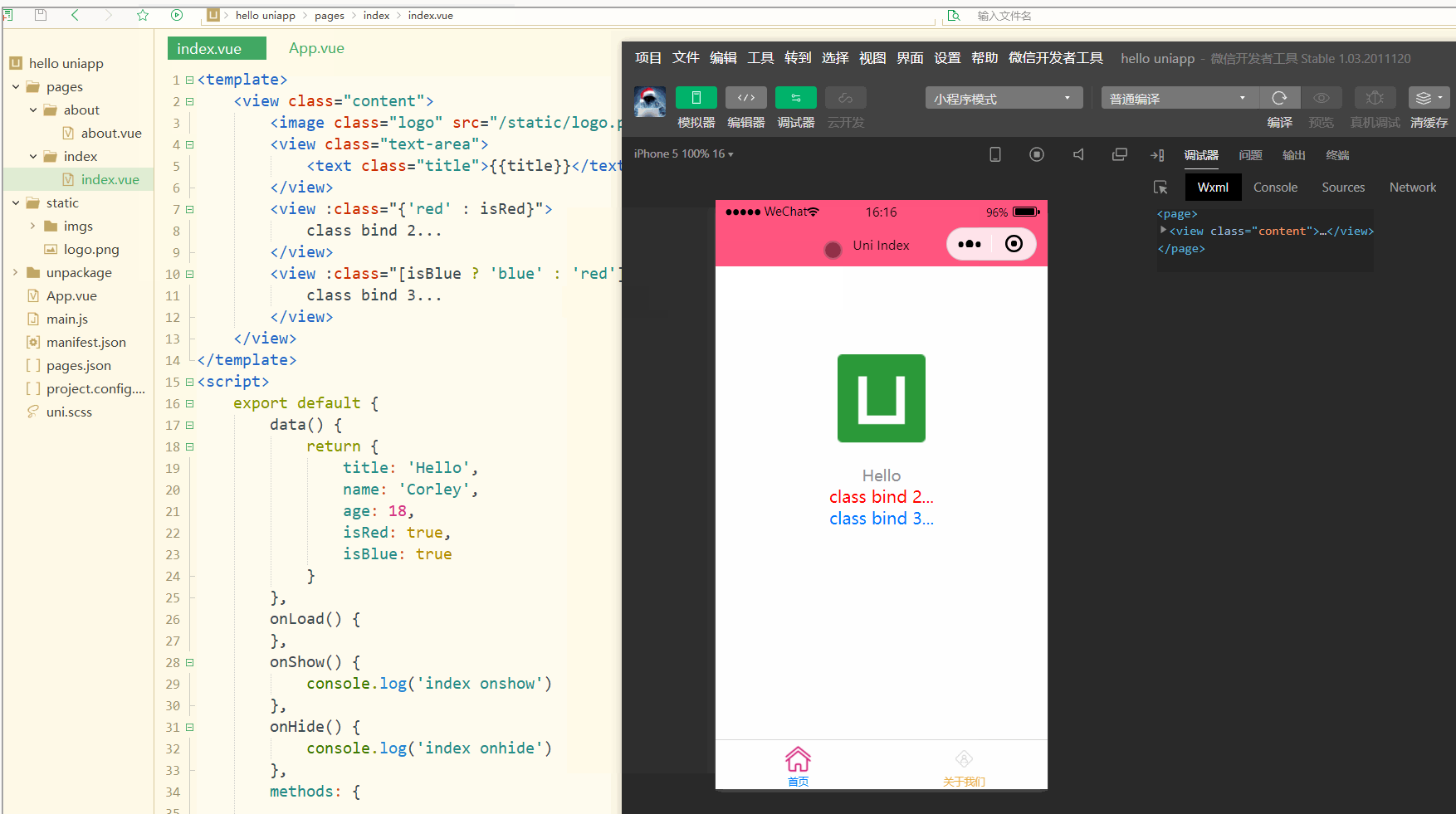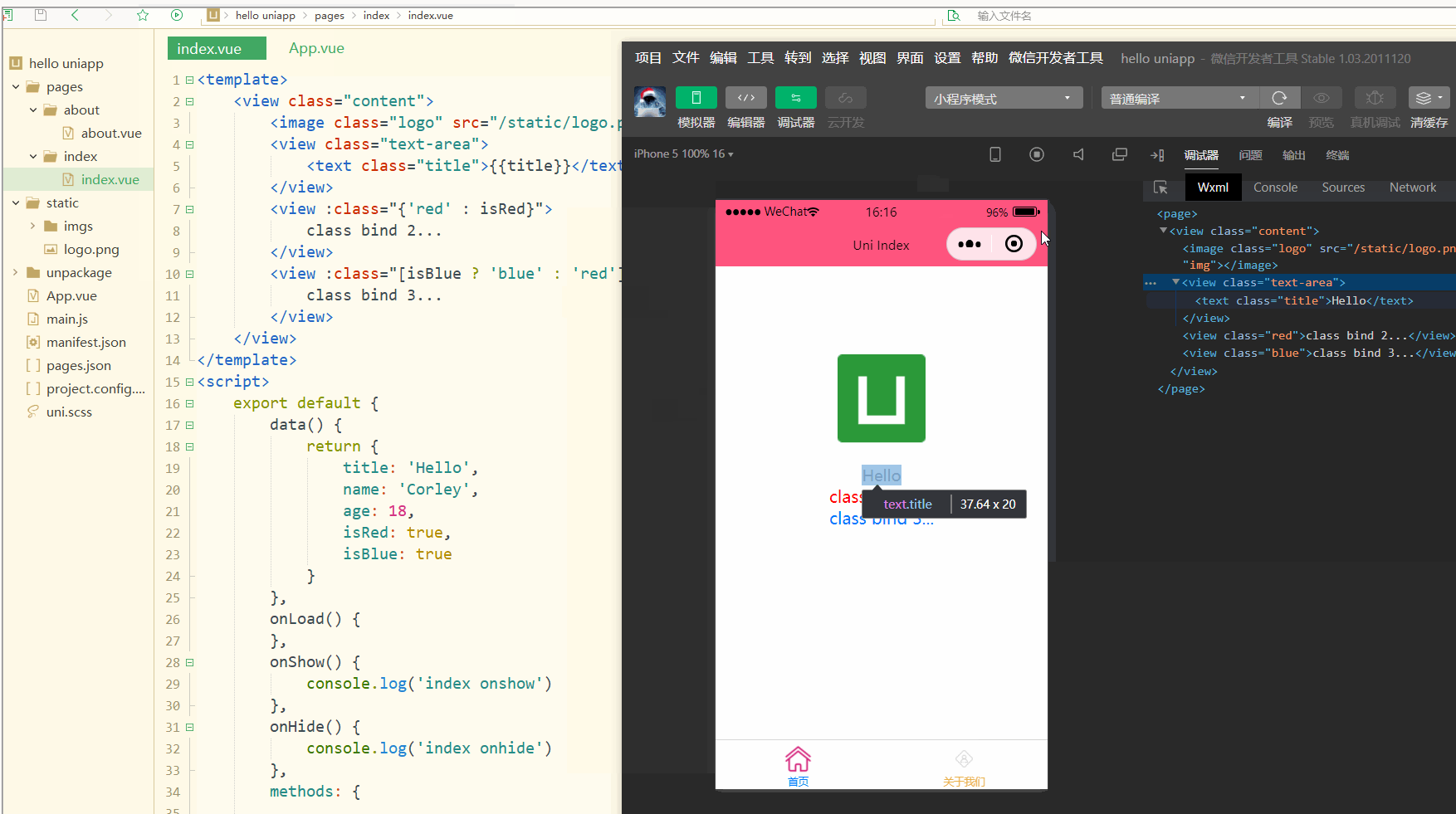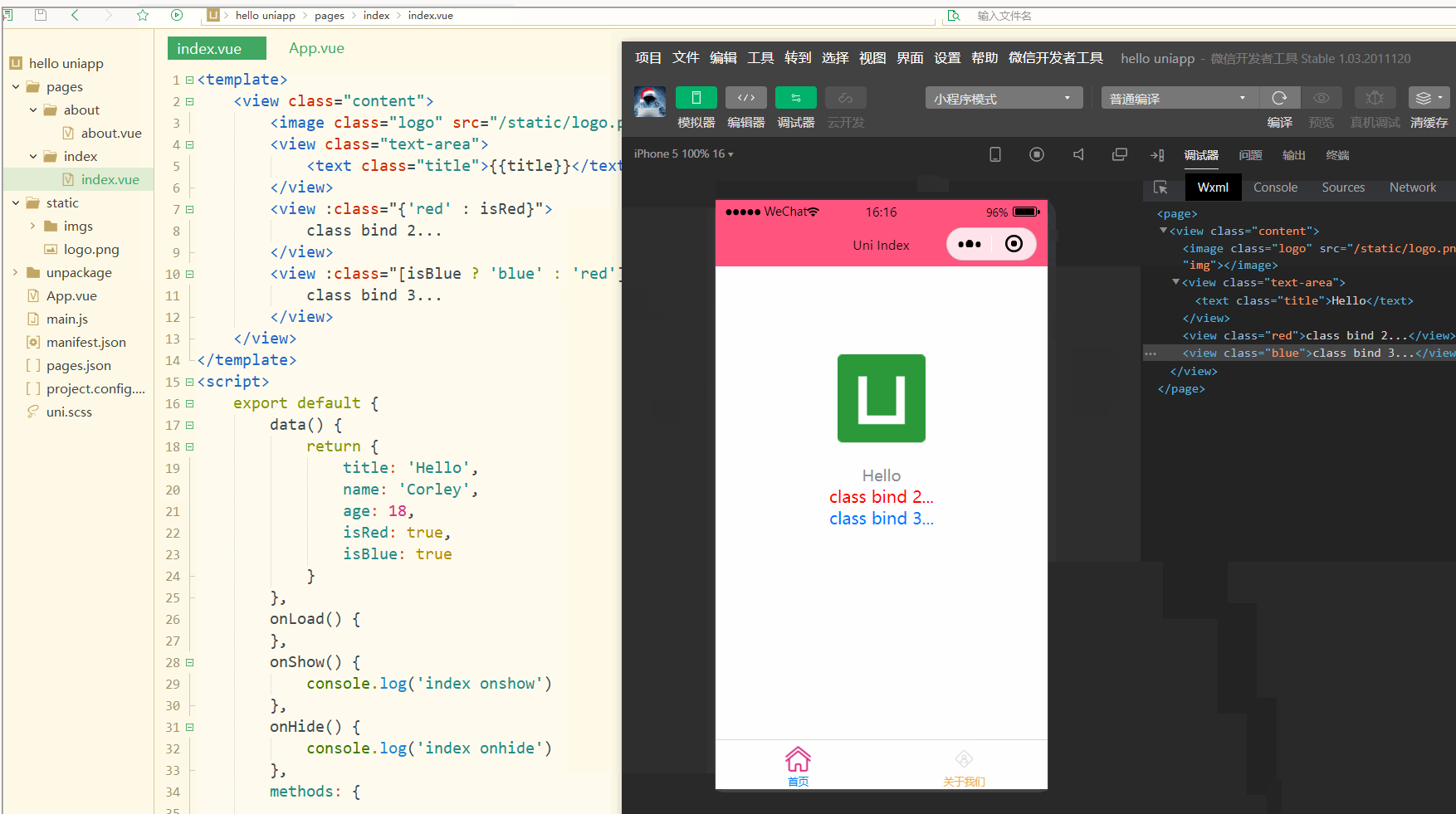
可以看到,在进行编译选然后,微信开发者工具中wxml显示的是被渲染后的class值。
2.style语法
style 支持的语法如下:
<!-- 1 -->
<view v-bind:style="{ color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }">111</view>
<!-- 2 -->
<view v-bind:style="[{ color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }]">222</view>
<!-- 3 -->
<view :style="{ color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }">333</view>
<!-- 4 -->
<view :style="[{ color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }]">444</view>其中,前2种为完整形式,后2种为简写形式。
index.vue如下:
<template>
<view class="content">
<image class="logo" src="/static/logo.png"></image>
<view class="text-area">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
</view>
<view style="font-size: 10px;">
style static...
</view>
<view :style="{fontSize: fontSize+'px'}">
class dynamic...
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
title: 'Hello',
name: 'Corley',
age: 18,
fontSize: 20
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this;
setTimeout(function(){
_self.fontSize = 30;
}, 3000)
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.logo {
height: 200rpx;
width: 200rpx;
margin-top: 200rpx;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
}
.text-area {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
color: #8f8f94;
}
.blue {
color: #007AFF;
}
</style>
显示:
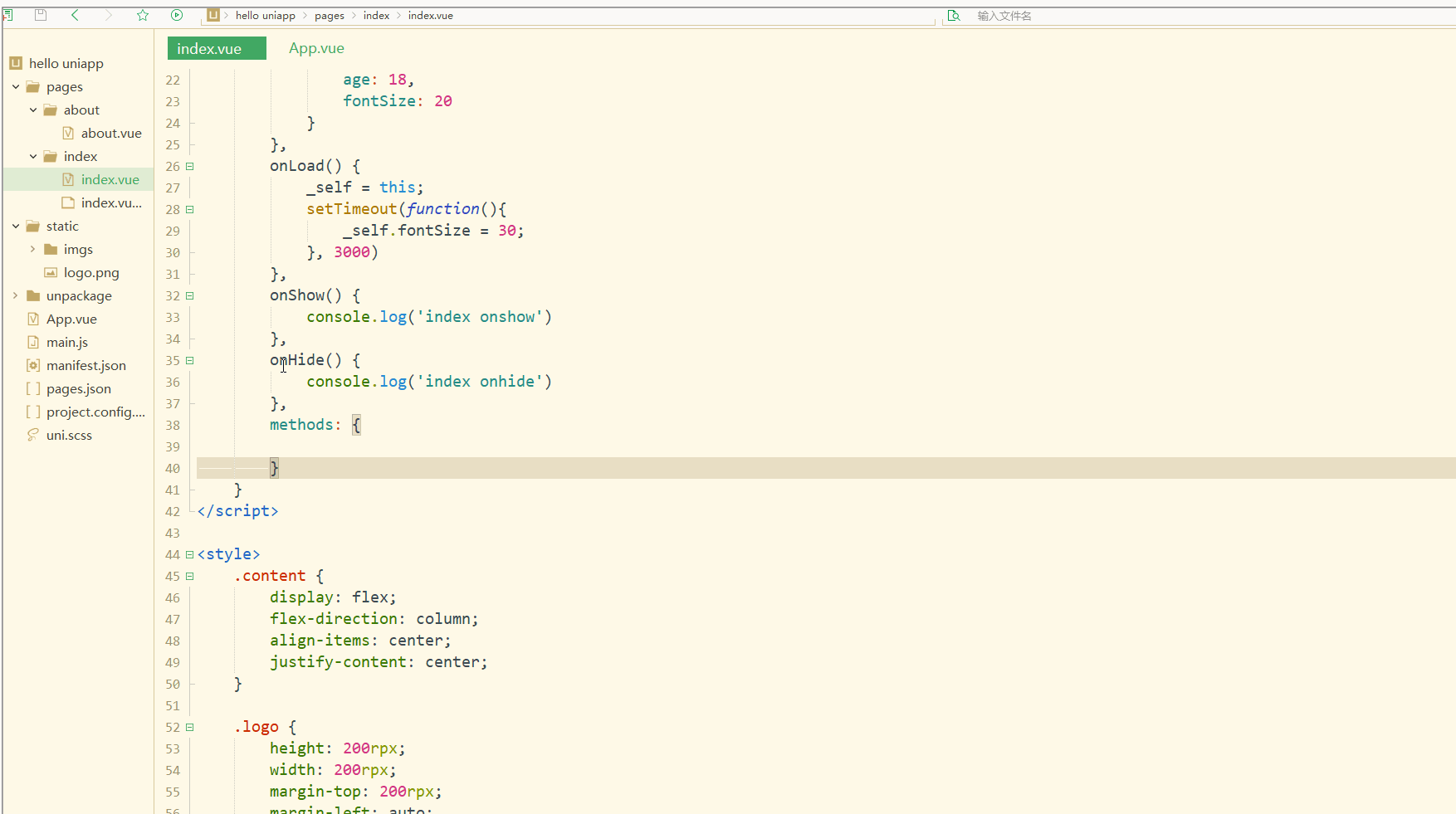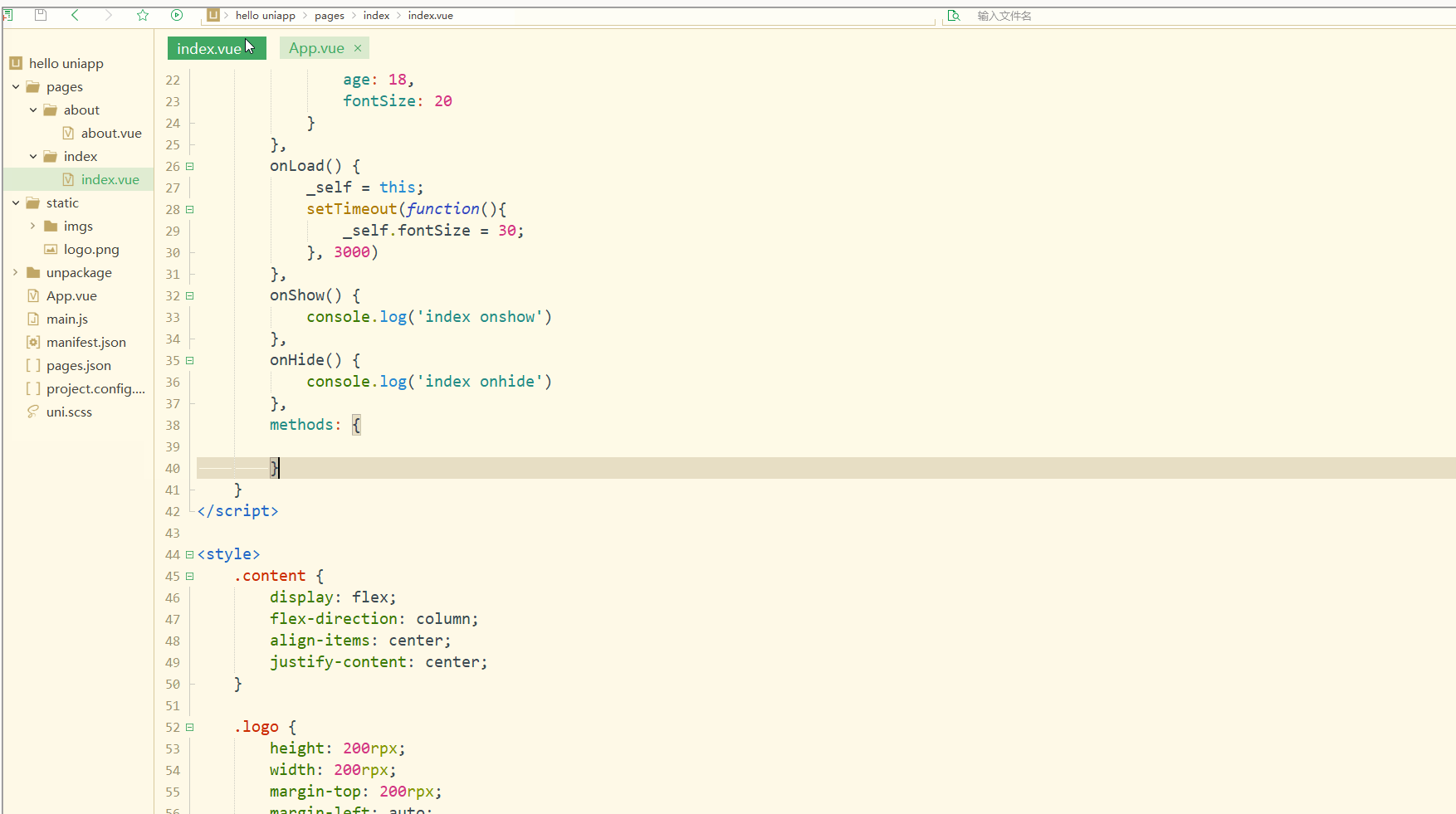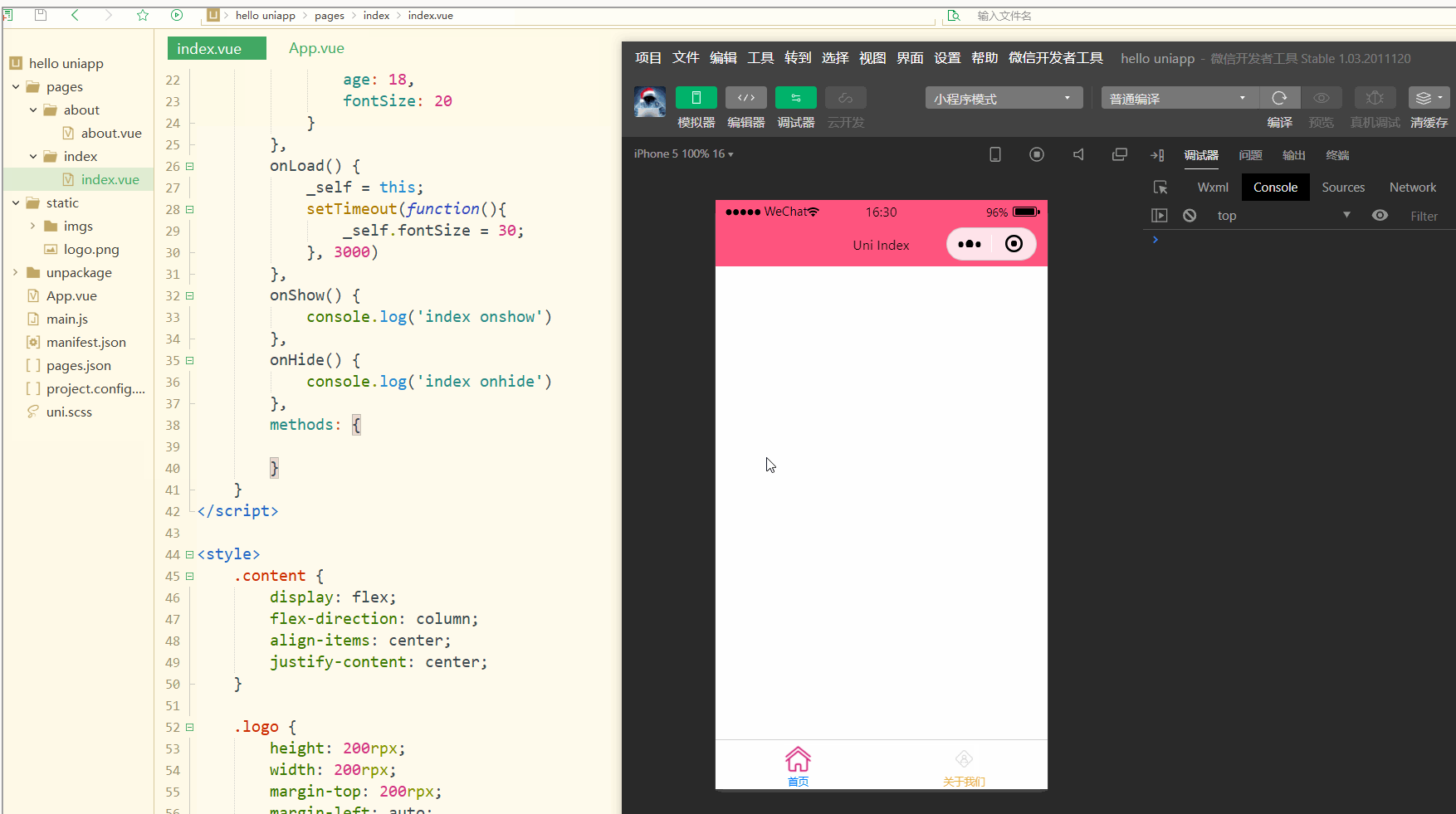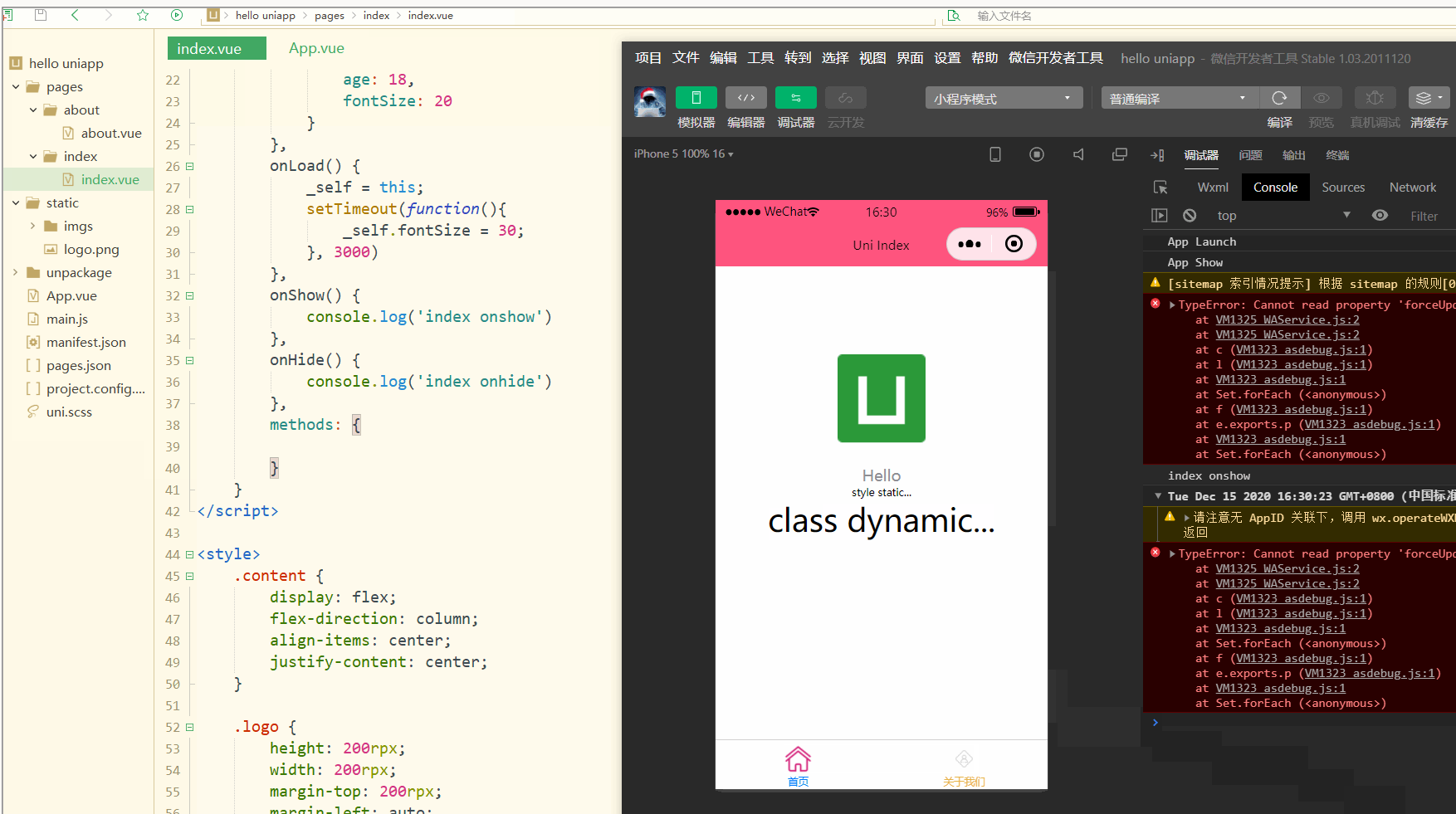
显然,样式可以动态发生变化。
需要注意,uni-app不支持 Vue官方文档中Class 与 Style 绑定 中的 classObject 和 styleObject 语法,但是可以用 computed 方法生成 class 或者 style 字符串,插入到页面中,如下:
<template>
<view>
<!-- 支持 -->
<view class="container" :class="computedClassStr"></view>
<view class="container" :class="{active: isActive}"></view>
<!-- 不支持 -->
<view class="container" :class="computedClassObject"></view>
</view>
</template>关于Class和Style动态绑定的进一步讲解和更多用法可参考uni-app入门教程(8)在uni-app中使用Vue。
3.案例--动态菜单切换
本案例实现动态切换导航栏。
先展示横向排列的导航栏,index.vue如下:
<template>
<view>
<view v-for="(item, index) in menus" class="menu">
{{item}}
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
menus: [
'新闻', '汽车', '读书'
]
}
},
onLoad() {
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.menu {
padding: 10px;
float: left;
margin: 5px;
line-height: 36px;
}
</style>
显示:
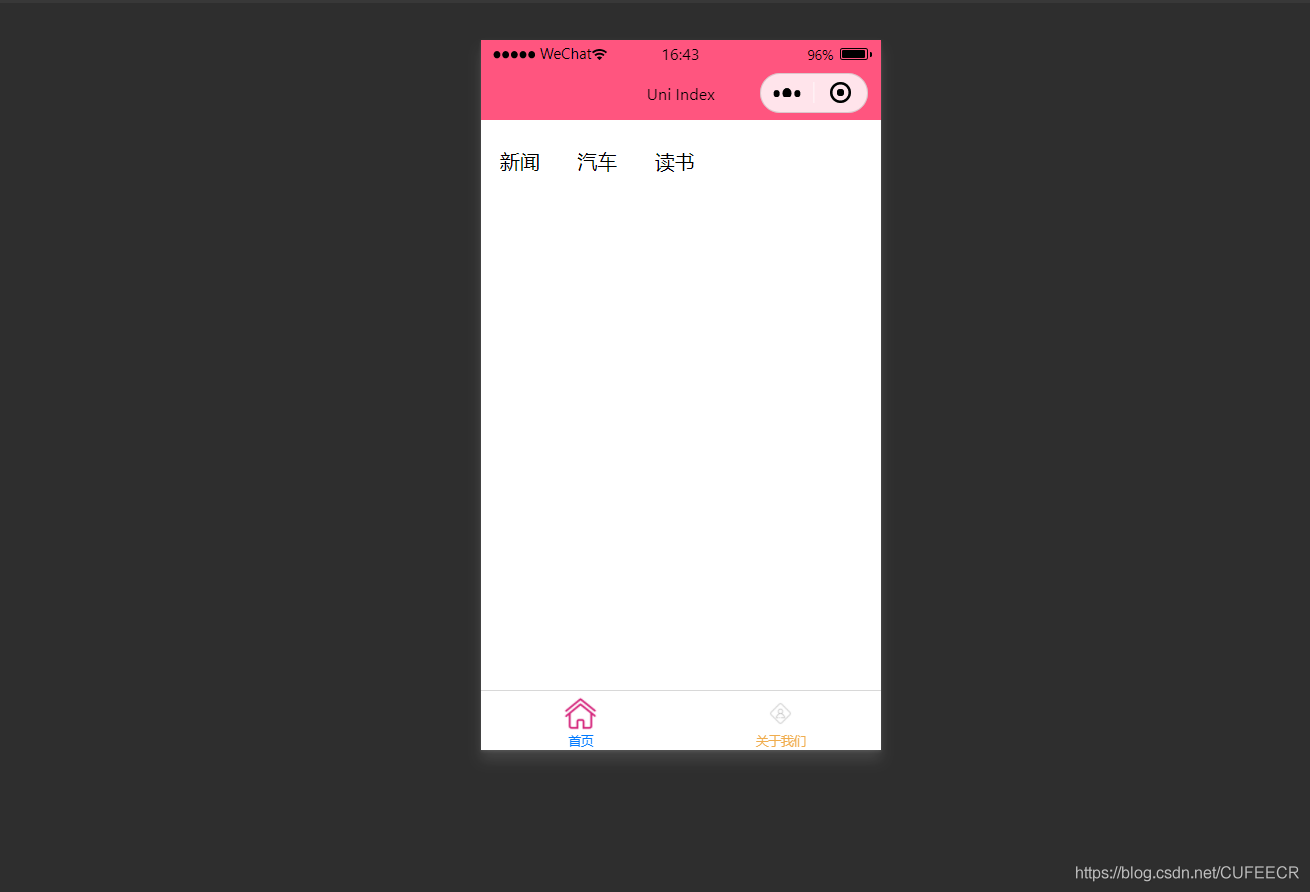
此时已经可以将导航栏横向展示了。
再实现当前的导航栏显示不一样的颜色,如下:
<template>
<view>
<view v-for="(item, index) in menus" class="menu" :class="[activeIndex==index?'menuActive':'']">
{{item}}
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
menus: [
'新闻', '汽车', '读书'
],
activeIndex: 0
}
},
onLoad() {
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
.menu {
padding: 10px;
float: left;
margin: 5px;
line-height: 36px;
}
.menuActive {
color: #FF0000 !important;
}
</style>
显示:
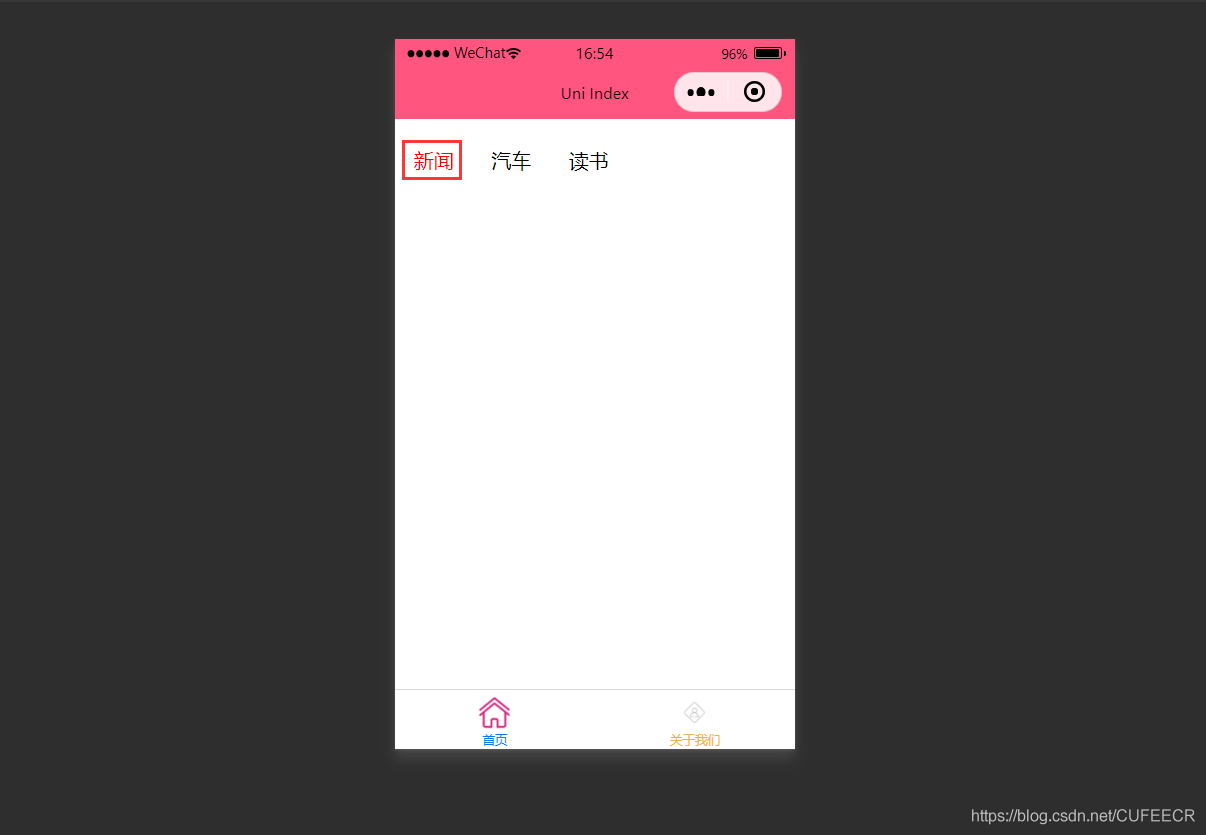
此时,第1个导航栏变为红色。
进一步实现点击时,颜色动态变化,如下:
<template>
<view>
<view v-for="(item, index) in menus" class="menu" :class="[activeIndex==index?'menuActive':'']" @click="menuClick" :id="index">
{{item}}
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
menus: [
'新闻', '汽车', '读书'
],
activeIndex: 0
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
menuClick: function(e){
var aid = e.target.id;
console.log(aid);
_self.activeIndex = aid;
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.menu {
padding: 10px;
float: left;
margin: 5px;
line-height: 36px;
}
.menuActive {
color: #FF0000 !important;
}
</style>
使用了事件来达到动态切换的效果。
显示:
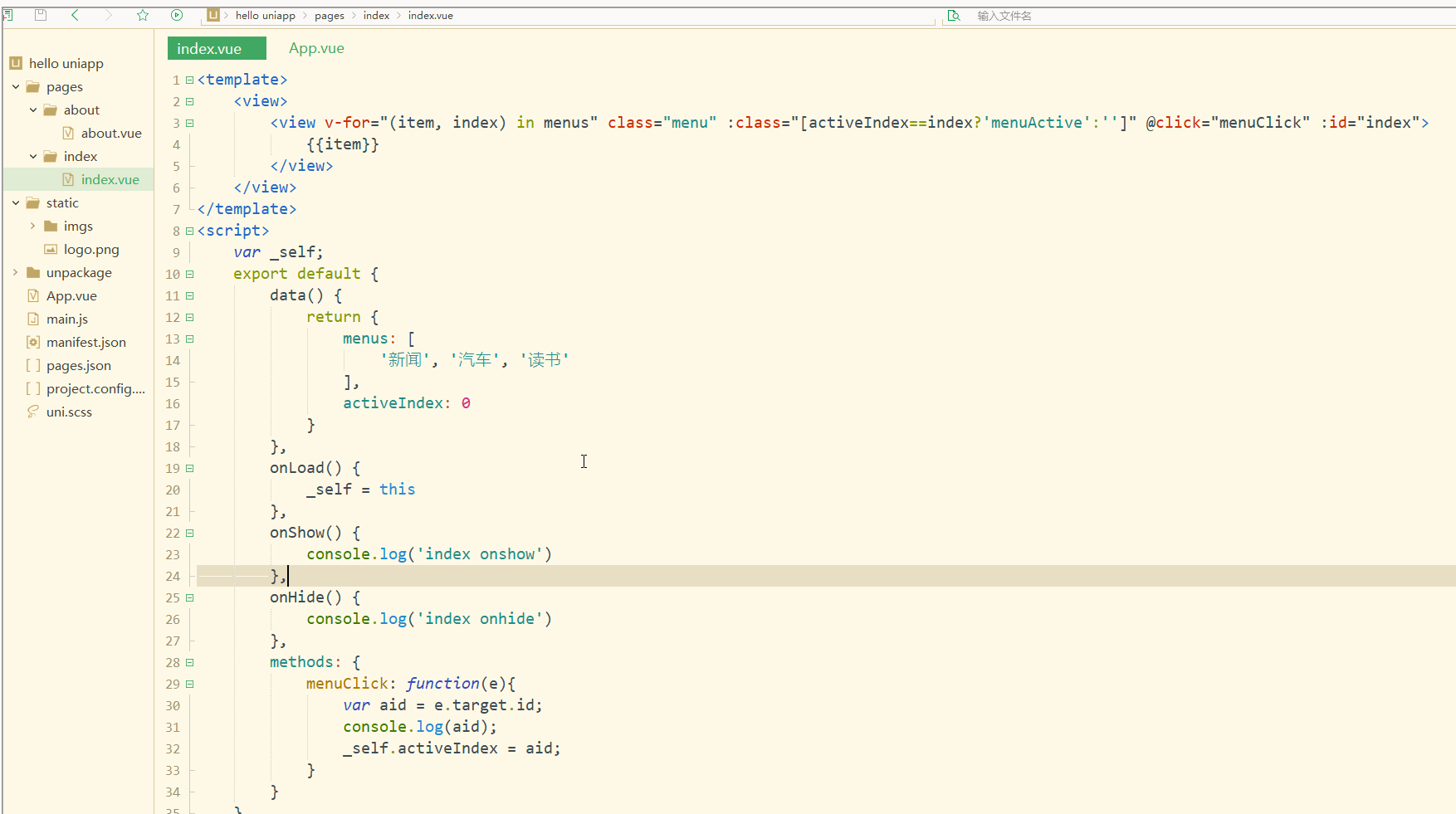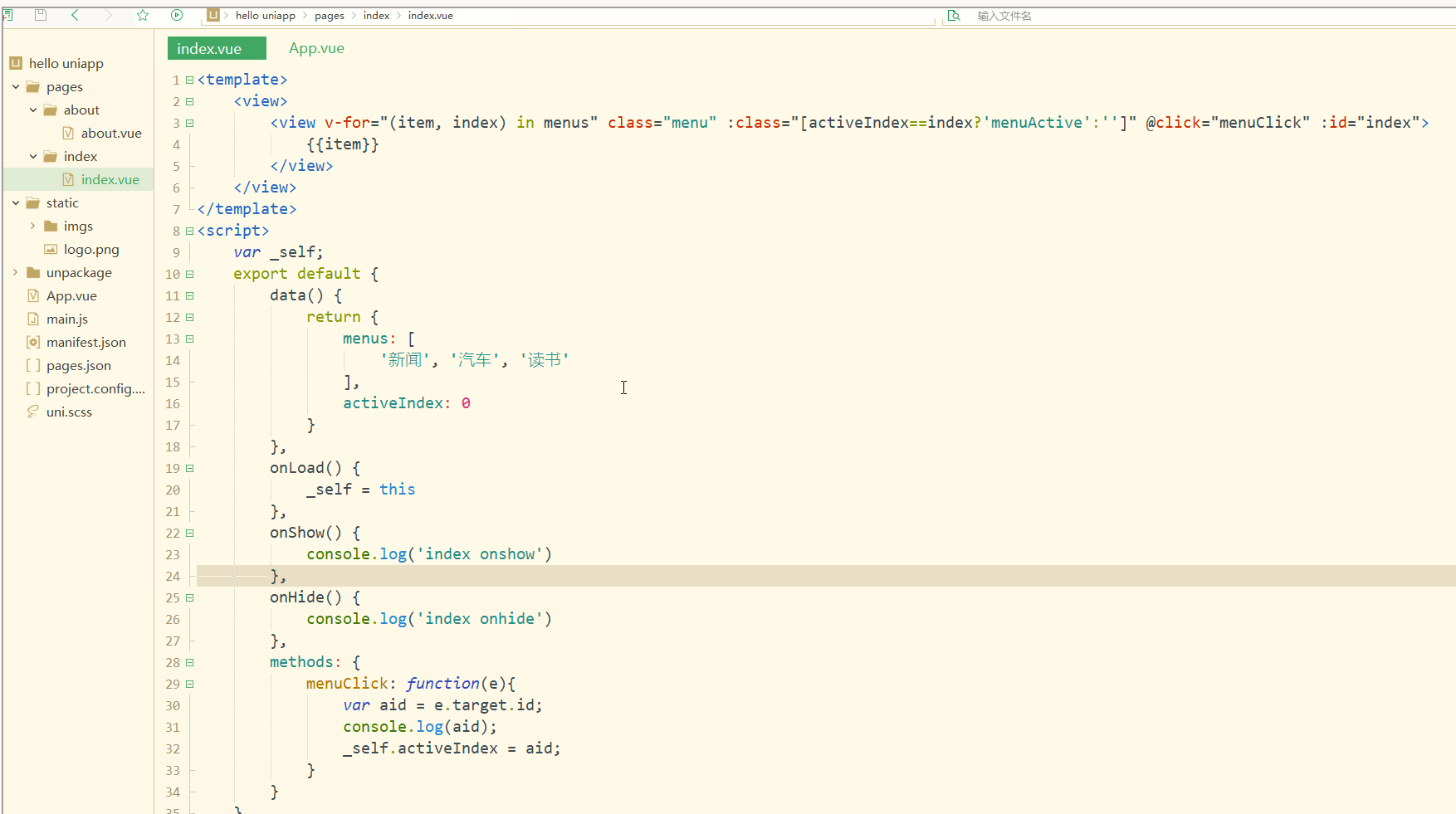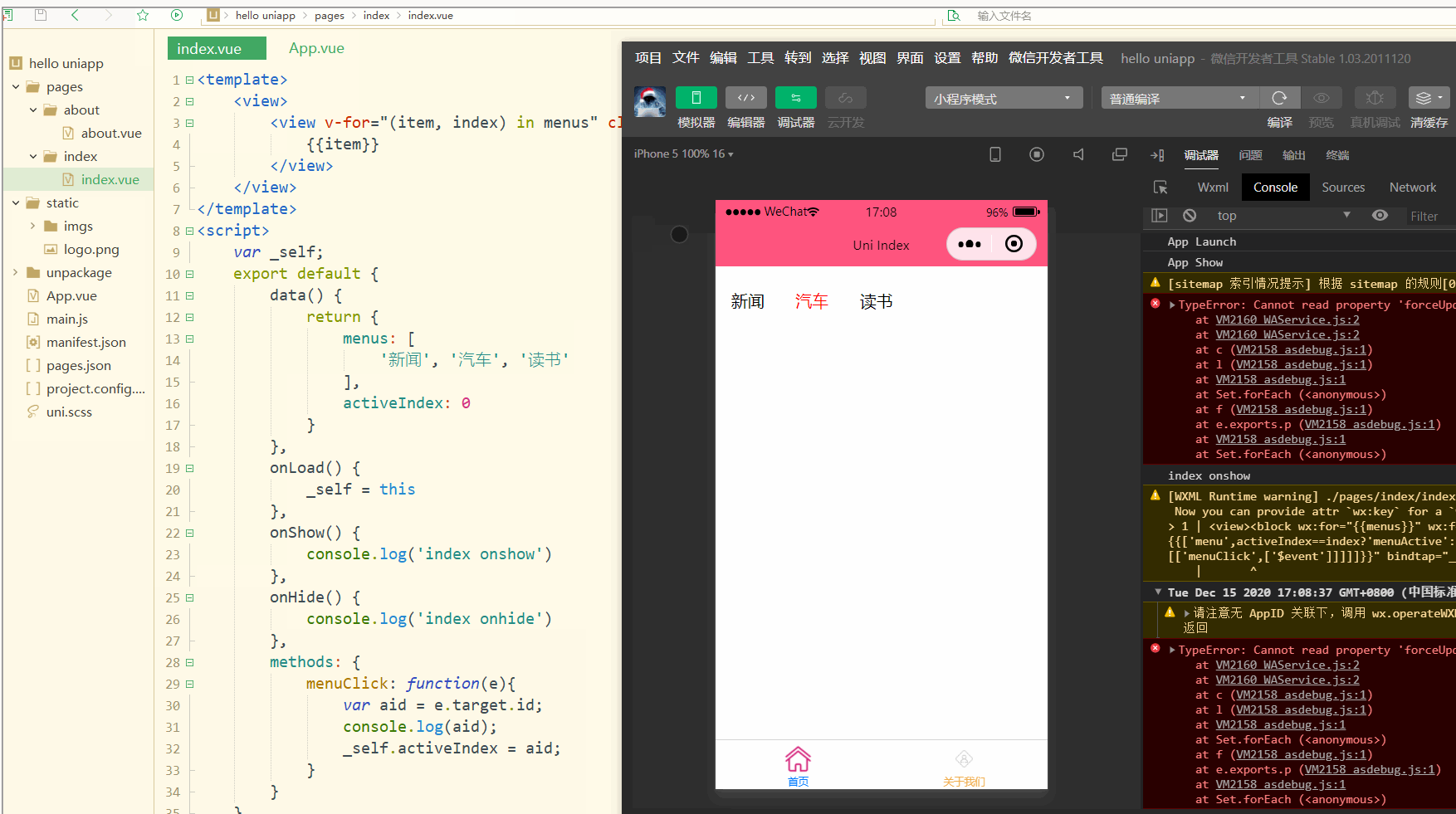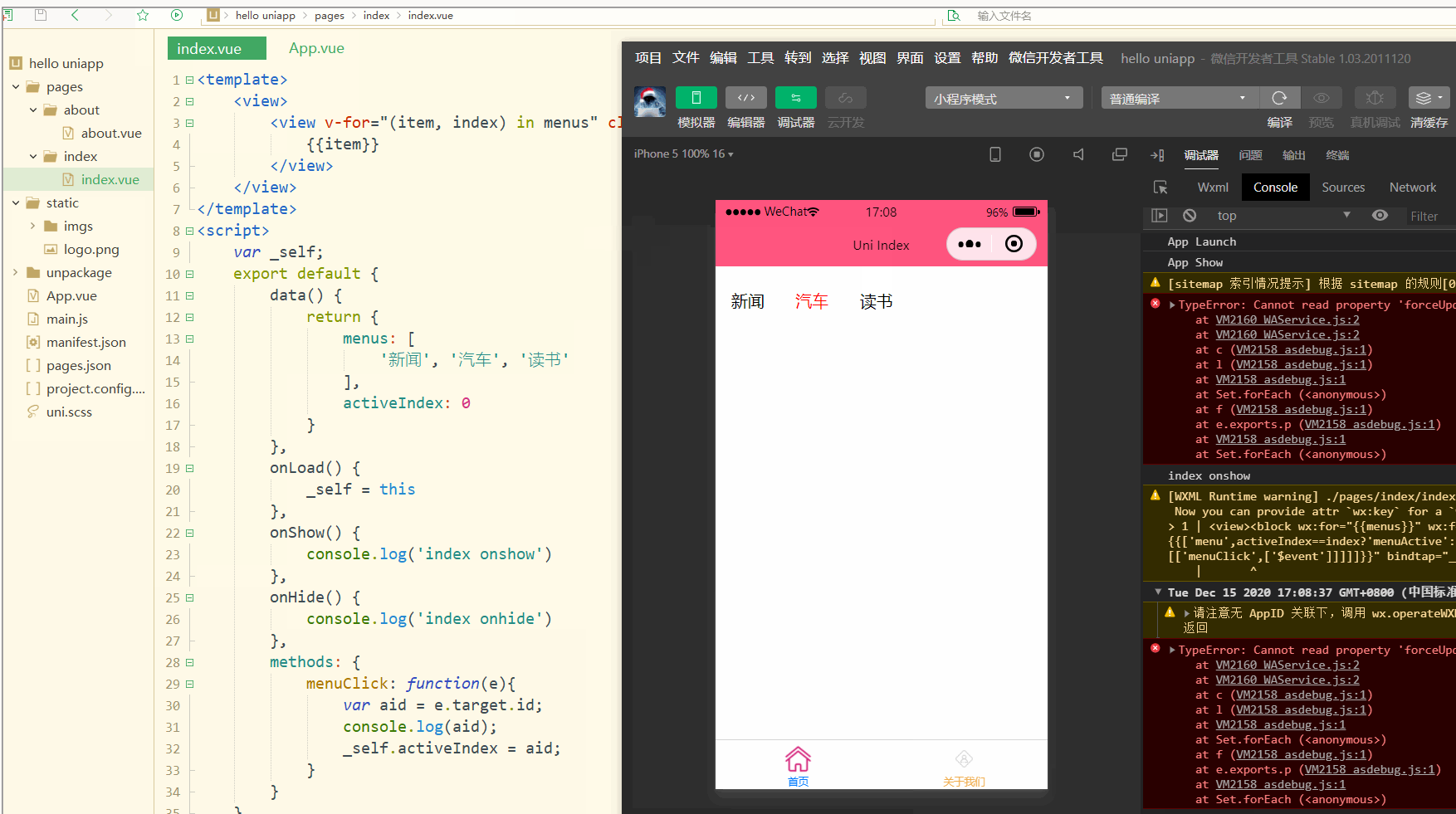
可以看到,点击不同的导航栏实现了颜色同步变化的效果。
三、事件和事件绑定
1.uni-app事件
事件映射表定义了WEB事件和uni-app事件之间的对应关系,具体如下: Web事件|uni-app事件|说明 -----|-----|----- click| 'tap'|被点击 touchstart|'touchstart'|手指开始在元素上触摸时 touchmove|'touchmove'|移动 touchcancel|'touchcancel'|取消 touchend|'touchend'|结束 tap|'tap'|单机 longtap|'longtap'|长按 input|'input'|输入 change|'change'|改变 submit|'submit'|表单提交 blur|'blur'|失焦 focus| 'focus'|聚焦 reset|'reset'|表单重置 confirm|'confirm'|确认 columnchange|'columnchange'|字段变化 linechange| 'linechange'|行比那花 error|'error'|错误 scrolltoupper| 'scrolltoupper'|滚动到顶部 scrolltolower|'scrolltolower'|滚动到底部 scroll|'scroll'|滚动
说明:
(1)在 input 和 textarea 中 change 事件会被转为 blur 事件;
(2)列表中没有的原生事件也可以使用,例如map组件的regionchange 事件直接在组件上添加@regionchange修饰即可,同时这个事件也非常特殊,它的 event type 有 begin 和 end 两个,导致我们无法在handleProxy 中区分到底是什么事件,所以在监听此类事件的时候同时监听事件名和事件类型,即<map @regionchange="functionName" @end="functionName" @begin="functionName"><map>;
(3)由于平台的差异,bind 和 catch 事件同时绑定时,只会触发 bind,catch 不会被触发,使用时需要注意。
(4)件修饰符:
- 使用stop会阻止冒泡,但是同时绑定了一个非冒泡事件,会导致该元素上的 catchEventName 失效;
- prevent 可以直接结束事件,因为uni-app里没有什么默认事件,比如 submit 并不会跳转页面;
- self 没有可以判断的标识;
- once 也不能做,因为uni-app没有 removeEventListener, 虽然可以直接在 handleProxy 中处理,但是并不优雅;
(5)按键修饰符: uni-app运行在手机端,没有键盘事件,所以不支持按键修饰符。
2.事件绑定
使用@对元素进行事件绑定,当事件被触发时,会导致相应的操作。
index.vue如下:
<template>
<view>
<view class="demo" @click="clickTest" @longtap="longtap"></view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
clickTest : function(e){
console.log("click")
},
longtap : function(e){
console.log("longtap")
},
}
}
</script>
<style>
.demo {
width: 600rpx;
height: 600rpx;
background: #DD524D;
}
</style>
显示:
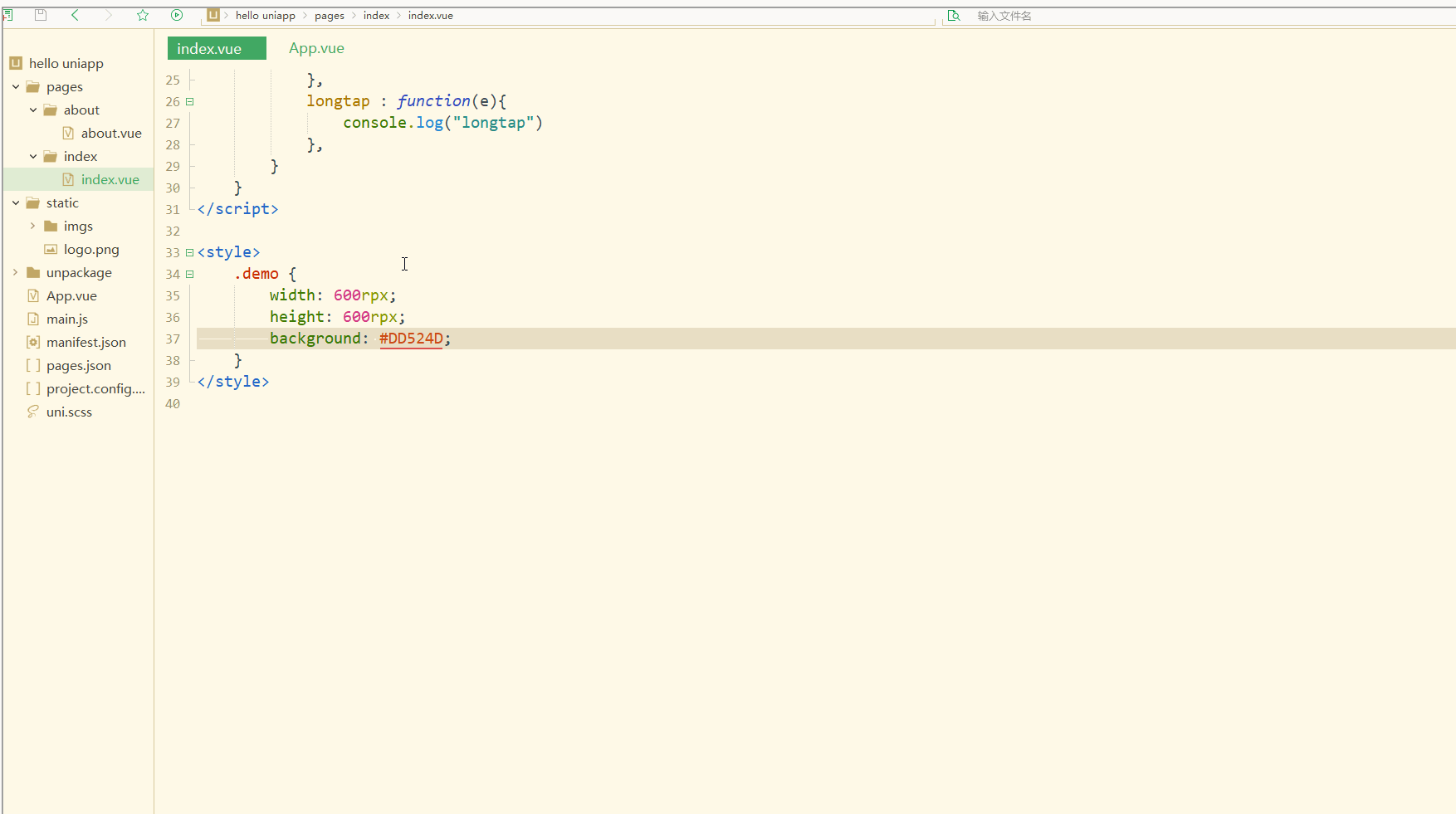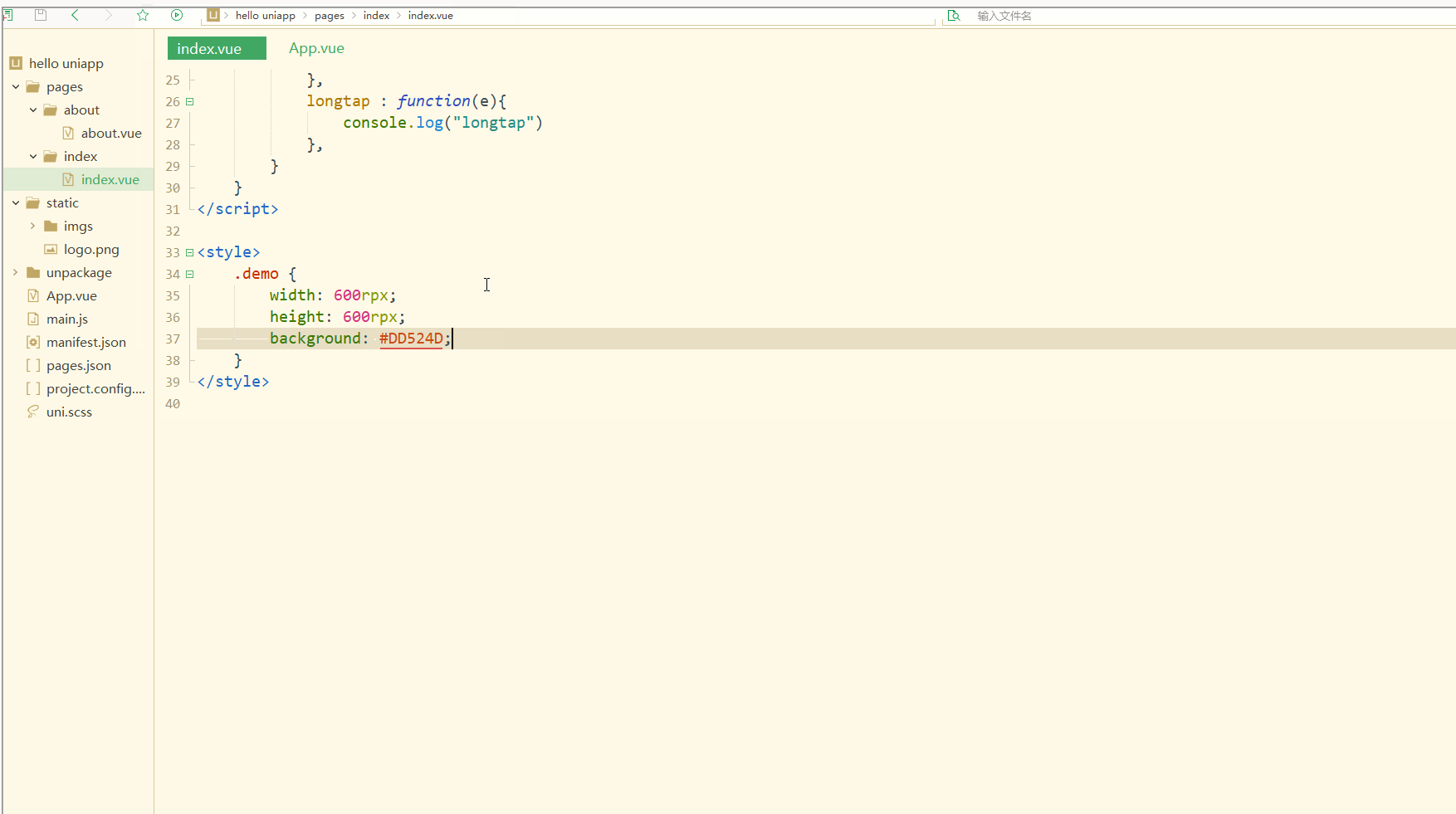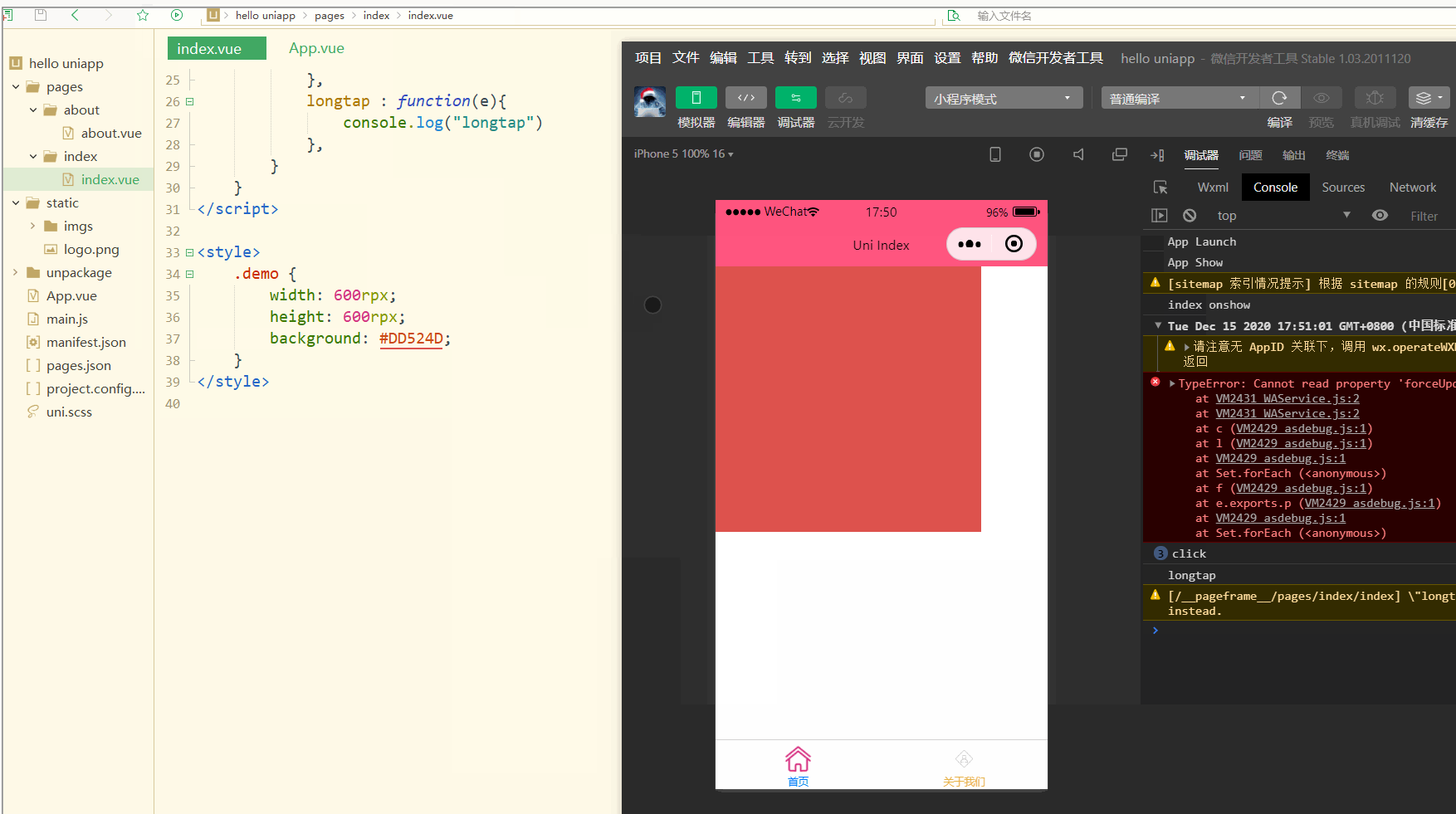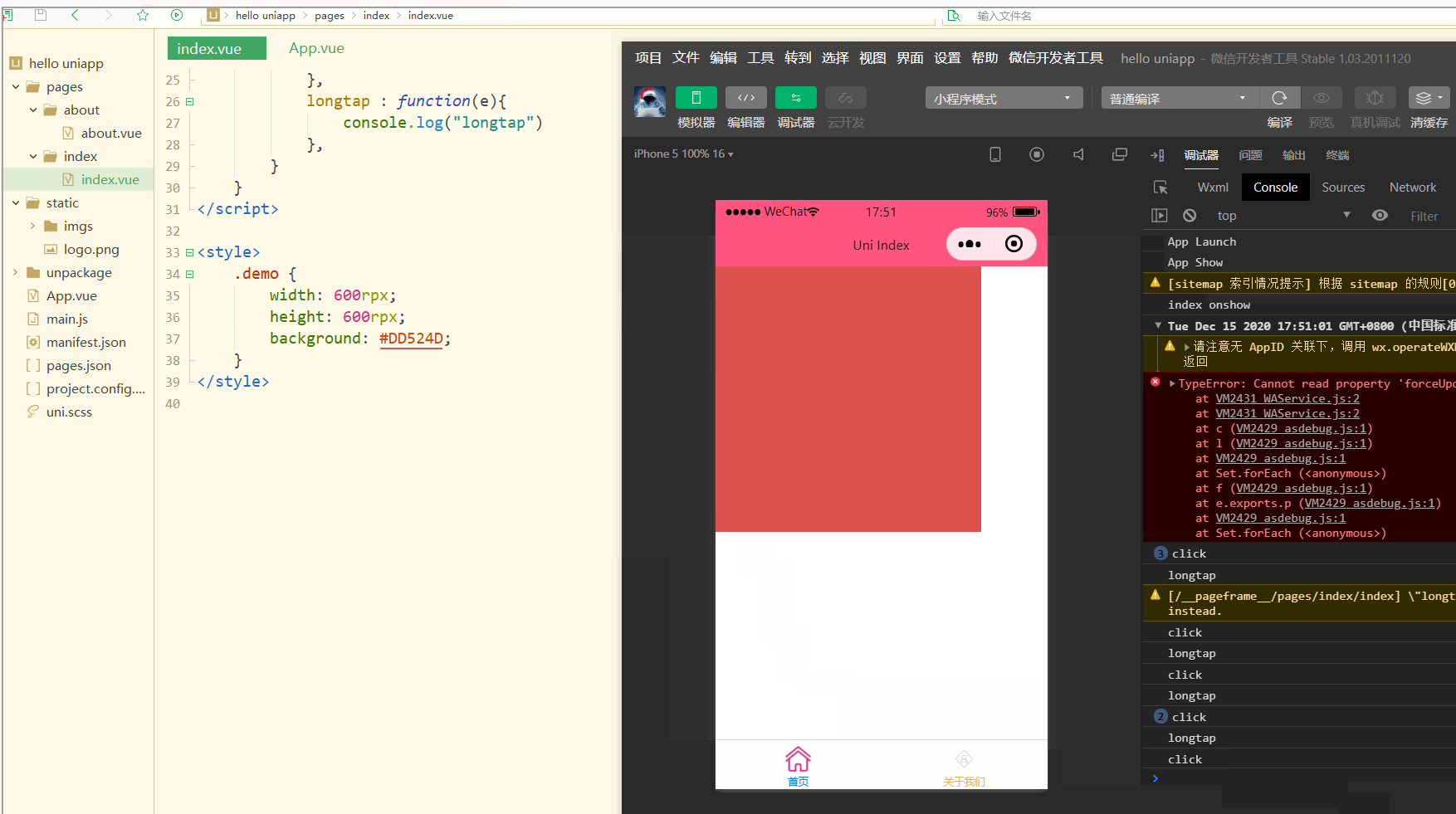
可以看到,在进行点击和长按时,会触发不同的事件、执行不同的操作。
可以在小程序中观察对应事件对象,并利用此对象获取更多信息。
3.事件传参
在触发事件时,还可以传入动态参数。
如下:
<template>
<view>
<view v-for="(item, index) in students" class="persons" @click="menuClick" v-bind:id="index">{{index}} - {{item.name}}</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
students: [{
name: "张三",
age: 18
},
{
name: "李四",
age: 20
}
]
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
menuClick: function(e) {
console.log(e);
console.log(e.target.id);
},
}
}
</script>
<style>
.demo {
width: 600rpx;
height: 600rpx;
background: #DD524D;
}
</style>
显示:
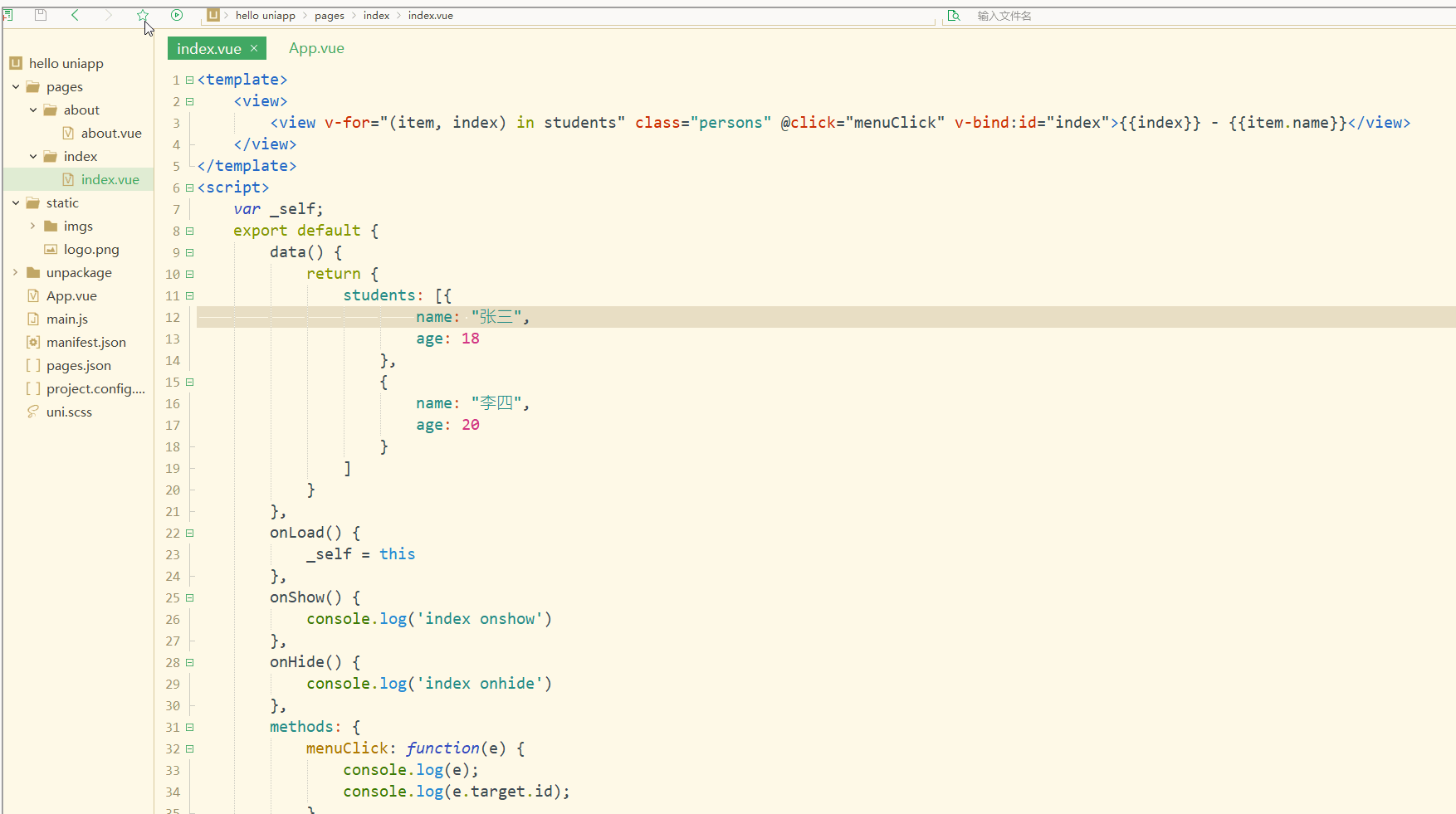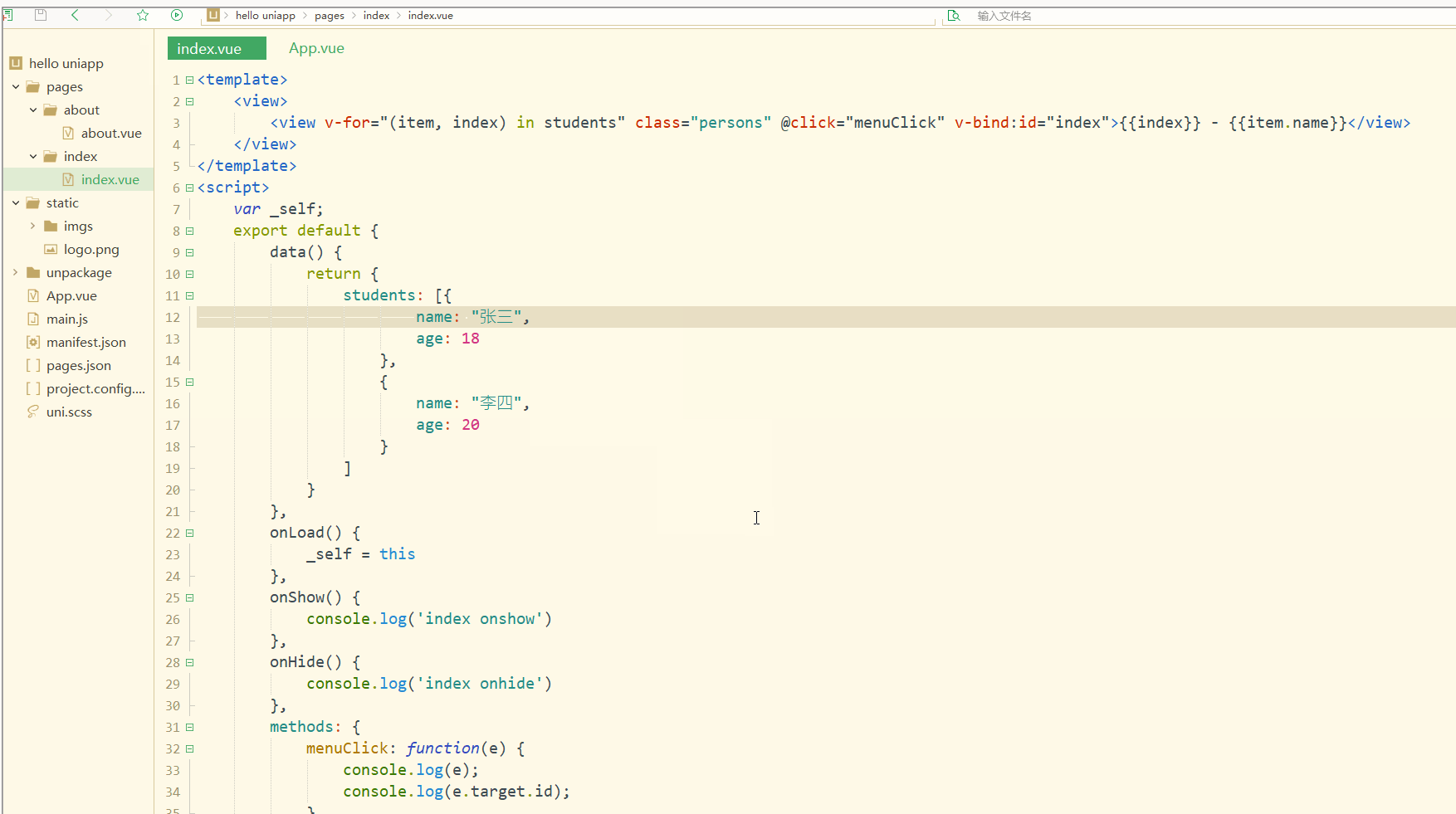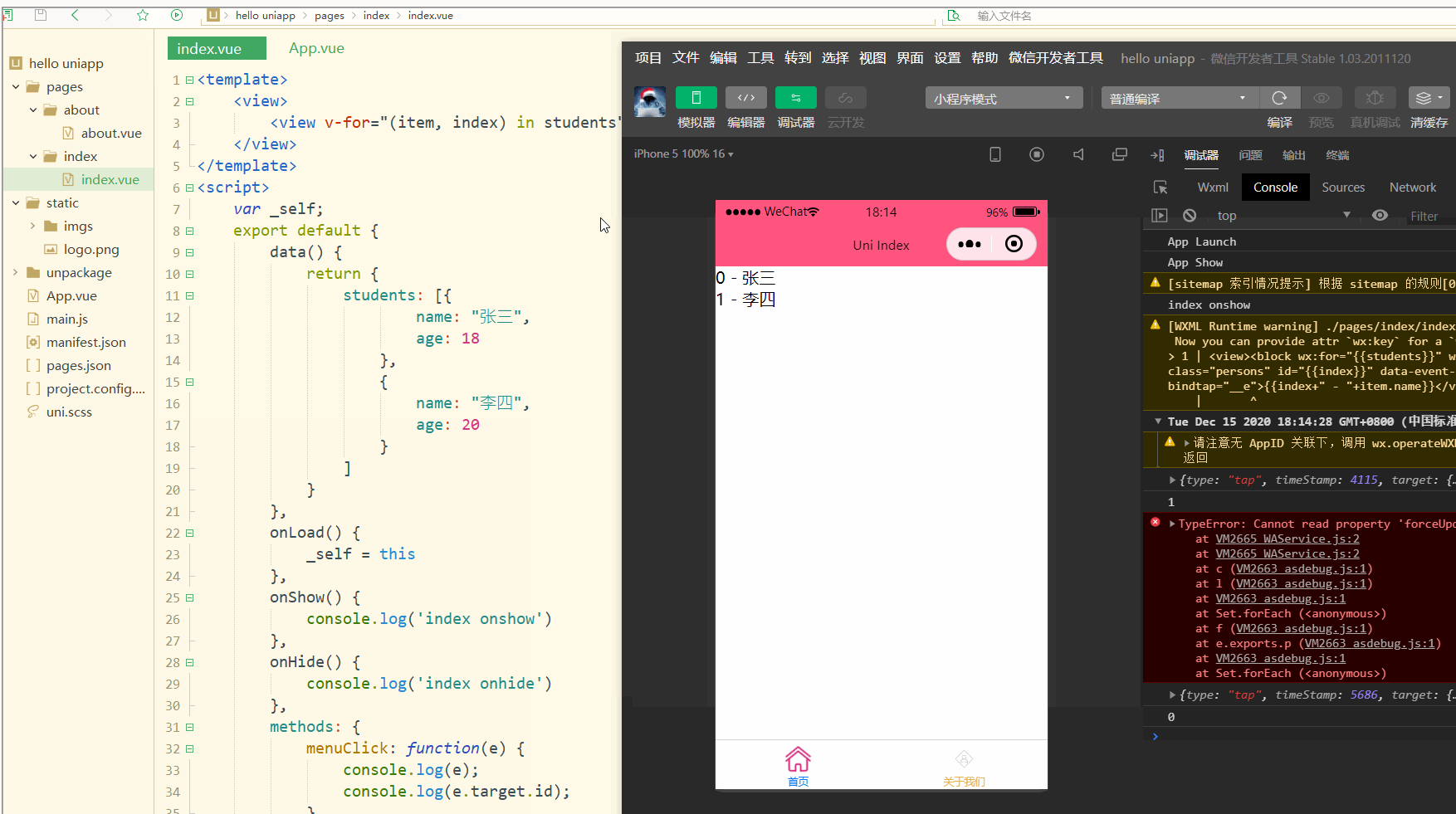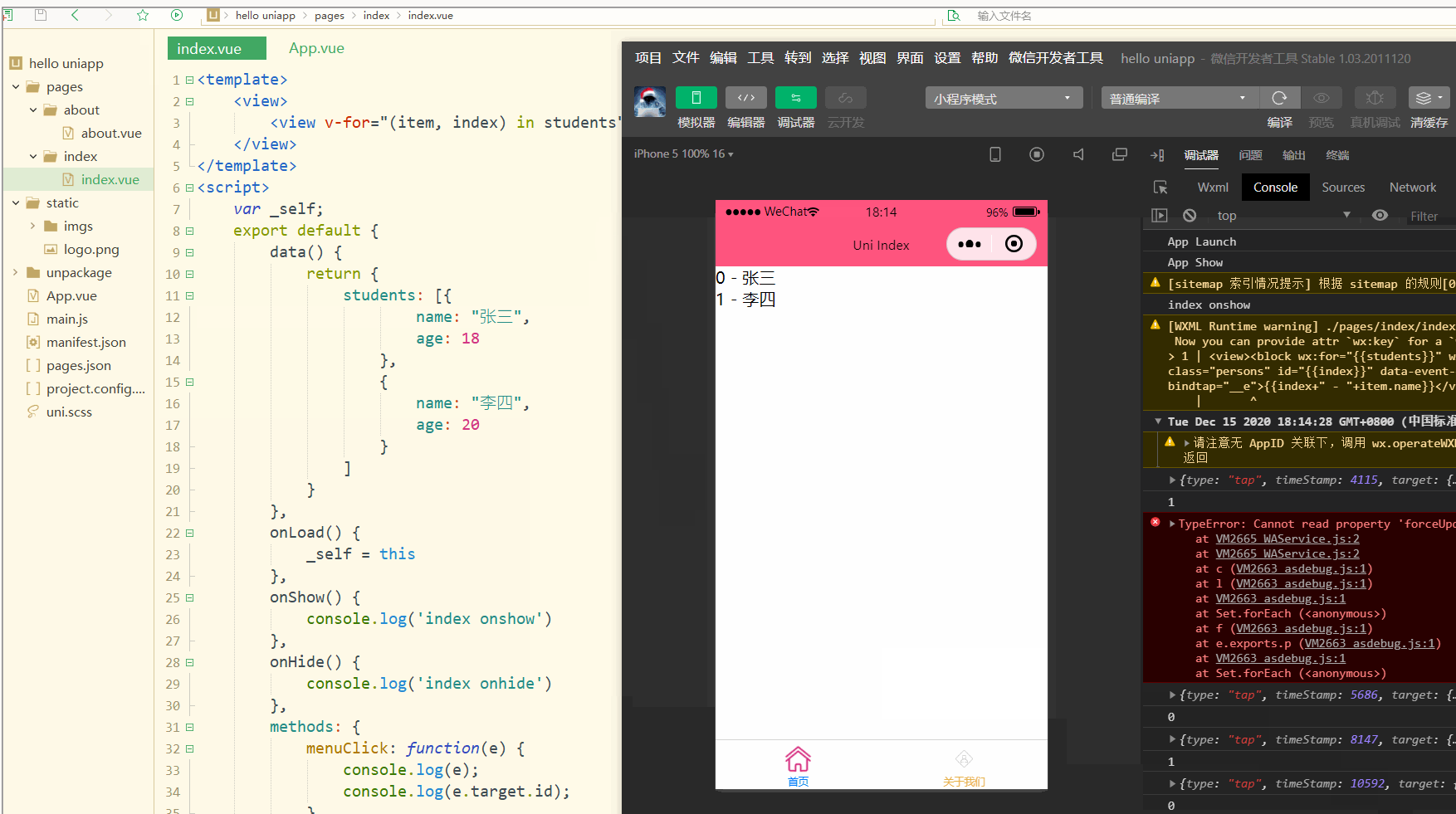
可以看到,在进行点击时,控制台打印出了事件对象和e.target.id的值。
再如:
<template>
<view>
<view class="demo" id="outid" @click="clickTest" @longtap="longtap">
<view id="inid" style="width: 400rpx;height: 400rpx;background: #007AFF;"></view>
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
var _self;
export default {
data() {
return {
}
},
onLoad() {
_self = this
},
onShow() {
console.log('index onshow')
},
onHide() {
console.log('index onhide')
},
methods: {
clickTest : function(e){
console.log(e.currentTarget.id)
console.log(e.target.id)
},
longtap : function(e){
console.log("longtap")
},
}
}
</script>
<style>
.demo {
width: 600rpx;
height: 600rpx;
background: #DD524D;
}
</style>
显示:
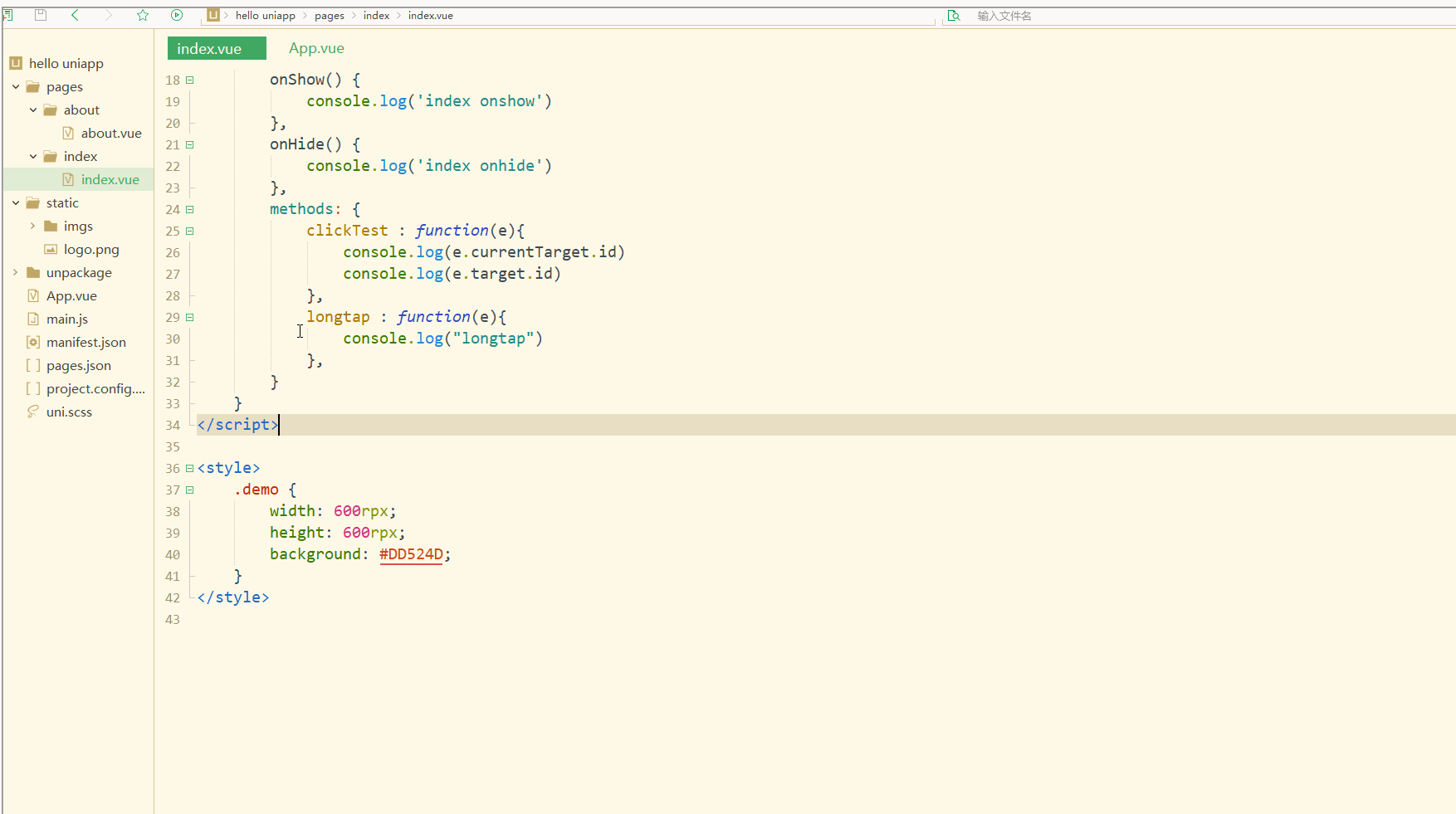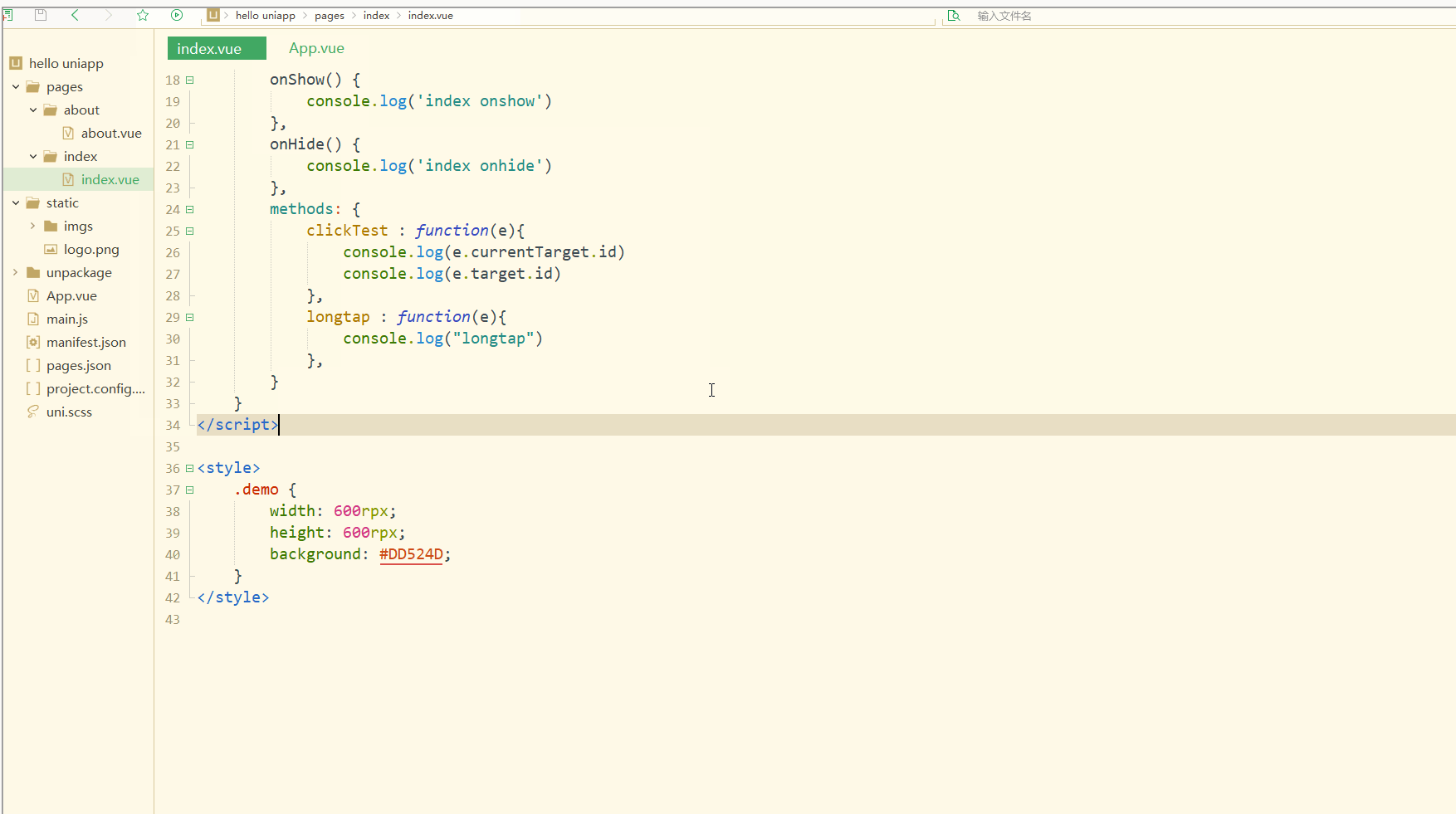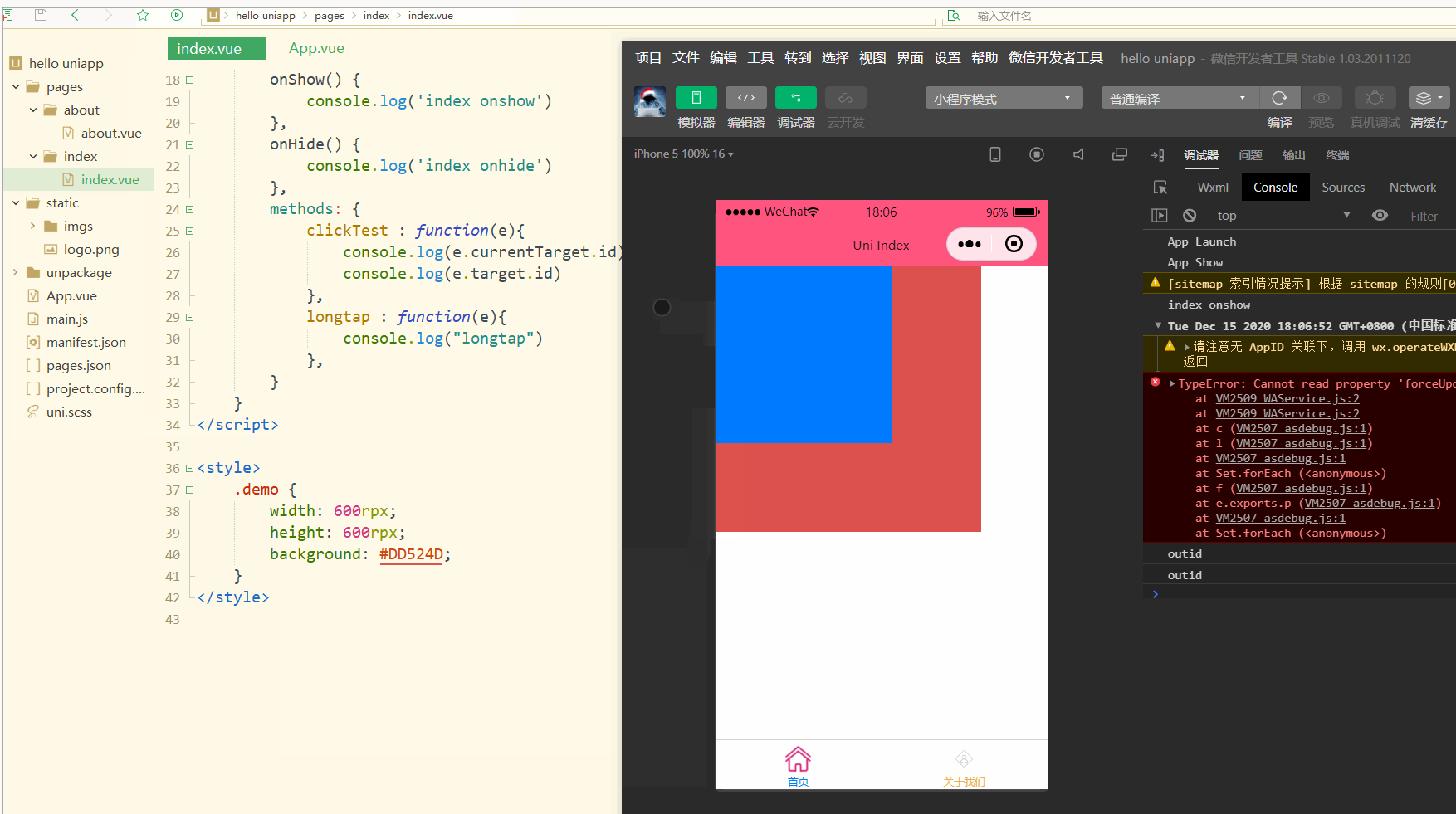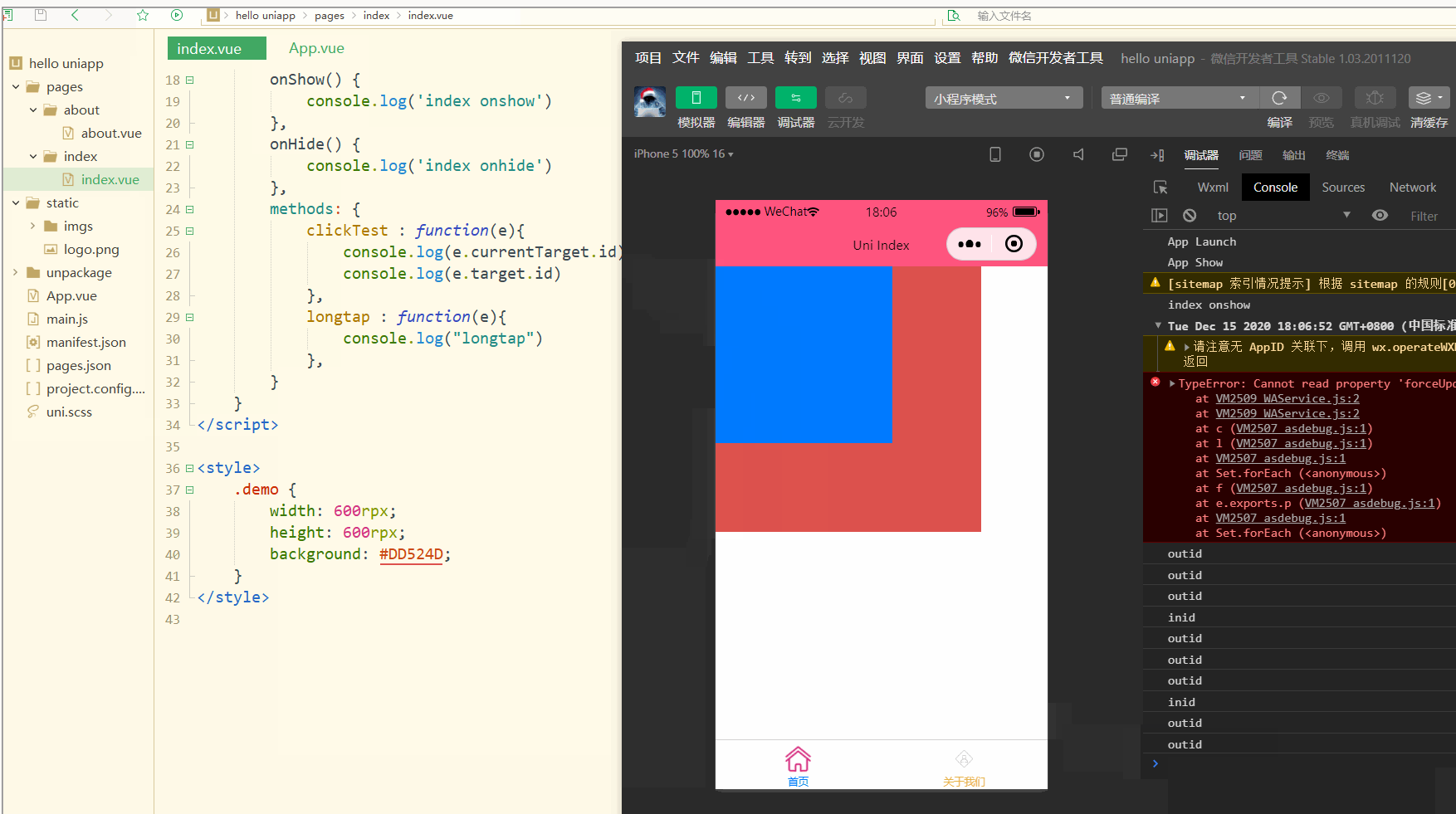
可以看到,在点击外部红色区域时,打印的两个id值相同;
而在点击内部蓝色区域时,e.target变为内部的view元素,所以打印出的也是inid,所以在使用属性传参时尽量使用e.currentTarget。
总结
在uni-app中,不论是对于数据(变量),还是对于以class或style定义的样式,亦或定义的事件,都可以进行动态绑定、同步变化,这些特性有利于更高效地开发出所需功能,大大降低了开发成本。
本文原文首发来自https://blog.csdn.net/CUFEECR,可点击https://blog.csdn.net/CUFEECR/article/details/111240593查看。

