1,创建表时加入的约束
a) 非空约束,not null
b) 唯一约束,unique
c) 主键约束,primary key
d) 外键约束,foreign key
1,非空约束,针对某个字段设置其值不为空,如:学生的姓名不能为空
drop table if exists t_student;
create table t_student(
student_id int(10),
student_name varchar(20) not null,
sex char(2) default 'm',
birthday date,
email varchar(30),
classes_id int(3)
)
反例,如果插入时 student_name为空违反了约束则报错
insert into t_student(student_id, birthday, email, classes_id)
values
(1002, '1988-01-01', 'qqq@163.com', 10)
2,唯一性约束,它可以使某个字段的值不能重复,如:email不能重复
drop table if exists t_student;
create table t_student(
student_id int(10),
student_name varchar(20) not null,
sex char(2) default 'm',
birthday date,
email varchar(30) unique,
classes_id int(3)
)
drop table if exists t_student;
create table t_student(
student_id int(10),
student_name varchar(20) not null,
sex char(2) default 'm',
birthday date,
email varchar(30) ,
classes_id int(3) ,
constraint email_unique unique(email)/*表级约束*/
3,主键约束
每个表应该具有主键,主键可以标识记录的唯一性,主键分为单一主键和复合(联合)主键,单一主键是由一个字段构成的,复合(联合)主键是由多个字段构成的。
drop table if exists t_student;
create table t_student()
student_id int(10) primary key,/*列级约束*/
student_name varchar(20) not null,
sex char(2) default 'm',
birthday date,
email varchar(30) ,
classes_id int(3)
)
或者
drop table if exists t_student;
create table t_student(
student_id int(10),
student_name varchar(20) not null,
sex char(2) default 'm',
birthday date,
email varchar(30) ,
classes_id int(3),
CONSTRAINT p_id PRIMARY key (student_id)/*表级约束*/
)
4,外键约束
外键主要是维护表之间的关系的,主要是为了保证参照完整性,如果表中的某个字段为外键字段,那么该字段的值必须来源于参照的表的主键。
首先建立班级表t_classes
drop table if exists t_classes;
create table t_classes(
classes_id int(3),
classes_name varchar(40),
constraint pk_classes_id primary key(classes_id)
)
在t_student中加入外键约束
drop table if exists t_student;
create table t_student(
student_id int(10),
student_name varchar(20),
sex char(2),
birthday date,
email varchar(30),
classes_id int(3),
constraint student_id_pk primary key(student_id),
constraint fk_classes_id foreign key(classes_id) references t_classes(classes_id)
)
当我们向t_student中加入数据
insert into t_student(student_id, student_name, sex, birthday, email, classes_id)values(1001, 'zhangsan', 'm', '1988-01-01', 'qqq@163.com', 10)
出现错误,因为在班级表中不存在班级编号为10班级,外键约束起到了作用
存在外键的表就是子表,参照的表就是父表,所以存在一个父子关系,也就是主从关系,主表就是班级表,从表就是学生表。
上面的例子中如果插入的时候把外键值设为null,可以插入成功。成功的插入了学生信息,但是classes_id没有值,这样会影响参照完整性,所以我们建议将外键字段设置为非空。
当需要删除班级数据,也会报错,因为子表(t_student)存在一个外键classes_id,它参照了父表(t_classes)中的主键,所以先删除子表中的引用记录,再修改父表中的数据。
因为子表(t_student)存在一个外键classes_id,它参照了父表(t_classes)中的主键,所以先删除父表,那么将会影响子表的参照完整性,所以正确的做法是,先删除子表中的数据,再删除父表中的数据,采用drop table也不行,必须先drop子表,再drop父表
例如级联更新
mysql对有些约束的修改比较麻烦,所以我们可以先删除,再添加
alter table t_student drop foreign key fk_classes_id;
alter table t_student add constraint fk_classes_id_1 foreign key(classes_id) references t_classes(classes_id) on update cascade;
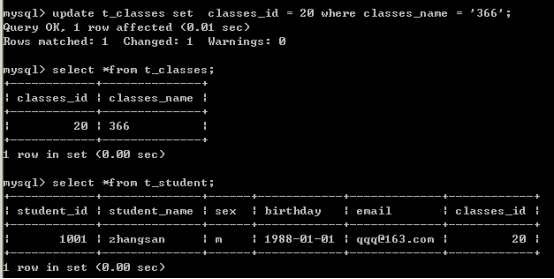
级联之后,我们只修改了父表中的数据,但是子表中的数据也会跟着变动。
2,需不需要外键
主键和索引是不可少的,不仅可以优化数据检索速度,开发人员还省不其它的工作,
矛盾焦点:数据库设计是否需要外键。这里有两个问题:一个是如何保证数据库数据的完整性和一致性;二是第一条对性能的影响。
正方观点:
1,由数据库自身保证数据一致性,完整性,更可靠,因为程序很难100%保证数据的完整性,而用外键即使在数据库服务器当机或者出现其他问题的时候,也能够最大限度的保证数据的一致性和完整性。
eg:数据库和应用是一对多的关系,A应用会维护他那部分数据的完整性,系统一变大时,增加了B应用,A和B两个应用也许是不同的开发团队来做的。他们如何协调保证数据的完整性,而且一年以后如果又增加了C应用呢?
2,有主外键的数据库设计可以增加ER图的可读性,这点在数据库设计时非常重要。
3,外键在一定程度上说明的业务逻辑,会使设计周到具体全面。
反方观点:
1,可以用触发器或应用程序保证数据的完整性
2,过分强调或者说使用主键/外键会平添开发难度,导致表过多等问题
3,不用外键时数据管理简单,操作方便,性能高(导入导出等操作,在insert, update, delete 数据的时候更快)
eg:在海量的数据库中想都不要去想外键,试想,一个程序每天要insert数百万条记录,当存在外键约束的时候,每次要去扫描此记录是否合格,一般还不 止一个字段有外键,这样扫描的数量是成级数的增长!我的一个程序入库在3个小时做完,如果加上外键,需要28个小时!
结论:
1,在大型系统中(性能要求不高,安全要求高),使用外键;在大型系统中(性能要求高,安全自己控制),不用外键;小系统随便,最好用外键。
2,用外键要适当,不能过分追求
3,不用外键而用程序控制数据一致性和完整性时,应该写一层来保证,然后个个应用通过这个层来访问数据库。
需要注意的是:MySQL允许使用外键,但是为了完整性检验的目的,在除了InnoDB表类型之外的所有表类型中都忽略了这个功能。这可能有些怪异,实际上却非常正常:对于数据库的所有外键的每次插入、更新和删除后,进行完整性检查是一个耗费时间和资源的过程,它可能影响性能,特别是当处理复杂的或者是缠绕的连接树时。因而,用户可以在表的基础上,选择适合于特定需求的最好结合。所以,如果需要更好的性能,并且不需要完整性检查,可以选择使用MyISAM表类型,如果想要在MySQL中根据参照完整性来建立表并且希望在此基础上保持良好的性能,最好选择表结构为innoDB类型











