1.异常概念
异常指的是程序在执行过程中出现的非正常的情况,导致JVM的非正常停止。在Java中,异常是一个类,产生异常就是创建异常对象并抛出一个异常对象。
异常指的并不是语法错误,语法错误,编译不会通过,而是编译通过后,程序执行异常。
异常的作用是帮助我们找到程序中的问题。
2.异常产生过程解析
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}
}

运行过程解析:
- 在 arr 数组中提取索引 3,由于数组没有索引3,导致了运行异常,JVM对这个异常做了识别,并抛出异常给 main 方法。
- 由于 main 方法并没有异常处理,main 方法又把异常返回给 JVM。
- JVM 收到异常后,打印异常详细信息到控制台,同时中断程序。
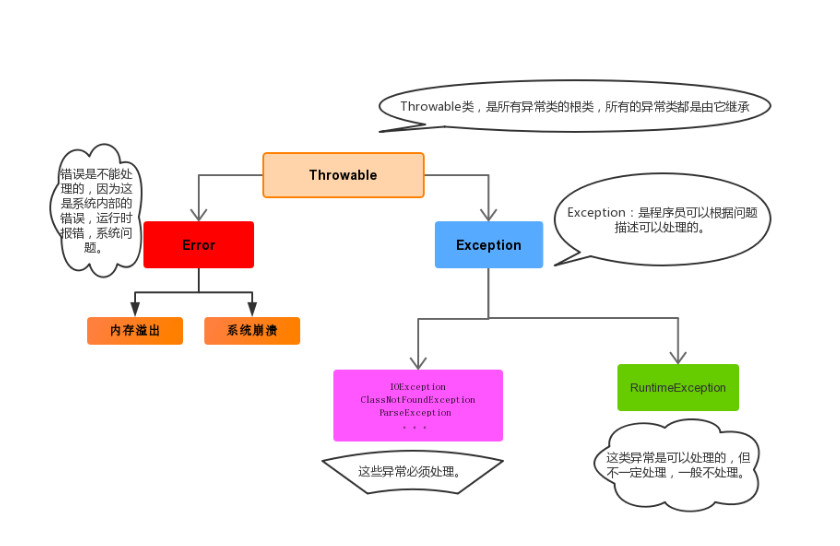
3.异常类
java.lang.Throwable 是异常的根类。
Throwable 体系:
- java.lang.Error:严重错误,不在我们处理范围内。
- java.lang.Exception:平时所说的异常是此类。我们可以通过修改代码纠正错误,使程序能正常运行。异常又分为checked异常(编译异常)和runtime异常(运行异常)。
Throwable 常用方法:
- public void printStackTrace():打印异常的详细信息。
- public String getMessage():获取异常发生的原因。
4.异常处理
Java 异常处理的五个关键字: try、catch、finally、throw、throws。
- throw 抛出异常。
- throws 声明异常。
- try...catch...finally 捕获异常。
throw:
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
int index = 3;
if (index < 0 || index > arr.length -1){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组越界");
}
System.out.println(arr[index]);
}
}
throws 用于方法声明之上,表示当前方法不处理异常,并提醒该方法的调用者来处理异常。
若该方法可能有多种异常情况产生,那么在throws后面可以写多个异常类,用逗号隔开。
public class TestException {
public static void getIndex(int index) throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
if (index < 0 || index > arr.length -1){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组越界");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
getIndex(4);
}
}
try-catch 用于对异常有针对性的语句进行捕获,可以对出现的异常进行制定方式处理。finally代码块无论有无捕获异常都会执行。
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
//捕获数组越界异常
try{
System.out.println(arr[4]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();//获取异常详细信息
}finally{
System.out.println("程序继续执行");
}
//继续执行
System.out.println(arr[2]);
}
}
可以写多个catch 捕获多个异常。需要注意的是catch捕获异常不能相同,异常子类一般要写在异常父类上面,否则异常被父类捕获,子类无法捕获详细异常。
在继承关系当中,如果父类抛出异常,那么子类重写父类方法时,抛出和父类相同的异常或者不抛出异常。如果父类没有抛出异常,子类重写父类该方法时也不可抛出异常,若该子类方法产生异常,只能捕获不能声明抛出。
5.自定义异常类
原理:自定义异常类继承 Exception 根类。
//自定义异常类
class CustomException extends Exception{
//无参构造方法
public CustomException(){};
//有参
public CustomException(String msg){
super(msg);//继承Exception 构造方法
}
}
//测试
public class TestCustomException {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
int index = 3;
try{
if (index<0 || index>arr.length-1){
throw new CustomException("数组越界");
}
}catch (CustomException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

温馨提示
- 如果您对本文有疑问,请在评论部分留言,我会在最短时间回复。
- 如果本文帮助了您,也请评论关注,作为对我的一份鼓励。
- 如果您感觉我写的有问题,也请批评指正,我会尽量修改。








