Android IPC(跨进程通信)之AIDL
IPC——跨进程通信,是指两个进程之间的数据交换过程。在说IPC的同时我们要知道什么是进程,什么是线程。线程是CPU调度的最小单元,进程可以理解为一个程序或者一个应用。一个进程中可以运行多个线程,而在Android程序中有一个主线程,也叫UI线程。
在Android上,一个应用代表一个进程,当你运行应用的是时候,Android会为你分配一个独立的虚拟机,这也就相当于给你分配一块独立的内存,程序中使用的对象以及数据可以在这里共享的。但当你开启多进程时,这个进程的内存跟应用的内存就是两块不同的内存,这个时候两个内存之间的数据是不可以共享的。
多进程会产生以下几个问题:
(1)静态成员和单例模式完全失效。
(2)线程同步机制完全失效。
(3)SharedPreferences的可靠性下降。
(4)Application会多次创建。
跨进程通信的方式有多种,如Bundle、AIDL、文件共享、Messenger、ContentProvider和Socket等,今天主要介绍的AIDL的使用。
一、项目代码文件结构
这里以书店为例讲解一下,这里实现的功能是书店(服务端)把自家拥有哪些书籍告知客户(客户端),而且客户(客户端)还进行了消息订阅,当书店(服务端)有新书了就通知客户(客户端)。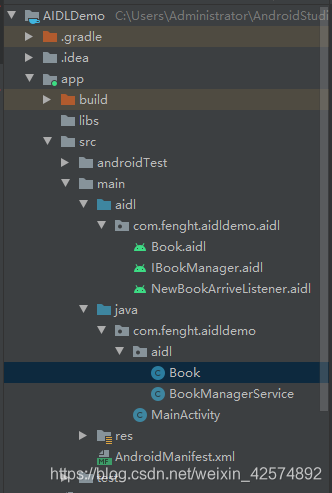
二、代码实现与讲解
1、新建实体类Book.java,使用Pracelable实现序列化。
package com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Book implements Parcelable {
private int bookId;
private String bookName;
public Book(int bookId, String bookName) {
this.bookId = bookId;
this.bookName = bookName;
}
private Book(Parcel in) {
bookId = in.readInt();
bookName = in.readString();
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeInt(bookId);
dest.writeString(bookName);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Book> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Book>(){
@Override
public Book createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new Book(source);
}
@Override
public Book[] newArray(int size) {
return new Book[size];
}
};
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"bookId=" + bookId +
", bookName='" + bookName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2、右击Book.java,新建Book.aidl和IBookManager.aidl以及NewBookArriveListener.aidl文件,AS会自动帮你把文件路径建好,不需要再新建文件夹。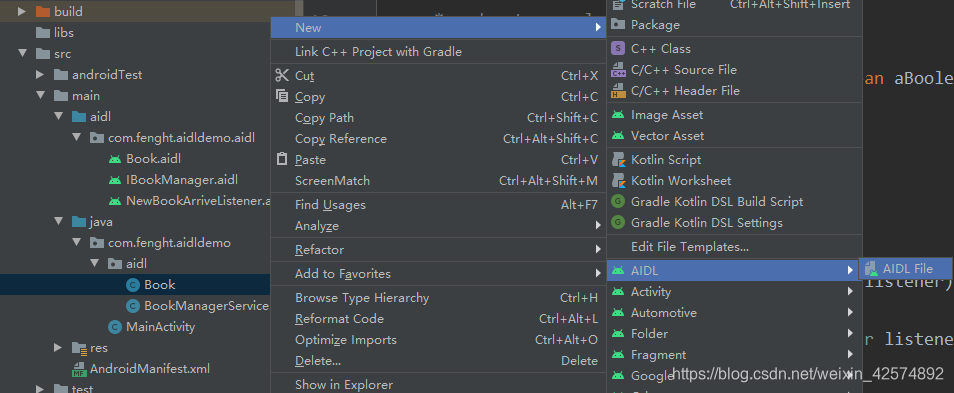
Book.aidl文件代码
// Book.aidl
package com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
parcelable Book;
IBookManager.aidl文件代码
// IBookManager.aidl
package com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl;
import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.Book;
import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.NewBookArriveListener;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IBookManager {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat,
double aDouble, String aString);
List<Book> getBookList();
void addBook(in Book book);
void registerListener(NewBookArriveListener listener);
void unregisterListener(NewBookArriveListener listener);
}
NewBookArriveListener.aidl文件代码
// NewBookArriveListener.aidl
package com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl;
import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.Book;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface NewBookArriveListener {
//通知方法
void newBookArrived(in Book newBook);
}
添加代码之后,点击Make Project重新编译项目。
注意:包名必须是一样com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl,不然后续编译会报错,如下图。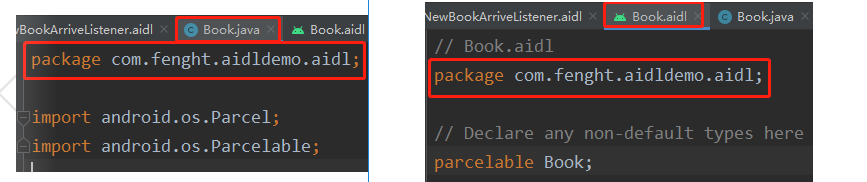
在aidl文件中写相关方法时AS没有自动帮你引入相关类,你需要自己引入。如在IBookManager.aidl文件中添加方法List<Book> getBookList(); 你可能需要手动引入import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.Book; Book.java的类。否则会报错:Failed to resolve ‘Book’
而且每次在aidl文件中添加相关代码之后需要重新编译一下项目。
3、远程服务端service的实现,新建BookManagerService.java服务。
package com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteCallbackList;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
/**
* 数据管理服务
* @author fht
* @time 2020年8月1日14:02:38
*/
public class BookManagerService extends Service {
private CopyOnWriteArrayList<Book> mBookList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
private AtomicBoolean isDestory = new AtomicBoolean(false);
//使用RemoteCallbackList可以对监听进行反注册,否则反注册会失败
private RemoteCallbackList<NewBookArriveListener> listeners = new RemoteCallbackList<>();
private Binder mBinder = new IBookManager.Stub() {
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) throws RemoteException {
}
@Override
public List<Book> getBookList() throws RemoteException {
return mBookList;
}
@Override
public void addBook(Book book) throws RemoteException {
mBookList.add(book);
}
@Override
public void registerListener(NewBookArriveListener listener) throws RemoteException {
//注册监听
listeners.register(listener);
}
@Override
public void unregisterListener(NewBookArriveListener listener) throws RemoteException {
//反注册
listeners.unregister(listener);
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mBookList.add(new Book(1,"android"));
mBookList.add(new Book(2,"java"));
//启动线程
new Thread(new ServiceWorker()).start();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
int check = checkCallingOrSelfPermission("com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.BOOK_SERVICE");
if (check == PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED) {
return null;
}
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
isDestory.set(true);
super.onDestroy();
}
private class ServiceWorker implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (!isDestory.get()){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
int bookId = mBookList.size() + 1;
Book newBook = new Book(bookId,"新书" + bookId);
mBookList.add(newBook);
Log.e("fht","服务中添加新书:" + newBook.toString());
final int size = listeners.beginBroadcast();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++) {
//获取监听
NewBookArriveListener newBookArriveListener = listeners.getBroadcastItem(i);
if (newBookArriveListener != null) {
//发送通知
newBookArriveListener.newBookArrived(newBook);
}
}
//beginBroadcast和finishBroadcast必须配对使用
listeners.finishBroadcast();
//中断重连测试
// if (bookId == 9) {
// //结束当前进程,测试Binder死亡回调
// android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid());
// return;
// }
} catch (InterruptedException | RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
注意:在AndroidMainfest.xml中添加如下代码,开启多进程:
<service android:name=".aidl.BookManagerService"
android:process=":remote"/>
4、接着在Mainactivity.java中绑定服务,接收数据。
package com.fenght.aidldemo;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.Book;
import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.BookManagerService;
import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.IBookManager;
import com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.NewBookArriveListener;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView tv_book;
private IBookManager iBookManager;
private Handler handler = new Handler(new Handler.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
switch (msg.what){
case 1:
Log.e("fht","新书:" + msg.obj.toString());
tv_book.setText(msg.obj.toString());
break;
}
return false;
}
});
//服务连接
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
iBookManager = IBookManager.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
//设置binder死亡代理,binder死亡时有回调
service.linkToDeath(deathRecipient,0);
//获取数据
List<Book> list = iBookManager.getBookList();
Log.e("fht","书本:" + list.toString());
iBookManager.addBook(new Book(3,"这是客户端发送的书"));
List<Book> list1 = iBookManager.getBookList();
Log.e("fht","书本:" + list1.toString());
iBookManager.registerListener(newBookArriveListener);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
//回调方法:当binder死亡时,系统会回调binderDied方法
private IBinder.DeathRecipient deathRecipient = new IBinder.DeathRecipient() {
@Override
public void binderDied() {
if (iBookManager == null) {
return;
}
//先解除binder旧的死亡监听,在ServiceConnection中会重新新的设置监听
iBookManager.asBinder().unlinkToDeath(deathRecipient,0);
iBookManager = null;
//死亡时,重新启动连接
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, BookManagerService.class);
bindService(intent,serviceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
};
//新书监听
private NewBookArriveListener newBookArriveListener = new NewBookArriveListener.Stub() {
@Override
public void newBookArrived(Book newBook) throws RemoteException {
//发送消息,由UI线程处理数据
handler.obtainMessage(1,newBook).sendToTarget();
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_book = findViewById(R.id.tv_book);
Intent intent = new Intent(this, BookManagerService.class);
bindService(intent,serviceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
if (iBookManager != null && iBookManager.asBinder().isBinderAlive()) {
try {
//反注册监听
iBookManager.unregisterListener(newBookArriveListener);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
unbindService(serviceConnection);
super.onDestroy();
}
}
AndroidManifest.xml代码,注意跟自己的比对一下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.fenght.aidldemo">
<permission android:name="com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.BOOK_SERVICE"
android:protectionLevel="normal"/>
<uses-permission android:name="com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.BOOK_SERVICE"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".aidl.BookManagerService"
android:process=":remote"/>
</application>
</manifest>
项目跑起来就可以了
三、注意点以及相关代码讲解
1、如何监听Binder是否死亡?
有时候服务端进程由于某些意外停止了,这回导致Binder的意外死亡,这时候需要我们重新连接服务。我们如何Binder是否死亡呢?给Binder设置DeathRecipient监听,当Binder死亡时,我们会收到binderDied方法的回调。相关代码在MainActivity.java。
(1)设置代理的代码为:
//设置binder死亡代理,binder死亡时有回调
service.linkToDeath(deathRecipient,0);
(2)回调方法代码为:
//回调方法:当binder死亡时,系统会回调binderDied方法
private IBinder.DeathRecipient deathRecipient = new IBinder.DeathRecipient() {
@Override
public void binderDied() {
if (iBookManager == null) {
return;
}
//先解除binder旧的死亡监听,在ServiceConnection中会重新新的设置监听
iBookManager.asBinder().unlinkToDeath(deathRecipient,0);
iBookManager = null;
//死亡时,重新启动连接
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, BookManagerService.class);
bindService(intent,serviceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
};
(3)验证方法就是放开如下代码:
2、如何进行权限验证?
默认情况下,我们的远程服务任何人都可以连接的,但这是不安全的,我们需要加入权限验证以保护数据的安全性。验证通过才可以连接,验证失败则不能连接。相关代码如下:
(1)在AndroidManifest.xml添加权限,这是连接服务需要的权限,自己定义的:
<permission android:name="com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.BOOK_SERVICE"
android:protectionLevel="normal"/>
(2)在BookManagerService.java中进行权限控制:
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
int check = checkCallingOrSelfPermission("com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.BOOK_SERVICE");
if (check == PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED) {
return null;
}
return mBinder;
}
(3)在AndroidManifest.xml声明权限,跟(1)中的权限要一致:
<uses-permission android:name="com.fenght.aidldemo.aidl.BOOK_SERVICE"/>
3、因为反注册的需要,这里使用RemoteCallbackList,不需要注册与反注册监听的可以使用CopyOnWriteArrayList,具体原因不多说了。