1. 应用测试的介绍
一般我们在写完代码之后,代码的测试是会给专门的测试人员来测试的,如果一个测试跑到你的工位上对你说,你的代码好像有Bug,你肯定会不爽,反正我就是这样的🙃。所以为了显示自己的代码质量高一点,在功能提交给测试之前,我们会自己测试一下,接下来给大家介绍一下 Spring Boot Test 应用测试框架。
Spring Boot Test 其实就是Spring Test,只是在Spring Boot 中集成变得更简单了,像我们开发自己测试,一般都是单元测试Junit测试,不出bug就谢天谢地啦,Spring Test与JUnit结合起来提供了高效便捷的测试解决方案,而Spring Boot Test是在Spring Test之上增加了切片测试并增强了Mock能力。
Spring Boot Test支持的测试种类,主要分为以下三类:
单元测试,面向方法的测试,常用注解有@Test。(一般都是用这个)
功能测试,面向业务的测试,同时也可以使用切面测试中的Mock能力,常用的注解有@RunWith,@SpringBootTest等。(这个也用得多)
切片测试,面向难于测试的边界功能,介于单元测试和功能测试之间,常用注解有@RunWith,@WebMvcTest等。
测试过程中的关键要素及支撑方式如下:
- 测试运行环境,通过@RunWith和@SpringBootTest启动Spring容器。
- Mock能力,Mockito提供Mock能力。
- 断言能力,AssertJ、Hamcrest、JsonPath提供断言能力。
接下来我带领大家学习如何简单使用Spring Boot Test框架。
2. Spring Boot Test 的使用
- 2.1 引入依赖
在Spring Boot中开启测试只需要引入spring-boot-starter-test依赖,使用@RunWith和@SpringBootTest注解就可以开始测试。我们就简单测试一下接口,首先我们引入pom依赖:
pom.xml:
<!--springboot父工程-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!--springboot框架web组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis整合springboot组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql数据库连接驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.18</version>
</dependency>
<!--lombok组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring boot-test组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--单元测试junit组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring-test组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<!--springboot的maven插件-->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>-parameters</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
2.2 代码编写
测试代码我们一般都写在与main文件夹平级的test文件夹下,建议文件夹的名称和main文件夹下的文件夹对应好,测试类的名称也要对应好,就像下面这样,当然这只是建议。
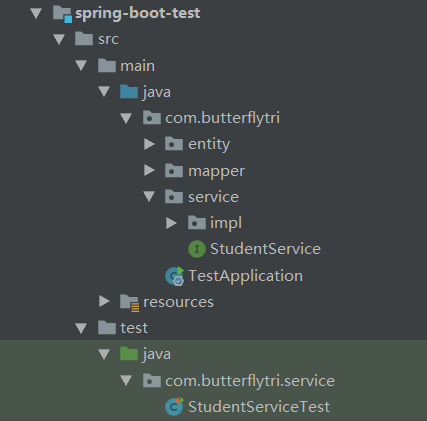
Spring Boot 的启动类我就不再写了,没有加什么特别的内容,直接上测试类吧。
StudentServiceTest.java:对了,这里测试的每一个方法都和
StudentService.java这个服务类的方法名对应着的,建议大家也是这样。package com.butterflytri.service; import com.butterflytri.TestApplication; import com.butterflytri.entity.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; import java.util.List; /** * @author: WJF * @date: 2020/5/23 * @description: StudentServiceTest */ /** * {@link SpringBootTest}:配置文件属性的读取。读取classes标志的启动类的配置文件和运行环境,并加载。 * {@link RunWith}:'RunWith'注解就是一个运行器,加载value的Class测试环境。 */ @SpringBootTest(classes = TestApplication.class) @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) public class StudentServiceTest { @Resource private StudentService studentService; @Test public void findAllTest() { List<Student> list = studentService.findAll(); for (Student student : list) { System.out.println(student); } } @Test public void findOneTest() { Student student = studentService.findOne(1L); System.out.println(student); } @Test public void findByStudentNoTest() { Student student = studentService.findByStudentNo("G030511"); System.out.println(student); } }每一个测试方法都是可以独立运行的,因为在运行的时候会加载Spring Test的测试环境,同时会将你测试的工程的运行环境的配置加载进来,使用的都是工程的配置和环境,方便我们自己进行测试。
3. 项目地址
本项目传送门:spring-boot-test
此教程会一直更新下去,觉得博主写的可以的话,关注一下,也可以更方便下次来学习。