欢迎访问我的GitHub
这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
本篇概览
- 本文是《MyBatis初级实战》系列的第五篇,从多表获取数据是个常见的场景,一般有以下两种方式:
- 联表查询:join操作,一次查询完成
- 多次查询:用第一次查询的结果作为条件,再做查询(MyBatis中叫做嵌套查询)
- 本篇的内容就是学习MyBatis对上述两种查询的支持,全文由以下章节组成:
- 准备数据;
- 本次实战的java工程
- 最简单的联表(两个表的数据保存在一个实体类的不同字段);
- 一对一联表查询(两个表的数据分别保存在不同实体类,假设是A和B,A是B的成员变量)
- 一对一嵌套查询(两个表的数据分别保存在不同实体类,假设是A和B,A是B的成员变量)
源码下载
- 如果您不想编码,可以在GitHub下载所有源码,地址和链接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog\_demos):
名称
链接
备注
项目主页
https://github.com/zq2599/blog\_demos
该项目在GitHub上的主页
git仓库地址(https)
https://github.com/zq2599/blog\_demos.git
该项目源码的仓库地址,https协议
git仓库地址(ssh)
git@github.com:zq2599/blog_demos.git
该项目源码的仓库地址,ssh协议
- 这个git项目中有多个文件夹,本章的应用在mybatis文件夹下,如下图红框所示:
- mybatis是个父工程,里面有数个子工程,本篇的源码在relatedoperation子工程中,如下图红框所示:
准备数据
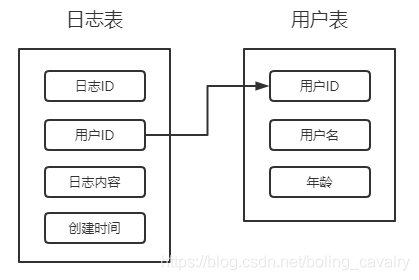
本次实战,在名为mybatis的数据库中建立两个表(和前面几篇文章中的表结构一模一样):user和log表;
user表记录用户信息,非常简单,只有三个字段:主键、名称、年龄
log表记录用户行为,四个字段:主键、用户id、行为描述、行为时间
user和log的关系如下图:
建表和添加数据的语句如下:
use mybatis;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS
user;CREATE TABLE
user(idint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,namevarchar(32) NOT NULL,ageint(32) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;DROP TABLE IF EXISTS
log;CREATE TABLE
log(idint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,user_idint(32),actionvarchar(255) NOT NULL,create_timedatetime not null, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;INSERT INTO mybatis.user (id, name, age) VALUES (3, 'tom', 11);
INSERT INTO mybatis.log (id, user_id, action, create_time) VALUES (3, 3, 'read book', '2020-08-07 08:18:16'); INSERT INTO mybatis.log (id, user_id, action, create_time) VALUES (4, 3, 'go to the cinema', '2020-09-02 20:00:00'); INSERT INTO mybatis.log (id, user_id, action, create_time) VALUES (5, 3, 'have a meal', '2020-10-05 12:03:36'); INSERT INTO mybatis.log (id, user_id, action, create_time) VALUES (6, 3, 'have a sleep', '2020-10-06 13:00:12'); INSERT INTO mybatis.log (id, user_id, action, create_time) VALUES (7, 3, 'write', '2020-10-08 09:21:11');
本次实战的java工程
在父工程mybatis下新建子工程relatedoperation,pom.xml如下:
4.0.0 com.bolingcavalry mybatis 1.0-SNAPSHOT ../pom.xml com.bolingcavalry relatedoperation 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT relatedoperation Demo project for Mybatis related operation in Spring Boot <java.version>1.8</java.version> org.projectlombok lombok org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.mybatis.spring.boot mybatis-spring-boot-starter mysql mysql-connector-java runtime org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test io.springfox springfox-swagger2 io.springfox springfox-swagger-ui com.alibaba druid-spring-boot-starter junit junit test org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin 基本配置文件application.yml:
server: port: 8080
spring: #1.JDBC数据源 datasource: username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.50.43:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #2.连接池配置 druid: #初始化连接池的连接数量 大小,最小,最大 initial-size: 5 min-idle: 5 max-active: 20 #配置获取连接等待超时的时间 max-wait: 60000 #配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000 # 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 30000 # 配置一个连接在池中最大生存的时间,单位是毫秒 max-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000 validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM user test-while-idle: true test-on-borrow: true test-on-return: false # 是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache 官方建议MySQL下建议关闭 个人建议如果想用SQL防火墙 建议打开 pool-prepared-statements: true max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20 # 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙 filters: stat,wall,slf4j filter: stat: merge-sql: true slow-sql-millis: 5000 #3.基础监控配置 web-stat-filter: enabled: true url-pattern: /* #设置不统计哪些URL exclusions: ".js,.gif,.jpg,.png,.css,.ico,/druid/" session-stat-enable: true session-stat-max-count: 100 stat-view-servlet: enabled: true url-pattern: /druid/ reset-enable: true #设置监控页面的登录名和密码 login-username: admin login-password: admin allow: 127.0.0.1 #deny: 192.168.1.100
mybatis配置
mybatis:
配置文件所在位置
config-location: classpath:mybatis-config.xml
映射文件所在位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mappers/*Mapper.xml
日志配置
logging: level: root: INFO com: bolingcavalry: relatedoperation: mapper: debug
再准备名为application-test.yml的配置文件,这是执行单元测试时用到的,和application.yml的不同之处是spring.datasource.druid.web-stat-filter.enabled配置设置成false;
mybatis的配置文件mybatis-config.xml如下:
数据源配置类DruidConfig.java:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration public class DruidConfig {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DruidConfig.class); @Value("${spring.datasource.url}") private String dbUrl; @Value("${spring.datasource.username}") private String username; @Value("${spring.datasource.password}") private String password; @Value("${spring.datasource.driver-class-name}") private String driverClassName; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.initial-size}") private int initialSize; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.max-active}") private int maxActive; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.min-idle}") private int minIdle; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.max-wait}") private int maxWait; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.pool-prepared-statements}") private boolean poolPreparedStatements; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size}") private int maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.time-between-eviction-runs-millis}") private int timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.min-evictable-idle-time-millis}") private int minEvictableIdleTimeMillis; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.max-evictable-idle-time-millis}") private int maxEvictableIdleTimeMillis; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.validation-query}") private String validationQuery; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.test-while-idle}") private boolean testWhileIdle; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.test-on-borrow}") private boolean testOnBorrow; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.test-on-return}") private boolean testOnReturn; @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.filters}") private String filters; @Value("{spring.datasource.druid.connection-properties}") private String connectionProperties; /** * Druid 连接池配置 */ @Bean public DruidDataSource dataSource() { DruidDataSource datasource = new DruidDataSource(); datasource.setUrl(dbUrl); datasource.setUsername(username); datasource.setPassword(password); datasource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName); datasource.setInitialSize(initialSize); datasource.setMinIdle(minIdle); datasource.setMaxActive(maxActive); datasource.setMaxWait(maxWait); datasource.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis); datasource.setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(minEvictableIdleTimeMillis); datasource.setMaxEvictableIdleTimeMillis(minEvictableIdleTimeMillis); datasource.setValidationQuery(validationQuery); datasource.setTestWhileIdle(testWhileIdle); datasource.setTestOnBorrow(testOnBorrow); datasource.setTestOnReturn(testOnReturn); datasource.setPoolPreparedStatements(poolPreparedStatements); datasource.setMaxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize(maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize); try { datasource.setFilters(filters); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("druid configuration initialization filter", e); } datasource.setConnectionProperties(connectionProperties); return datasource; }}
swagger配置类:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder; import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors; import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors; import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo; import springfox.documentation.service.Tag; import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType; import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket; import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .tags(new Tag("UserController", "用户服务"), new Tag("LogController", "日志服务")) .select() // 当前包路径 .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.controller")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } //构建 api文档的详细信息函数,注意这里的注解引用的是哪个 private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() //页面标题 .title("MyBatis CURD操作") //创建人 .contact(new Contact("程序员欣宸", "https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos", "zq2599@gmail.com")) //版本号 .version("1.0") //描述 .description("API 描述") .build(); }}
springboot引导类:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.mapper") public class RelatedOperationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(RelatedOperationApplication.class, args); }}
用户表的实体类:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.entity;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data @NoArgsConstructor @ApiModel(description = "用户实体类") public class User {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户ID") private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名", required = true) private String name; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户地址", required = false) private Integer age;}
日志表的实体类:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.entity;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import java.sql.Date;
@Data @NoArgsConstructor @ApiModel(description = "日志实体类") public class Log {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "日志ID") private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户ID") private Integer userId; @ApiModelProperty(value = "日志内容") private String action; @ApiModelProperty(value = "创建时间") private Date createTime;}
- 以上就是本篇的准备代码,接下来在此基础上实现各种多表关联查询
最简单的联表
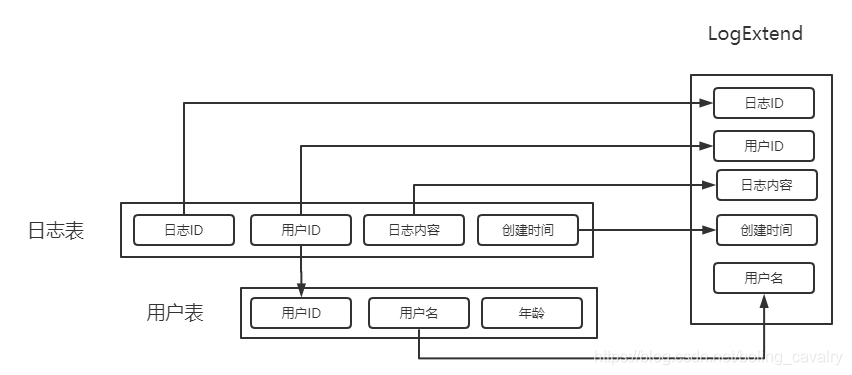
- 先实战的是最普通的联表,如下图所示,查询结果是名为LogExtend的实体类,这个类有5个字段,其中四个来自日志表log,一个来自用户表user:
- 下图是开发步骤:
实体类LogExtend的源码如下,可见和Log相比多了个userName字段:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.entity;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data @NoArgsConstructor @ApiModel(description = "日志实体类(含用户表的字段)") public class LogExtend extends Log {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名") private String userName;}
新建log表对应的映射文件LogMapper.xml,如下所示,里面是通过left join语法执行的简单的联表查询,以及查询结果对应的resultMap定义:
<!--联表查询,返回log对象,该对象有个userName字段,值是user表的user_name字段--> <select id="oneObjectSel" parameterType="int" resultMap="logExtendResultMap"> select l.id as id, l.user_id as user_id, l.action as action, l.create_time as create_time, u.name as user_name from log as l left join user as u on l.user_id = u.id where l.id = #{id} </select> <resultMap id="logExtendResultMap" type="logExtend"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result column="user_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="userId"/> <result column="action" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="action"/> <result column="create_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" property="createTime"/> <result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/> </resultMap>mapper接口代码:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.mapper;
import com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.entity.LogAssociateUser; import com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.entity.LogExtend; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository public interface LogMapper {
LogExtend oneObjectSel(int id);}
service层的代码在LogService.java文件中:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.service;
import com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.entity.LogAssociateUser; import com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.entity.LogExtend; import com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.mapper.LogMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service public class LogService {
@Autowired LogMapper logMapper; public LogExtend oneObjectSel(int id){ return logMapper.oneObjectSel(id); }}
controller层的代码在LogController.java文件中:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/log") @Api(tags = {
"LogController"}) public class LogController {
@Autowired private LogService logService; @ApiOperation(value = "根据ID查找日志记录,带userName字段,该字段通过联表查询实现", notes="根据ID查找日志记录,带userName字段,该字段通过联表查询实现") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "日志ID", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "Integer") @RequestMapping(value = "/aggregate/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public LogExtend oneObjectSel(@PathVariable int id){ return logService.oneObjectSel(id); }编写单元测试的代码ControllerTest.java,由于今天的测试涉及到user和log两个表,因此在测试类ControllerTest的内部准备了两个内部类,分别用于测试user和log表:
package com.bolingcavalry.relatedoperation.controller;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.junit.jupiter.api.*; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@SpringBootTest @DisplayName("Web接口的单元测试") @AutoConfigureMockMvc @ActiveProfiles("test") @Slf4j public class ControllerTest {
/** * 查询方式:联表 */ final static String SEARCH_TYPE_LEFT_JOIN = "leftjoin"; /** * 查询方式:嵌套 */ final static String SEARCH_TYPE_NESTED = "nested"; final static int TEST_USER_ID = 3; final static String TEST_USER_NAME = "tom"; @Autowired MockMvc mvc; @Nested @TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class) @DisplayName("用户服务") class User { } @Nested @TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class) @DisplayName("日志服务") class Log { final static int TEST_LOG_ID = 5; @Test @DisplayName("通过日志ID获取日志信息,带userName字段,该字段通过联表查询实现") @Order(1) void oneObjectSel() throws Exception { mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/log/aggregate/" + TEST_LOG_ID) .accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.id").value(TEST_LOG_ID)) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.userName").value(TEST_USER_NAME)) .andDo(print()); } }}
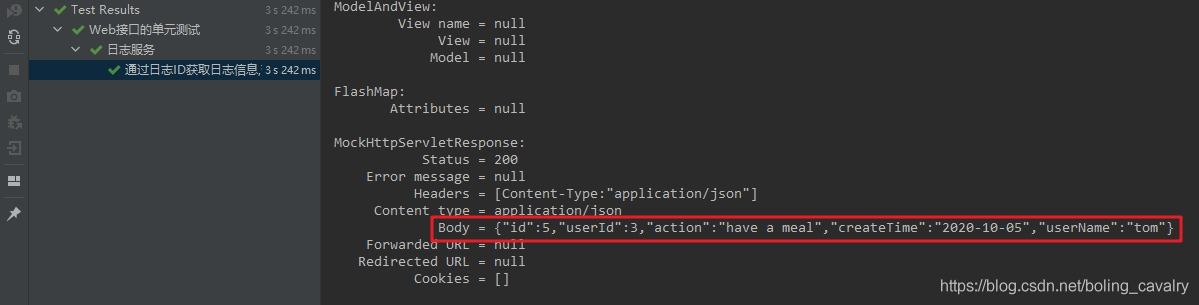
执行上述单元测试方法,结果如下图,红框中就是controller层返回的数据,可见已通过Mybatis成功取得LogExtend实例:
- 下一站是一对一联表查询;
关于一对一关联的两种方式
前面的查询有个特点:尽管查询了两个表,但结果都在同一实体类的不同字段,而更符合业务逻辑的关系应该是log类中有个user类的成员变量,即如下形式:
@Data @NoArgsConstructor @ApiModel(description = "日志实体类") public class LogAssociateUser {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "日志ID") private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户对象") private User user; @ApiModelProperty(value = "日志内容") private String action; @ApiModelProperty(value = "创建时间") private Date createTime;}
接下来的实战就是如何用MyBatis查询得到上述LogAssociateUser 类型的结果;
一对一关联的实现有联表和嵌套查询两种,它们的差异在Mybatis中体现在association的子节点上:
- 联表时,association内使用result子节点,将联表查询的结果映射到关联对象;
- 嵌套时,association内使用select子节点,触发一次新的查询;
一对一(联表)
所谓一对一,就是一个对象关联了另一个对象,例如一条log记录中,带有对应的user信息;
下面是新的实体类LogAssociateUser,该类对应的是log表记录,有个user字段,类型是User对象:
@Data @NoArgsConstructor @ApiModel(description = "日志实体类") public class LogAssociateUser {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "日志ID") private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户对象") private User user; @ApiModelProperty(value = "日志内容") private String action; @ApiModelProperty(value = "创建时间") private Date createTime;}
映射文件LogMapper.xml中,sql和resultMap如下,可见查询的时候将user表的字段都查出来了,然后在resultMap中用association节点去处理sql中查出的user表的数据,通过javaType属性转为User类的实例:
<!--联表查询,返回log对象,它的成员变量中有user对象--> <select id="leftJoinSel" parameterType="int" resultMap="leftJoinResultMap"> select l.id as log_id, l.action as log_action, l.create_time as log_create_time, u.id as user_id, u.name as user_name, u.age as user_age from log as l left join user as u on l.user_id = u.id where l.id = #{id} </select> <resultMap id="leftJoinResultMap" type="LogAssociateUser"> <id property="id" column="log_id"/> <result property="action" column="log_action" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/> <result property="createTime" column="log_create_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" /> <association property="user" javaType="User"> <id property="id" column="user_id"/> <result property="name" column="user_name"/> <result property="age" column="user_age"/> </association> </resultMap>以上就是一对一(联表)的关键点,接下来按部就班的在LogMapper、LogService、LogController中添加方法即可,下面是LogController中对应的web接口,稍后会在单元测试中调用这个接口进行验证:
@ApiOperation(value = "根据ID查找日志记录,带用户对象,联表查询实现", notes="根据ID查找日志记录,带用户对象,联表查询实现") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "日志ID", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "Integer") @RequestMapping(value = "/leftjoin/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public LogAssociateUser leftJoinSel(@PathVariable int id){ return logService.leftJoinSel(id); }最后是单元测试的代码(ControllerTest.java文件),用来测试上述代码是否有效,注意下面的queryAndCheck私有方法,该方法中发起请求并验证结果:
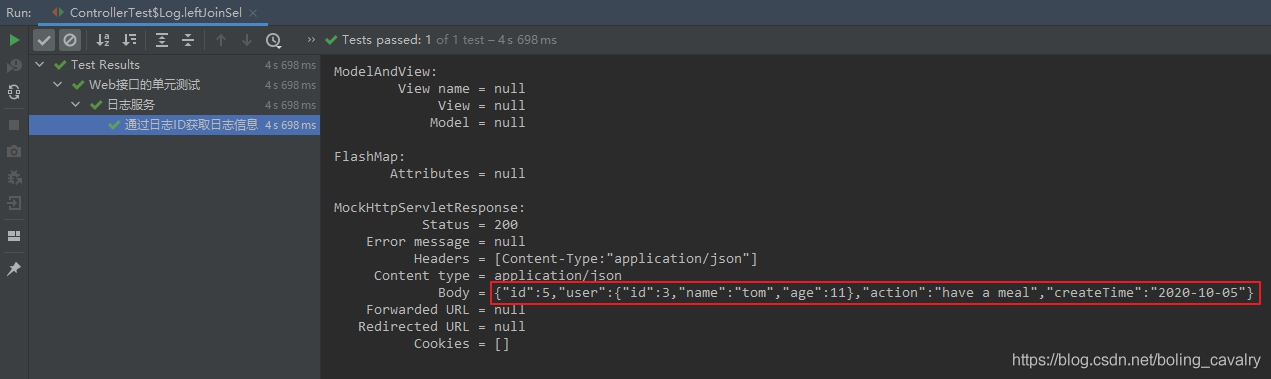
/** * 通过日志ID获取日志信息有两种方式:联表和嵌套查询, * 从客户端来看,仅一部分path不同,因此将请求和检查封装到一个通用方法中, * 调用方法只需要指定不同的那一段path * @param subPath * @throws Exception */ private void queryAndCheck(String subPath) throws Exception { String queryPath = "/log/" + subPath + "/" + TEST_LOG_ID; log.info("query path [{}]", queryPath); mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get(queryPath) .accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.id").value(TEST_LOG_ID)) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.user.id").value(TEST_USER_ID)) .andDo(print()); } @Test @DisplayName("通过日志ID获取日志信息(关联了用户),联表查询") @Order(2) void leftJoinSel() throws Exception { queryAndCheck(SEARCH_TYPE_LEFT_JOIN); }执行单元测试结果如下,可见:内部嵌套了一个json对象,就是user表的数据:
一对一(嵌套)
接下来试试嵌套的方式;
LogMapper.xml中对应的sql:
<!--嵌套--> <select id="nestedSel" parameterType="int" resultMap="nestedResultMap"> select l.id as log_id, l.user_id as log_user_id, l.action as log_action, l.create_time as log_create_time from mybatis.log as l where l.id = #{id} </select>上述sql对应的resultMap如下,可见association节点中有个select属性,这就是MyBatis支持嵌套查询的关键,该属性的值是个select节点:
<!-- association节点的select属性会触发嵌套查询--> <resultMap id="nestedResultMap" type="LogAssociateUser"> <!-- column属性中的log_id,来自前面查询时的"l.id as log_id" --> <id property="id" column="log_id"/> <!-- column属性中的log_action,来自前面查询时的"l.action as log_action" --> <result property="action" column="log_action" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/> <!-- column属性中的log_create_time,来自前面查询时的"l.create_time as log_create_time" --> <result property="createTime" column="log_create_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" /> <!-- select属性,表示这里要执行嵌套查询,将log_user_id传给嵌套的查询 --> <association property="user" column="log_user_id" select="selectUserByUserId"></association> </resultMap>上述节点中select属性的值,对应一个select节点,如下:
<select id="selectUserByUserId" parameterType="int" resultType="User"> select u.id, u.name, u.age from mybatis.user as u where u.id = #{log_user_id} </select>以上就是一对一(嵌套)的关键点,接下来按部就班的在LogMapper、LogService、LogController中添加方法即可,下面是LogController中对应的web接口,稍后会在单元测试中调用这个接口进行验证:
@ApiOperation(value = "根据ID查找日志记录,带用户对象,嵌套查询实现", notes="根据ID查找日志记录,带用户对象,嵌套查询实现") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "日志ID", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "Integer") @RequestMapping(value = "/nested/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public LogAssociateUser nestedSel(@PathVariable int id){ return logService.nestedSel(id); }最后是单元测试的代码(ControllerTest.java文件),用来测试上述代码是否有效,如下可见,直接调用了前面的queryAndCheck来验证:
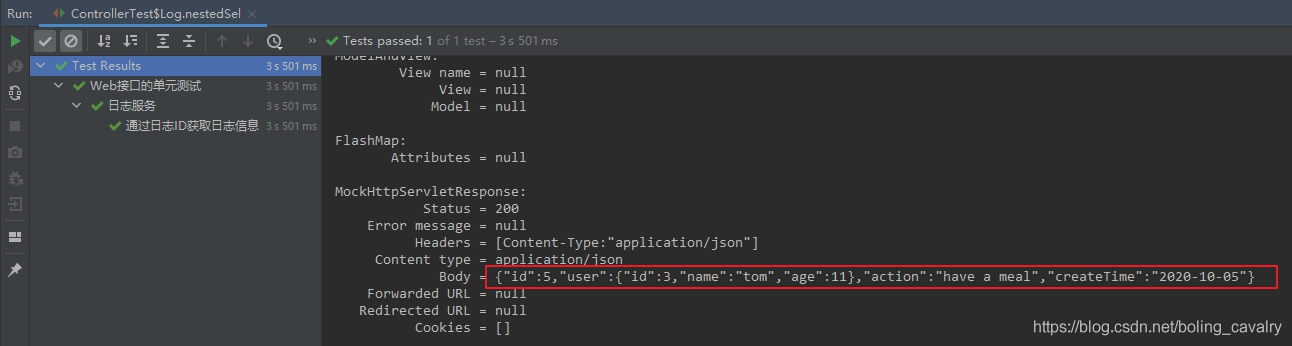
@Test @DisplayName("通过日志ID获取日志信息(关联了用户),嵌套查询") @Order(3) void nestedSel() throws Exception { queryAndCheck(SEARCH_TYPE_NESTED); }执行上述单元测试代码,结果如下,可见嵌套查询的方式也能将user表的数据成功获取,放入log实例的成员变量中:
最后是对比联表和嵌套查询的差异,先看联表查询的MyBatis日志,如下图红框所示,只有一次sql查询:

再看嵌套查询的日志,如下图,红框是第一次查询,结果中的userid作为绿框中的第二次查询的条件:
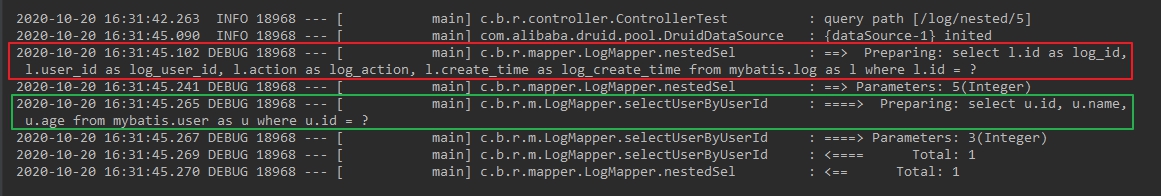
- 至此,一对一的多表查询实战就完成了,本篇的逻辑是一条log记录关联一条user记录,下一篇文章,咱们学习一对多关联,即一个user有多条log记录;
欢迎关注公众号:程序员欣宸
微信搜索「程序员欣宸」,我是欣宸,期待与您一同畅游Java世界…
本文同步分享在 博客“程序员欣宸”(CSDN)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。













