欢迎访问我的GitHub
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java、Docker、Kubernetes、DevOPS等;
本文是《MyBatis初级实战》系列的第二篇,通过前文我们知道了如何在SpringBoot中集成MyBatis,本篇就一起来练习基本功:增删改查;
本篇概览
本篇要练习的内容如下:
- 单表的增删改查
- 批量新增
- 联表查询
全文由以下部分组成:
- 新建工程
- 增加启动类
- 增加swagger的配置类,工程包含了swagger,以便稍后在浏览器上验证
- 增加配置文件
- 增加实体类
- 增加mapper配置文件
- 增加mapper接口
- 增加service,调用mapper接口
- 增加controller,调用service服务
- 编写单元测试用例
- 验证
源码下载
- 如果您不想编码,可以在GitHub下载所有源码,地址和链接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog\_demos):
名称
链接
备注
项目主页
https://github.com/zq2599/blog\_demos
该项目在GitHub上的主页
git仓库地址(https)
https://github.com/zq2599/blog\_demos.git
该项目源码的仓库地址,https协议
git仓库地址(ssh)
git@github.com:zq2599/blog_demos.git
该项目源码的仓库地址,ssh协议
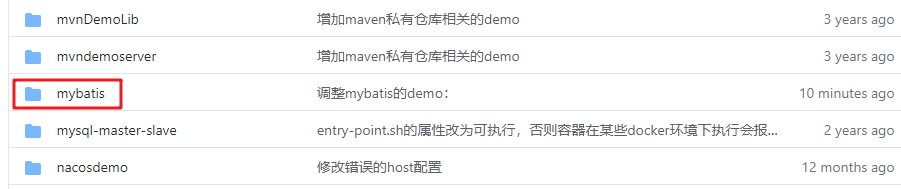
- 这个git项目中有多个文件夹,本章的应用在mybatis文件夹下,如下图红框所示:
开发
本文的实战使用的数据库和表结构与前文《MyBatis初级实战之一:Spring Boot集成》一模一样;
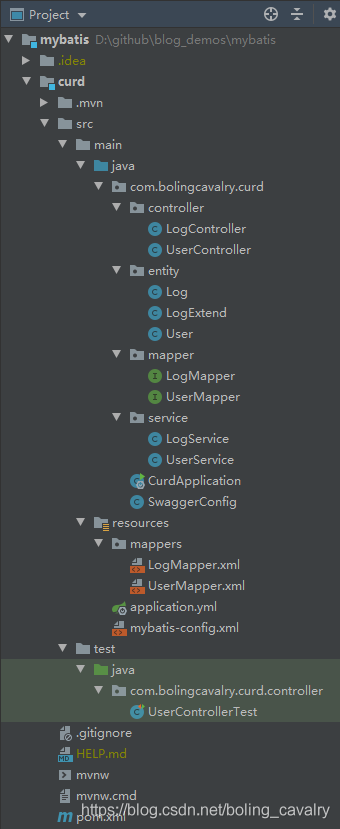
前文《MyBatis初级实战之一:Spring Boot集成》新建了父工程mybatis,本文继续在此工程中新增子工程,名为curd,整个子工程文件结构如下:
修改父工程mybatis的pom.xml,在dependencyManagement节点下新增两个dependency节点,如下所示,这么做是为了统一管理依赖库的版本:
io.springfox springfox-swagger-ui 2.5.0 com.google.code.gson gson 2.8.6 名为curd子工程,其pom.xml内容如下:
4.0.0 com.bolingcavalry mybatis 1.0-SNAPSHOT ../pom.xml com.bolingcavalry curd 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT curd Demo project for Mybatis CURD in Spring Boot <java.version>1.8</java.version> org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.mybatis.spring.boot mybatis-spring-boot-starter mysql mysql-connector-java runtime org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test org.junit.vintage junit-vintage-engine io.springfox springfox-swagger2 io.springfox springfox-swagger-ui junit junit test com.google.code.gson gson org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin 增加启动类,注意要用MapperScan注释来指定mapper接口代码的包路径:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.bolingcavalry.curd.mapper") public class CurdApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(CurdApplication.class, args); }}
本次实战用到了swagger,这样可以很方便的通过浏览器向各个controller接口发送请求,以下是配置类:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder; import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors; import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors; import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo; import springfox.documentation.service.Tag; import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType; import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket; import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .tags(new Tag("UserController", "用户服务"), new Tag("LogController", "日志服务")) .select() // 当前包路径 .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.bolingcavalry.curd.controller")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } //构建 api文档的详细信息函数,注意这里的注解引用的是哪个 private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() //页面标题 .title("MyBatis CURD操作") //创建人 .contact(new Contact("程序员欣宸", "https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos", "zq2599@gmail.com")) //版本号 .version("1.0") //描述 .description("API 描述") .build(); }}
application.yml内容如下:
server: port: 8080
spring:
数据源
datasource: username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.50.43:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis配置
mybatis:
配置文件所在位置
config-location: classpath:mybatis-config.xml
映射文件所在位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mappers/*Mapper.xml
日志配置
logging: level: root: INFO com: bolingcavalry: curd: mapper: debug
增加user表的实体类User.java,里面带有swagger的注解,方便在swagger页面展示:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
@ApiModel(description = "用户实体类") public class User {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户ID") private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名", required = true) private String name; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户地址", required = false) private Integer age; @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } // 省去get和set方法,请您自行补齐}
增加log表的实体类Log.java,里面带有swagger的注解,方便在swagger页面展示:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import java.sql.Date;
/**
- @Description: 实体类
- @author: willzhao E-mail: zq2599@gmail.com
- @date: 2020/8/4 8:24
*/ @ApiModel(description = "日志实体类") public class Log {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "日志ID") private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户ID") private Integer userId; @ApiModelProperty(value = "日志内容") private String action; @ApiModelProperty(value = "创建时间") private Date createTime; @Override public String toString() { return "Log{" + "id=" + id + ", userId=" + userId + ", action='" + action + '\'' + ", createTime=" + createTime + '}'; } // 省去get和set方法,请您自行补齐}
为联表查询的结果准备一个bean,名为LogExtend.java,继承自Log.java,自己只有个userName字段,对应联表查询user表的name字段:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
@ApiModel(description = "日志实体类(含用户表的字段)") public class LogExtend extends Log {
public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名") private String userName; @Override public String toString() { return "LogExtend{" + "id=" + getId() + ", userId=" + getUserId() + ", userName='" + getUserName() + '\'' + ", action='" + getAction() + '\'' + ", createTime=" + getCreateTime() + '}'; }}
增加user表的mapper映射文件,可见都是些很简单sql,要注意的是批量新增的节点,这里面用到了foreach语法,可以通过集合动态生成sql:
<select id="sel" parameterType="int" resultType="user"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> <!--新增单条记录--> <insert id="insertWithFields" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into user (id, name, age) values (#{id}, #{name}, #{age}) </insert> <!--批量新增--> <insert id="insertBatch" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into user (id, name, age) values <foreach collection="users" item="user" separator=","> (#{user.id}, #{user.name}, #{user.age}) </foreach> </insert> <!--按照名称查找--> <select id="findByName" parameterType="String" resultType="user"> select id, name, age from user where name like concat('%', #{name}, '%') </select> <!--删除指定数据--> <delete id="delete"> delete from user where id= #{id} </delete> <!--删除所有数据--> <delete id="clearAll"> delete from user </delete> <!--更新--> <update id="update"> update user set name = #{name}, age = #{age} where id = #{id} </update> <!--获取总数--> <select id="totalCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer"> select count(*) from user </select>增加log表的mapper映射文件,如下所示,请关注联表操作selExtend,其结果是logExtendResultMap:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.bolingcavalry.curd.mapper.LogMapper">
<resultMap id="logExtendResultMap" type="logExtend">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result column="user_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="userId"/>
<result column="action" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="action"/>
<result column="create_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" property="createTime"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" property="userName"/>
</resultMap>
<!--新增单条记录-->
<insert id="insertWithFields" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" parameterType="log">
insert into log (id, user_id, action, create_time) values (#{id}, #{userId}, #{action}, #{createTime})
</insert>
<select id="selExtend" parameterType="int" resultMap="logExtendResultMap">
select l.id as id,
l.user_id as user_id,
l.action as action,
l.create_time as create_time,
u.name as user_name
from log as l
left join user as u
on l.user_id = u.id
where l.id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 增加用户表的mapper接口类UserMapper.java ,对应着映射文件中的sql节点的id:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.mapper;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.LogExtend;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
User sel(int id);
int insertWithFields(User user);
int insertBatch(List<User> users);
int clearAll();
List<User> findByName(String name);
int update(User user);
int delete(int id);
int totalCount();
LogExtend selExtend(int id);
}
- 增加日志表的mapper接口类LogMapper.java,对应着映射文件中的sql节点的id:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.mapper;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.Log;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.LogExtend;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface LogMapper {
Log sel(int id);
LogExtend selExtend(int id);
int insertWithFields(Log log);
}
- mapper接口完成后就是service层,先写user表的service,如下所示,可见都是对mapper接口的调用:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.service;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.User;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
public User sel(int id) {
return userMapper.sel(id);
}
public User insertWithFields(User user) {
userMapper.insertWithFields(user);
return user;
}
public List<User> insertBatch(List<User> users) {
userMapper.insertBatch(users);
return users;
}
public int clearAll() {
return userMapper.clearAll();
}
public List<User> findByName(String name) {
return userMapper.findByName(name);
}
public int update(User user) {
return userMapper.update(user);
}
public int delete(int id) {
return userMapper.delete(id);
}
public int totalCount() {
return userMapper.totalCount();
}
}
- 还有log表的service:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.service;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.Log;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.LogExtend;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.User;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.mapper.LogMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class LogService {
@Autowired
LogMapper logMapper;
public Log sel(int id){
return logMapper.sel(id);
}
public LogExtend selExtend(int id) {
return logMapper.selExtend(id);
}
public Log insertWithFields(Log log) {
logMapper.insertWithFields(log);
return log;
}
}
- 最后是controller层了,由于使用了swagger,导致controller相对上一篇略微复杂(多了些注解):
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.controller;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.User;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.service.UserService;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Api(tags = {
"UserController"})
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@ApiOperation(value = "新增user记录", notes="新增user记录")
@RequestMapping(value = "/insertwithfields",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public User create(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.insertWithFields(user);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "批量新增user记录", notes="批量新增user记录")
@RequestMapping(value = "/insertbatch", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public List<User> insertBatch(@RequestBody List<User> users) {
return userService.insertBatch(users);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "删除指定ID的user记录", notes="删除指定ID的user记录")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public int delete(@PathVariable int id){
return userService.delete(id);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "删除user表所有数据", notes="删除user表所有数据")
@RequestMapping(value = "/clearall", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public int clearAll(){
return userService.clearAll();
}
@ApiOperation(value = "根据ID修改user记录", notes="根据ID修改user记录")
@RequestMapping(value = "/update", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public int update(@RequestBody User user){
return userService.update(user);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "根据名称模糊查找所有user记录", notes="根据名称模糊查找所有user记录")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "name", value = "用户名", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "String")
@RequestMapping(value = "/findbyname/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> findByName(@PathVariable("name") String name){
return userService.findByName(name);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "根据ID查找user记录", notes="根据ID查找user记录")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public User GetUser(@PathVariable int id){
return userService.sel(id);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "获取总数", notes="获取总数")
@RequestMapping(value = "/totalcount", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public int totalcount(){
return userService.totalCount();
}
}
- log的controller如下:
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.controller;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.Log;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.LogExtend;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.service.LogService;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/log")
@Api(tags = {
"LogController"})
public class LogController {
@Autowired
private LogService logService;
@ApiOperation(value = "根据ID查找日志记录", notes="根据ID查找日志记录")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "日志ID", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public LogExtend logExtend(@PathVariable int id){
return logService.selExtend(id);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "新增日志记录", notes="新增日志记录")
@RequestMapping(value = "/insertwithfields",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public Log create(@RequestBody Log log) {
return logService.insertWithFields(log);
}
}
- 最后是一段单元测试的代码,咱们试试通过junit进行自测,如下所示,可见一共测试了三个controller接口:先新增,再查找,最后删除,要注意的是MockMvc的用法,以及jsonPath方法的用法,还有就是通过Order注解控制执行顺序(一定要添加TestMethodOrder注解,否则Order注解不生效):
package com.bolingcavalry.curd.controller;
import com.bolingcavalry.curd.entity.User;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonArray;
import com.google.gson.JsonParser;
import org.junit.Ignore;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.UUID;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.hasSize;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.core.IsEqual.equalTo;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.*;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)
class UserControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
// user表的name字段,这里为了保证测试时新增和删除的记录是同一条,用UUID作为用户名
static String testName;
@BeforeAll
static void init() {
testName = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-","");;
}
@Test
@Order(1)
void insertWithFields() throws Exception {
String jsonStr = "{\"name\": \"" + testName + "\", \"age\": 10}";
mvc.perform(
MockMvcRequestBuilders.put("/user/insertwithfields")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(jsonStr)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.name", is(testName)))
.andDo(print())
.andReturn()
.getResponse()
.getContentAsString();
}
@Test
@Order(2)
void findByName() throws Exception {
mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/user/findbyname/"+ testName).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$", hasSize(1)))
.andDo(print());
}
@Test
@Order(3)
void delete() throws Exception {
// 先根据名称查出记录
String responseString = mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/user/findbyname/"+ testName).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$", hasSize(1)))
.andDo(print())
.andReturn()
.getResponse()
.getContentAsString();
// 反序列化得到数组
JsonArray jsonArray = JsonParser.parseString(responseString).getAsJsonArray();
// 反序列化得到user实例
User user = new Gson().fromJson(jsonArray.get(0), User.class);
// 执行删除
mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.delete("/user/"+ user.getId()).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("1")))
.andDo(print());
}
}
- 至此编码结束,开始验证上述功能;
单元测试验证
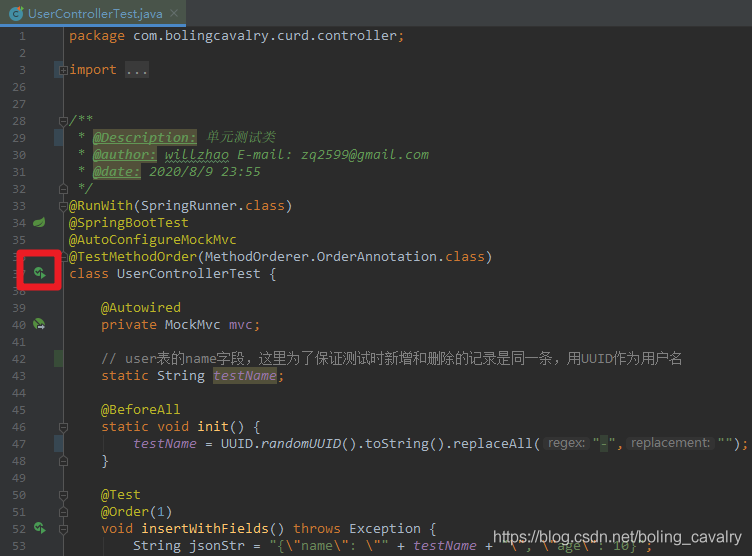
- IDEA打开UserControllerTest.java,点击下图红框中的图标即可开始执行单元测试:
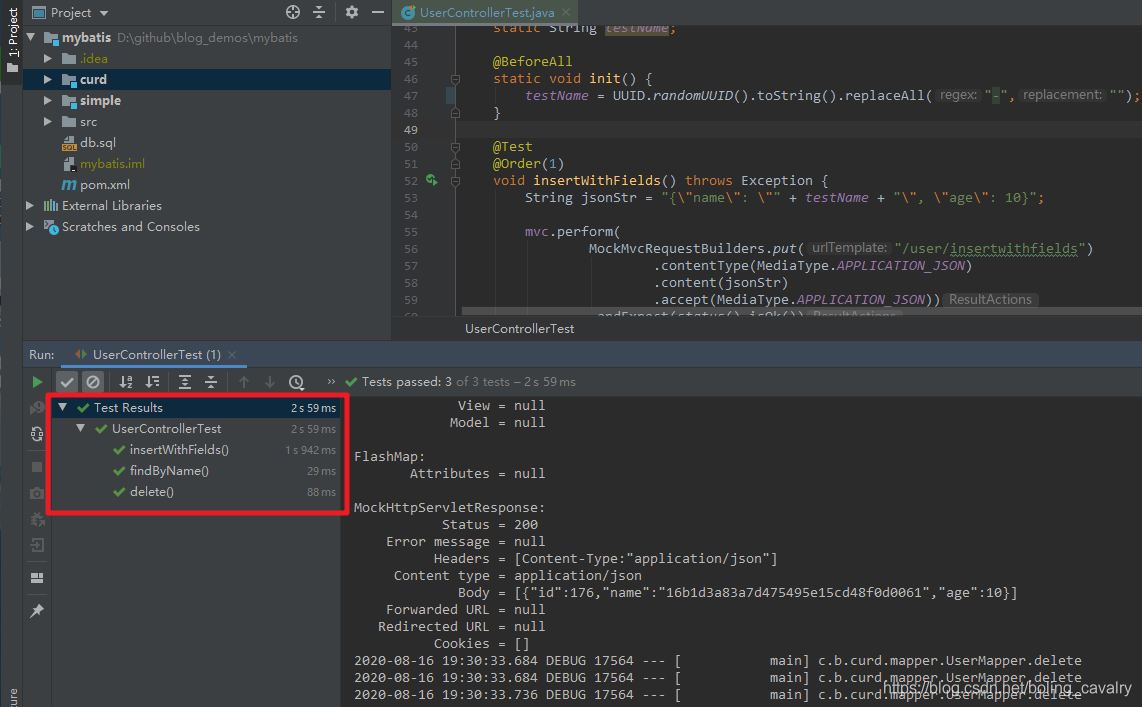
- 单元测试完成后IDEA会给出结果,如下图,红框右侧可以查看详细的测试过程数据:
- 篇幅所限,这只有少量的单元测试用例,接下来用swagger来验证每个接口;
swagger验证web接口
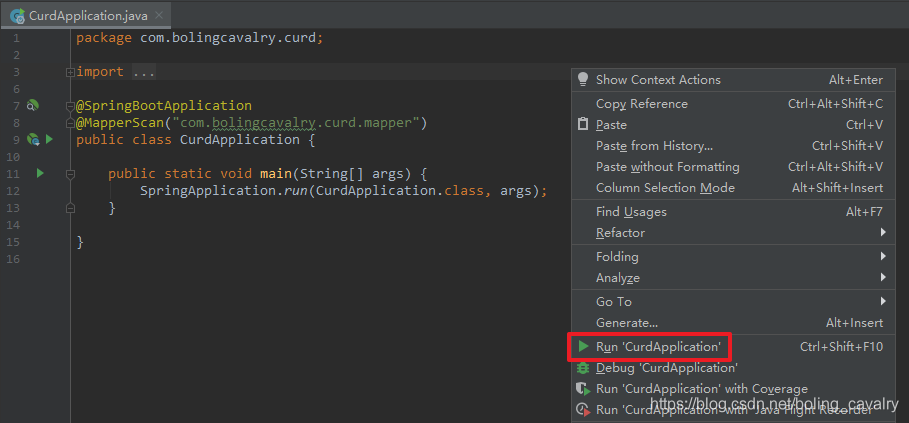
如下图,启动CurdApplication类:
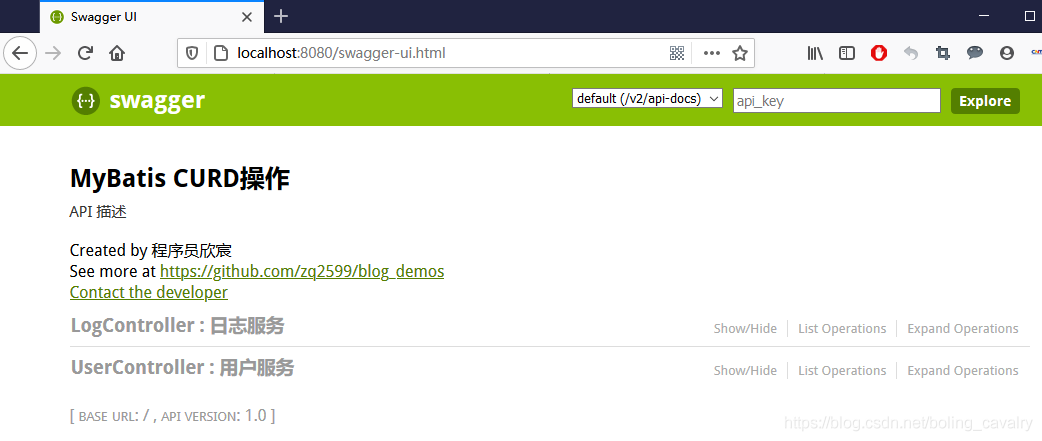
浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html ,即可打开swagger页面,如下图:
先试试新增的接口,操作如下图:
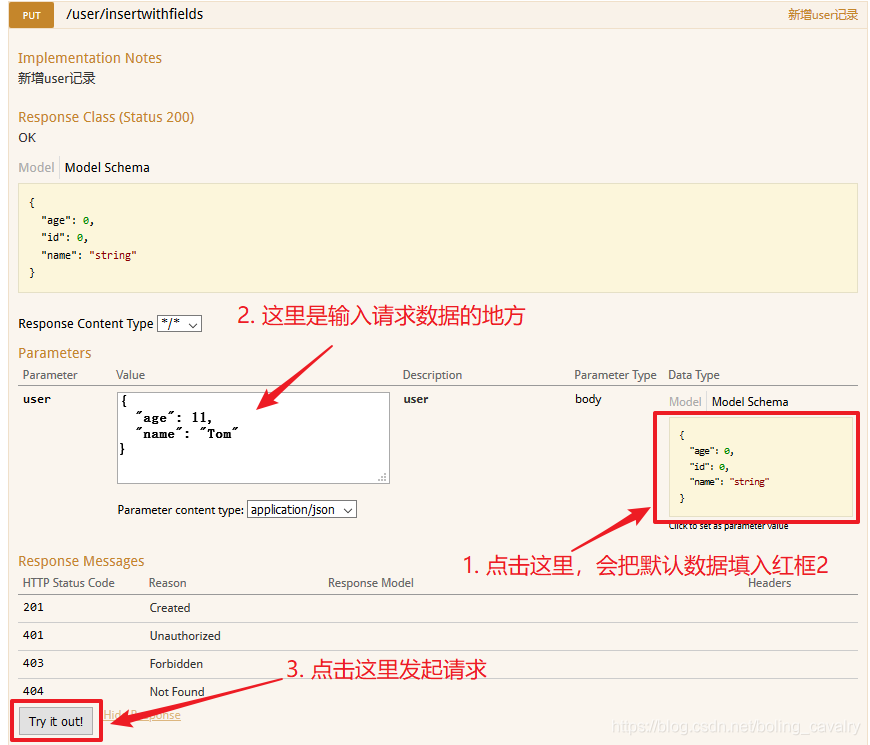
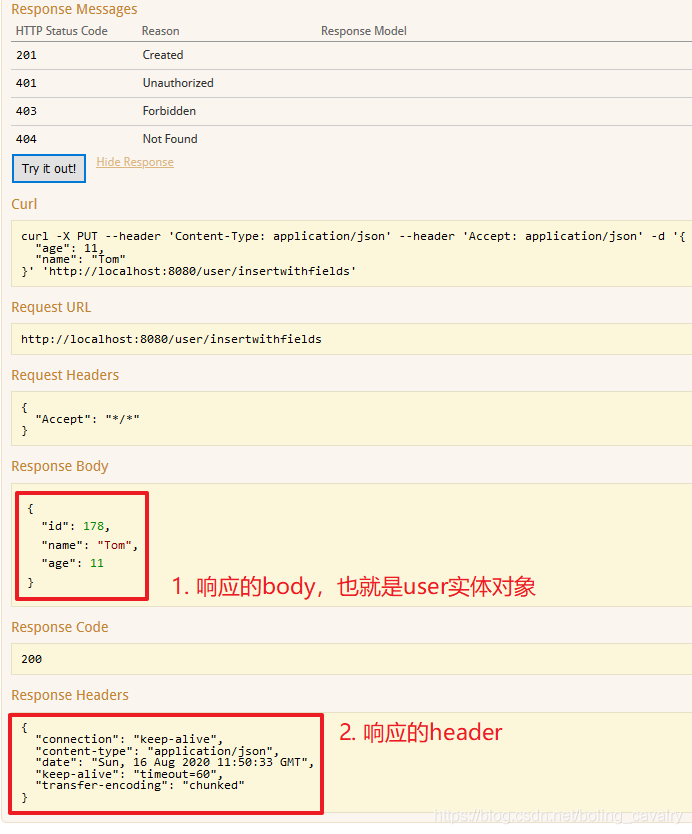
点击了上图红框3的Try it out!按钮后,响应信息如下图,可见操作成功:
限于篇幅,其他接口的测试就不逐一列出了,请您自行验证;
- 至此,MyBatis的基本增删改查和简单的联表操作的实战就完成了,接下来咱们会继续探索MyBatis的基本操作;
欢迎关注我的公众号:程序员欣宸

本文同步分享在 博客“程序员欣宸”(CSDN)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。













