AQS是什么?
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer简称AQS是一个抽象同步框架,可以用来实现一个依赖状态的同步器。
Provides a framework for implementing blocking locks and related synchronizers (semaphores, events, etc) that rely on first-in-first-out (FIFO) wait queues. This class is designed to be a useful basis for most kinds of synchronizers that rely on a single atomic int value to represent state.
提供一个框架,用于实现依赖先进先出(FIFO)等待队列的阻塞锁和相关同步器(信号量,事件等)。该类被设计为大多数类型的同步器的有用依据,这些同步器依赖于单个原子int值来表示状态。
This class supports either or both a default exclusive mode and a shared mode.
此类支持默认独占模式和共享模式。
Even though this class is based on an internal FIFO queue, it does not automatically enforce FIFO acquisition policies. The core of exclusive synchronization takes the form:
即使这个类基于内部FIFO队列,它也不会自动执行FIFO采集策略。 排他同步的核心形式如下:
Acquire:
while (!tryAcquire(arg)) {
enqueue thread if it is not already queued;
possibly block current thread;
}
Release:
if (tryRelease(arg))
unblock the first queued thread;
(共享模式类似,但可能包含级联信号。)
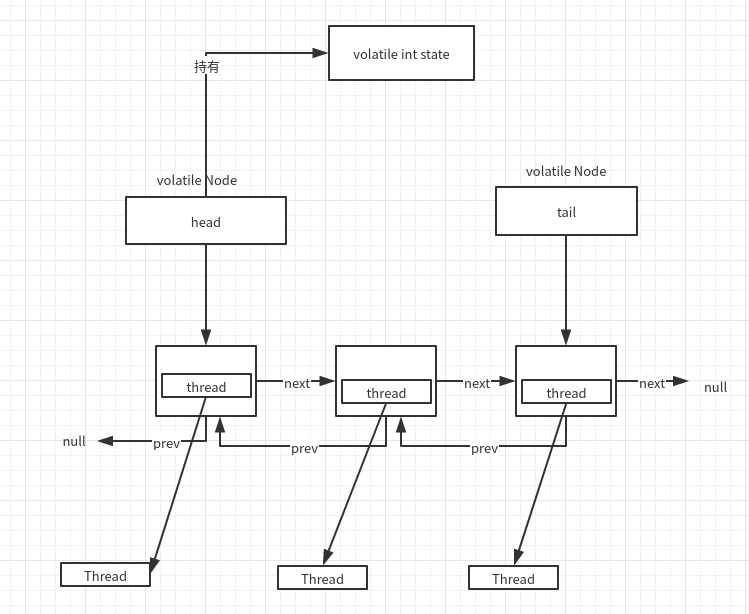
AQS 结构
/**
* 当前持有独占锁的线程
*/
private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;
/**
* 等待队列的头结点,一般为当前持有锁的线程 (volatile)
*/
private transient volatile Node head;
/**
* 等待队列的尾结点,每次新结点进来,都是加到尾部,形成了链表 (volatile)
*/
private transient volatile Node tail;
/**
* 锁的状态,0 表示没有被占用,具体由子类实现 (volatile)
*/
private volatile int state;
// 等待队列的结点
static final class Node {
// 标识节点当前在共享模式下
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
// 标识节点当前在独占模式下
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
// 大于等于0 表明这个结点的线程取消了争抢这个锁,不需要去唤醒
/**
* The values are arranged numerically to simplify use.
* Non-negative values mean that a node doesn't need to
* signal. So, most code doesn't need to check for particular
* values, just for sign.
*
* The field is initialized to 0 for normal sync nodes, and
* CONDITION for condition nodes. It is modified using CAS
* (or when possible, unconditional volatile writes).
*/
volatile int waitStatus;
// 前一个结点
volatile Node prev;
// 下一个结点
volatile Node next;
// 等待的线程
volatile Thread thread;
...
}
CLH队列 -- Craig, Landin, and Hagersten lock queue
CLH是一个非阻塞的 FIFO 队列。也就是说往里面插入或移除一个节点的时候,在并发条件下不会阻塞,而是通过自旋锁和 CAS 保证节点插入和移除的原子性。
源码导读:ReentrantLock 公平锁
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
lock.lock();
lock.unlock();
}
我们先看一下lock, 然后是 unlock
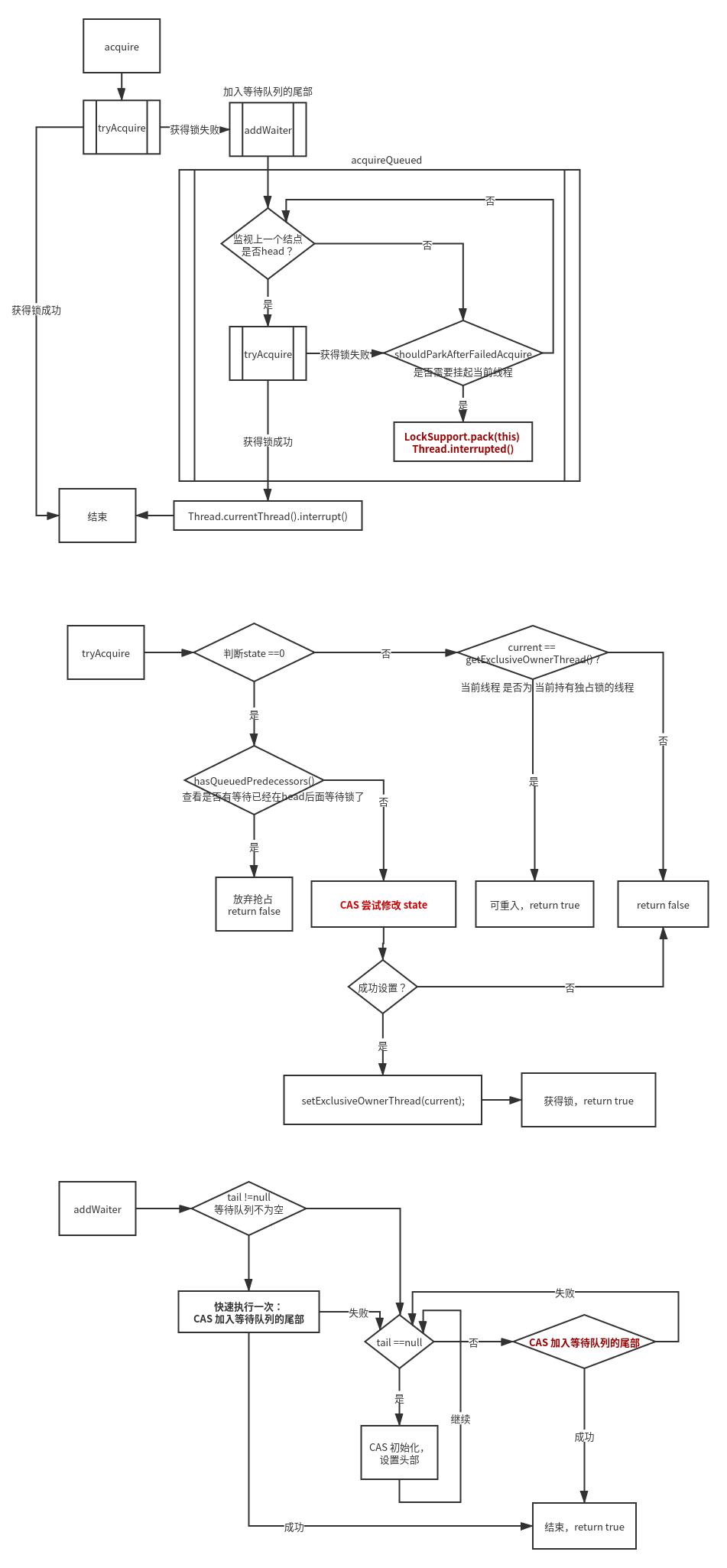
获得锁的流程和源码解读
// ReentrantLock.FairSync
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
// AQS
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 1) 当前线程尝试获得锁,如果成功,结束
// 2)如果获得锁失败,当前线程加入等待队列,加入后不断循环监视上一个结点状态
// 如果上一个结点是头结点head ,-尝试获得锁,获得成功,跳出循环
// 否则,根据上一个结点的waitStatus,进行调整,包括挂起当前线程,或调整上一个结点为非取消状态的结点
// 3)最后当前线程发起中断 Thread.currentThread().interrupt()
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
// ReentrantLock.FairSync
// 当前线程尝试获得锁
// 返回true:1.没有线程在等待锁;2.重入锁,线程本来就持有锁,也就可以理所当然可以直接获取
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// 1)查看是否有等待已经在head后面等待锁了,如果有当前线程放弃抢占锁
// 2)如果没有线程等待,CAS 尝试修改 state, 如果成功,获得锁
// 3)设置的当前线程为 当前持有独占锁的线程
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 4)如果state不为0, 说明为可重入,只需要判断 当前线程 是否为 当前持有独占锁的线程
// 5)如果是,可重入,state增加
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
//6) 其他情况,获得锁失败
return false;
}
// AQS
// 构造结点,采用CAS 加入等待队列的尾部
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
Node pred = tail;
//1) 如果等待队列不为空,则CAS 将当前线程加入等待队列的尾部
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 2)如果等待队列为空,则CAS 新建初始化CLH队列,并当前线程加入等待队列的尾部
enq(node);
return node;
}
// AQS
// 如果获得锁失败,当前线程加入等待队列
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
// 注意,这是一个循环,只有获得锁,或抛异常才会退出
// 如果上一个节点是头结点 head,则尝试获得锁
// 否则,如果当前线程需要挂起,则挂起等待锁的释放
for (;;) {
// 1)查看当前结点的上一个结点,如果是头结点head,尝试获得锁
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 2)如果当前结点的上一个结点不是头结点head,或获得锁失败,则判断一下是否需求挂起当前线程?
// 3)如果需要挂起,则 park 挂起当前线程
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
// 4)如果获得锁失败,并且抛异常,则当前线程取消抢占
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// AQS
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
// 1)如果上一个结点的状态是 -1, 则当前结点 需要挂起
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
// 2)如果上一个结点的状态 大于0,表示取消抢占了, 那么循环往前找到一个结点的状态 <=0,然后将当前结点的上一个结点 设置为 找到的结点
if (ws > 0) {
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
}
// 3)如果上一个结点<=0且不等于-1, 那么结点状态为 0(加入等待队列的初始状态), -2,-3,
// 此时需要 用CAS将上一个节点的waitStatus设置为Node.SIGNAL(也就是-1)
else {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
// AQS
// 挂起当前线程,并测试返回当前线程是否中断状态
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
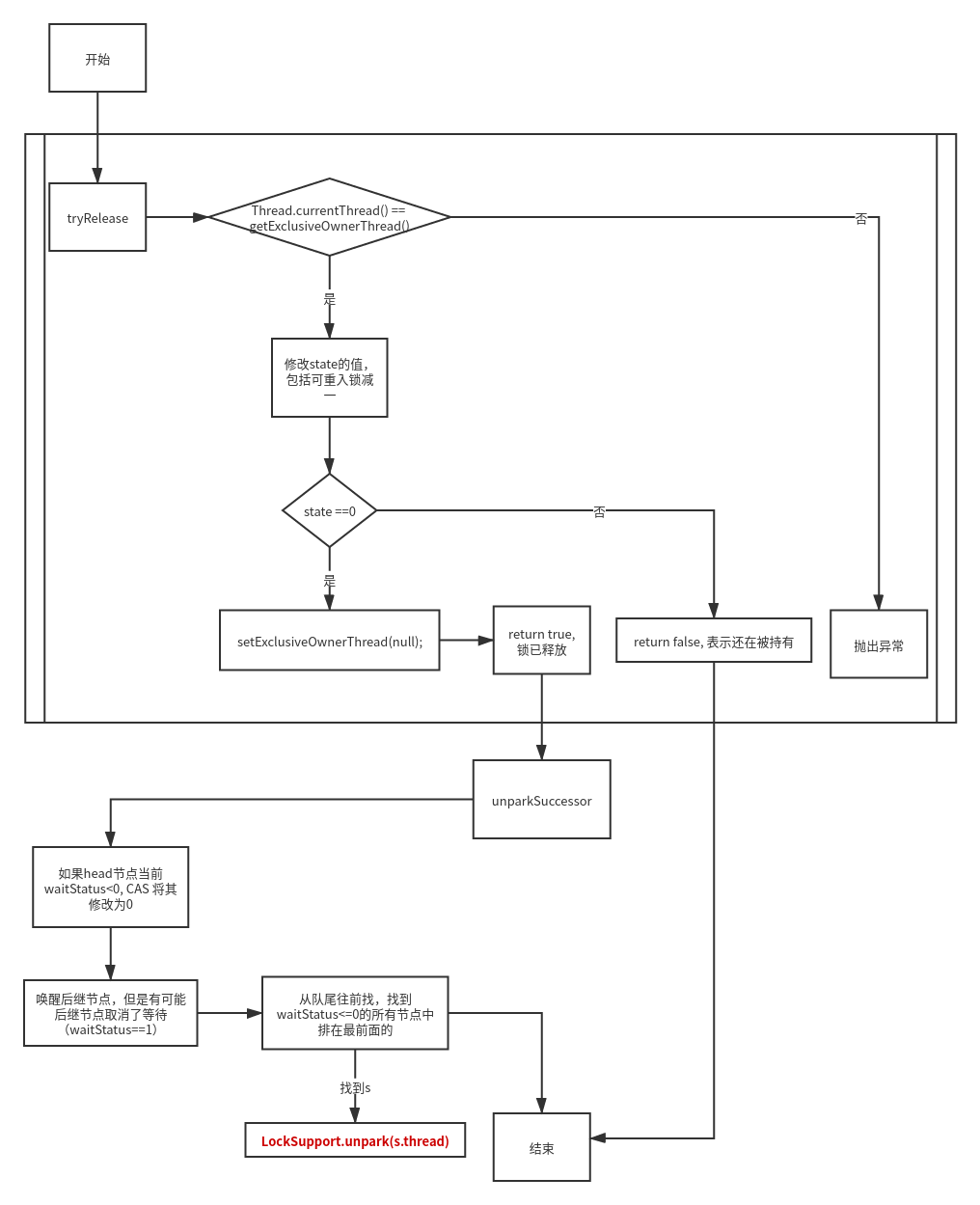
释放锁的流程和源码解读
// ReentrantLock
final void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// AQS
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 1)释放锁,尝试修改state的值
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
// 2)如果等待队列有线程,则将头部的结点状态修正,并唤醒头结点的下一个不是取消状态的线程
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ReentrantLock
// 判断当前线程 是否为 当前持有独占锁的线程
// 如果是,修改state的值,包括可重入锁减一
// 如果不是,抛出异常
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
// AQS
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
// 如果head节点当前waitStatus<0, CAS 将其修改为0
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
// 唤醒后继节点,但是有可能后继节点取消了等待(waitStatus==1)
// 从队尾往前找,找到waitStatus<=0的所有节点中排在最前面的
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
// 唤醒线程
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
by 斯武丶风晴 https://my.oschina.net/langxSpirit









