在这篇文章中,我们将学习如何使用Node.js开发一个比特币实时价格行情的GraphQL API。
比特币开发相关链接:
1、创建项目目录
在终端中执行如下命令创建一个新目录并进入该目录:
mkdir btc-gql-api && cd btc-gql-api
2、初始化项目
在终端中执行yarn init初始化项目目录,得到的package.json类似以下内容:
{
"name": "my-new-project",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "My New Project description.",
"main": "index.js",
"repository": {
"url": "https://example.com/your-username/my-new-project",
"type": "git"
},
"author": "Your Name <you@example.com>",
"license": "MIT"
}
在终端执行touch index.js创建一个空的js文件,然后在package.json中添加如下内容:
...
"scripts": {
"start": "node index.js"
},
...
最终的package.json文件看起来类似如下内容:
{
"name": "my-new-project",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "My New Project description.",
"main": "index.js","scripts": {
"start": "node index.js"
},
"repository": {
"url": "https://example.com/your-username/my-new-project",
"type": "git"
},
"author": "Your Name <you@example.com>",
"license": "MIT"
}
在项目目录中创建一个graph目录,得到如下的目录结构:
+ btc-gql-api
|__ graphql
|__ package.json
|__ index.json
在graph目录中创建3个js文件:types.js、resolver.js和request.js,最终得到如下的目录结构:
+ btc-gql-api
|__+graphql
|____request.js
|____resolvers.js
|____types.js
|__ package.json
|__ index.json
3、安装依赖包
在这个项目中,我们将需要axios和graphql-yoga,因此在项目根目录 执行如下命令:
yarn add axios graphql-yoga
好了,可以开始写代码了。
4、类型定义
在GraphQL Schema中最基础的组件就是对象类型,它标识你可以从服务中提取的对象类型,以及其中包含哪些字段。例如:
type User {
name: String!
email: String!
}
GraphQL有一些内置的基础类型:
- Int:32位有符号整数
- Float:双精度有符号浮点数
- String:UTF-8字符序列
- Boolean:布尔型,true或false
- ID:唯一标识符,通常用于作为对象的键
更详细的文档可以参考graphql schema。
现在让我们定义类型。打开./graphql/types.js文件,输入如下内容:
const typeDefs = `
scalar JSON
type Price {
price:JSON!
}`;
module.exports = typeDefs;
在上面的代码中,我们定义了一个类型Price,它只有一个非空字段price,字段类型为JSON:
type Price {
price:JSON!
}
JSON并不是graphql的内置类型,是我们自定义的:
scalar JSON
5、查询
GraphQL是关于数据管理的,查询基本上就是请求对象的指定字段。 例如:
query {
getPrices {
price
}
}
得到如下结果:
{
"data": {
"getPrices": {
"price": {
"USD": {
"15m": 10436.54,
"last": 10436.54,
"buy": 10436.54,
"sell": 10436.54,
"symbol": "$"
}
...
}
}
}
}
可以看到,查询结果和请求有相同的结构。
6、查询与修改
在一个schema内有两种类型:查询(query)与修改(mutation)。
每个GraphQL服务至少有一个查询类型,可能有一个修改类型。这些类型和常规的对象类型一样,但是它们定义了每个GraphQL查询的入口点。看起来像这样:
scalar JSON
type Price {
price:JSON!
}
type Query {
getPrices: Price!
getPrice(currency:String!): Price!
}
上面代码的意思是,我们的GraphQL服务有一个Query类型,其中包含 getPrices和getPrice字段,其类型都是Price。我们也可以看到字段 getPrice有参数(currency:String!)。在GraphQL对象类型中的每个 字段都可以有0或多个参数。
参数可以是必需的或可选的,在上面的例子中,我们要求一个必需的 参数currency用来选择要查询的币种。
7、请求辅助工具
在我们继续GraphQL之前,我们需要一个辅助工具来获取比特币实时价格。为此我们将使用blockchain.com的API,但是你可以换成任何你喜欢的服务。
打开./graphql/request.js文件,输入以下内容:
const axios = require("axios");module.exports = {
getPrices: async () => {
const url = "https://blockchain.info/ticker";
try {
return await axios.get(url);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
};
上面的代码使用axios来构造GET请求,当然你也可以换成其他你熟悉的工具。
8、解析器
每个类型的每个字段背后都对应一个解析器函数,该函数应当由GraphQL服务端开发者提供。当一个字段执行时,对应的解析器就被调用并生成结果。
如果一个字段生成一个标量值例如字符串或数字,那么执行就结束了。然而,如果一个字段生成一个对象值,那么查询将包含另外的字段,这将继续解析直到最终得到的字段都是标量值。
每个GraphQL服务的顶层是所有可能的入口类型,通常被称为根(Root)类型或查询(Query)类型。
打开文件./graphql/resolvers.js,输入以下内容:
const requests = require("./requests");
const resolvers = {
Query: {
// Get all available prices
async getPrices(parent, args, ctx, info) {
const prices = await requests.getPrices();
return { price: prices.data };
},
// Get the price of a given currency symbol
async getPrice(parent, args, ctx, info) {
const prices = await requests.getPrices();
return { price: { [args["currency"]]: prices.data[args["currency"]] } };
}
}
};
module.exports = resolvers;
让我们分解说明下以上代码。
首先引入我们查询比特币实时行情的辅助工具:
const request = require("./request");
然后定义解析器:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
// Get all available prices
async getPrices(parent, args, ctx, info) {
const prices = await requests.getPrices();
return { price: prices.data };
},
// Get the price of a given currency symbol
async getPrice(parent, args, ctx, info) {
const prices = await requests.getPrices();
return { price: { [args["currency"]]: prices.data[args["currency"]] } };
}
}
};
我们的解析器有一个根字段Query,在该对象内我们将定义GraphQL Schema中的所有解析器。注意这些解析器的命名与types.js中一致。
每个解析器都是一个函数,有4个参数:
- parent:父对象
- args:参数
- ctx:上下文
- info:字段特定信息
9、服务器
现在我们已经有了类型、解析器和辅助工具,要做的就是整合起来。
打开index.js文件,输入以下内容:
const { GraphQLServer } = require("graphql-yoga");
const typeDefs = require("./graphql/types.js");
const resolvers = require("./graphql/resolvers.js");
const server = new GraphQLServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
context: {
//if we pass anything here can be available in all resolvers
}
});
server.start(() => console.log("Server is running on localhost:4000☄"));
首先我们创建GraphQLServer实例:
...
const server = new GraphQLServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
context: {
//if we pass anything here can be available in all resolvers
}
});
...
然后运行该实例:
server.start(() => console.log("Server is running on localhost:4000☄"));
运行后可以看到如下输出:
Server is running on localhost:4000☄
现在打开浏览器访问http://localhost:4000,测试如下查询:
query($currency:String!){
getPrice(currency:$currency){
price
}
}
# Variables:
{
"currency": "USD"
}
得到如下结果:
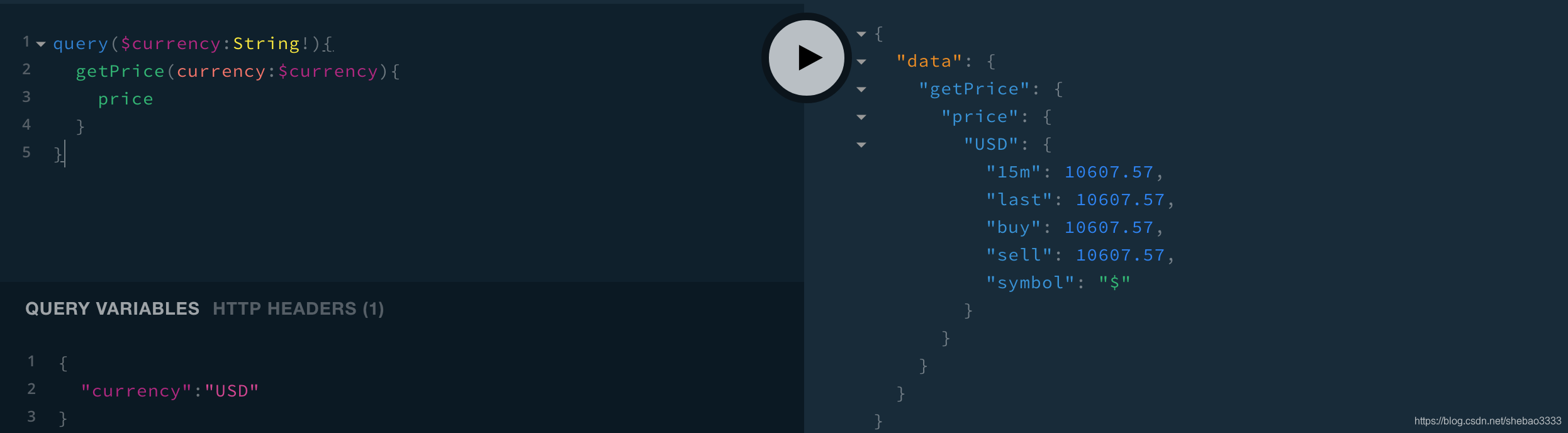
非常好!













