一、构造注入
在类被实例化的时候,它的构造方法被调用并且只能调用一次。所以它被用于类的初始化操作。
方法传递参数。现在以一个简单的输出学生信息的实例演示如何为构造方法传递参数。
实例程序创建过程如下。
(1)建立 Student 接口,它是对学生类的简单抽象。程序代码如下
[java] view plain copy 
package com.linbingwen;
public interface Student {
public void printInfo();
}
(2)建立实现 Student 接口的 Stu1 类,定义姓名、年龄、性别 3 个属性和包含这 3个参数的构造方法,在实现接口的 printInfo()方法中输出所有属性信息。程序代码如下
[java] view plain copy 
package com.linbingwen;
public class Stu1 implements Student {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public Stu1(String name, String sex, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("姓名:" + name);
System.out.println("年龄:" + age);
System.out.println("性别:" + sex);
}
}
( 3 ) applicationContext.xml 是 装 配 JavaBean 的 配 置 文 件 , 它 通 过 3 个
码如下。
[html] view plain copy 
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd"\>
- <bean id="stu1" class="com.linbingwen.Stu1">
- <constructor-arg>
- <value>飞龙</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg>
- <value>男</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg>
- <value>26</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- </bean>
- </beans>
注意:这里要把applicationContext.xml放在src文件夹下。添加Spring和包不懂看这里
(4)创建 Info 类。它是实例的主类,负责载入容器,从容器中获得 Stu1 类的实例,并调用 Stu1 类的 pringInfo()方法打印学生信息。程序代码如下
[java] view plain copy 
package com.linbingwen;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Info {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student student = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("stu1");
student.printInfo();
}
}
实例运行结果如图 所示。
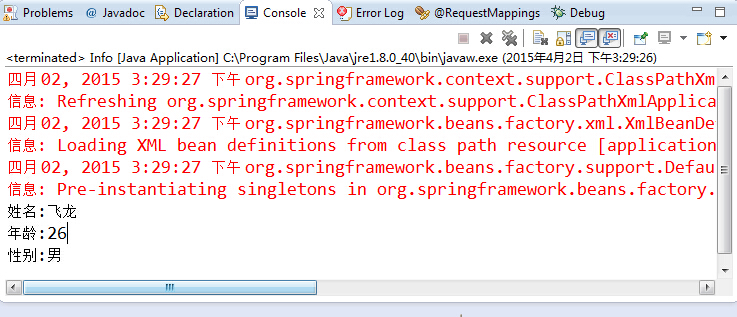
通过这个实例,可以看到容器通过多个
type 属性:可以指定参数类型以确定要为构造方法的哪个参数赋值。当需要赋值的属性在构造方法中没有相同的类型时,可以使用这个参数。因此实例中 stu1 的配置信息可以
这样写:
[html] view plain copy 
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd"\>
- <bean id="stu1" class="com.linbingwen.Stu1">
- <constructor-arg>
- <value>飞龙</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg>
- <value>男</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg type="int">
- <value>26</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- </bean>
- </beans>
index 属性: 用于指定构造方法的参数索引,指定当前
导致 name 和 sex 参数无法判断正确性。这时需要设置 index 属性定义赋值索引来指定构造方法的参数位置。修改后的 applicationContext.xml 配置文件内容如下。
[html] view plain copy 
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd"\>
- <bean id="stu1" class="com.linbingwen.Stu1">
- <constructor-arg index="0">
- <value>飞龙</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg index="1">
- <value>男</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- <constructor-arg type="int">
- <value>26</value>
- </constructor-arg>
- </bean>
- </beans>
在修改后的代码中,两个 String 类型的参数通过“index”属性指定了在构造方法中的位置,确保了传参的正确性,第 3 个
“index=2”。现在的 3 个
二、设值注入
一个简单的 JavaBean 最明显的规则就是以一个私有属性对应 set()和 get()方法,来实现对属性的封装。既然 JavaBean 有 set()方法来设置 Bean 的属性,Spring 就会有相应的支持。除了为构造方法传递参数的
设置 Moniter 类属性和 set()/get()方法。程序代码如下。
[java] view plain copy 
package com.linbingwen;
public class Moniter implements Student {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("姓名:" + name);
System.out.println("年龄:" + age);
System.out.println("性别:" + sex);
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
修改 applicationContext.xml 配置文件。添加名称为 Moniter 的 Java Bean 的定义,用
[html] view plain copy 
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd"\>
<bean id="stu1" class="com.linbingwen.Stu1">
<constructor-arg index="0">
<value>飞龙</value>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1">
<value>男</value>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="int">
<value>26</value>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="moniter" class="com.linbingwen.Moniter">
<property name="age">
<value>26</value>
</property>
<property name="name">
<value>欣欣</value>
</property>
<property name="sex">
<value>女</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
程序运行结果如图 所示
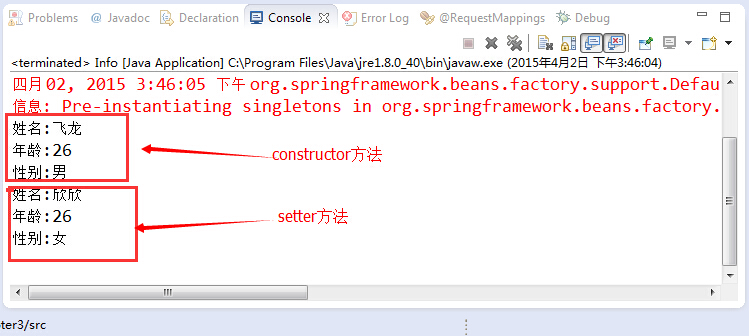
三、接口注入(interface injection)
==============================
接口注入指的就是在接口中定义要注入的信息,并通过接口完成注入。
具体步骤如下
①.编写一个接口IBuniness,各种数据库的注入将通过这个接口进行。代码如下
[java] view plain copy 
package ch3;
public interface IBusiness {
public void createDI(DataBase db);
}
②.任何想要使用数据库实例的类都必须实现这个接口,业务逻辑类Business实现这个接口IBusiness。代码如下
[java] view plain copy 
package ch3;
public class Business implements IBusiness {
private DataBase db;
@Override
public void createDI(DataBase db) {//接口注入
this.db = db;
}
// 根据注入的数据库,从XXX数据库中取得数据。
public void getData(){
db.getData();
}
}
3.编写测试类TestBusiness。代码如下
[java] view plain copy 
- package ch3;
- public class TestBusiness {
- private Business business = new Business();
- // 根据注入的数据库类,从oracle中取得数据库。
- public void getData() {
- business.createDI(new OracleDataBase()); // 注入实际的数据库类型。如要变更式样,只需改变此处即可,达到重用目的。
- business.getData();
- }
- }
如果要完成依赖关系注入的对象,必须实现IBusiness接口。
四、JavaBean 的赋值标签
以上只介绍了如何用
任何如
1.
这是一个普通的赋值标签,可直接在成对的
[html] view plain copy 
- <value>arg</value>
arg:传递给 JavaBean 的属性值。
2.标签
这个标签可以引用其他 JavaBean 的实例对象,当传递的参数是其他 JavaBean 的实例对象时使用此标签。语法格式如下。
[html] view plain copy 
- <ref bean="JavaBean"/>
bean:指定引用的 JavaBean。
3.
这是为 JavaBean 赋 Null 空值的标签。当 JavaBean 的某个属性暂不使用,要将其设置为 Null 值时使用此标签。语法格式如下。
[html] view plain copy 
或
[html] view plain copy 
- <null></null>
4.标签
这是为 List 集合类或数组赋值的标签。当 JavaBean 的某个属性是 List 集合类型或数组时,需要使用此标签为 List 集合类型或数组的每一个元素赋值。语法格式如下。
[html] view plain copy 
- <list>
- <value>arg1</value>
- <value>arg2</value>
- </list>
标签指定的属性赋值。也可以使用其他赋值标签作为集合类赋值标签的子标签,例如或 3.2.7 节中介绍的使用
JavaBean 的方法。此标签应用在
[html] view plain copy 
- <bean id="school" class="School">
- <property name="studentList">
- <list>
- <ref bean=" student1"/>
- <value>student2</value>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
5.
和标签类似,
[html] view plain copy 
- <set>
- <ref bean="arg1"/>
- <value>arg2</value>
- ……
- </set>
此标签应用在
[html] view plain copy 
- <bean id="school" class="School">
- <property name="student">
- <set>
- <ref bean=" student1"/>
- <value>name</value>
- </set>
- </property>
- <bean>
6.
[html] view plain copy 
- <map>
- <entry key="key1">
- <ref bean="arg1" />
- </entry>
- </map>
[html] view plain copy 
- <bean id="school" class="School">
- <property name="student">
- <map>
- <entry key="key1">
- <ref bean=" student1" />
- </entry>
- <entry key="key2">
- <value> student2</value>
- </entry>
- </map>
- </property>
- </bean>
7.
这是为 java.util.Properties 类型属性赋值的标签,和
[html] view plain copy 
- <props>
- <prop key="key1">value</prop>
- </props>
[html] view plain copy 
- <bean id="school" class="School">
- <property name="student">
- <props>
- <prop key="key1">student1</prop>
- <prop key="key2">student2</prop>
- </props>
- </property>
- </bean>
8 匿名内部 JavaBean 的创建
通过前面的介绍,读者应该对如何使用 XML 装配 JavaBean 有了一定的了解。但是编程中经常遇到匿名的内部类,在 Spring 中该如何利用 XML 装配呢?其实非常简单,在需要匿名内部类的地方直接用
[html] view plain copy 
- <bean id="school" class="School">
- <property name="student">
- <bean class="Student"/>
- </property>
- </bean>
代码中定义了匿名的 Student 类,将这个匿名内部类赋给了 school 类的实例对象。
五、 list、set、map注入使用范例
还是接上面的工程,新建一个School.java,代码如下:
[java] view plain copy 
package com.linbingwen;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class School {
private List listStu;
private Set setStu;
private Map mapStu;
public List getListStu() {
return listStu;
}
public void setListStu(List listStu) {
this.listStu = listStu;
}
public Set getSetStu() {
return setStu;
}
public void setSetStu(Set setStu) {
this.setStu = setStu;
}
public Map getMapStu() {
return mapStu;
}
public void setMapStu(Map mapStu) {
this.mapStu = mapStu;
}
public void printSchool(){
System.out.println("--------list--------");
for (int i = 0; i < listStu.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(listStu.get(i));
}
System.out.println("--------set--------");
for(Object s : setStu){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("--------map--------");
Iterator it=mapStu.entrySet().iterator();
System.out.println(mapStu.entrySet().size());
String key;
String value;
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)it.next();
key=entry.getKey().toString();
value=entry.getValue().toString();
System.out.println(key+"===="+value);
}
}
}
applicationContext.xml如下:
[java] view plain copy 
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd"\>
<bean id="stu1" name="student1" class="com.linbingwen.Stu1">
<constructor-arg index="0">
飞龙 <constructor-arg index="1">
男 <constructor-arg type="int">
26 <bean id="moniter" name="student2" class="com.linbingwen.Moniter">
<property name="age">
26 <property name="name">
欣欣 <property name="sex">
女 <bean id="school" class="com.linbingwen.School">
<property name="listStu">
<bean class="com.linbingwen.Moniter">
1 hello <property name="setStu">
<bean class="com.linbingwen.Stu1">
<constructor-arg value="大平" index="0">
<constructor-arg value="男" index="1">
<constructor-arg value="10" index="2">
333333 Evankaka <property name="mapStu">
<entry key="key1">
<entry key="key2">
<bean class="com.linbingwen.Moniter">
<entry key="key3">
student2 <entry key="key4">
56
如下:
[java] view plain copy 
package com.linbingwen;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Info {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student student = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("stu1");
student.printInfo();
Student moniter = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("moniter");
moniter.printInfo();
School school=(School) applicationContext.getBean("school");
school.printSchool();
}
}
输出结果:
四月 02, 2015 5:36:38 下午 org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext prepareRefresh
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@addb54: startup date [Thu Apr 02 17:36:38 CST 2015]; root of context hierarchy
四月 02, 2015 5:36:38 下午 org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinitions
信息: Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [applicationContext.xml]
四月 02, 2015 5:36:38 下午 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory preInstantiateSingletons
信息: Pre-instantiating singletons in org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@ebcd03: defining beans [stu1,moniter,school]; root of factory hierarchy
姓名:飞龙
年龄:26
性别:男
姓名:欣欣
年龄:26
性别:女
--------list--------
姓名:欣欣;年龄:26;性别:女
姓名:欣欣;年龄:26;性别:女
姓名:飞龙;年龄:26;性别:男
姓名:阿屁;年龄:20;性别:男
1
hello
--------set--------
姓名:欣欣;年龄:26;性别:女
姓名:飞龙;年龄:26;性别:男
姓名:大平;年龄:10;性别:男
333333
Evankaka
--------map--------
4
key1====姓名:欣欣;年龄:26;性别:女
key2====姓名:小王;年龄:80;性别:男
key3====student2
key4====56
六、 总结
设值注入和构造注入的比较
1、设值注入的优点
(1)与传统的JavaBean的写法更相似,更容易让人理解,依赖关系显得更加直观、自然。
(2)对于复杂的依赖关系,如果采用构造注入会导致构造器过于臃肿,难以阅读。因为Spring在创建Bean实例时,需要同时实例化其依赖的全部实例,因而导致Struts+Spring+Hibernate整合开发性能下降。设值注入可以避免这些问题。
(3)在某些属性可选的情况下,多参数的构造器更加笨重。
2、构造注入的优点
(1) 可以在构造器中决定依赖关系的注入顺序。例如,组件中其他依赖关系的注入,常常需要依赖于Datasource的注入。采用构造注入时,可以在代码中清晰地决定注入顺序,优先依赖先注入。
(2)对于依赖关系无须变化的bean,构造注入更有用处。因为没有setter,所有的关系都在构造器中设定,因此无需担心后续代码对依赖关系产生破坏。
(3) 依赖关系只能在构造器中设定,因为只有组件的创建者才能改变组件的依赖关系。对于组件的调用者而言,组件内部的依赖关系完全透明,更符合高内聚的原则。
建议采用设值注入为主,构造注入为辅的注入策略。
Spring Bean的其他说明
1、 Bean的标识(id,name,class)
id:bean的唯一标识。
2、name:bean的别名,可以有多个。
class:bean的具体实现类
3、 Bean的作用域
(1) singleton:单例,在IOC容器里只有一个实例
[html] view plain copy 
- <beanidbeanid="loginAction"class="net.vzhang.spring3.action.LoginAction" scope="singleton"/>
(2) prototype:
[html] view plain copy 
- <beanidbeanid="loginAction2"class="net.vzhang.spring3.action.LoginAction2" scope="prototype"/>
request:针对Web应用的每次请求都生成一个新的实例
每次对bean请求时,都会创建一个新的实例。
对bean的请求:将其注入到另外一个bean中,或者调用BeanFactory的getBean方法。
session:HttpSessio














