本文主要内容:
(1)商品修改功能开发
(2)@RequestMapping
(3)Controller类中方法的返回值
(4)参数绑定
(5)post中文乱码
(6)SpringMVC和Struts2的区别
1.商品修改功能开发
1.1需求
操作流程:
(1)进入商品查询列表页面;
(2)点击修改,进入商品修改页面,页面中显示了要修改的商品(从数据库查询),
要修改的商品从数据库查询,根据商品id(主键)查询商品信息;
(3)在商品修改页面,修改商品信息,修改后,点击提交。
1.2开发mapper
mapper:
根据id查询商品信息
根据id更新Items表的数据
不用开发了,使用逆向工程生成的代码,Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis深入学习及搭建(十)——MyBatis逆向工程
1.3开发service
接口功能:
根据id查询商品信息
修改商品信息
public interface ItemsService {
//商品查询列表
public List
//根据id查询商品信息
public ItemsCustom findItemsById(Integer id) throws Exception;
//修改商品信息
public void updateItems(Integer id,ItemsCustom itemsCustom) throws Exception;
}
public class ItemsServiceImpl implements ItemsService{
@Autowired
private ItemsMapperCustom itemsMapperCustom;
@Autowired
private ItemsMapper itemsMapper;
@Override
public List<ItemsCustom> findItemsList(ItemsQueryVo itemsQueryVo)
throws Exception {
//通过ItemsMapperCustom查询数据库
return itemsMapperCustom.findItemsList(itemsQueryVo);
}
@Override
public ItemsCustom findItemsById(Integer id) throws Exception {
Items items=itemsMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
//中间对商品信息进行业务处理
//....
//返回Items的扩展类ItemsCustom
ItemsCustom itemsCustom=new ItemsCustom();
//将items的属性值拷贝到itemsCustom
BeanUtils.copyProperties(items, itemsCustom);
return itemsCustom;
}
@Override
public void updateItems(Integer id, ItemsCustom itemsCustom)
throws Exception {
//添加业务校验,通常在service接口对关键参数进行校验
//校验id是否为空,如果为空抛出异常
//更新商品信息使用updateByPrimaryKeyWithBLOBs根据id更新items表中所有字段,包括大文本类型字段
//updateByPrimaryKeyWithBLOBs要求必须传入id
itemsCustom.setId(id);
itemsMapper.updateByPrimaryKeyWithBLOBs(itemsCustom);
}
}
1.4开发controller
方法:
商品信息修改页面显示
商品信息修改提交
@Controller public class ItemsController {
@Autowired
private ItemsService itemsService;
//商品查询http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC\_MyBatis/queryItems.action
@RequestMapping("/queryItems")
public ModelAndView queryItems() throws Exception{
//调用service查找数据库,查询商品列表
List<ItemsCustom> itemsList=itemsService.findItemsList(null);
//返回ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("itemsList", itemsList);
//指定视图
// modelAndView.setViewName("/WEB-INF/jsp/items/itemsList.jsp"); //下边的路径,如果在视图解析器中配置jsp路径的前缀和jsp路径的后缀,修改为 modelAndView.setViewName("items/itemsList"); return modelAndView; }
//商品信息修改页面显示
@RequestMapping("/editItems")
public ModelAndView editItems() throws Exception{
//调用service根据商品id查询商品信息
ItemsCustom itemsCustom=itemsService.findItemsById(1);
//返回ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView();
//将商品信息放到model
modelAndView.addObject("itemsCustom",itemsCustom);
//商品修改页面
modelAndView.setViewName("items/editItems");
return modelAndView;
}
//商品信息修改提交
@RequestMapping("/editItemsSubmit")
public ModelAndView editItemsSubmit() throws Exception{
//调用service更新商品信息,页面需要将商品信息传到此方法
//......
//返回ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView();
//返回一个成功页面
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
}
1.5 编写jsp
itemsList.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"%>
editItems.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"%>
1.6 商品修改调试
访问地址:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC\_MyBatis/queryItems.action 点击修改
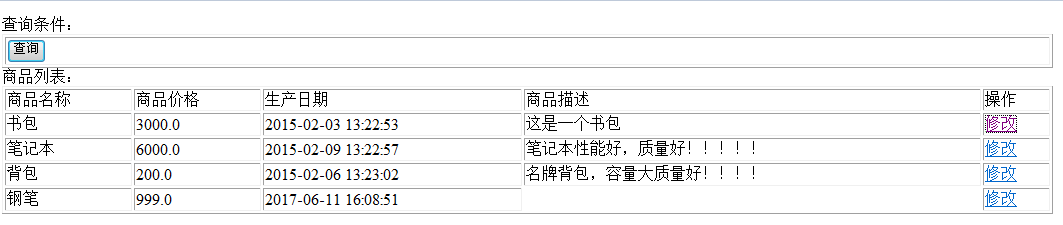

接下来,学习一些特性:
2. @RequestMapping
通过RequestMapping注解可以定义不同的处理器映射规则。
2.1URL路径映射
@RequestMapping(value="/item")或@RequestMapping("/item")
value的值是数组,可以将多个url映射到同一个方法.
2.2窄化请求映射
在Controller Class上添加@RequestMapping(url)指定通用请求前缀, 限制此类下的所有方法请求url必须以请求前缀开头,通过此方法对url进行分类管理。

那么前面jsp中的请求的地址要相应改变
itemsList.jsp中:


editItems.jsp中:

2.3请求方法限定
出于安全性考虑,对http的链接进行方法限制。
如果限制请求为post,进行get请求时,则报错:


3.Controller类中方法的返回值
3.1返回ModelAndView
Controller方法中定义ModelAndView对象并返回,对象中可添加model数据、指定view。
3.2返回字符串
3.2.1逻辑视图名
controller方法返回字符串可以指定逻辑视图名,通过视图解析器解析为物理视图地址。
真正视图(jsp路径)=前缀+逻辑+逻辑视图名+后缀
@RequestMapping(value="/editItems",method={RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET}) public String editItems(Model model) throws Exception{ //调用service根据商品id查询商品信息 ItemsCustom itemsCustom=itemsService.findItemsById(1);
//通过形参中的model将model数据传到页面
//相当于modelAndView.addObject方法
model.addAttribute("itemsCustom", itemsCustom);
return "items/editItems";
}
3.2.2Redirect重定向
需求:商品修改提交后,重定向到商品查询列表。
redirect重定向特点:浏览器地址栏中的url会变化。修改提交的request数据无法传到重定向的地址。因为重定向后重新进行request(request无法共享)
@RequestMapping("/editItemsSubmit") public String editItemsSubmit(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception{ //调用service更新商品信息,页面需要将商品信息传到此方法 //......
//重定向到商品的查询列表
return "redirect:queryItems.action";
}
}
3.2.3forward页面转发
通过forward进行页面转发,浏览器地址栏url不变,request可以共享。
@RequestMapping("/editItemsSubmit") public String editItemsSubmit(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception{ //调用service更新商品信息,页面需要将商品信息传到此方法 //......
//重定向到商品的查询列表
// return "redirect:queryItems.action"; //页面转发 return "forward:queryItems.action"; }
验证request是否可以共享:
在editItems.jsp中提交了一个id,在queryItems.action获取id。
//商品查询http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC\_MyBatis/items/queryItems.action @RequestMapping("/queryItems") public ModelAndView queryItems(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception{ //测试forward后request是否可以共享 System.out.println(request.getParameter("id"));
//调用service查找数据库,查询商品列表
List<ItemsCustom> itemsList=itemsService.findItemsList(null);
//返回ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("itemsList", itemsList);
//指定视图
// modelAndView.setViewName("/WEB-INF/jsp/items/itemsList.jsp"); //下边的路径,如果在视图解析器中配置jsp路径的前缀和jsp路径的后缀,修改为 modelAndView.setViewName("items/itemsList"); return modelAndView; }
3.3返回void
在controller方法形参上可以定义request和response,使用request或response指定响应结果:
(1)使用request转发页面,如下:
request.getRequestDispatcher("页面路径").forward(request, response);
(2)也可以通过response页面重定向:
response.sendRedirect("url");
(3)也可以通过response指定响应结果,例如响应json数据如下:
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8"); response.getWriter().write("json串");
4.参数绑定
struts接收数据时,是在action类的成员变量中定义你需要接收的参数。
4.1spring参数绑定过程
从客户端请求key/value数据,经过参数绑定,将key/value数据绑定到controller方法的形参上。
springmvc中,接收页面提交的数据是通过方法形参来接收。而不是在controller类定义成员变量接收!

4.2默认支持的类型
直接在controller方法形参上定义下边类型的对象,就可以使用这些对象。在参数绑定过程中,如果遇到下边类型直接进行绑定。
4.2.1HttpServletRequest
通过request对象获取请求信息。
4.2.2HttpServletResponse
通过response处理响应信息
4.2.3HttpSession
通过session对象得到session中存放的对象。
4.2.4Model/ModelMap
作用:将model数据填充到request域。
ModelMap是Model接口的实现类,通过Model或ModelMap向页面传递数据,如下:
//调用service查询商品信息 Items item = itemService.findItemById(id); model.addAttribute("item", item);
页面通过${item.XXXX}获取item对象的属性值。
使用Model和ModelMap的效果一样,如果直接使用Model,springmvc会实例化ModelMap。
4.3简单类型
通过@RequestParam对简单类型的参数进行绑定。
如果不使用@RequestParam,要求request传入参数名称和controller方法的形参名称一致,方可绑定成功。

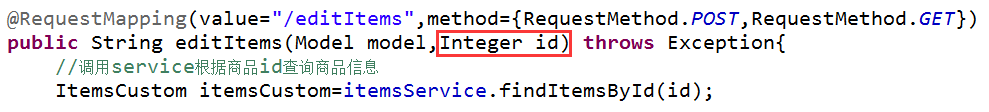
如果使用@RequestParam,不用限制request传入参数名称和controller方法的形参名称一致。
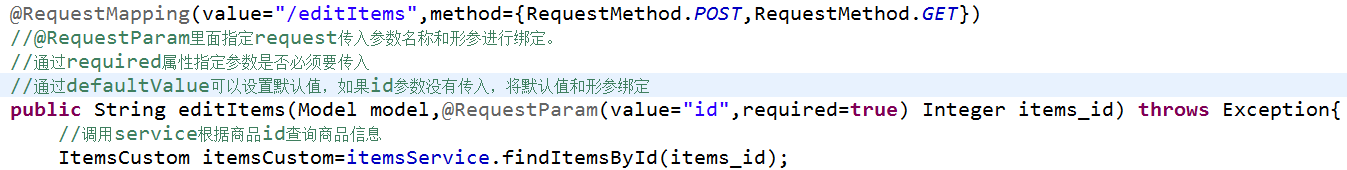
通过required属性指定参数是否必须要传入,如果设置为true,没有传入参数,报下边错误:

4.4 pojo绑定
@RequestMapping("/editItemsSubmit") public String editItemsSubmit(HttpServletRequest request,Integer id,ItemsCustom itemsCustom) throws Exception{ //调用service更新商品信息,页面需要将商品信息传到此方法 itemsService.updateItems(id, itemsCustom);
//重定向到商品的查询列表
// return "redirect:queryItems.action"; //页面转发 return "forward:queryItems.action"; }
页面中的name和controller的pojo形参中的属性名称一致,会自动将页面中的数据绑定到pojo。
页面定义:

controller的pojo形参的定义:

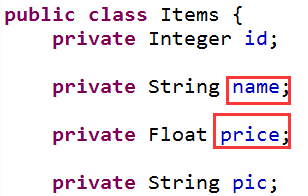
4.4.1简单pojo
将pojo对象中的属性名与传递进来的属性名对应,如果传进来的参数名称和对象中的属性名称一致则将参数值设置在pojo对象中。
页面定义如下:
Controller方法定义如下:
@RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit") public String editItemSubmit(Items items)throws Exception{ System.out.println(items);
请求参数名称和pojo的属性名称一致,会自动将请求参数赋值给pojo的属性。
4.4.2包装pojo
如果采用类似struts中对象.属性的方式命名,需要将pojo对象作为一个包装对象的属性,Controller方法中以该包装对象最为形参。
包装对象定义如下:
public class QueryVo { private Items items; }
页面定义:
Controller方法定义如下:
public String useraddsubmit(Model model,QueryVo queryVo)throws Exception{ System.out.println(queryVo.getItems());
4.5自定义参数绑定
需求:
对于controller形参中pojo对象,如果属性中有日期类型,需要自定义参数绑定。将请求日期参数串转成日期类型,要转换的日期类型和pojo中日期属性的类型保持一致。
所有自定义参数绑定将日期串转成java.util.Date类型。
需要向处理器适配器中注入自定义的参数绑定组件。
4.5.1自定义日期类型绑定
package joanna.yan.ssm.controller.converter;
import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter; /** * 日期转换器 * @author Joanna.Yan * */ public class CustomDateConverter implements Converter<String, Date>{
@Override
public Date convert(String source) {
System.out.println("source="+source);
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
return sdf.parse(source);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
4.5.2配置方式
4.5.2.1配置方式1
classpath下springmvc.xml中加:
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService">
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<!-- 转换器 -->
<property name="converters">
<list>
<!-- 日期类型转换 -->
<bean class="joanna.yan.ssm.controller.converter.CustomDateConverter"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
4.5.2.2配置方式2
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<property name="webBindingInitializer" ref="customBinder"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 自定义webBinder -->
<bean id="customBinder"
class="org.springframework.web.bind.support.ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer">
<property name="conversionService" ref="conversionService" />
</bean>
<!-- conversionService -->
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<!-- 转换器 -->
<property name="converters">
<list>
<bean class="joanna.yan.ssm.controller.converter.CustomDateConverter"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
4.6集合类
4.6.1字符串数组
页面定义如下:
页面选中多个checkbox向controller方法传递:
传递到controller方法中的格式是:001,002,003
Controller方法中可以用String[]接收,定义如下:
public String deleteitem(String[] item_id)throws Exception{ System.out.println(item_id); }
4.6.2List
List中存放对象,并将定义的List放在包装类中,controller使用包装对象接收。
包装类中定义List对象,并添加get/set方法如下:
Public class QueryVo {
Private List
//get/set方法.. }
页面定义如下:
上边的静态代码改为动态jsp代码如下:
<c:forEach items="${itemsList }" var="item" varStatus="s">
Contrller方法定义如下:
public String useraddsubmit(Model model,QueryVo queryVo)throws Exception{ System.out.println(queryVo.getItemList()); }
4.6.3Map
在包装类中定义Map对象,并添加get/set方法,controller使用包装对象接收。
包装类中定义Map对象如下:
Public class QueryVo { private Map<String, Object> itemInfo = new HashMap<String, Object>(); //get/set方法.. }
页面定义如下:
Contrller方法定义如下:
public String useraddsubmit(Model model,QueryVo queryVo)throws Exception{ System.out.println(queryVo.getStudentinfo()); }
5.post中文乱码
在web.xml中加入:
以上可以解决post请求乱码问题。
对于get请求中文参数出现乱码解决方法有两个:
修改Tomcat配置文件添加编码与工程编码一致,如下:
<Connector **URIEncoding="utf-8"** connectionTimeout="20000" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" redirectPort="8443"/>
另外一种方法对参数进行重新编码:
String userName=new String(request.getParamter("userName").getBytes("ISO8859-1"),"utf-8");
ISO8859-1是Tomcat默认编码,需要将Tomcat编码后的内容按utf-8编码。
6.SpringMVC和Struts2的区别
(1)SpringMVC的入口是一个Servlet即前端控制器,而Struts2的入口是一个filter过滤器。
(2)SpringMVC是基于方法开发(一个url对应一个方法),请求参数传递到方法的形参,可以设计为单例或多例(建议单例),struts2是基于类开发,传递参数是通过类的成员变量,只能设计为多例。
SpringMVC将url和Controller方法映射,映射成功后SpringMVC生成一个Handler对象,对象中止包括了一个method。方法执行结束后,形参数据销毁。
SpringMVC的Controller开发类似service开发。
(3)Strut采用值栈存储请求和响应的数据,通过OGNL存取数据,SpringMVC通过参数解析器将request请求内容解析,并给方法形参赋值,将数据和视图封装成ModelAndView对象,最后又将ModelAndView中的模型数据通过request域传输到页面。jsp视图解析器默认使用jstl。
(4)经过实际测试,Struts2速度慢在于使用Struts标签,如果使用Struts建议使用jstl。













