数据类型
计算机顾名思义就是可以做数学计算的机器,因此,计算机程序理所当然地可以处理各种数值。但是,计算机能处理的远不止数值,还可以处理文本、图形、音频、视频、网页等各种各样的数据,不同的数据,需要定义不同的数据类型。在Python中,能够直接处理的数据类型有以下几种:
- 整数
Python可以处理任意大小的整数,当然包括负整数,在程序中的表示方法和数学上的写法一模一样,例如:1,100,-8080,0,等等。
计算机由于使用二进制,所以,有时候用十六进制表示整数比较方便,十六进制用0x前缀和0-9,a-f表示,例如:0xff00,0xa5b4c3d2,等等。
- 浮点数
浮点数也就是小数,之所以称为浮点数,是因为按照科学记数法表示时,一个浮点数的小数点位置是可变的,比如,1.23×109和12.3×108是完全相等的。浮点数可以用数学写法,如1.23,3.14,-9.01,等等。但是对于很大或很小的浮点数,就必须用科学计数法表示,把10用e替代,1.23×109就是1.23×e9,或者12.3×e8,0.000012可以写成1.2×e−5,等等。
整数和浮点数在计算机内部存储的方式是不同的,整数运算永远是精确的(除法难道也是精确的?是的!),而浮点数运算则可能会有四舍五入的误差。
- 字符串
字符串是以单引号'或双引号"括起来的任意文本,比如'abc',"xyz"等等。请注意,''或""本身只是一种表示方式,不是字符串的一部分,因此,字符串'abc'只有a,b,c这3个字符。如果'本身也是一个字符,那就可以用""括起来,比如"I'm OK"包含的字符是I,',m,空格,O,K这6个字符。
import sysa =3b =4c = 1.09d = 2.35e = complex(c,d)f = complex(float(a),float(b))g = "hello python"print("a is type ",type(a))print("c is type ",type(c))print("e is type ",type(e))print("g is type ",type(g))
a is type <class 'int'>c is type <class 'float'>e is type <class 'complex'>g is type <class 'str'>
运算符
Python语言支持以下类型的运算符:
算术运算符
比较(关系)运算符
赋值运算符
逻辑运算符
位运算符
成员运算符
身份运算符
算术运算符
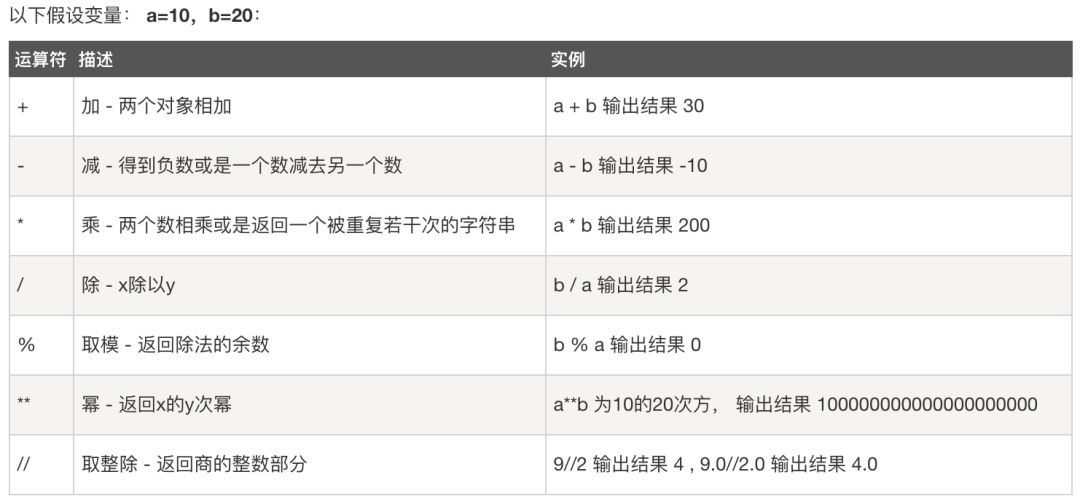
# coding=utf-8#两个数字相加sumNumber=1+2print(sumNumber) #输出结果:3#两个字符串相加sumString="Nice" + "work"print(sumString) #输出结果:Nicework#两个数字相减subNumber=2-1print(subNumber) #输出结果:1#两个数字相乘或者字符串重复multiplicationNumber=2*3print(multiplicationNumber) #输出结果:6multiplicationString="hello"*2print(multiplicationString) #输出结果:hellohello#两个数相除divisionNumber=9/2print(divisionNumber) #输出结果:4divisionNumber=9.0/2print(divisionNumber) #输出结果:4.5divisionNumber=9/2.0print(divisionNumber) #输出结果:4.5#/---除数或被除数中有任意一个是小数的话,商也会保留小数,反之取整---/#除法运算// 返回商的整数部分,抛弃余数divisorNumber=10//3print(divisorNumber) #输出结果:3#除法运算% 返回商的余数部分,抛弃商divisorNumber=10%3print(divisorNumber) #输出结果:1divisorNumber=10%1print(divisorNumber) #输出结果:0 /--没有余数则返回0--/divisorNumberx=10//3 #divisorNumberx是商的整数部分divisorNumbery=10%3 #divisorNumbery是余数divisorNumberz=3*divisorNumberx+divisorNumbery #divisorNumberz是除数乘以商的整数部分加上余数,得到的divisorNumberz的值就是被除数print(divisorNumberz) #输出结果:10#求幂运算powerNumber=2**3 #相当于2的3次幂,就是2*2*2 关于幂运算大家应该在数学里都很熟悉了print(powerNumber) #输出结果:8
3Nicework16hellohello4.54.54.5310108
比较(关系)运算符
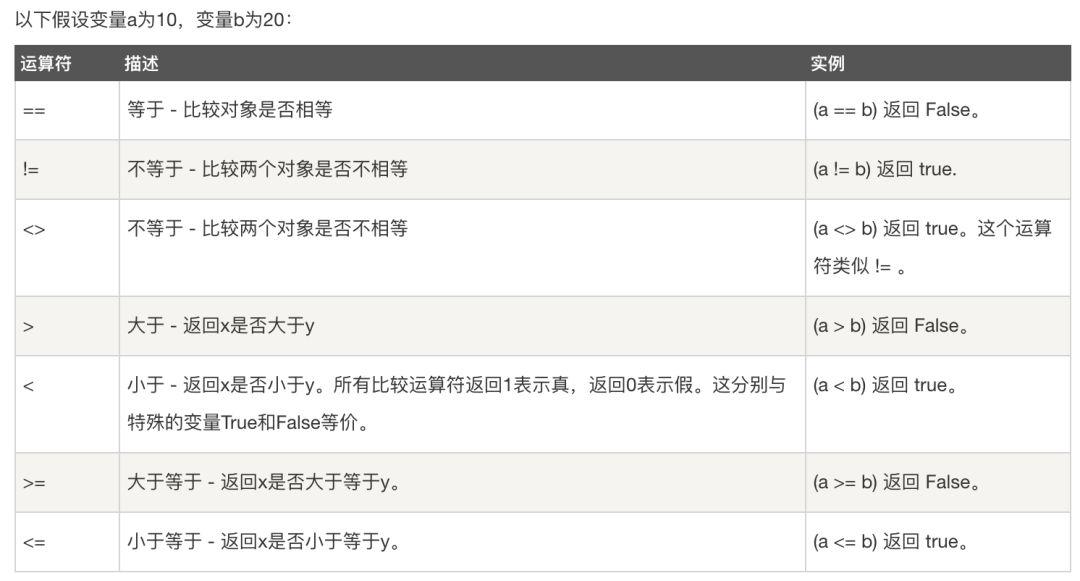
#小于符号,返回值是bool值lessThan=1<2print(lessThan) #输出结果:TruelessThan=1<1print(lessThan) #输出结果:False#大于符号,返回值是bool值moreThan=2>1print(moreThan) #输出结果:TruemoreThan=2>2print(moreThan) #输出结果:False#不等于符号 返回值是Bool值notEqual=1!=2print(notEqual) #输出结果:TruenotEqual=1!=1print(notEqual) #输出结果:False
TrueFalseTrueFalseTrueFalse
赋值运算符
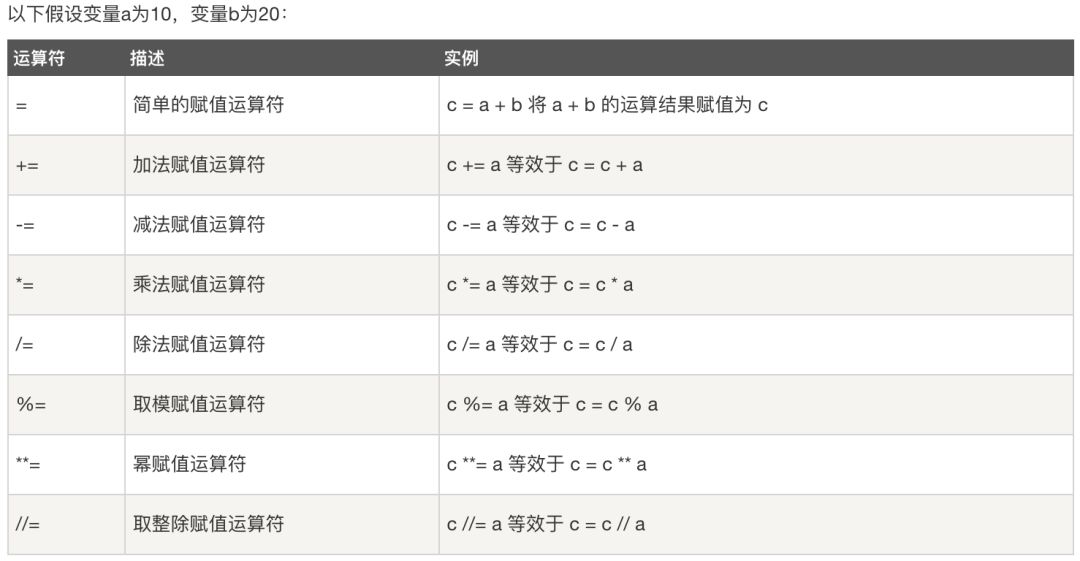
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-a = 21b = 10c = 0c = a + bprint("1 - c 的值为:", c)c += aprint("2 - c 的值为:", c)c *= aprint("3 - c 的值为:", c)c /= a print("4 - c 的值为:", c)c = 2c %= aprint("5 - c 的值为:", c)c **= aprint("6 - c 的值为:", c)c //= aprint("7 - c 的值为:", c)
1 - c 的值为: 312 - c 的值为: 523 - c 的值为: 10924 - c 的值为: 52.05 - c 的值为: 26 - c 的值为: 20971527 - c 的值为: 99864
逻辑运算符
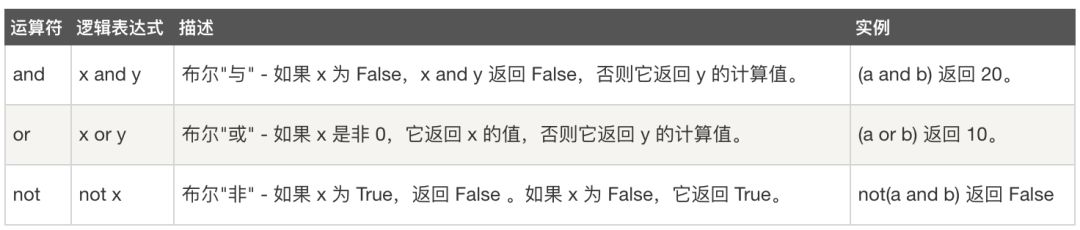
#逻辑非 notoperationx=Trueoperationy=not operationxprint(operationy) #输出结果:Falseoperationz=Falseprint(not operationz) #输出结果:True#逻辑与 andprint(True and True) #输出结果:True#逻辑或 orprint(False or False) #输出结果:False
FalseTrueTrueFalse
位运算符
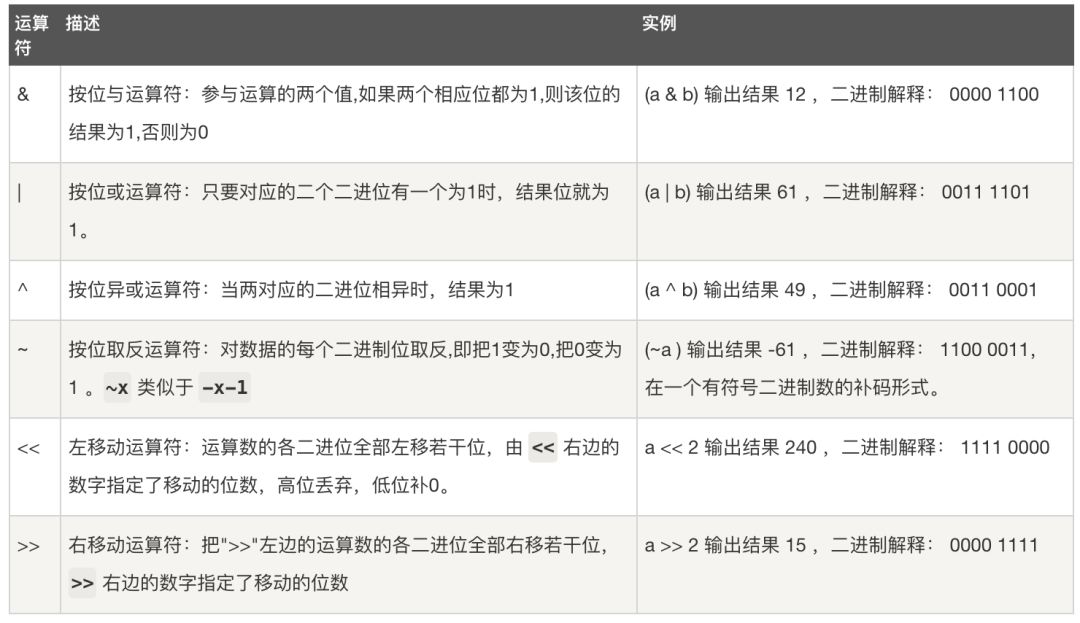
#按位与运算&, 按位与是指一个数字转化为二进制,然后这些二进制的数按位来进行与运算operationNumber=7&18print(operationNumber) #输出结果:2#按位或运算|, 按位或是指一个数字转化为二进制,然后这些二进制的数按位来进行或运算operationNumber=7|18print(operationNumber) #输出结果:23 #结题思路和按位与运算的一样,可以参考按位与运算#按位异或operationNumber=7^18print(operationNumber) #输出结果:21 #结题思路和按位与运算的一样,可以参考按位与运算#按位翻转 ~按位翻转公式:~x= - (x+1)operationNumber=~{12}#~12=- (12+1) = -13print(operationNumber) #输出结果:-13 #结题思路和按位与运算的一样,可以参考按位与运算#左移<<operationNumber=12<<1print(operationNumber) #输出结果:24operationNumber=3<<3print(operationNumber) #输出结果:24#右移>>operationNumber=12>>1print(operationNumber) #输出结果:6operationNumber=12>>2print(operationNumber) #输出结果:3
22321-13242463
比较运算符
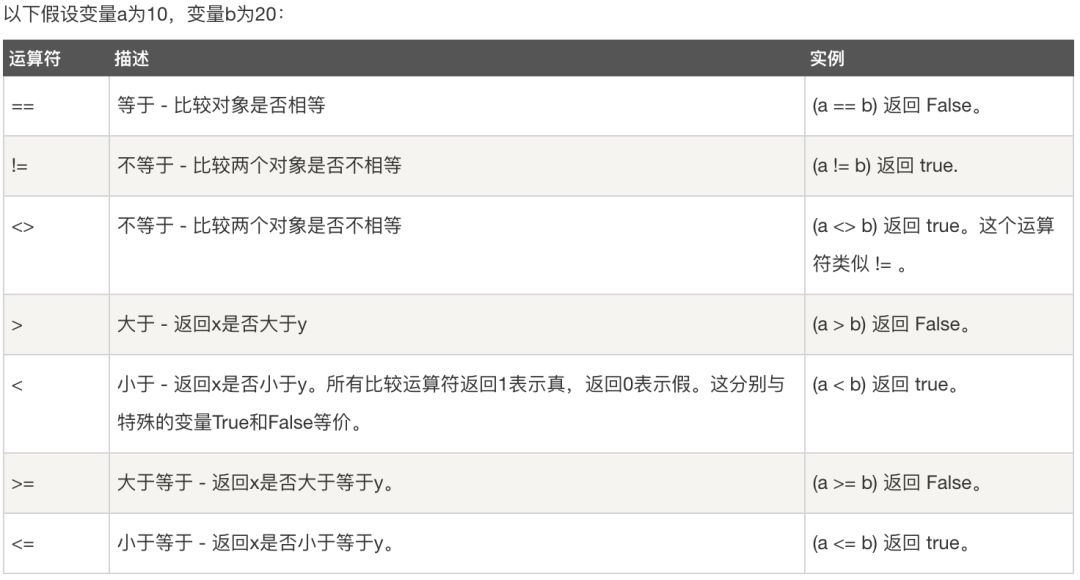
#小于等于<= 比较运算,小于或等于返回一个bool值operationNumber=3<=3print(operationNumber) #输出结果:TrueoperationNumber=3<=2print(operationNumber) #输出结果:False#大于等于>= 比较运算,大于或等于返回一个bool值operationNumber=2>=3print(operationNumber) #输出结果:FalseoperationNumber=3>=2print(operationNumber) #输出结果:True#比较两个对象是否相等==operationNumber=3==2print(operationNumber) #输出结果:FalseoperationString="hi"=="hi"print(operationString) #输出结果:True
TrueFalseFalseTrueFalseTrue
成员运算符
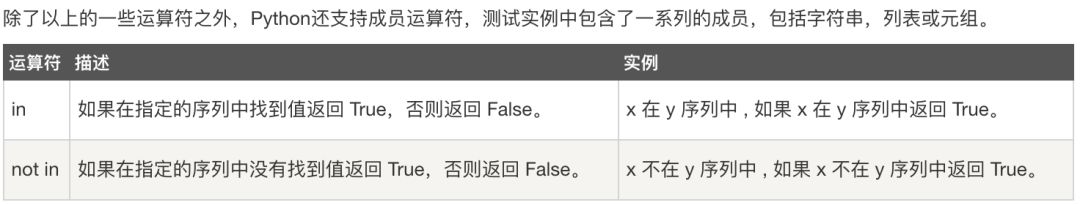
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-a = 10b = 20list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];if ( a in list ): print("1 - 变量 a 在给定的列表中 list 中")else: print("1 - 变量 a 不在给定的列表中 list 中")if ( b not in list ): print("2 - 变量 b 不在给定的列表中 list 中")else: print("2 - 变量 b 在给定的列表中 list 中")# 修改变量 a 的值a = 2if ( a in list ): print("3 - 变量 a 在给定的列表中 list 中")else: print("3 - 变量 a 不在给定的列表中 list 中")
1 - 变量 a 不在给定的列表中 list 中2 - 变量 b 不在给定的列表中 list 中3 - 变量 a 在给定的列表中 list 中
身份运算符
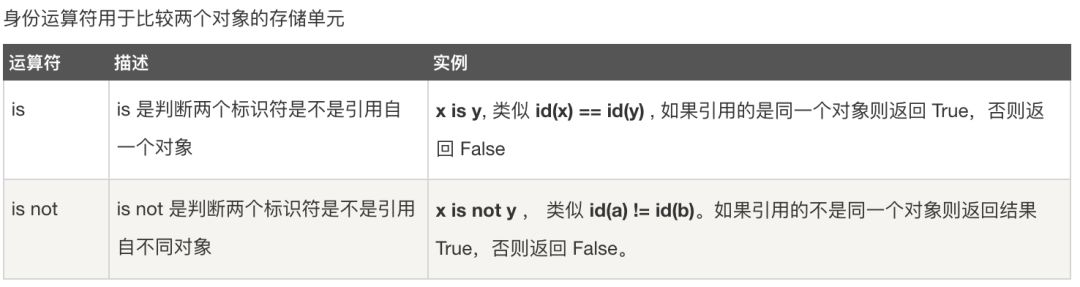
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-a = 20b = 20if ( a is b ): print("1 - a 和 b 有相同的标识")else: print("1 - a 和 b 没有相同的标识")if( a is not b ): print("2 - a 和 b 没有相同的标识")else: print("2 - a 和 b 有相同的标识")# 修改变量 b 的值b = 30if ( a is b ): print("3 - a 和 b 有相同的标识")else: print("3 - a 和 b 没有相同的标识")if ( a is not b ): print("4 - a 和 b 没有相同的标识")else: print("4 - a 和 b 有相同的标识")
1 - a 和 b 有相同的标识2 - a 和 b 有相同的标识3 - a 和 b 没有相同的标识4 - a 和 b 没有相同的标识
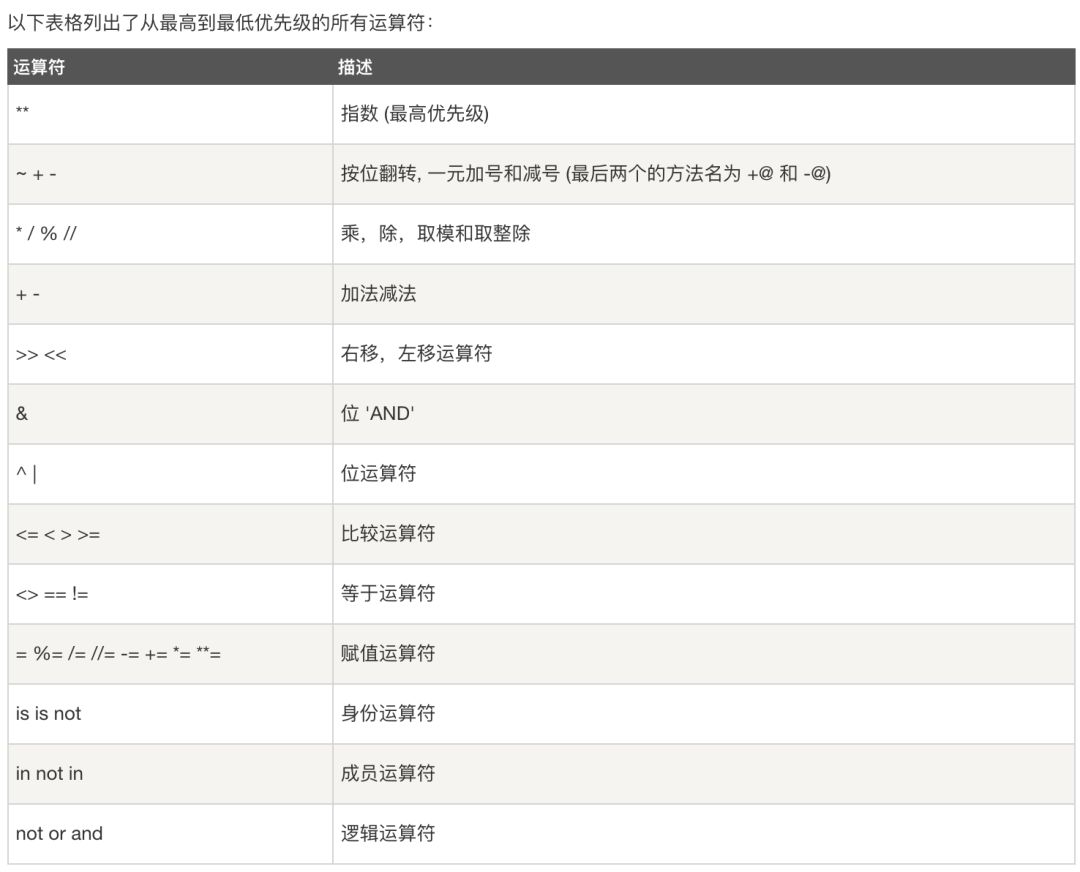
运算符优先级
容器
本文整理几种基本容器:
列表(list)
元组(tuple)
字典(dict)
集合(set)
列表
list是一种有序的集合,可以随时添加和删除其中的元素。
# 初始化列表li = [1, 2, 3, 'abc', 4.5, [2, 3, 4], {1:'one'}]# 获取长度print(len(li)) # 结果为:7print('')# 根据索引读写print(li[0]) #索引从零开始,结果为:1print(li[3]) #结果为:'abc'print(li[-1]) #索引从后往前,结果为:{1: 'one'}print(li[-3]) #结果为:4.5print('')# 添加元素li = [1, 2, 3]li.append('a')li.append('b')print(li) #结果为:[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b']li.append([4, 5, 6]) #添加一个列表[4,5,6]print(li) #结果为:[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', [4, 5, 6]]li = [1, 2, 3]li.extend([4, 5, 6]) #往列表中添加数字4,5,6print(li) #结果为:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]print('')# 删除元素li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]li.pop() #采用pop的方法,按照栈的方式弹出,结果为:[1, 2, 3, 4]print(li)del(li[0]) #删掉第一个数据,现在li的数据排列为[2,3,4,5]del(li[1]) #删掉[2,3,4,5]中的第二个数据print(li) #结果为:[2, 4]print('')# 元素是否存在li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]print(1 in li) #结果为Trueprint(6 in li) #结果为Falseprint('')# 列表是否为空li = []if not li: print('Empty')else: print('Not empty')print('')# 字符串ss = 'abcdefg'li = list(ss)li[4] = 'E' #取第五个字符并置为'E'li[5] = 'F' #取第六个字符并置为'F'print(li) #结果为:['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'E', 'F', 'g']ss = ''.join(li) #去掉引号print(ss) #结果为:abcdEFgprint('')# 遍历li = [1, 2, 3]for i in li: print(i)for i in range(len(li)): print(li[i])
71abc{1: 'one'}4.5[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b'][1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', [4, 5, 6]][1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6][1, 2, 3, 4][2, 4]TrueFalseEmpty['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'E', 'F', 'g']abcdEFg123123
元组
另一种有序列表叫元组:tuple。tuple和list非常类似,但是tuple一旦初始化就不能修改。
其中需要注意的是:tuple所谓的“不变”是说,tuple的每个元素,指向永远不变。
#创建 tuplenumber_tuple = (1,3,5,7,9) #数字print("number_tuple: " + str(number_tuple))print(number_tuple[4])string_tuple = ("adc","sdf","python") #字符串print("string_tuple: " + str(string_tuple))print(string_tuple[1])mixed_tuple = ("python",1,5) #数字+字符串print("mixed_tuple: " + str(mixed_tuple))print(mixed_tuple[0])#访问tuple元素a = number_tuple[2]b = string_tuple[1]c = mixed_tuple [0]print("a:{0}\nb:{1}\nc:{2}\n".format(a,b,c))#tuple的截取abcd_tuple = ('a','b','c','d')print(abcd_tuple[1])print(abcd_tuple[-2])print(abcd_tuple[1:])#tuple 中嵌入list mix_tuple = (1,2,['a','b'])print("mix_tuple: " + str(mix_tuple))mix_tuple[2][0] = 'c'mix_tuple[2][1] = 'd'print("mix_tuple: " + str(mix_tuple))#list 中嵌入tuplemix_list = [1,2,('a','b')]print("mix_list: " + str(mix_list))mix_list[2] = ('c','d')print("mix_list: " + str(mix_list))# 遍历tup = (1,2,3)for i in tup: print(i)for i in range(len(tup)): print(tup[i])
number_tuple: (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)9string_tuple: ('adc', 'sdf', 'python')sdfmixed_tuple: ('python', 1, 5)pythona:5b:sdfc:pythonbc('b', 'c', 'd')mix_tuple: (1, 2, ['a', 'b'])mix_tuple: (1, 2, ['c', 'd'])mix_list: [1, 2, ('a', 'b')]mix_list: [1, 2, ('c', 'd')]123123
字典
字典由keys(键)和values(值)组成。字典的每个键值(key=>value)对,用冒号(:)分割,每个对之间用逗号(,)分割,整个字典包括在花括号({})中.键必须是唯一的,但值则不必。值可以取任何数据类型,但键必须是不可变的,如字符串,数字或元组。
# 初始化d = {'a':1, 2:'b', 'c':3, 4:'d'}print(d) #结果为:{'a': 1, 2: 'b', 'c': 3, 4: 'd'}print(d.keys()) #结果为:dict_keys(['a', 2, 'c', 4])print(d.values()) #结果为:dict_values([1, 'b', 3, 'd'])print('')# 获取长度print(len(d)) #结果为:4print('')# 根据key读写d['a'] = 100d[4] = 'dd'print(d) #结果为:{'a': 100, 2: 'b', 'c': 3, 4: 'dd'}print('')# 添加元素d['e'] = 5d[6] = 'f'print(d) #结果为:{'a': 100, 2: 'b', 'c': 3, 4: 'dd', 'e': 5, 6: 'f'}print('')# 删除元素d = {'a':1, 2:'b', 'c':3, 4:'d'}del(d['a'])del(d[2])print(d) #结果为:{'c': 3, 4: 'd'}print('')# 判断key是否存在d = {'a':1, 2:'b', 'c':3, 4:'d'}if 'a' in d: print('a in d')if 2 in d: print('2 in d')if not ('x' in d): print('x not in d')print('')# 判断字典是否为空d = {}if not d: print('d is empty')print('')# 遍历d = {'a':1, 2:'b', 'c':3, 4:'d'}for k in d.keys(): print(str(k) + ': ' + str(d[k]))for k, v in d.items(): print(str(k) + ': ' + str(v))
{'a': 1, 2: 'b', 'c': 3, 4: 'd'}dict_keys(['a', 2, 'c', 4])dict_values([1, 'b', 3, 'd'])4{'a': 100, 2: 'b', 'c': 3, 4: 'dd'}{'a': 100, 2: 'b', 'c': 3, 4: 'dd', 'e': 5, 6: 'f'}{'c': 3, 4: 'd'}a in d2 in dx not in dd is emptya: 12: bc: 34: da: 12: bc: 34: d
集合(set)
set是基本数据类型的一种集合类型,它有可变集合(set())和不可变集合(frozenset)两种。创建集合set、集合set添加、集合删除、交集、并集、差集的操作都是非常实用的方法。
# 初始化s_a = set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])s_b = set([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5])print(s_a) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}print(s_b) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}print('')# 获取长度print(len(s_a)) # 结果为:5print(len(s_b)) # 结果为:5print('')# 添加元素s_a.add(6)s_a.add(6)s_a.update([5, 6, 7, 8, 9])print(s_a) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}print('')# 删除元素s_a.remove(8)s_a.remove(9)print(s_a) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}print('')# 判断元素是否存在print(1 in s_a) # 结果为:Trueprint(10 in s_a) # 结果为:Falseprint('')# 判断集合是否为空s_a = set([])if not s_a: print('set is empty')else: print('set is not empty')print('')# 遍历s_a = set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])for i in s_a: print(i)print('')# 集合操作s_a = set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])s_b = set([4, 5, 6, 7, 8])# 并集print(s_a | s_b) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}print(s_a.union(s_b)) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}# 交集print(s_a & s_b) # 结果为:{4, 5}print(s_a.intersection(s_b)) # 结果为:{4, 5}# 差集 s_a - (s_a and s_b)print(s_a - s_b) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3}print(s_a.difference(s_b)) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3}# 对称差print(s_a ^ s_b) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}print((s_a | s_b) - (s_a & s_b)) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}print(s_a.symmetric_difference(s_b)) # 结果为:{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}55{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}TrueFalseset is empty12345{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}{4, 5}{4, 5}{1, 2, 3}{1, 2, 3}{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}
参考
廖雪峰Python教程(https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000)
Python 运算符 (http://www.runoob.com/python/python-operators.html#ysf6)

-长按关注-
本文分享自微信公众号 - AI异构(gh_ed66a0ffe20a)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。













