1.Integer与Long对象初始化
Integer a = 100,b = 100; Integer a1 = 128,b1 = 128; System.out.println(a==b); System.out.println(a1==b1); Long m = 100L,n = 100L; Long m1 = 128L,n1 = 128L; System.out.println(m==n); System.out.println(m1==n1); 执行结果: true false true false
解释说明:
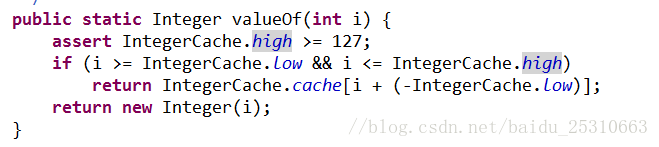
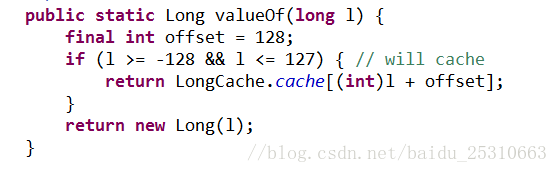
装箱的本质是什么呢?当我们给一个Integer(Long)对象赋一个int(long)值的时候,会调用Integer类的静态方法valueOf,如果整型字面量的值在-128到127之间,那么不会new新的Integer对象,而是直接引用常量池中的Integer对象
参考源码:
2.自动类型转换
低 ------------------------------------> 高
byte,short,char—> int —> long—> float —> double
long l = 128L;
float f = l; //long可以自动转成float
应用:switch(expr),expr可以是byte,short,char,int,还可以是枚举