前言
1. 什么是regulator?
regulator翻译为"调节器",分为voltage regulator(电压调节器)和current(电流调节器)。一般电源管理芯片(Power Management IC)中会包含一个甚至多个regulator。
2. regulator有什么作用?
通常的作用是给电子设备供电。大多数regulator可以启用(enable)和禁用(disable)其输出,同时也可以控制其输出电压(voltage)和电流(current)。
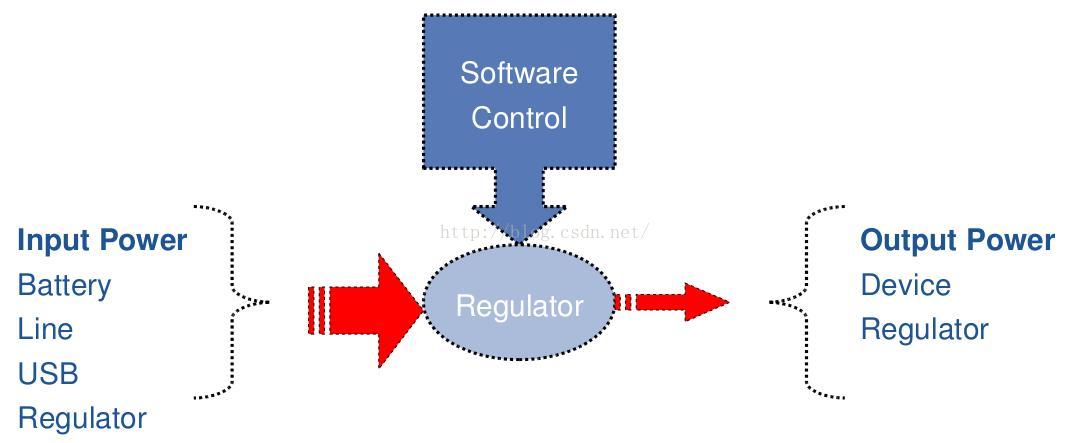
从上图可以看出,input power会经过 regulator 转化为output power,regulator会做如下的约束:
- Voltage control: 输入5V输出1.8V
- Current limiting: 电流的输出最大为20MA
- Power switch: 可以控制电压enable/disable
问题
1. 如果一个系统只有一个regulator,而且只对一个设备控制的话,完全没必要使用linux regulator framework机制。但是如果一个系统几个甚至十几个regulator,每个regulator之间还存在级连关系,这时候就需要Linux regulator framework。
2. 如果一个regulator控制多个设备,而每个设备的电压或电流需求方式不同,linux regulator framework会怎么管理这些设备?
3. 有些设备只需要enable/disable电源即可,而有些设备在运行的过程中需要动态的改变voltage或者current,Linux regulator Framework会如何处理这些问题?
4. regulator的错误配置可能也会对硬件有非常严重的后果,所以需要小心设计regulaor,同时也要规范的使用regulator。
Linux Regulator Framework
1. Linux Regulator Framework设计出主要是提供一个标准的内核接口来控制电压和电流调节器。目的是允许系统动态控制regulator power输出以节省能源延长电池寿命。这适用于voltage regulator和current regulator(其中电压和电流都是可控的)。
2. Linux Regulator Framework分为四个部分,分别是machine,regulator,consumer,sys-class-regulator。
machine
machine可以理解为regulator在板级的硬件配置,使用regulator_init_data结构体代表regulator板级的配置。

struct regulator_init_data {
const char *supply_regulator; /* or NULL for system supply */
struct regulation_constraints constraints;
int num_consumer_supplies;
struct regulator_consumer_supply *consumer_supplies;
/* optional regulator machine specific init */
int (*regulator_init)(void *driver_data);
void *driver_data; /* core does not touch this */
};

.supply_regulator: regulator的parent。用于级联regulator使用。
.constraints: 此regulator的约束,比如输出电压范围,输出电流范围等。
.num_consumer_supplies: 此regulator提供的consumer的个数,也就是控制外设的个数。
.consumer_supplies: 使用此结构确定regulator和consumer之间的联系。
.regulator_init: regulator注册时候的回调函数。
.driver_data: regulator_init回调函数的参数。
而regulator板级的配置,也可以称为约束,定义在regulation_constraints结构中。

struct regulation_constraints {
const char *name;
/* voltage output range (inclusive) - for voltage control */
int min_uV;
int max_uV;
int uV_offset;
/* current output range (inclusive) - for current control */
int min_uA;
int max_uA;
/* valid regulator operating modes for this machine */
unsigned int valid_modes_mask;
/* valid operations for regulator on this machine */
unsigned int valid_ops_mask;
/* regulator input voltage - only if supply is another regulator */
int input_uV;
/* regulator suspend states for global PMIC STANDBY/HIBERNATE */
struct regulator_state state_disk;
struct regulator_state state_mem;
struct regulator_state state_standby;
suspend_state_t initial_state; /* suspend state to set at init */
/* mode to set on startup */
unsigned int initial_mode;
unsigned int ramp_delay;
unsigned int enable_time;
/* constraint flags */
unsigned always_on:1; /* regulator never off when system is on */
unsigned boot_on:1; /* bootloader/firmware enabled regulator */
unsigned apply_uV:1; /* apply uV constraint if min == max */
unsigned ramp_disable:1; /* disable ramp delay */
};

.name: 描述该约束的名字。
.min_uV/max_uV: 最小/最大的输出电压。
.uV_offset: consumer看到的电源和实际电源之间的偏移值,用于电源补偿。
.min_uA/max_uA: 最小/最大的输出电流。
.valid_modes_mask: 该regulator支持的操作模式。
#define REGULATOR_MODE_FAST 0x1 //快速改变模式
#define REGULATOR_MODE_NORMAL 0x2 //正常模式,大多数驱动都使用这种模式
#define REGULATOR_MODE_IDLE 0x4 //设备在idle状态,regulator给设备提供服务
#define REGULATOR_MODE_STANDBY 0x8 //设备在standby状态,regulator给设备提供服务
.valid_ops_mask: 该regulator支持的操作。
#define REGULATOR_CHANGE_VOLTAGE 0x1 //该regulator可以改变电压
#define REGULATOR_CHANGE_CURRENT 0x2 //该regulator可以改变电流
#define REGULATOR_CHANGE_MODE 0x4 //该regulator可以改变mode
#define REGULATOR_CHANGE_STATUS 0x8 //该regulator可以改变状态,也就是enable/disable power
#define REGULATOR_CHANGE_DRMS 0x10 //该regulator可以动态该变mode
#define REGULATOR_CHANGE_BYPASS 0x20 //该regulator支持bypass mode
.input_uV: 表示该regulator的input是另一个regulator。
.state_disk/state_mem/state_standby: 代表该regulator的各种suspend状态。
.always_on: 是否在系统启动后一直使能。
.boot_on: 是否在boot阶段使能。
.apply_uV: 当min_uV=max_uV的时候时使用。
.ramp_delay: 改变电压到电源稳定后时间。因为硬件原因,改变电源后不能立刻就成功,其中需要有一定的延迟。
.enable_time: regulator的使能时间。
....未完
参考地址:https://blog.csdn.net/longwang155069/article/details/53129378













