
上篇内容回顾可以参考;Mybatis深入源码分析之SQLSession一级缓存原理分析
这里再概括下上篇源码分析内容:
一:Mybatis一级缓存
mybatis的一级缓存是SqlSession缓存,在操作数据库的时候需要先创建SQL会话对象,在对象中有个HashMap用于存储缓存数据,此HashMap是当前对象私有的,其它SqlSession会话对象无法访问。
具体流程:
- 第一次执行select完毕会将查到的数据写入SqlSession内的HashMap中缓存起来
- 第二次执行select会从缓存中查数据,如果select相同且传参数一样,那么就能从缓存中返回数据,不用去查询数据库了,从而提高程序执行效率。
注意事项:
- 如果SqlSession执行了DML操作(insert、update、delete),并commit了,那么mybatis就会清空当前SqlSession缓存中所有的缓存数据,这样可以保证缓存中的缓存数据永远和数据库中的一致,避免出现脏读。
- 当一个SqlSession结束后,那么它里面的一级缓存也就不存在了,Mybatis默认是开启一级缓存,不需要配置。
- mybatis缓存是基于【namespzce:sql语句:参数】来进行缓存的,意思就是:sqlSession的HashMap存储缓存数据时,是使用【namespace:sql:参数】作为key
- 注意服务器集群的时候,每个sqlSession都有自己独立的缓存且互不共享,所以在服务器集群的时候容易产生数据冲突问题。
如何禁止一级缓存
- 方案1 在sql语句上 随机生成 不同的参数 存在缺点:map集合可能爆 内存溢出的问题
- 方案2 开启二级缓存
- 方案3 使用sqlSession强制清除缓存
- 方案4 创建新的sqlSession连接。
二:Mybatis二级缓存SessionFactory
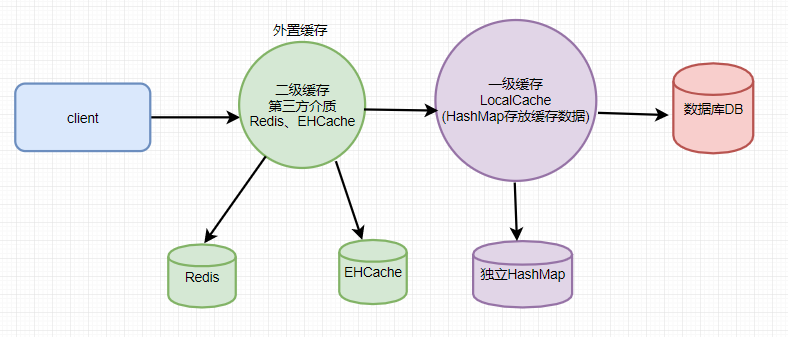
MyBatis使用Redis作为二级缓存
二级缓存默认是没有开启的,需要在setting全局参数中配置开启二级缓存,还需要对实体类实现序列化接口
开启二级缓存
在mapper配置文件中加入下面这段配置:表示缓存淘汰策略,和指定缓存类型
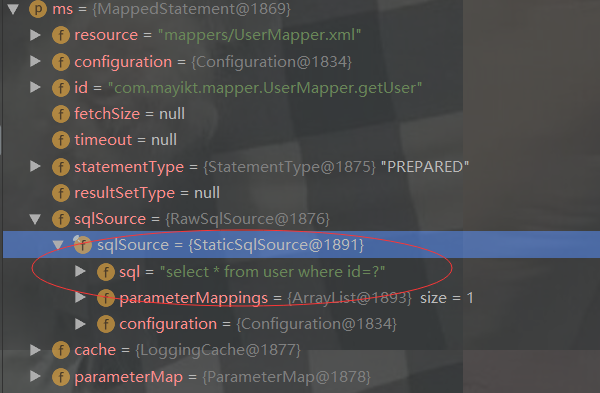
在源码中,是如何解析配置的缓存呢?下面我们找到这段源码:
private void configurationElement(XNode context) { try { String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace"); if (namespace != null && !namespace.equals("")) { this.builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace); this.cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref")); this.cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache")); //解析mapper配置文件中配置的缓存结点cache this.parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap")); this.resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap")); this.sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql")); this.buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete")); } else { throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty"); } } catch (Exception var3) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + var3, var3); } }
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL"); Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = this.typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type); String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU"); //淘汰策略 Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = this.typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction); Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval"); Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size"); boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false); boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false); Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); this.builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);//使用Java的反射机制初始化 } }
this.builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass, Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass, Long flushInterval, Integer size, boolean readWrite, boolean blocking, Properties props) { Cache cache = (new CacheBuilder(this.currentNamespace)).implementation((Class)this.valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class)).addDecorator((Class)this.valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class)).clearInterval(flushInterval).size(size).readWrite(readWrite).blocking(blocking).properties(props).build(); this.configuration.addCache(cache); //将cache配置添加到configura中 this.currentCache = cache; return cache; }
测试代码
// 4.获取Session SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 5.操作Mapper接口 UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println("第一次调用...."); UserEntity o = sqlSession.selectOne("com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser", 1); //断点① System.out.println(o.getName());
System.out.println("第二次调用...."); UserEntity o2 = sqlSession2.selectOne("com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser", 1); //断点② System.out.println(o2.getName());

public
public
public
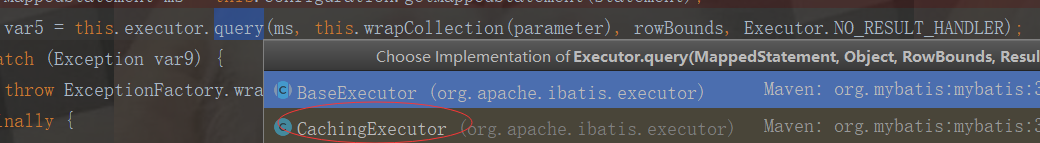
因为我们配置了外置缓存Redis缓存所以先走CacheExecutor执行器(代表二级缓存)
public
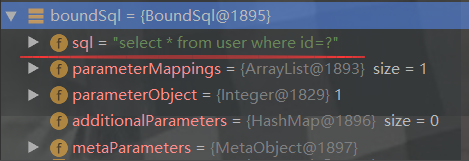
CacheKey key = this.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);//创建缓存key
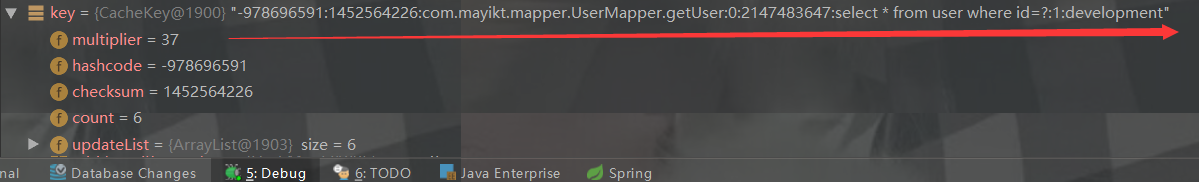
执行query方法:
return this.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
public
cache不为空:
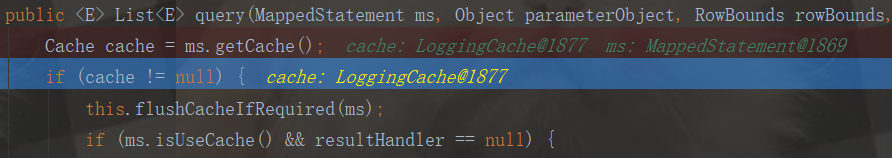
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) { Cache cache = ms.getCache(); if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { this.tcm.clear(cache); //缓存不为空,清空缓存 } }
list = this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
二级缓存没有数据,就执行BaseExecutor查询一级缓存数据
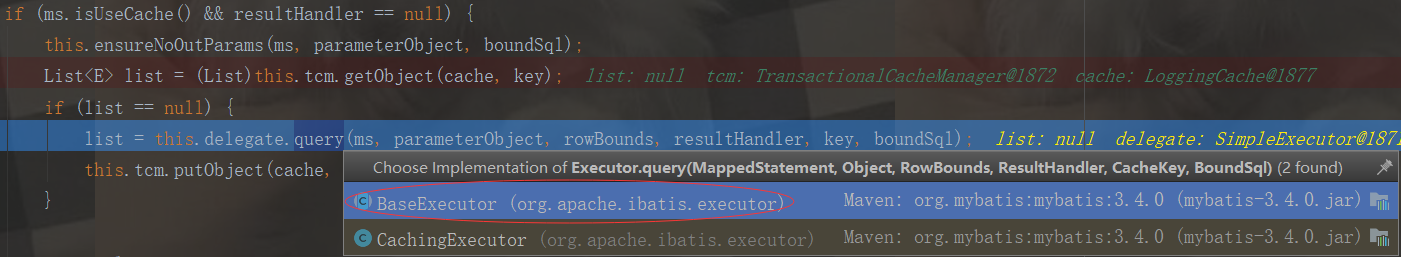
public
while(i$.hasNext()) {
BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad deferredLoad = (BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad)i$.next();
deferredLoad.load();
}
this.deferredLoads.clear();
if (this.configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
this.clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
}
list = this.queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);//查询数据库
private
this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);再把一级缓存数据放入二级缓存中
发现第二次查询的时候:二级缓存还是没有数据,这是为什么?
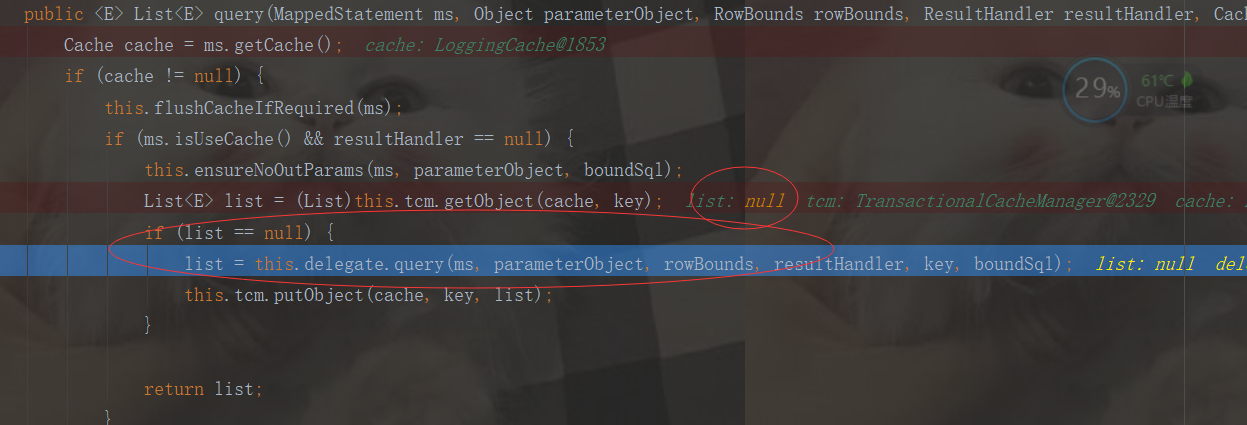
我们地清除地知道,每次调用openSession地时候,开启了二级缓存,每次都会new CacheExecutor执行器(二级缓存)
Executor executor = this.configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? this.defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Object executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (this.cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor((Executor)executor); //每次开启了二级缓存,都会器new 一个CachingExecutor二级缓存执行器 } Executor executor = (Executor)this.interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
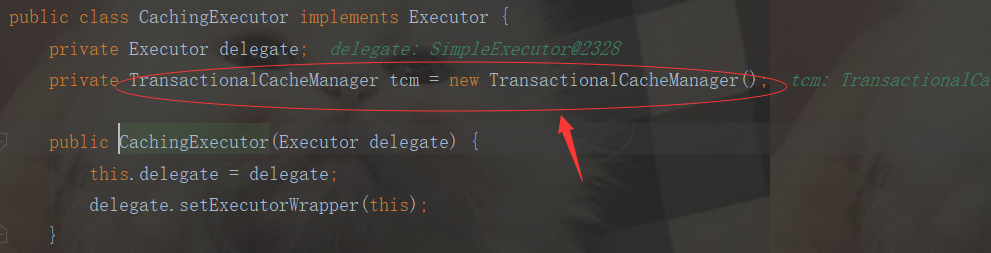
我们可以知道了:每次new一个CachingExecutor二级缓存执行器,都会new TransactionalCacheManager()
所以:TransactionalCacheManager管理我们地TransactionalCache和SQLSession绑定
我们执行下代码:发现执行了两次SQL查询
第一次调用....
11:08:35.474 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=null
Cache Hit Ratio [com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.0
Opening JDBC Connection
Created connection 294184992.
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1188e820]
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, name, update_time
<== Row: 1, xuyu, 2019-03-13 14:27:49.0
<== Total: 1
xuyu
第二次调用....
11:08:35.704 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=null
Cache Hit Ratio [com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.0
Opening JDBC Connection
Created connection 1268959798.
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@4ba2ca36]
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, name, update_time
<== Row: 1, xuyu, 2019-03-13 14:27:49.0
<== Total: 1
xuyu
假如我们在查询中间添加:
sqlSession.close();
结果如下:我们发现,第一次查询了数据库,第二次直接走缓存了,没有再去查询数据库,缓存生效了,这是为什么呢?下面我们开始源码分析
第一次调用....
11:10:06.121 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=null
Cache Hit Ratio [com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.0
Opening JDBC Connection
Created connection 294184992.
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1188e820]
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, name, update_time
<== Row: 1, xuyu, 2019-03-13 14:27:49.0
<== Total: 1
xuyu
11:10:06.350 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>putObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=[com.mayikt.entity.UserEntity@1dd02175]
Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1188e820]
Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1188e820]
Returned connection 294184992 to pool.
第二次调用....
11:10:06.404 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=[com.mayikt.entity.UserEntity@2357d90a]
Cache Hit Ratio [com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.5
xuyu
重点来看下这段代码:
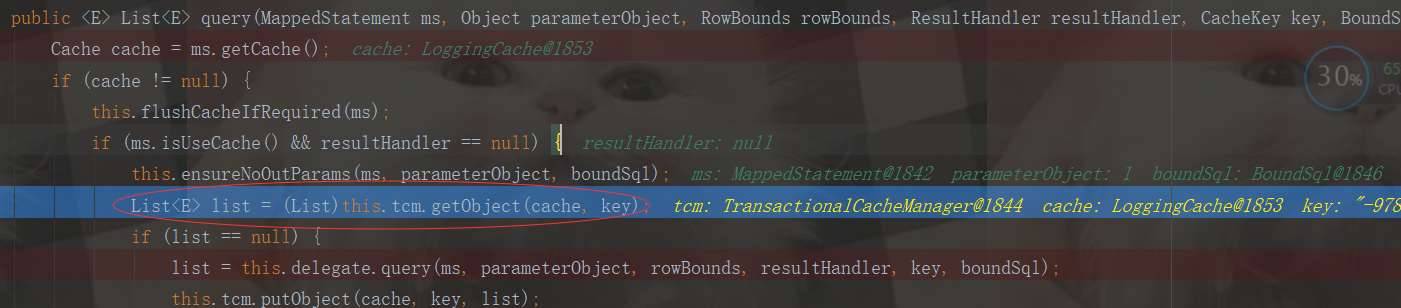
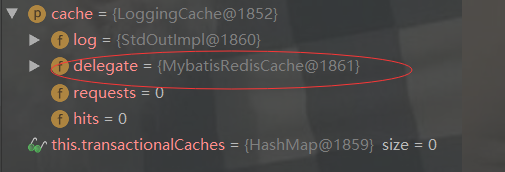
先看下tcm指什么?指的是TransactionalCacheManager,作为二级缓存查询
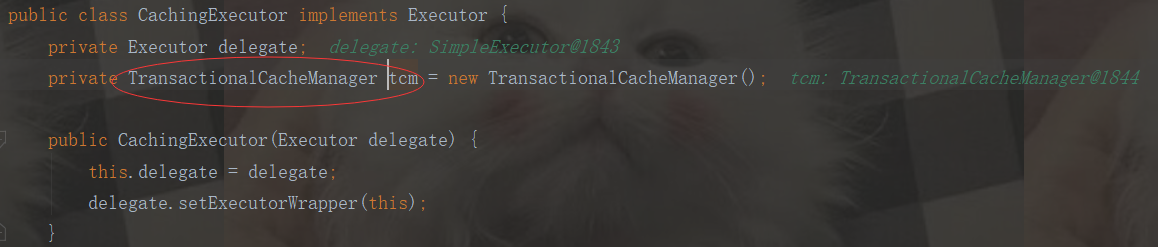
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) { return this.getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key); }
public Object getObject(Object key) { Object object = this.delegate.getObject(key); if (object == null) { this.entriesMissedInCache.add(key); } return this.clearOnCommit ? null : object; }
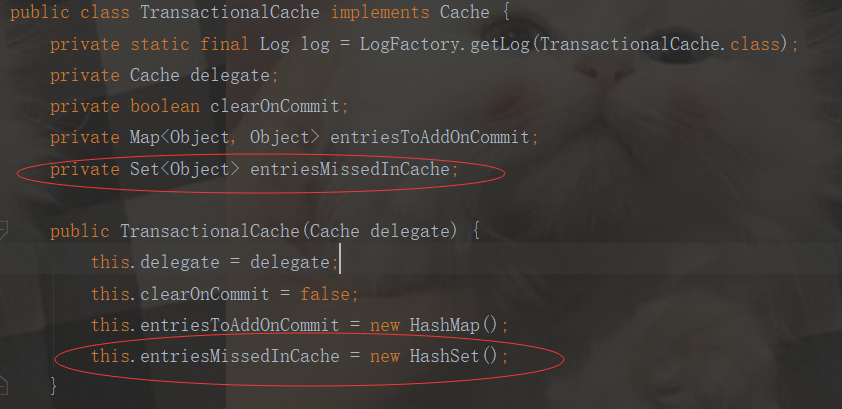
private Set
下面我们来debug源码分析下:
List
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) { return this.getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key); }
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) { TransactionalCache txCache = (TransactionalCache)this.transactionalCaches.get(cache); // if (txCache == null) { txCache = new TransactionalCache(cache); //二级缓存没有数据,就创建一个新的TransactionalCache this.transactionalCaches.put(cache, txCache); //把缓存数据添加到TransactionalCache里 } return txCache; }
//transactionalCaches为map集合
private Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap();
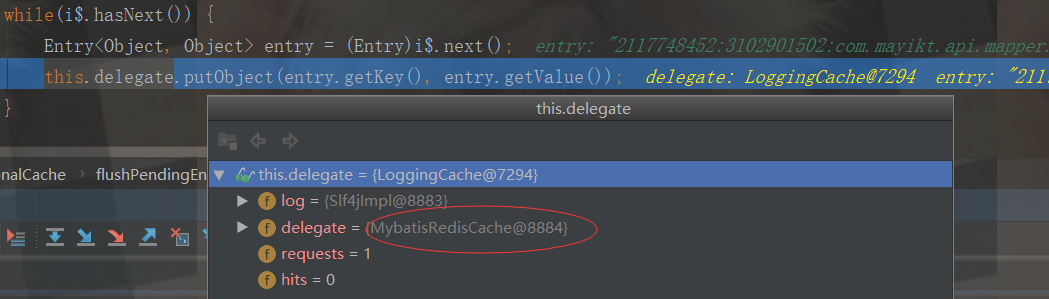
这个cache指的是我们自定义Redis二级缓存
最后回到getObject方法:
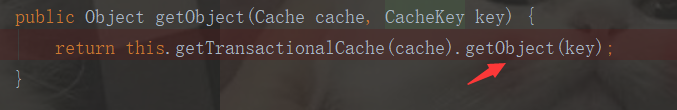
public Object getObject(Object key) { Object object = this.delegate.getObject(key); if (object == null) { this.entriesMissedInCache.add(key); } return this.clearOnCommit ? null : object; }
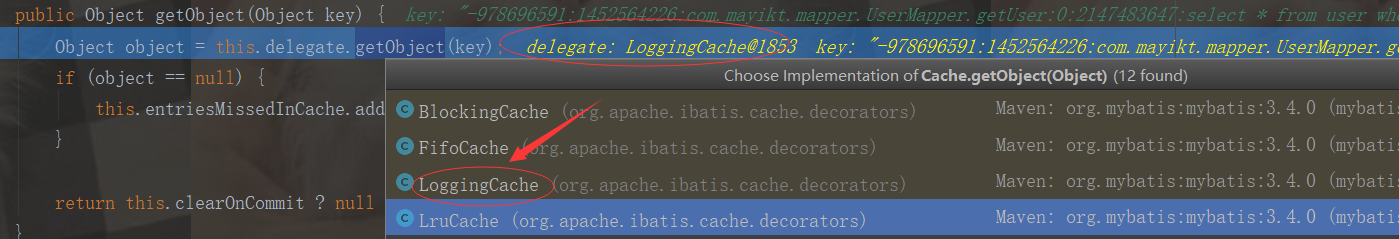
public Object getObject(Object key) { ++this.requests; //记录每次查询次数 Object value = this.delegate.getObject(key); if (value != null) { ++this.hits; } if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) { this.log.debug("Cache Hit Ratio [" + this.getId() + "]: " + this.getHitRatio()); } return value; }
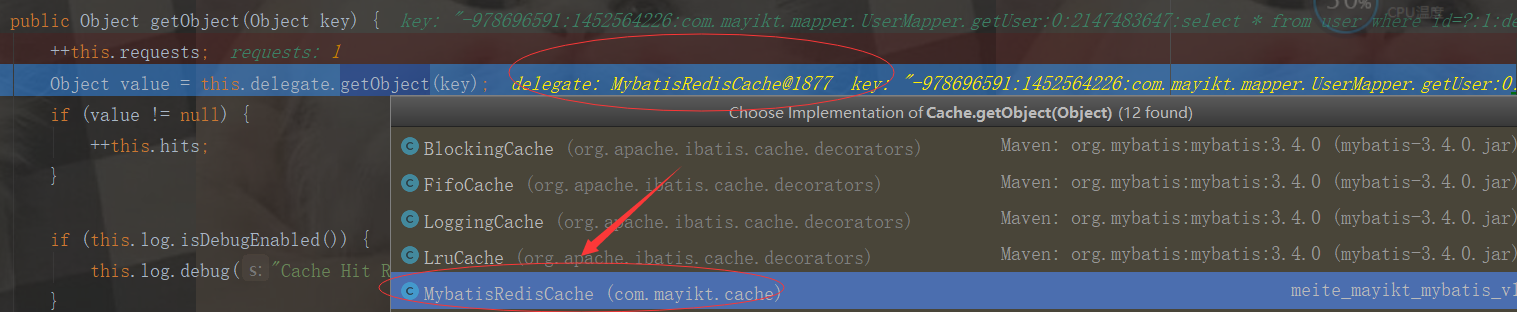
由上图可知,开始调用我们自定义的MybatisRedisCache外置缓存方法
public Object getObject(Object key) { Object value = SerializeUtil.unserialize(redisClient.get(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()))); logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:" + key + "=" + value); return value; }
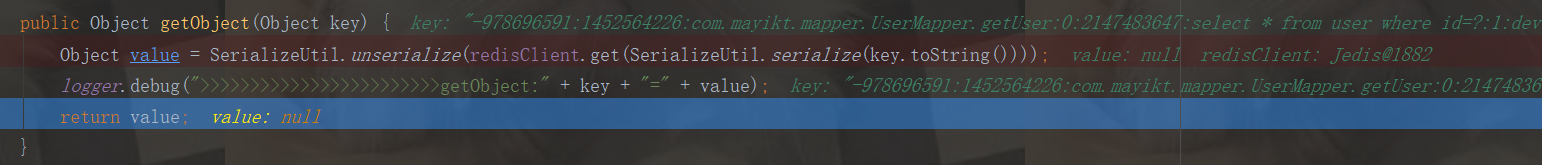
我们知道了,我们第一次查询,二级缓存是没有数据的,最后进入entriesMissedInCache去添加我们的缓存数据
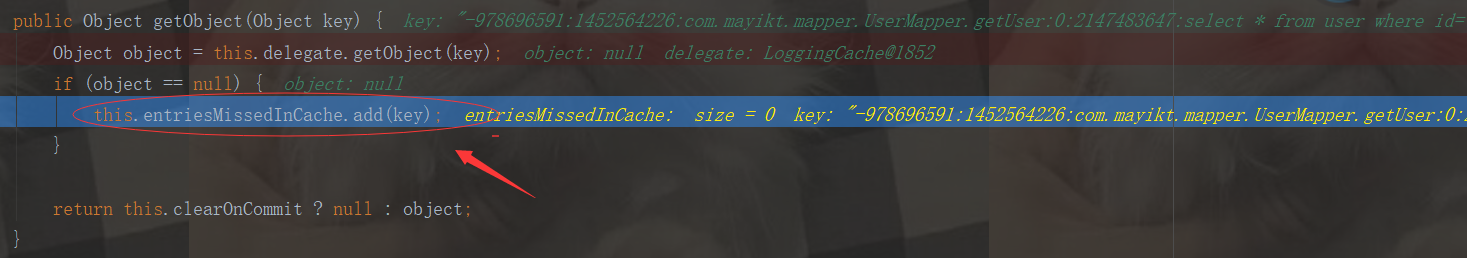
最后返回到
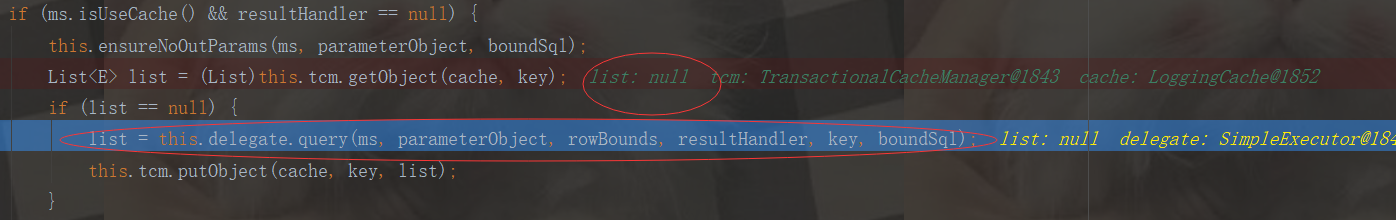
再去一级缓存查询数据
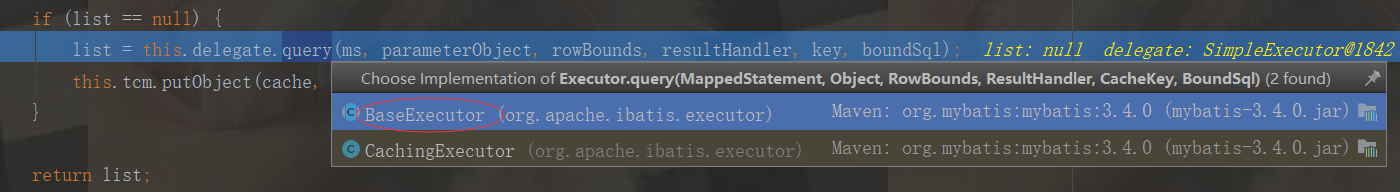
一级缓存没有数据,就查询数据库,查询到数据,将结果返回给一级缓存,一级缓存再把数据缓存给二级缓存
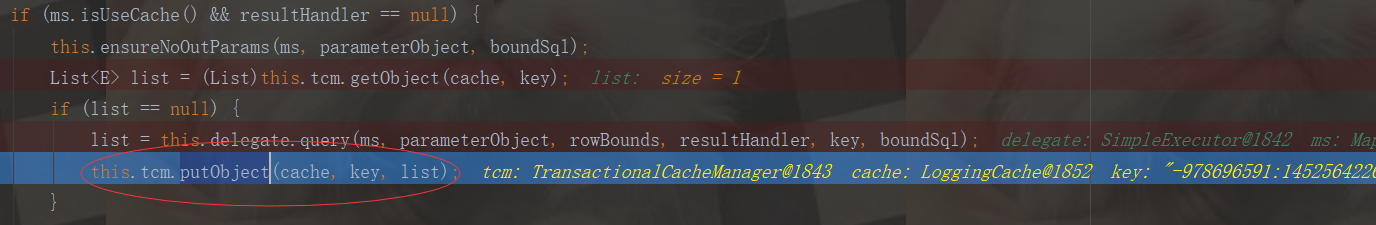
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) { this.getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value); }
就回去调用getTransactionalCache方法创建事务的缓存
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) { TransactionalCache txCache = (TransactionalCache)this.transactionalCaches.get(cache); if (txCache == null) { txCache = new TransactionalCache(cache); this.transactionalCaches.put(cache, txCache); }
return txCache;
}

调用
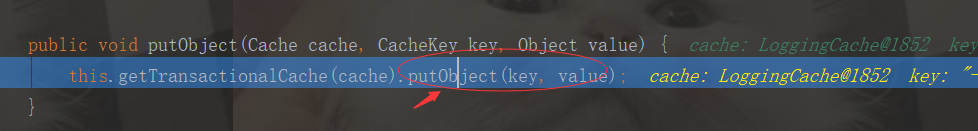
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) { this.entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object); }
private Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
我们知道了entriesToAddOnCommit集合为临时存储的事务缓存(一级缓存数据添加到二级缓存先添加到entriesToAddOnCommit集合临时缓存起来)
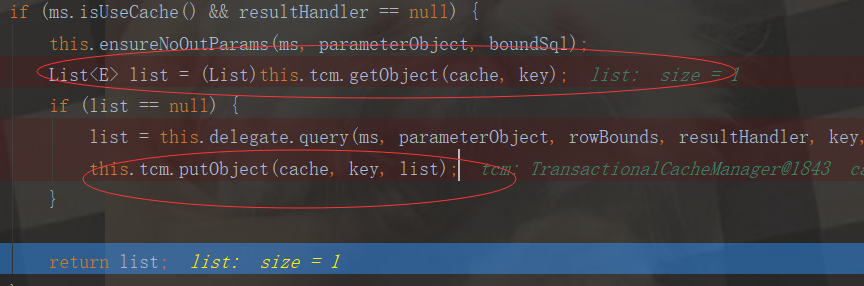
List
this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);//只是将数据存放到getTransactionalCache的entriesToAddOnCommit的map集合中
那什么时候去取出getTransactionalCache中的缓存数据呢?下面我们代码进入sqlSession.close()方法
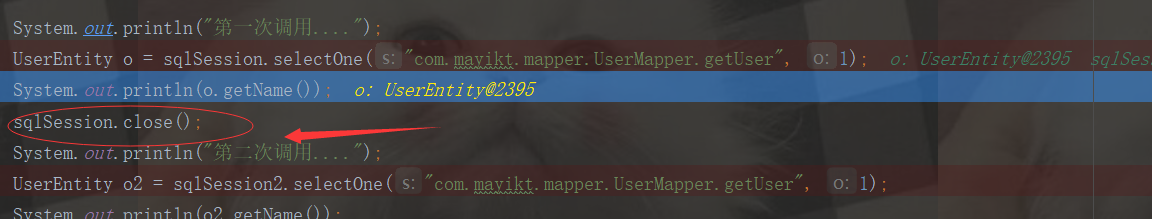
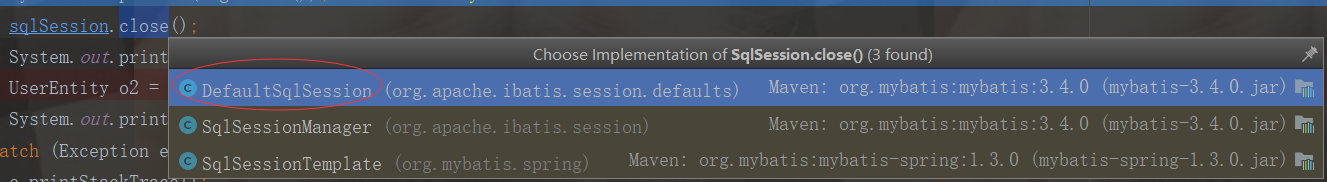
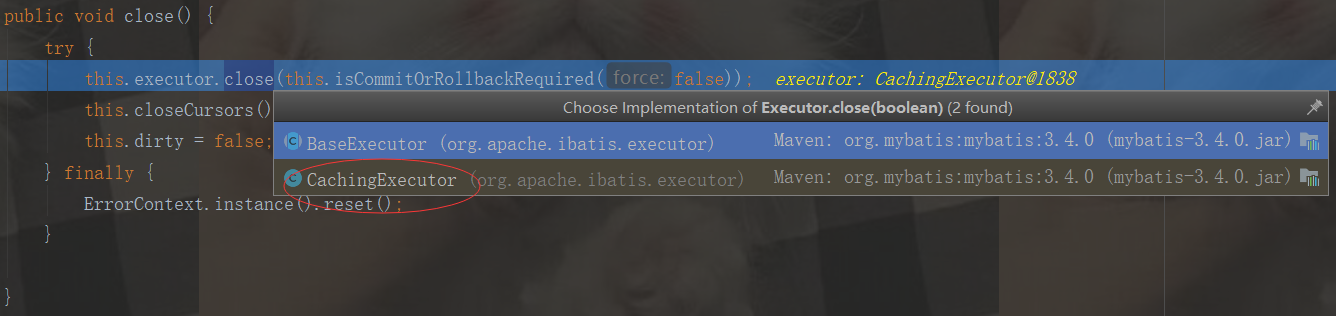
public void close(boolean forceRollback) { try { if (forceRollback) { //是否需要强制回滚,我们是不需要的 this.tcm.rollback(); } else { this.tcm.commit(); //这块重点了,表示要提交数据到redis了 } } finally { this.delegate.close(forceRollback); }
}
public void commit() { Iterator i$ = this.transactionalCaches.values().iterator(); while(i$.hasNext()) { //循环迭代TransactionalCache TransactionalCache txCache = (TransactionalCache)i$.next(); txCache.commit(); } }
public void commit() { if (this.clearOnCommit) { this.delegate.clear(); }
this.flushPendingEntries();
this.reset();
}
private void flushPendingEntries() { Iterator i$ = this.entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Entry<Object, Object> entry = (Entry)i$.next();
this.delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); //遍历entriesToAddOnCommit,把数据刷新到redis中
}
i$ = this.entriesMissedInCache.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Object entry = i$.next();
if (!this.entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
this.delegate.putObject(entry, (Object)null);
}
}
}
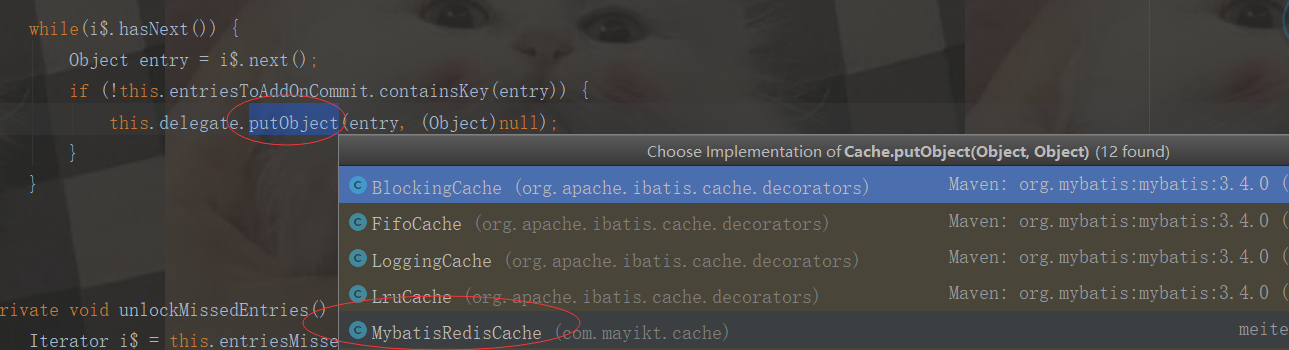
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>putObject:" + key + "=" + value); redisClient.set(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()), SerializeUtil.serialize(value)); }
我们可知:最后将临时缓存数据提交到了redis缓存中
再次查询
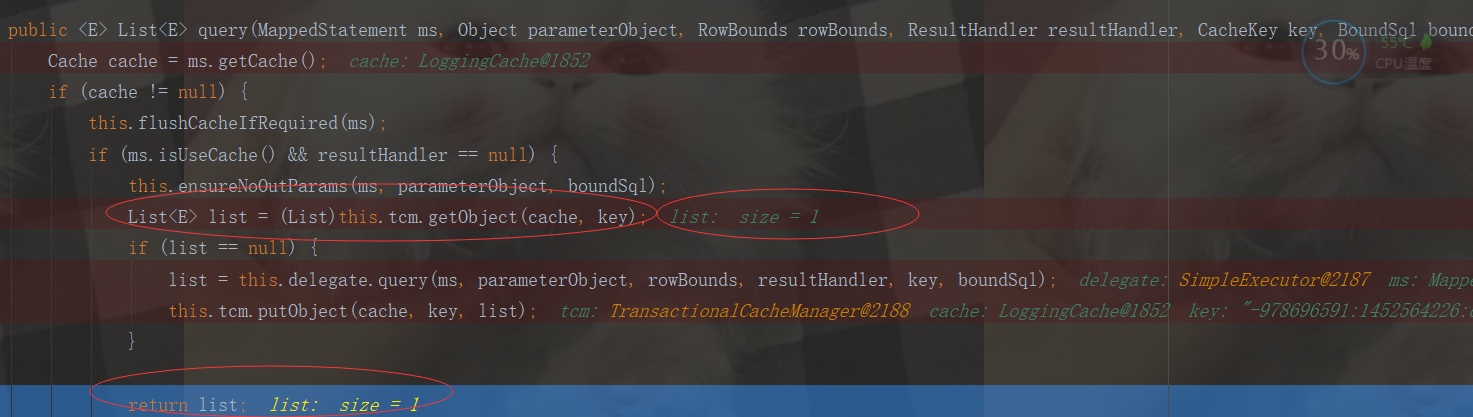
就直接从redis缓存中取出数据了。
结果:
第一次调用....
12:57:19.090 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=null
Cache Hit Ratio [com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.0
Opening JDBC Connection
Created connection 294184992.
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@1188e820]
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, name, update_time
<== Row: 1, xuyu, 2019-03-13 14:27:49.0
<== Total: 1
xuyu
12:57:19.318 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>putObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=[com.mayikt.entity.UserEntity@1dd02175]
第二次调用....
12:57:19.360 [main] DEBUG com.mayikt.cache.MybatisRedisCache - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:-978696591:1452564226:com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper.getUser:0:2147483647:select * from user where id=?:1:development=[com.mayikt.entity.UserEntity@2357d90a]
Cache Hit Ratio [com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.5
xuyu
我们思考下,我们要使得缓存生效,每次都要调用close()方法,这样不是很麻烦?
如果使用相同的sqlsession缓存,那么也是查询一次,但是使用的缓存只是一级缓存,那么我们有没有办法调用同一个sqlsession,也使得二级缓存生效。
sqlSession.close(); //sqlSession.commit();
我们先看下二级缓存回收策略
- LRU:最近最少使用的策略,移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
- FIFO:先进先出策略,按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
- SOFT:软引用策略,移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
- WEAK:弱引用策略,更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
软引用与弱引用的区别:
- 软引用: 软引用是用来描述一些有用但并不是必需的对象, 对于软引用关联着的对象,只有在内存不足的时候JVM才会回收该对象
- 弱引用: 弱引用也是用来描述非必需对象的,当JVM进行垃圾回收时,无论内存是否充足,都会回收被弱引用关联的对象
回到我们实际springboot项目中 整合redis缓存
mapper层:
@CacheNamespace(implementation = MybatisRedisCache.class) public interface OrderMapper { @Insert("insert order_info values (null,#{orderName},#{orderDes})") public int addOrder(OrderEntity OrderEntity);
@Select("SELECT * FROM order_info;")
public List
redis
@Component public class RedisToken { @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; /** * 获取Token */ public String getToken() { //1. 使用uuid生成Token String token = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", ""); //2. 将Token存放到Redis中 setString(token, token, 7200l); return token; } public Boolean findByToken(String token) { if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { return false; } String redisToken = getString(token); if(StringUtils.isEmpty(redisToken)){ return false; } delKey(redisToken); return true; } private void setString(String key, Object data, Long timeout) { if (data instanceof String) { String value = (String) data; stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value); } if (timeout != null) { stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } private String getString(String key) { return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); } private void delKey(String key) { stringRedisTemplate.delete(key); } }
MybatisRedisCache
** * mybatis二级缓存整合Redis */ public class MybatisRedisCache implements Cache { private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisRedisCache.class); private Jedis redisClient = createReids(); private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); private String id; public MybatisRedisCache(final String id) { if (id == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cache instances require an ID"); } logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>MybatisRedisCache:id=" + id); this.id = id; } public String getId() { return this.id; } public int getSize() { return Integer.valueOf(redisClient.dbSize().toString()); } public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>putObject:" + key + "=" + value); redisClient.set(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()), SerializeUtil.serialize(value)); } public Object getObject(Object key) { Object value = SerializeUtil.unserialize(redisClient.get(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()))); logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>getObject:" + key + "=" + value); return value; } public Object removeObject(Object key) { return redisClient.expire(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()), 0); } public void clear() { redisClient.flushDB(); } public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() { return readWriteLock; } protected static Jedis createReids() { JedisPool pool = new JedisPool("127.0.0.1", 6379); return pool.getResource(); } }
启动类
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.mayikt.api.mapper") @EnableCaching public class OrderApp {
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderApp.class);
}
}
访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/getOrderList
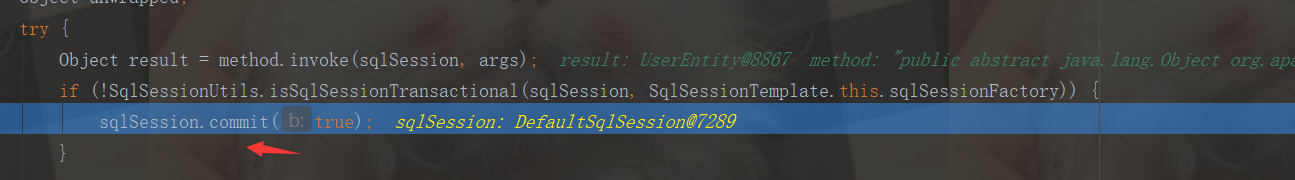
最终被SqlSessionInterceptor拦截器拦截了, sqlSession.commit(true);也被调用了
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler { private SqlSessionInterceptor() { } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
Object unwrapped;
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!SqlSessionUtils.isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
unwrapped = result;
} catch (Throwable var11) {
unwrapped = ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var11);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
SqlSessionUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException)unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw (Throwable)unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
SqlSessionUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
return unwrapped;
}
}
提交数据
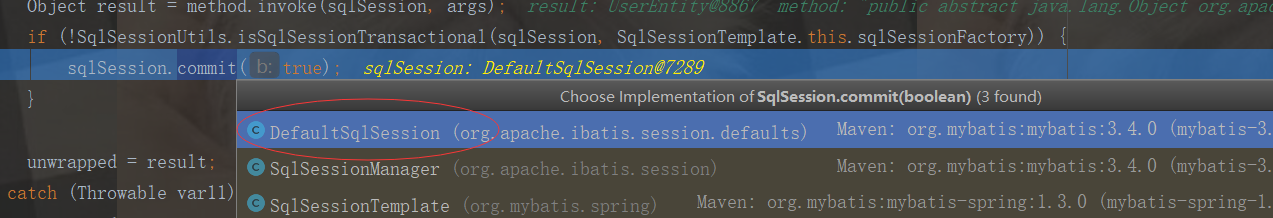
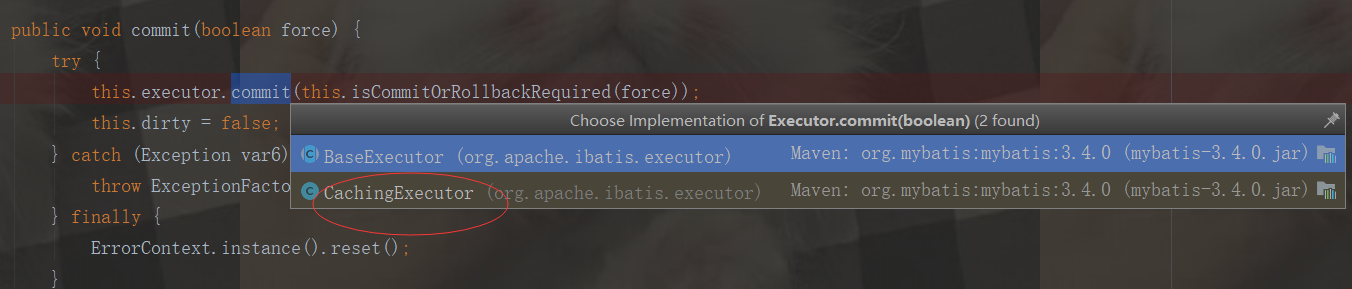
public void commit(boolean force) { try { this.executor.commit(this.isCommitOrRollbackRequired(force)); this.dirty = false; } catch (Exception var6) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error committing transaction. Cause: " + var6, var6); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
private boolean isCommitOrRollbackRequired(boolean force) { return !this.autoCommit && this.dirty || force; }
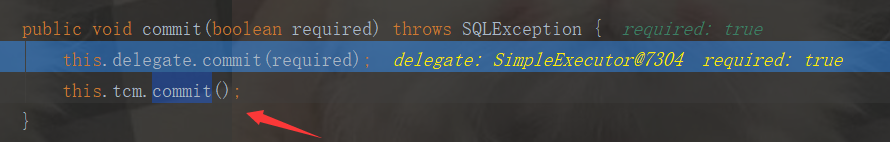
public void commit() { Iterator i$ = this.transactionalCaches.values().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
TransactionalCache txCache = (TransactionalCache)i$.next();
txCache.commit();
}
}
public void commit() { if (this.clearOnCommit) { this.delegate.clear(); }
this.flushPendingEntries();
this.reset();
}
private void flushPendingEntries() { Iterator i$ = this.entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Entry<Object, Object> entry = (Entry)i$.next();
this.delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
i$ = this.entriesMissedInCache.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Object entry = i$.next();
if (!this.entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
this.delegate.putObject(entry, (Object)null);
}
}
}
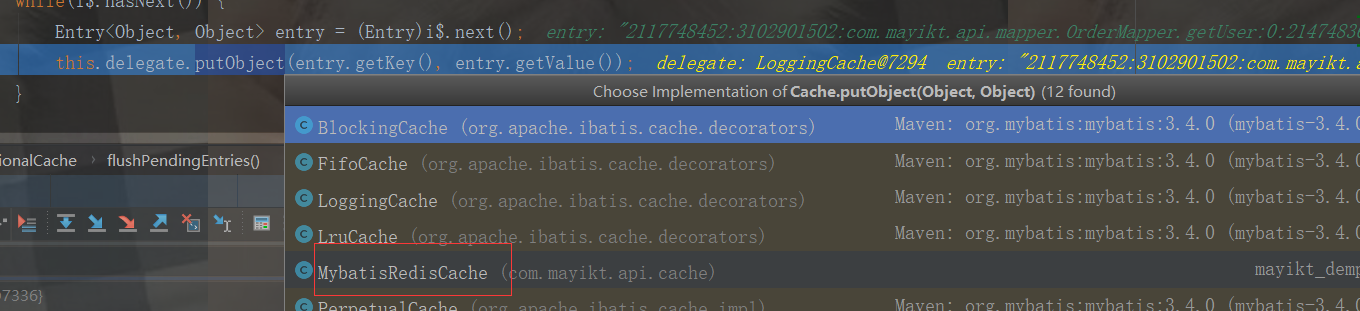
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>putObject:" + key + "=" + value); redisClient.set(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()), SerializeUtil.serialize(value)); }

看下redis是否有数据了。

这里最终会把当前session关闭掉。
最后,我们来总结下上面的源码分析
总结:
TransactionalCache
继承自Cache接口,主要作用是保存SqlSession在事务中需要向某个二级缓存提交的缓存数据
因为在事务过程中的数据可能会回滚,所以不能直接把数据提交给二级缓存,而是暂存于TransactionalCache中,在事务提交后再将存放在其中的数据提交给二级缓存,如果事务回滚,则将数据清除掉。
TransactionalCacheManager
- 用于管理CacheExecutor使用的二级缓存对象,只定义了一个transactionalCaches字段
- private final Cache delegate; //对应的二级缓存对象
- private boolean clearOnCommit; //是否在commit时清除二级缓存的标记
- // 需要在commit时提交到二级缓存的数据
- private final Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
- // 缓存未命中的数据,事务commit时,也会放入二级缓存(key,null)
- private final Set
StatementHandler
StatementHandler接口的实现大致有四个,其中三个实现类都是和JDBC中的Statement响对应的:
- SimpleStatementHandler,这个很简单了,就是对应我们JDBC中常用的Statement接口,用于简单SQL的处理; 存在sql注入攻击问题
- PreparedStatementHandler,这个对应JDBC中的PreparedStatement,预编译SQL的接口;防止sql注入
- CallableStatementHandler,这个对应JDBC中CallableStatement,用于执行存储过程相关的接口;
- RoutingStatementHandler,这个接口是以上三个接口的路由,没有实际操作,只是负责上面三个StatementHandler的创建及调用。
ResultSetHandler
就是将Statement实例执行之后返回的ResultSet结果集转换成我们需要的List结果集
一级缓存与二级缓存区别
①、一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存。在操作数据库时需要构造sqlSession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构(HashMap)用于存储缓存数据。不同的sqlSession之间的缓存数据区域(sqlHashMap)是互相不影响的。
②、二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,多个SqlSession去操作同一个Mapper的语句,多个SqlSession可以共用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的。
注意:sqlSession缓存底层存在线程安全问题。
本文参考:













