注解说明
@ControllerAdvice,是Spring3.2提供的新注解,从名字上可以看出大体意思是控制器增强。让我们先看看@ControllerAdvice的实现:
/**
* Specialization of {@link Component @Component} for classes that declare
* {@link ExceptionHandler @ExceptionHandler}, {@link InitBinder @InitBinder}, or
* {@link ModelAttribute @ModelAttribute} methods to be shared across
* multiple {@code @Controller} classes.
*
* <p>Classes with {@code @ControllerAdvice} can be declared explicitly as Spring
* beans or auto-detected via classpath scanning. All such beans are sorted via
* {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator
* AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}, i.e. based on
* {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} and
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered}, and applied in that order
* at runtime. For handling exceptions, an {@code @ExceptionHandler} will be
* picked on the first advice with a matching exception handler method. For
* model attributes and {@code InitBinder} initialization, {@code @ModelAttribute}
* and {@code @InitBinder} methods will also follow {@code @ControllerAdvice} order.
*
* <p>Note: For {@code @ExceptionHandler} methods, a root exception match will be
* preferred to just matching a cause of the current exception, among the handler
* methods of a particular advice bean. However, a cause match on a higher-priority
* advice will still be preferred to a any match (whether root or cause level)
* on a lower-priority advice bean. As a consequence, please declare your primary
* root exception mappings on a prioritized advice bean with a corresponding order!
*
* <p>By default the methods in an {@code @ControllerAdvice} apply globally to
* all Controllers. Use selectors {@link #annotations()},
* {@link #basePackageClasses()}, and {@link #basePackages()} (or its alias
* {@link #value()}) to define a more narrow subset of targeted Controllers.
* If multiple selectors are declared, OR logic is applied, meaning selected
* Controllers should match at least one selector. Note that selector checks
* are performed at runtime and so adding many selectors may negatively impact
* performance and add complexity.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 3.2
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface ControllerAdvice {
/**
* Alias for the {@link #basePackages} attribute.
* <p>Allows for more concise annotation declarations e.g.:
* {@code @ControllerAdvice("org.my.pkg")} is equivalent to
* {@code @ControllerAdvice(basePackages="org.my.pkg")}.
* @since 4.0
* @see #basePackages()
*/
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
/**
* Array of base packages.
* <p>Controllers that belong to those base packages or sub-packages thereof
* will be included, e.g.: {@code @ControllerAdvice(basePackages="org.my.pkg")}
* or {@code @ControllerAdvice(basePackages={"org.my.pkg", "org.my.other.pkg"})}.
* <p>{@link #value} is an alias for this attribute, simply allowing for
* more concise use of the annotation.
* <p>Also consider using {@link #basePackageClasses()} as a type-safe
* alternative to String-based package names.
* @since 4.0
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #value()} for specifying the packages
* to select Controllers to be assisted by the {@code @ControllerAdvice}
* annotated class.
* <p>Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package
* that serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* @since 4.0
*/
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* Array of classes.
* <p>Controllers that are assignable to at least one of the given types
* will be assisted by the {@code @ControllerAdvice} annotated class.
* @since 4.0
*/
Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {};
/**
* Array of annotations.
* <p>Controllers that are annotated with this/one of those annotation(s)
* will be assisted by the {@code @ControllerAdvice} annotated class.
* <p>Consider creating a special annotation or use a predefined one,
* like {@link RestController @RestController}.
* @since 4.0
*/
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotations() default {};
}
该注解使用@Component注解,这样的话当我们使用context:component-scan扫描时也能扫描到。
通过类型的描述,可以得知几点:
- @ControllerAdvice是一个@Component,用于定义@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder和@ModelAttribute方法,适用于所有使用@RequestMapping方法。
- Spring4之前,@ControllerAdvice在同一调度的Servlet中协助所有控制器。Spring4已经改变:@ControllerAdvice支持配置控制器的子集,而默认的行为仍然可以利用。
- 在Spring4中, @ControllerAdvice通过annotations(), basePackageClasses(), basePackages()方法定制用于选择控制器子集
不过据经验之谈,只有配合@ExceptionHandler最有用,其它两个不常用。
如果单使用@ExceptionHandler,只能在当前Controller中处理异常。但当配合@ControllerAdvice一起使用的时候,就可以摆脱那个限制了。
实现方式
一、统一异常处理中心(Handler)
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
/**
* 统一异常处理
* @ClassName: GlobalExceptionHandler
* @Description: TODO
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年8月29日 下午2:19:42
*
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* 处理所有不可知的异常
* @Title: handleException
* @Description: TODO
* @Date 2018年8月29日 下午2:21:10
* @author OnlyMate
* @param e
* @return
*/
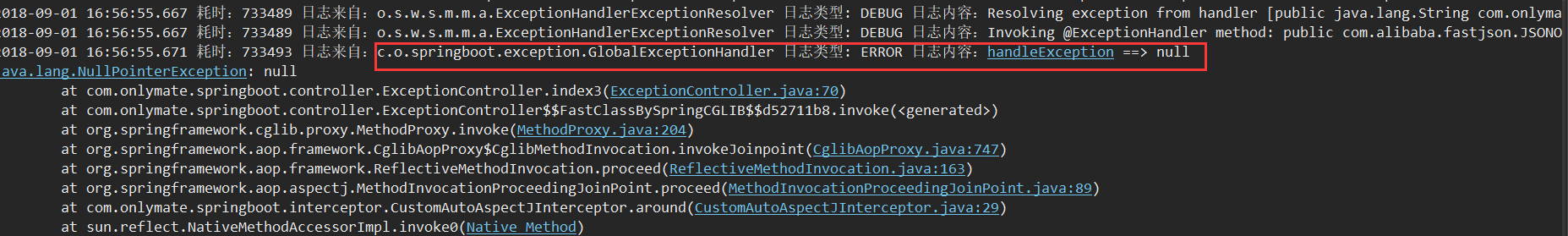
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public JSONObject handleException(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e){
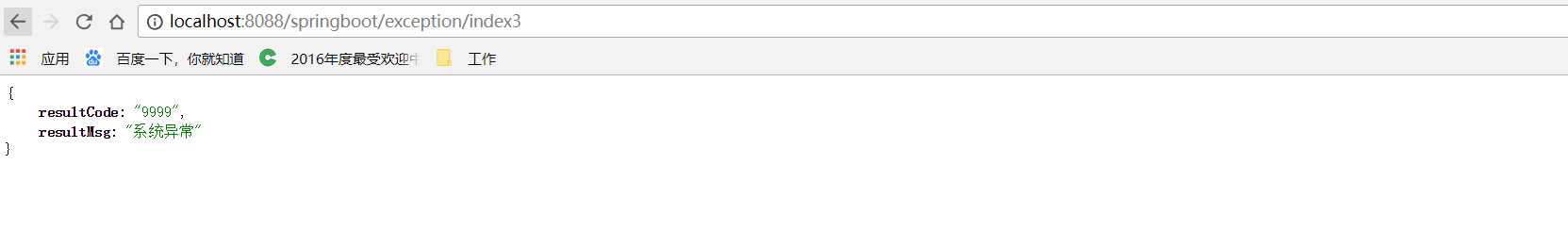
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(); Throwable throwable = e.getCause(); logger.error(throwable.getMessage(), e); if (throwable instanceof DuplicateSubmitException) { jsonObject.put("resultCode", ((DuplicateSubmitException) throwable).getCode()); jsonObject.put("resultMsg", ((DuplicateSubmitException) throwable).getMsg()); } else { jsonObject.put("resultCode", "9999"); jsonObject.put("resultMsg", "系统异常"); }
return jsonObject;
}
/**
* 处理自定义异常(这里处理的异常是继承RunTimeException的自定义的异常)
* @Title: handleBusinessException
* @Description: TODO
* @Date 2018年8月29日 下午2:24:55
* @author OnlyMate
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(CustomBizRuntimeException.class)
public JSONObject handleBusinessException(CustomBizRuntimeException e){
logger.error("handleBusinessException ==> "+ e.getErrorMessage(), e);
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
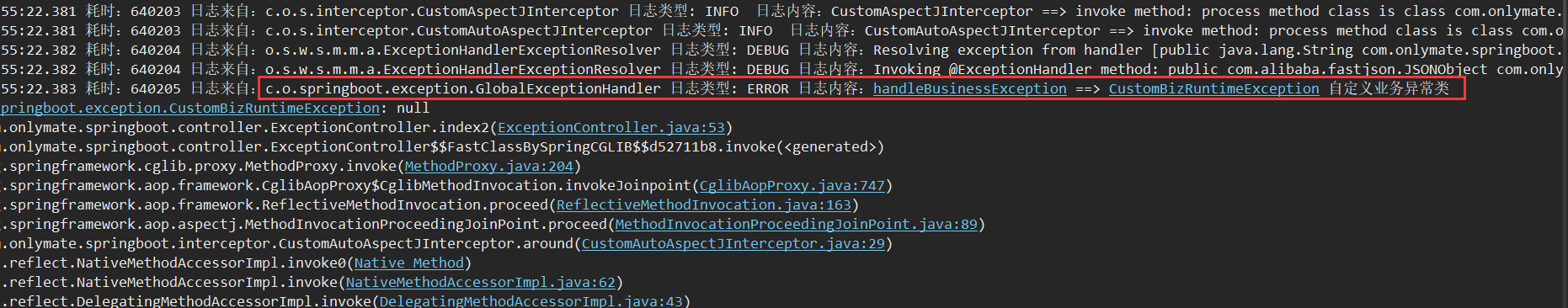
jsonObject.put("resultCode", "9999");
jsonObject.put("resultMsg", "CustomBizRuntimeException 自定义业务异常类 ==> 系统异常");
return jsonObject;
}
/**
* 处理自定义异常(这里处理的异常是继承Exception的自定义的异常)
* @Title: handleCommonException
* @Description: TODO
* @Date 2018年8月29日 下午2:24:55
* @author OnlyMate
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(CustomCommonException.class)
public JSONObject handleCommonException(CustomCommonException e){
logger.error("handleCommonException ==> "+ e.getErrorMessage(), e);
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("resultCode", "9999");
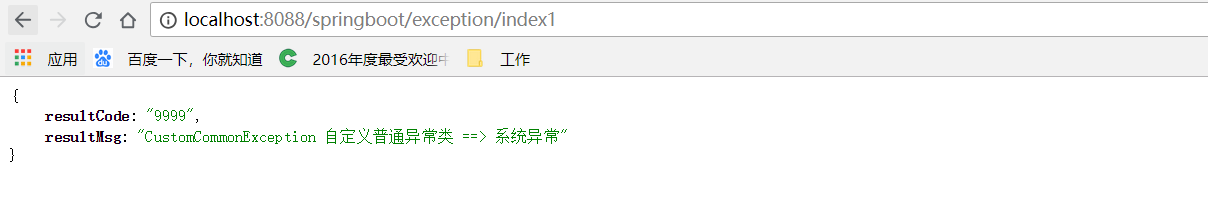
jsonObject.put("resultMsg", "CustomCommonException 自定义普通异常类 ==> 系统异常");
return jsonObject;
}
}
二、自定义异常
CustomBizRuntimeException,继承RuntimeException,可用于涉及事务操作时抛该异常回滚事务
/**
* 自定义业务异常类
* @ClassName: CustomBizRuntimeException
* @Description: TODO
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月1日 下午4:17:49
*
*/
public class CustomBizRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8021190492897458166L;
private String errorMessage = "CustomBizRuntimeException 自定义业务异常类 ";
public String getErrorMessage() {
return this.errorMessage;
}
}
CustomCommonException,普通自定义异常
/**
* 自定义普通异常类
* @ClassName: CustomCommonException
* @Description: TODO
* @author OnlyMate
* @Date 2018年9月1日 下午4:17:49
*
*/
public class CustomCommonException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8021190492897458166L;
private String errorMessage = "CustomCommonException 自定义普通异常类";
public String getErrorMessage() {
return this.errorMessage;
}
}
三、编写抛出对应异常的Controller
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.onlymate.springboot.exception.CustomBizRuntimeException;
import com.onlymate.springboot.exception.CustomCommonException;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/exception")
public class ExceptionController {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldController.class);
/**
* 抛出CustomCommonException异常,然后处理该异常
* @Title: index1
* @Description: TODO
* @Date 2018年9月1日 下午4:42:58
* @author OnlyMate
* @return
* @throws CustomCommonException
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/index1")
public String index1() throws CustomCommonException {
try {
String str = null;
logger.info(str.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CustomCommonException();
}
return "Success";
}
/**
* 抛出CustomBizRuntimeException异常,然后处理该异常
* @Title: index2
* @Description: TODO
* @Date 2018年9月1日 下午4:43:25
* @author OnlyMate
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/index2")
public String index2() {
try {
String str = null;
logger.info(str.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CustomBizRuntimeException();
}
return "Success";
}
/**
* 抛出Exception异常,然后处理该异常
* @Title: index3
* @Description: TODO
* @Date 2018年9月1日 下午4:43:49
* @author OnlyMate
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/index3")
public String index3() {
String str = null;
logger.info(str.toString());
return "Success";
}
}
效果图
一、抛出CustomCommonException异常效果图
页面访问:http://localhost:8088/springboot/exception/index1

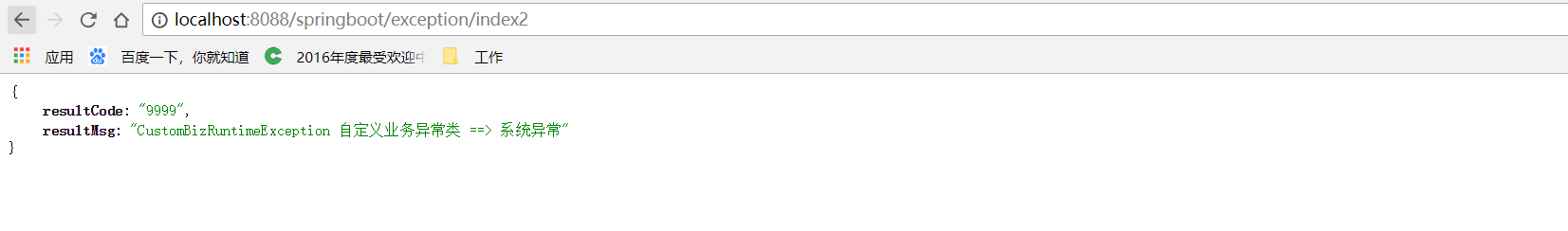
二、抛出CustomBizRuntimeException异常效果图
页面访问:http://localhost:8088/springboot/exception/index2
三、抛出Exception异常效果图
页面访问:http://localhost:8088/springboot/exception/index3