Executor 是JDK5新增的对于线程调度的新框架,主要用途是用来对线程进行调度和管理,
如下是Excutor框架的整体UML关系图;
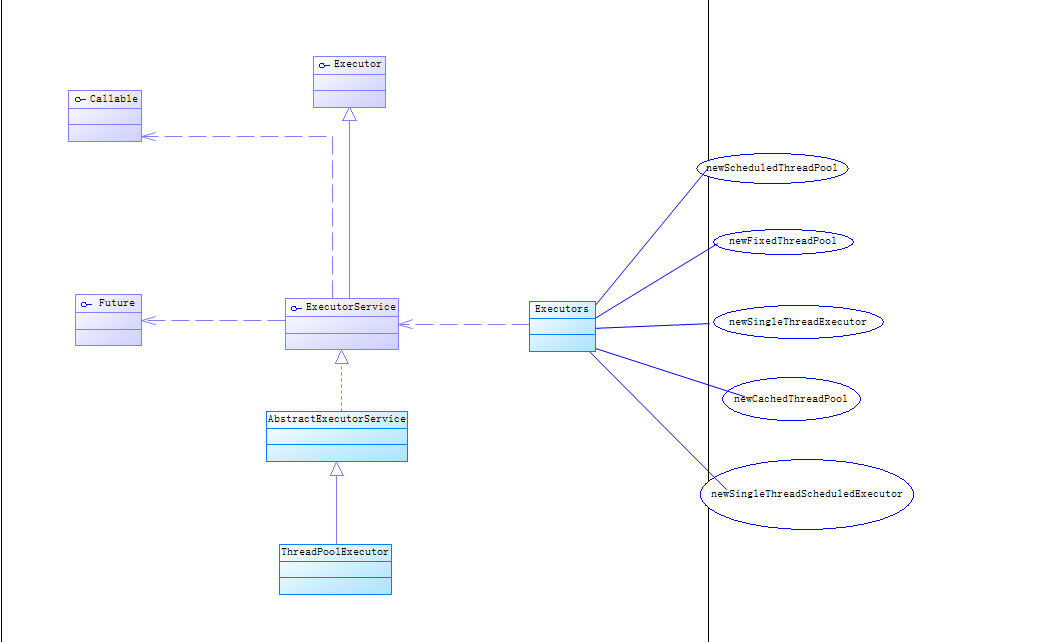
本文将基于以上图片进行线程池测试用例;
class FetchPicket implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("当前线程名字为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ~~~");
System.out.println("开始时间:"+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("结束时间:"+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
return new Random().nextInt();
}
}
- newCachedThreadPool
newCachedThreadPool 方法的java doc如下:

如果没有空闲线程,按照需要创建新的线程,不过当有空闲线程时,会复用已经创建好的线程.
优点:
1,可以提高编程性能,尤其对那些寿命短,异步的任务.
注意对于超过60s未使用的线程,将会从线程池中移除.
代码如下:
@Test
public void newCachedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < LOOP; i++) {
// 使用lambada表达式
Future<Integer> submit = newCachedThreadPool.submit(new FetchPicket());
try {
if (submit.get() > 0) {
System.out.println("callable 的返回值是:" + submit.get());
}
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
newCachedThreadPool.shutdown();
}
console打印如下:
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 14:47:40
结束时间:2017-03-29 14:47:50
callable 的返回值是:1172363209
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 14:47:50
结束时间:2017-03-29 14:48:00
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 14:48:00
结束时间:2017-03-29 14:48:10
callable 的返回值是:822004726
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-2 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 14:48:10
结束时间:2017-03-29 14:48:20
callable 的返回值是:547995146
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-2 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 14:48:20
结束时间:2017-03-29 14:48:30
- newFixedThreadPool
Java doc如下:

创建一个固定数目可重复利用的线程池,表现出一个共享无序的队列.如果线程池里所有的线程都是active,若在提交新的线程,这个线程将会被加到一个堵塞队列中直到有可用的线程.
@Test
public void newFixedThreadPool() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(SIZE);
for (int i = 0; i < LOOP; i++) {
Future<Integer> submit = newFixedThreadPool.submit(new FetchPicket());
try {
if (submit.get() > 0) {
System.out.println("callable 的返回值是:" + submit.get());
}
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
newFixedThreadPool.shutdown();
}
console打印如下:
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:12:19
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:12:29
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-2 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:12:29
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:12:39
callable 的返回值是:360730033
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:12:39
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:12:49
callable 的返回值是:1306633973
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-2 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:12:49
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:12:59
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:12:59
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:13:09
callable 的返回值是:1154663265
newFixedThreadPool 和 newCachedThreadPool 区别?
1,newFixedThreadPool 的线程是不可复用的,而newCachedThreadPool 线程是可复用的.
2,newFixedThreadPool 将会保持线程池内的线程active除非出现异常,而newCachedThreadPool 只会保持默认时间60s,因此,newFixedThreadPool 会不断的创建线程,有可能导致oom.
3,对于任务时间短异步任务,建议使用newCachedThreadPool,而执行任务时间比较长的建议使用newFixedThreadPool
英文翻译如下:
- newScheduledThreadPool
Java doc如下:

创建一个再给定的延迟时间按日期安排进行的线程池,
代码如下:
@Test
public void newScheduledThreadPool() {
ExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(SIZE);
for (int i = 0; i < LOOP; i++) {
Future<Integer> submit = newScheduledThreadPool.submit(new FetchPicket());
try {
if (submit.get() > 0) {
System.out.println("callable 的返回值是:" + submit.get());
}
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
newScheduledThreadPool.shutdown();
}
console打印如下:
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:36:03
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:36:13
callable 的返回值是:797384947
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:36:13
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:36:23
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-2 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:36:23
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:36:33
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:36:33
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:36:43
callable 的返回值是:1928166459
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-2 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:36:43
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:36:53
分析日志可以看出,哪个线程处于空闲状态,谁抢到资源,将会执行哪个线程.
- newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor
java doc如下

创建一个按照计划执行指令的单线程,如果该线程因为某些原因关闭,新的线程将会创建并替代他的位置.
@Test
public void newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {
ExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < LOOP; i++) {
Future<Integer> submit = newScheduledThreadPool.submit(new FetchPicket() );
try {
if (submit.get() > 0) {
System.out.println("callable 的返回值是:" + submit.get());
}
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
newScheduledThreadPool.shutdown();
}
console日志如下:
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:46:40
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:46:50
callable 的返回值是:387305211
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:46:50
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:47:00
callable 的返回值是:1772792044
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:47:00
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:47:10
callable 的返回值是:1354567240
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:47:10
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:47:20
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:47:20
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:47:30
callable 的返回值是:1825312382
分析日志可以看出,只有一个线程在打印日志.
- newSingleThreadExecutor

代码如下:
@Test
public void newSingleThreadExecutor() {
ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < LOOP; i++) {
Future<Integer> submit = newSingleThreadExecutor.submit(new FetchPicket());
try {
if (submit.get() > 0) {
System.out.println("callable 的返回值是:" + submit.get());
}
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
newSingleThreadExecutor.shutdown();
}
console打印如下:
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:51:33
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:51:43
callable 的返回值是:1323389732
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:51:43
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:51:53
callable 的返回值是:1419085557
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:51:53
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:52:03
callable 的返回值是:423848033
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:52:03
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:52:13
callable 的返回值是:1320865693
当前线程名字为:pool-1-thread-1 ~~~
开始时间:2017-03-29 15:52:13
结束时间:2017-03-29 15:52:23
分析日志,只有一个线程在执行任务.











