Entity
使用@Entity注解使javabean类成为实体类。
一般使用@Id注解在成员变量或者其对应的get方法设置实体类的主键。
例子:
package com.hgf.jpa.domain;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
/**
* Created by hgf on 16/8/21.
*/
@Entity
public class Employee {
@Id
private int id;
private String name;
private long salary;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public long getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(long salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", salary=" + salary +
'}';
}
}
注意:不能使用
@Id注解在setter方法上面。
Entity Manager
Entity Manager负责对Entity类的持久化。Entity的集合成为persistent context。
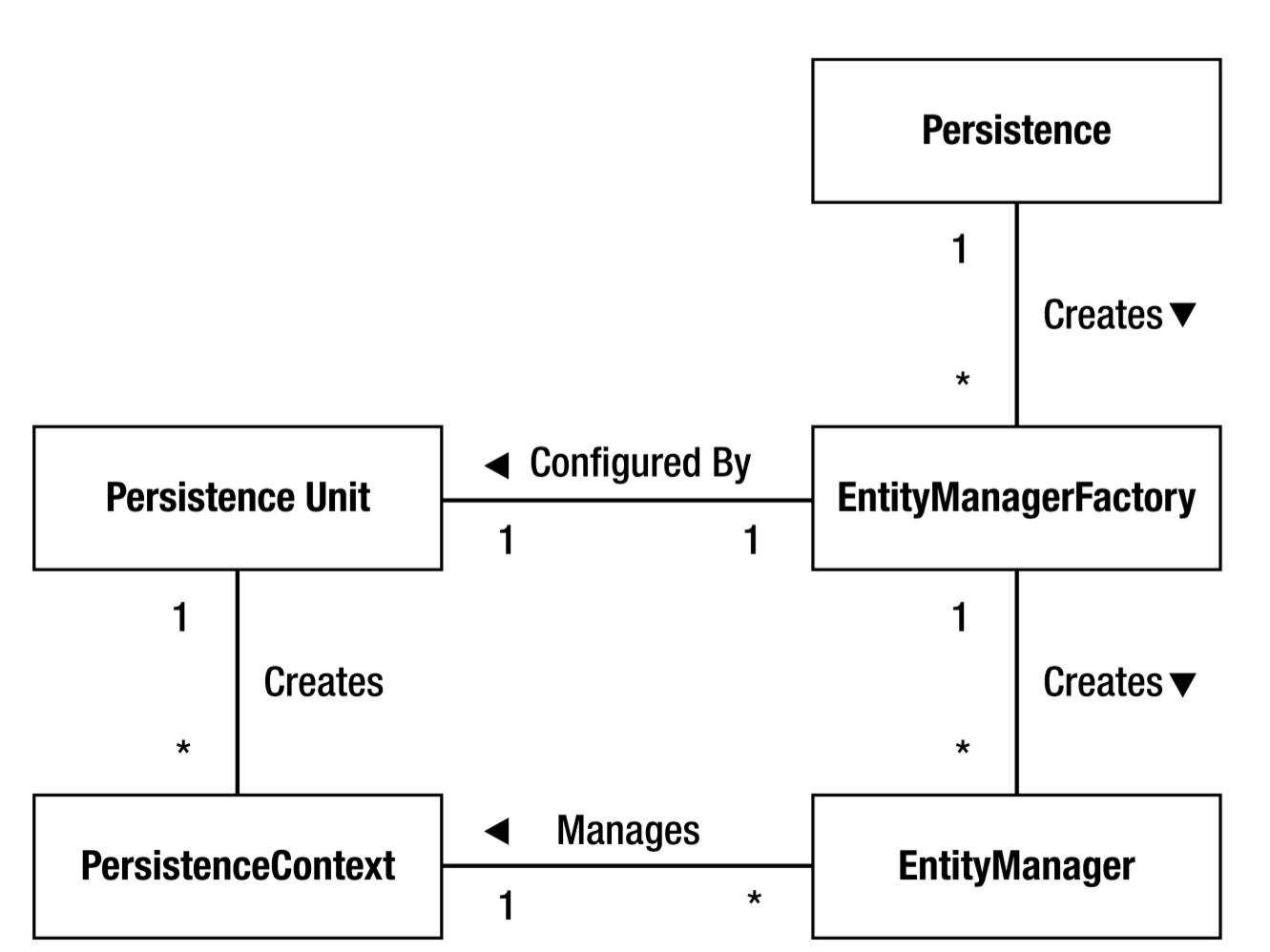 

一个persistent identity只有一个对应的实体实例在entity persistent context中。
EntityManagerFactory负责生成EntityManager。每个EntityManagerFactory对应着唯一名字的persistent unit。
一般获取EntityManagerFactory是通过Persistent类的静态方法Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory并指定persisitent unit的名称,构造。
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("EmployeeService");
所有的EntityManager都是由EntityManagerFactory构造。
例如:EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
持久化一个实体
将数据持久化例子:
Employee employee = new Employee(100);
em.persist();
可能会出现
PersistentException
更加规范:
public Employee createEmployee(int id, String name, long salary){
Employee employee = new Employee(id, name, salary);
em.persist();
}
查询数据
public Employee findEmployee(int id){
return em.find(Employee.class, id);
}
删除数据
public boolean removeEmployee(int id){
Employee employee = findEmployee(id);
if(employee!=null){
em.remove(employee);
}
}
更新数据
public Employee raiseEmployeeSalary(int id, long raise){
Employee emp = em.findEmployee(id);
if(emp!=null){
emp.setSalary(emp.getSalary()+raise);
return emp;
}
}
事务
em.getTransaction().begin();
//do somethings
em.getTransaction().commit();
sql查询
查询一般使用Query或者TypedQuery表示。通过EntityManager的静态方法设置查询语句。
TypedQuery<Employee> query = em.createQuery("select * from employee", Employee.class);
List<Employee> employees = query.getResultList();
Spring JPA
核心概念
CURD Repository:CURD表示创建(Create),更新(Update),读取(Retrieve),删除(Delete)。
CURD Pepository 的接口核心方法如下,其中泛型类型分别值得是实体类的类型和Id的类型(ID的类型必须是可以序列化的)。
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID extends Serializable>
extends Repository<T, ID> {
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
T findOne(ID primaryKey);
Iterable<T> findAll();
Long count();
void delete(T entity);
boolean exists(ID primaryKey);
// … more functionality omitted.
}
spring 也提供
JpaRepository和MongoRepository,他们继承自CurdRepository,并且使用特定的持久化技术实现。
PagingAndSortingRepository集成自CurdRepository,提供了通用简单的分页方法。
PagingAndSortingRepository接口:
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID extends Serializable>
extends CrudRepository<T, ID> {
Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort);
Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable);
}
如果每页显示User 20项,可以这么处理:
PagingAndSortingRepository<User, Long> repository = //get access to a bean
Page<User> users = repository.findAll(new PageRequest(1,20));
查询方法
使用Spring Data,查询方法分为四步:
声明一个继承自
Repository(或者其子接口)的接口,并指定实体类和ID类型。interface PersonRepository extends Repository<Person, Long> { … }接口中声明查询方法:
interface PersonRepository extends Repository<Person, Long> { List<Person> findByLastname(String lastname); }设置Spring,创建接口的代理实现。
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories; @EnableJpaRepositories class Config {} <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa.xsd"> <jpa:repositories base-package="com.acme.repositories"/> </beans>将接口注入
public class SomeClient { @Autowired private PersonRepository repository; public void doSomething() { List<Person> persons = repository.findByLastname("Matthews"); } }
定义repository接口
定义一个实体相关的repository接口,必须继承Repository或者其子类,并且确定实体类类型和ID类型,Id需要可序列化。
典型的可继承的接口有:Repository,CrudRepository,PagingAndSortingRepository。
如果不想继承Spring data接口,可以使用@RepositoryDefinationg注解,在自定义的接口上。
继承自 定义了一系列用于处理实体类方法的CurdRepository,并且可以选择性的暴露操作实体的方法。
例子,选择性的暴露CRUD方法:
@NoRepositoryBean
interface MyBaseRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends Repository<T, ID> {
T findOne(ID id);
T save(T entity);
}
interface UserRepository extends MyBaseRepository<User, Long> {
User findByEmailAddress(EmailAddress emailAddress);
}
注意:
@NoRepositoryBean,使用该注解后给repository接口后,SpringData不会在运行时给该接口生成实现类。
使用多个Spring data模块
在项目中使用多个不同的Spring data模块时,Spring data会在类路径上检查repository工厂类,必须使用严格的Repository定义才能生成正确的repository,绑定到特定的Springdata模块。
严格定义:
- 使用特定模块对应的repository;
- 使用特定模块repository对应的注解。
例如:
interface MyRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> { }
@NoRepositoryBean
interface MyBaseRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepository<T, ID> {
…
}
interface UserRepository extends MyBaseRepository<User, Long> {
…
}
上述例子中,MyRepository和UserRepository继承自JPA模块的特定repository,他们在多个Springdata模块共用的时候是有效的。
interface AmbiguousRepository extends Repository<User, Long> {
…
}
@NoRepositoryBean
interface MyBaseRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> {
…
}
interface AmbiguousUserRepository extends MyBaseRepository<User, Long> {
…
}
上例中使用通用的repository接口,AmbiguousRepository和AmbiguousUserRepository都继承自通用接口,在多个spring data模块的时候,相互之间不能互相区分,需要将通用的repository接口绑定到特定的repository。
interface PersonRepository extends Repository<Person, Long> {
…
}
@Entity
public class Person {
…
}
interface UserRepository extends Repository<User, Long> {
…
}
@Document
public class User {
…
}
上例中,PersonRepository接口继承自通用的接口,但是Person类使用了@Entity注解,该注解是特定的JPA注解,所以PersonRepository属于Spring Data JPA模块。UserRepository接口也是通用的Sping data模块,@Document 注解是Spring Data MongoDB的注解。
interface JpaPersonRepository extends Repository<Person, Long> {
…
}
interface MongoDBPersonRepository extends Repository<Person, Long> {
…
}
@Entity
@Document
public class Person {
…
}
上述类中,由于Person类注解了@Entity和@Document,Spring data不知道对应的Repository,出现问题。
使用多种不同模块的注解在同一个实体类上,可以服用实体类的定义,但是Sping Data不能区分不同的模块绑定。
最简单的方式就是使用基于包名的模块分类。即使用同一个Spring Data模块的类放在一个包中。
例如:
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.acme.repositories.jpa")
@EnableMongoRepositories(basePackages = "com.acme.repositories.mongo")
interface Configuration { }
上述定义中,基于包名划分Spring data模块,并且使用特定的模块扫描特定的包,就不会发生冲突。
定义查询方法
Spring data支持两种查询方式:
- 基于方法名的查询;
- 手动设定查询语句;
查询策略
设定查询策略方式:
- 在XML中使用
query-lookup-strategy; - 在配置类中,使用EnableJpaRepoditory等注解时,设置注解的属性
queryLookupStrategy。
常见的策略:
- CREATE 从方法名中构造保存数据请求。
- USE_DECLARED_QUERY 尝试查找一个声明的query,找不到时会抛出异常。
- CREATE_IF_NOT_FOUND 【默认】结合了
CREATE和USE_DECLARED_QUERY,首先去查找声明的query,没有找到,则根据方法名创建query。
创建查询
查询的属性必须是被管理的实体类的属性!!!
常见的方法名前缀有:find…By, read…By, query…By, count…By, get…By,还可包含Distinct将结果去重。
By扮演者前缀和实际查询判断标准(where)的分隔符。
例子:
public interface PersonRepository extends Repository<User, Long> {
List<Person> findByEmailAddressAndLastname(EmailAddress emailAddress, String lastname);
// Enables the distinct flag for the query
List<Person> findDistinctPeopleByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname);
List<Person> findPeopleDistinctByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname);
// 对一个参数忽略大小写
List<Person> findByLastnameIgnoreCase(String lastname);
// 对所有的参数都忽略大小写
List<Person> findByLastnameAndFirstnameAllIgnoreCase(String lastname, String firstname);
// Enabling static ORDER BY for a query
List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameAsc(String lastname);
List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameDesc(String lastname);
}
AND,OR,Between,LessThan,GreaterThan,Like。- 使用
IgnoreCase忽略某个属性的大小写;使用AllIgnoreCase忽略所有属性的大小写。 OrderBy定义排序,后面可确定排序的方式。Asc递增排序;Desc递减排序。
属性表达式
属性必须是被管理的实体类的属性。该属性既可以是基础数据类型,也可以是某个实体的引用属性。
Person有Address属性,Address有ZipCode属性,那么根据ZipCode查询Person可以使用
List<Person> findByAddressZipCode(ZipCode zipCode);
解析方法先获取AddressZipCode,并且当做属性,并检查管理的实体类中是否有该属性,如果没有,则解析方法按照驼峰命名的规则,从右往左,查找符合的属性。先找AddressZip 和Code属性,如果找到AddressZip,那么再判断AddresZip类中是否有Code属性,依次类推。如果AddressZip 和Code 不符合,则找Address和ZipCode。
为了这种模糊的查找过程可以在方法名中使用_手动的定义遍历点。
List<Person> findByAddress_ZipCode(ZipCode zipCode);
强烈建议遵循java规范,使用驼峰命名,不适用
_下划线。
特殊参数处理
Spring data会自动识别Pageable和Sort参数,去动态实现分页和排序的功能。
例子:
Page<User> findByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
Slice<User> findByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
List<User> findByLastname(String lastname, Sort sort);
List<User> findByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable是实现自动分页的。Page知道查询元素的总个数和页数,然后通过对所有元素的排序和数数确定每页的元素,每次查询都严重依赖排序。Slice是替代方案,Slice只知道是否还有下个分片。当结果集很大的时候使用Slice更加高效。
排序也可以通过Pageable实现,但是单纯的排序的话,最好使用Sort,并且返回一个List集合,不必再生成Page实例。
limit 查询结果
限制查询结果可以通过方法名中的first和top,Distinct限制。
User findFirstByOrderByLastnameAsc();
User findTopByOrderByAgeDesc();
Page<User> queryFirst10ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
Slice<User> findTop3ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
List<User> findFirst10ByLastname(String lastname, Sort sort);
List<User> findTop10ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
如果在限制查询后分页,那么分页是在限制后分页。
Stream 查询结果
查询结果也可以处理成java8 的Stream类型。
@Query("select u from User u")
Stream<User> findAllByCustomQueryAndStream();
Stream<User> readAllByFirstnameNotNull();
@Query("select u from User u")
Stream<User> streamAllPaged(Pageable pageable);
使用Stream后必须关闭stream!
可以通过Strea的close方法或者java7特性try-with-resource特性。
例如:try (Stream<User> stream = repository.findAllByCustomQueryAndStream()) { stream.forEach(…); }
异步查询
使用spring 异步方法执行能力,Repository 查询也可异步化。
这意味着这些方法会立即返回,实际的查询会作为一个task交给Spring TaskExecutor。
@Async
Future<User> findByFirstname(String firstname);
@Async
CompletableFuture<User> findOneByFirstname(String firstname);
@Async
ListenableFuture<User> findOneByLastname(String lastname);
创建repository实例
可以使用配置类和XML配置。
XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa.xsd">
<repositories base-package="com.acme.repositories" />
</beans:beans>
在上述设置中,spring会被指定扫描com.acme.repositories包和它的子包中继承自Repository或者它的子接口的接口。然后创建与查找到接口相关的FactoryBean,来生成代理类。每个代理bean的name都是使用接口名。
扫描的包名可以使用通配符设定。
过滤不需要的Repository。
在repositories标签中使用<include-filter />和<exclude-filter />来实现过滤。
例如:
<repositories base-package="com.acme.repositories">
<context:exclude-filter type="regex" expression=".*SomeRepository" />
</repositories>
配置类
使用@EnableXXXXRepositories注解配置。
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories("com.acme.repositories")
class ApplicationConfiguration {
@Bean
public EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory() {
// …
}
}
独立使用Spring Data Repository
在Spring 容器外可能也会用到Springdata Repository。
可以手动获取Repository。
RepositoryFactorySupport factory = … // Instantiate factory here
UserRepository repository = factory.getRepository(UserRepository.class);
自定义Spring Data Repository
给某个repository添加新的方法
- 自定义新的接口
- 定义实现类并实现接口
- 在其他接口中使用自定义接口。
自定义接口:
interface UserRepositoryCustom {
public void someCustomMethod(User user);
}
实现接口:
class UserRepositoryImpl implements UserRepositoryCustom {
public void someCustomMethod(User user) {
// Your custom implementation
}
}
注意:自定义实现类只比自定义接口多了
Impl,这样才能被找到!!!
使用repository-impl-postfix自定义实现类的后缀。
实现类是一个常见的Spring bean,可以使用依赖注入。
使用自定义接口:
interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<User, Long>, UserRepositoryCustom {
// Declare query methods here
}
给所有的Repository添加新的方法
给所有的Repository添加新的方法使用上节讲述的方法是行不通的。
为了所有的repository添加新的方法,首先需要添加一个中间接口定义所有的共享方法,中间接口继承自Repository或者其子接口。
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface MyRepository<T, ID extends Serializable>
extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> {
void sharedCustomMethod(ID id);
}
然后所有的独立Repository接口都必须集成自这个接口,而不是Repository接口。
然后实现中间接口,该类会作为repository代理类的基类。
public class MyRepositoryImpl<T, ID extends Serializable>
extends SimpleJpaRepository<T, ID> implements MyRepository<T, ID> {
private final EntityManager entityManager;
public MyRepositoryImpl(JpaEntityInformation entityInformation,
EntityManager entityManager) {
super(entityInformation, entityManager);
// Keep the EntityManager around to used from the newly introduced methods.
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
public void sharedCustomMethod(ID id) {
// implementation goes here
}
}
中间接口实现类必须有一个与特定存储技术相关的Repository, 使用的 工厂实现。
如上例中,覆盖含有EntityInformation和一个含有特定存储技术的对象(上例中的EntityManager)
在上例中,需要给中间接口添加@NoRepositoryBean注解,防止Spring给中间接口生成代理类与自己的实现冲突,得到意想不到的结果。
最后,使自定义Repository基类生效。
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(repositoryBaseClass = MyRepositoryImpl.class)
class ApplicationConfiguration { … }
<repositories base-package="com.acme.repository"
repository-base-class="….MyRepositoryImpl" />
在EnableXXXXRepositories注解中添加
repositoryBaseCLass属性。
Spring Data扩展
QueryDsl 扩展
QueryDsl是一个通过流式API实现的静态类型的像SQL语句的查询框架。
Spring Data通过QueryDslPredicateExecutor 与QueryDls整合。
public interface QueryDslPredicateExecutor<T> {
T findOne(Predicate predicate);
Iterable<T> findAll(Predicate predicate);
long count(Predicate predicate);
boolean exists(Predicate predicate);
// … more functionality omitted.
}
使用QueryDsl的特性,只需要在自己的Repository接口继承QueryDslPredicateExecutor。
interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<User, Long>, QueryDslPredicateExecutor<User> {
}
上例中支持基于QueryDslPredicate类的类型安全查询。
Predicate predicate = user.firstname.equalsIgnoreCase("dave")
.and(user.lastname.startsWithIgnoreCase("mathews"));
userRepository.findAll(predicate);
Spring data web support
使用@EnableSPringDataWebSupport开启Spring data web支持。
@EnableSPringDataWebSupport注册组件并且自动检测整合classpath上 出现的Spring HASTEOAS。
如果使用XML,
<bean class="org.springframework.data.web.config.SpringDataWebConfiguration" />
<!-- 如果使用Spring HATEOAS,使用这个bean替换掉上面的bean -->
<bean class="org.springframework.data.web.config.HateoasAwareSpringDataWebConfiguration" />
自动注册的组件有:
DomainClassConverter:Spring MVC可以解析请求参数或者路径上的参数为Repository重注册的实体类。HandlerMethodArgumentResolver使SpringMVC可以解析请求参数中的Pageable和Sort实例。分别对应PageableHandlerMethodArgumentResolver和SortHandlerMethodArgumentResolver两种resolver。
例如:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/{id}")
public String showUserForm(@PathVariable("id") User user, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "userForm";
}
}
上例中,直接解析参数中的id,并获取对应的User实例,而必须要显示的查询。DomainClassCOnverter会先获取路径上的id,然后使用findOne查询Repository中注册的实体类实例。
实体类必须实现
CurdRepository才能通过DomainClassConverter转换。
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver例子:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired UserRepository repository;
@RequestMapping
public String showUsers(Model model, Pageable pageable) {
model.addAttribute("users", repository.findAll(pageable));
return "users";
}
}
这个方法会使SpringMVC尝试从请求中获取Pageable实例。
请求中的参数:
- page: 想获取的页码,默认为0;
- size: 每页的大小,默认20;
- sort: 分页使用的排序方式,asc或者desc,例如
sort=firstname&sortlastname,asc
想自定义方法行为,可继承SpringDataWebConfiguration或者HateoasAwareSpringDataWebConfiguration,然后覆盖pageableResolver或sortResolver,然后使用自定义配置使继承类生效,而不是直接使用@EnableXXX注解。
当有多个Pageable和Sort实例需要从请求中解析时,可以使用spring的@Qualifier注解区分不同的实例,然后请求的参数必须以${qualifier}_为前缀。
例如:
public String showUsers(Model model,
@Qualifier("foo") Pageable first,
@Qualifier("bar") Pageable second) { … }
请求参数:foo_page,bar_page。
参数上默认的Pageable相当于PageRequest(0,20),可以使用@PageableDefaults注解在Pageable参数上来自定义分页参数。
Spring HATEOAS 带有表示层的PagedResources,可以通过Page转为PagedResource,转换功能由PagedResourcesAssembler提供。
@Controller
class PersonController {
@Autowired PersonRepository repository;
@RequestMapping(value = "/persons", method = RequestMethod.GET)
HttpEntity<PagedResources<Person>> persons(Pageable pageable,
PagedResourcesAssembler assembler) {
Page<Person> persons = repository.findAll(pageable);
return new ResponseEntity<>(assembler.toResources(persons), HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
- PagedResources中的内容为Page实例中的内容。
- PagedResources会获取一个由PageRequest和Page中信息填充的PageMetadata实例。
- PagedResources会获得一个
prev和next连接。
例如,上述请求完成后的结果:
{ "links" : [ { "rel" : "next",
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/persons?page=1&size=20 }
],
"content" : [
… // 20 Person instances rendered here
],
"pageMetadata" : {
"size" : 20,
"totalElements" : 30,
"totalPages" : 2,
"number" : 0
}
}
对于使用QueryDsl的,可能从Request请求中获取查询属性。使用QuerydslPredicateArgumentResolver完成查询解析。
例如:?firstname=Dave&lastname=Matthews
会被解析成:
QUser.user.firstname.eq("Dave").and(QUser.user.lastname.eq("Matthews"))
当classpath中存在QueryDsl时,
QuerydslPredicateArgumentResolver会在使用@EnableSpringDataWebSupport的时候自动激活。
使用@QueryPredicate注解会使Prediacte使用QueryDskPredicateExecutor执行。
由于在解析参数的时候,参数并不是一个实体的所有属性,不能唯一确定一个实体类,使用
QuerydslPredicate的root属性设置实体类类型会比较好。
@Controller
class UserController {
@Autowired UserRepository repository;
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
String index(Model model, @QuerydslPredicate(root = User.class) Predicate predicate,
Pageable pageable, @RequestParam MultiValueMap<String, String> parameters) {
model.addAttribute("users", repository.findAll(predicate, pageable));
return "index";
}
}
填充Repository
使用存储无关的JSON(通过Jackson)、XML(通过Spring OXM)作为数据源填充Repository。
例如,data.json
[ { "_class" : "com.acme.Person",
"firstname" : "Dave",
"lastname" : "Matthews" },
{ "_class" : "com.acme.Person",
"firstname" : "Carter",
"lastname" : "Beauford" } ]
定义json数组,每一行使用_class定义本行的数据类 类型,其后为实体类的属性和值。
定义填充:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:repository="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/repository"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/repository
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/repository/spring-repository.xsd">
<repository:jackson2-populator locations="classpath:data.json" />
</beans>
data.json会被反序列化,通过jackson的ObjectMapper读入。
传统web支持
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public UserController(UserRepository userRepository) {
Assert.notNull(repository, "Repository must not be null!");
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
@RequestMapping("/{id}")
public String showUserForm(@PathVariable("id") Long id, Model model) {
// Do null check for id
User user = userRepository.findOne(id);
// Do null check for user
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "user";
}
}
















