Java9之HttpClientAPI实战详解
前言
相信关注java9的小伙伴们都知道java9版本内置模块提供了Http功能,当然并不是说之前jdk之前并不支持,那么这次更新又多了什么呢?或者是解决了什么问题?
说明
自JDK 1.0以来,Java已经支持HTTP/1.1。 HTTP API由java.net包中的几种类型组成。 现有的API有以下问题:
- 它被设计为支持多个协议,如http,ftp,gopher等,其中许多协议不再被使用。
- 太抽象了,很难使用。
- 它包含许多未公开的行为。
- 它只支持一种模式,阻塞模式,这要求每个请求/响应有一个单独的线程。
2015年5月,IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force)发布了HTTP/2规范。 有关HTTP/2规范的完整文本,请访问https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7540。 HTTP/2不会修改应用程序级语义。 也就是说,对应用程序中的HTTP协议的了解和使用情况并没有改变。 它具有更有效的方式准备数据包,然后发送到客户端和服务器之间的电线。 所有之前知道的HTTP,如HTTP头,方法,状态码,URL等都保持不变。 HTTP/2尝试解决与HTTP/1连接所面临的许多性能相关的问题:
- HTTP/2支持二进制数据交换,来代替HTTP/1.1支持的文本数据。
- HTTP/2支持多路复用和并发,这意味着多个数据交换可以同时发生在TCP连接的两个方向上,而对请求的响应可以按顺序接收。 这消除了在对等体之间具有多个连接的开销,这在使用HTTP/1.1时通常是这种情况。 在HTTP/1.1中,必须按照发送请求的顺序接收响应,这称为head-of-line阻塞。 HTTP/2通过在同一TCP连接上进行复用来解决线路阻塞问题。
- 客户端可以建议请求的优先级,服务器可以在对响应进行优先级排序时予以遵守。
- HTTP首部(header)被压缩,这大大降低了首部大小,从而降低了延迟。
- 它允许从服务器到客户端的资源推送。
JDK 9不是更新现有的HTTP/1.1 API,而是提供了一个支持HTTP/1.1和HTTP/2的HTTP/2 Client API。 该API旨在最终取代旧的API。 新API还包含使用WebSocket协议开发客户端应用程序的类和接口。 有关完整的WebSocket协议规范,请访问https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455。新的HTTP/2客户端API与现有的API相比有以下几个好处:
- 在大多数常见情况下,学习和使用简单易用。
- 它提供基于事件的通知。 例如,当收到首部信息,收到正文并发生错误时,会生成通知。
- 它支持服务器推送,这允许服务器将资源推送到客户端,而客户端不需要明确的请求。 它使得与服务器的WebSocket通信设置变得简单。
- 它支持HTTP/2和HTTPS/TLS协议。
- 它同时工作在同步(阻塞模式)和异步(非阻塞模式)模式。
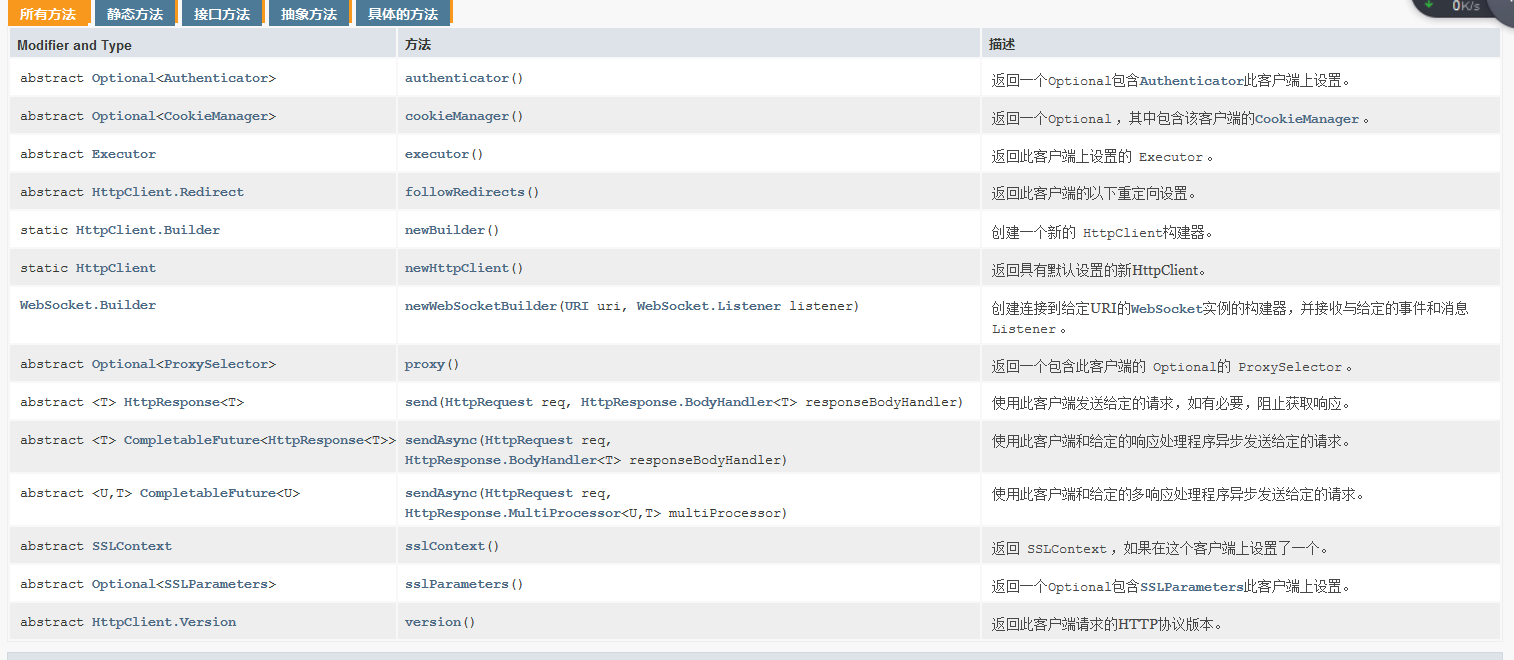
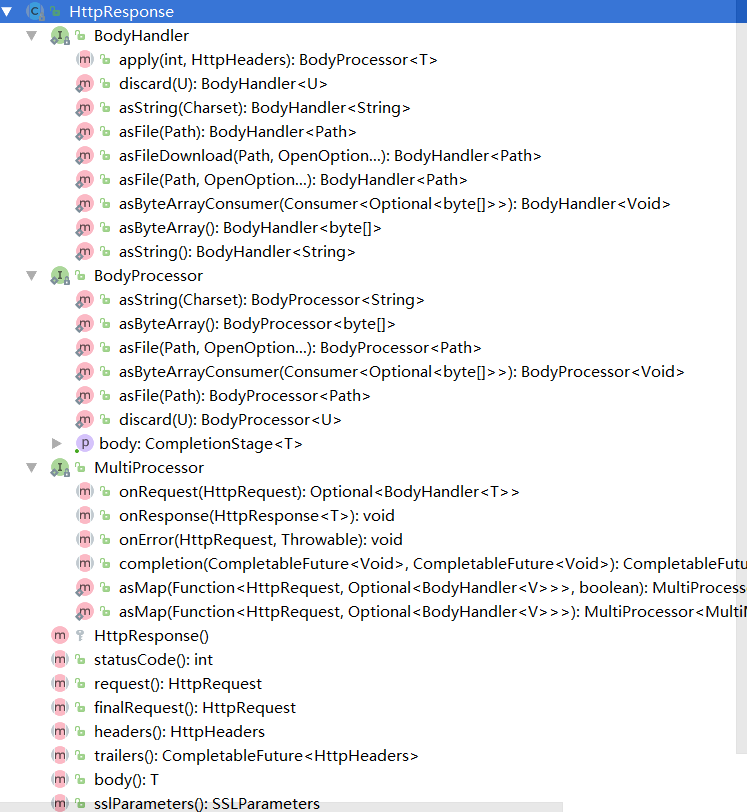
如果想使用Java9的HttpClient服务,那么你必须熟悉(jdk.incubator.http)包中的以下三个类:
HttpClient http客户端
该类是Java9开始引入的,官方文档的翻译说明是这样的
- HttpClient是一个对多个请求配置了公共信息的容器。所有的请求通过一个HttpClient进行发送。HttpClients是不可变的,通过HttpClient的newBuilder()创建返回。请求Builders被HttpRequest#newBuilder()来创建。
- 接口API
-
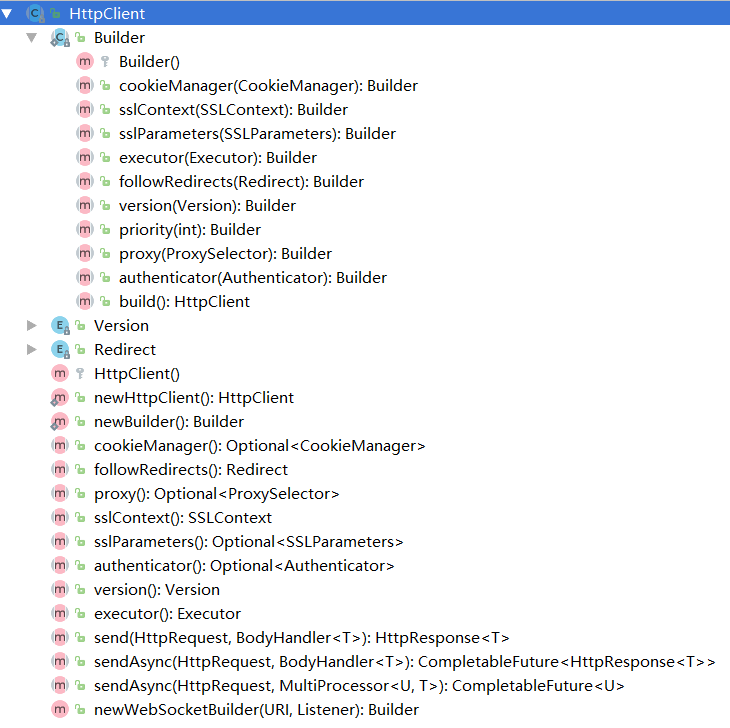
API中Builder部分用来构建客户端的配置,send相关的几个方法是进行请求发送,不同的是Async是异步操作。其他的基本是客户端的参数配置信息(包括代理,线程,版本,SSL,cookie等),同时也提供了socket支持。
使用示例
- 示例1,使用默认配置
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
- 示例2,自定义配置。
try { Authenticator authenticator=new Authenticator() { }; client= HttpClient.newBuilder() .authenticator(authenticator)//配置authenticator .sslContext(SSLContext.getDefault())//配置 sslContext .sslParameters(new SSLParameters())//配置 sslParameters .proxy(ProxySelector.getDefault())//配置 proxy .executor(Executors.newCachedThreadPool())//配置 executor .followRedirects(HttpClient.Redirect.ALWAYS)//配置 followRedirects .cookieManager(new CookieManager())//配置 cookieManager .version(HttpClient.Version.HTTP_2)//配置 version .build();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }说明
由于HttpClient隶属于jdk.incubator.httpclient,所以使用的时候需要添加模块依赖方可执行。 如果你是单个class,没有引入模块概念的话需要在 VM 参数中添加模块支持 --add-modules jdk.incubator.httpclient。如果你引入了模块的概念,需要在 你的module.info中添加 requires jdk.incubator.httpclient;依赖。
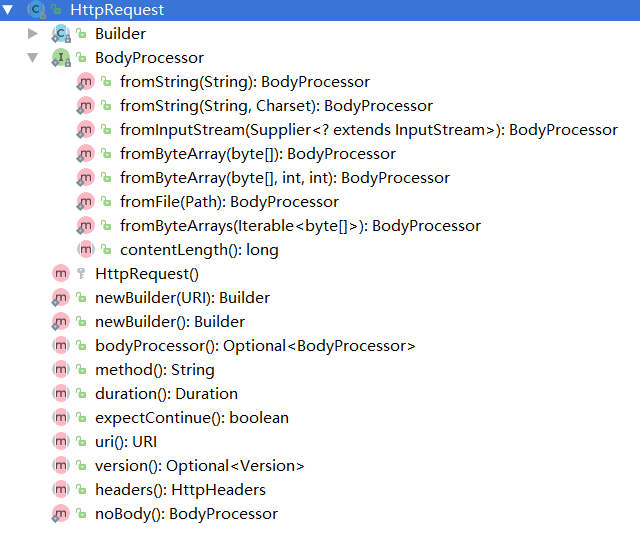
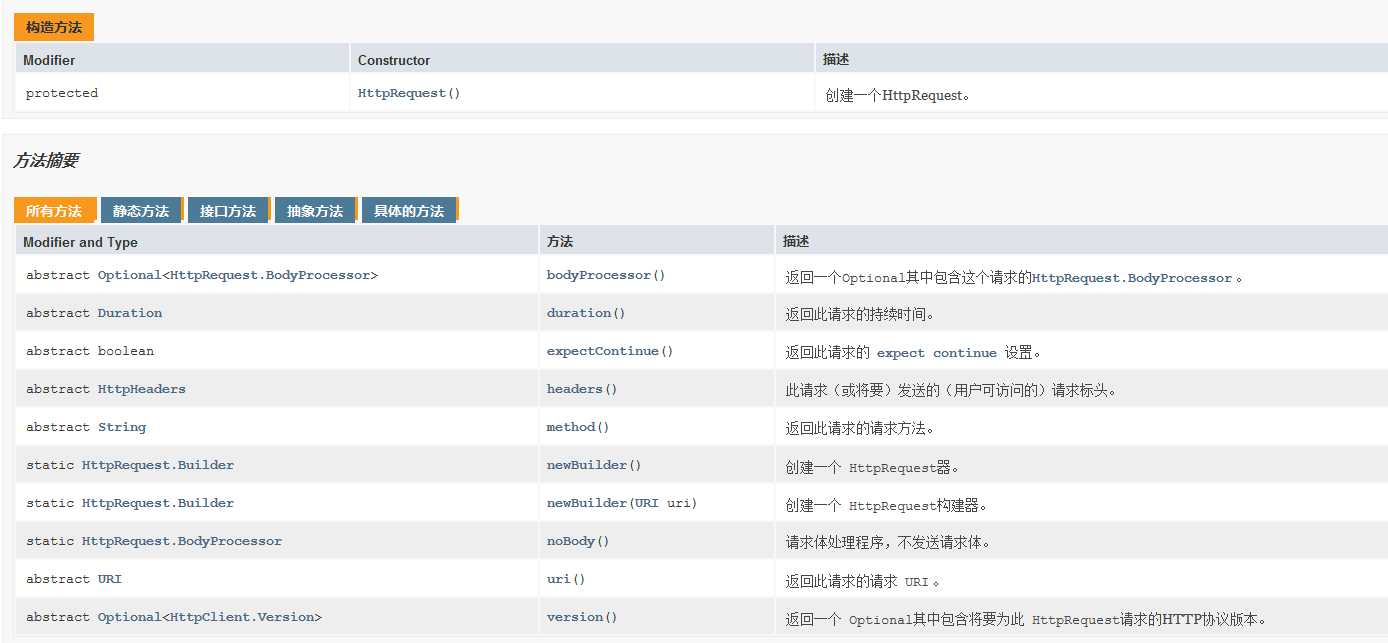
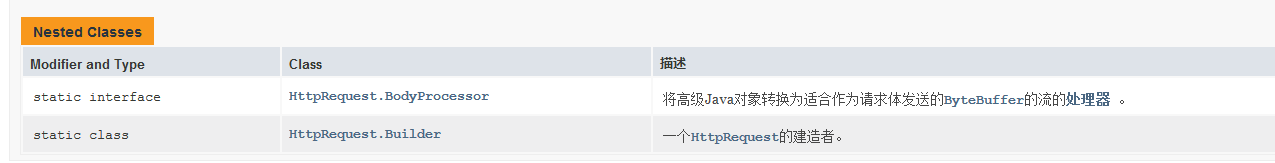
HttpRequest 请求
- API文档说明
表示可以发送到服务器的一个HTTP请求。 HttpRequest由HttpRequest builders构建生成。 HttpRequest通过调用HttpRequest.newBuilder获得实例。 一个请求的URI ,head和body都可以设置。 请求体提供了HttpRequest.BodyProcessor对象的DELETE , POST或PUT方法。 GET不用设置body。 一旦所有必需的参数都在构建器设置, HttpRequest.Builder.build()将返回一个HttpRequest实例 。 构建器也可以被多次复制和修改,以构建参数不同的多个相关请求。
使用示例
- 示例1,GET请求
HttpResponse
response = client.send( HttpRequest .newBuilder(new URI("http://www.foo.com/")) .headers("Foo", "foovalue", "Bar", "barvalue") .GET() .build(), BodyHandler.asString() ); int statusCode = response.statusCode(); String body = response.body(); - 示例2,POST请求。
HttpResponse
response = client.send( HttpRequest .newBuilder(new URI("http://www.foo.com/")) .headers("Foo", "foovalue", "Bar", "barvalue") .POST(BodyProcessor.fromString("Hello world")) .build(), BodyHandler.asFile(Paths.get("/path")) ); int statusCode = response.statusCode(); Path body = response.body(); // should be "/path" }
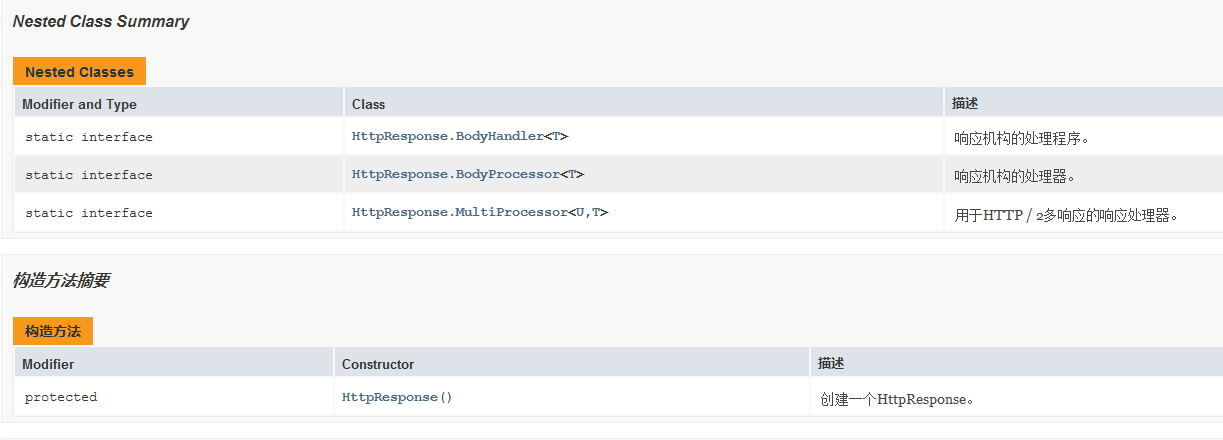
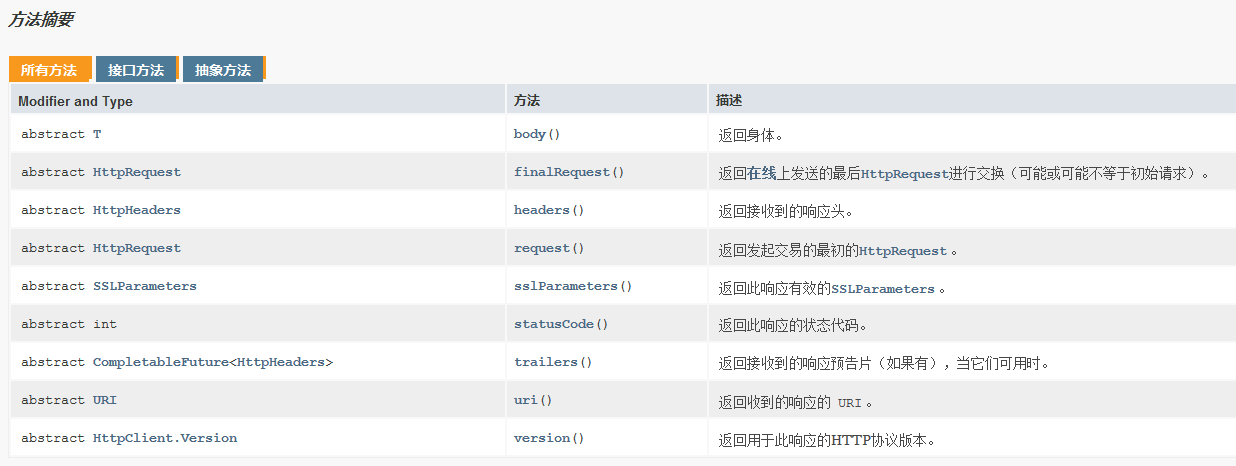
HttpResponse 响应
- API文档说明
表示HttpRequest的响应。 通常在响应正文,响应状态代码和headers被接收之后,HttpResponse才是可用的。 这取决于发送请求时提供的响应体处理程序。 在所有情况下,在Body被读取之前调用response body handler程序。 此类中提供了访问响应头和响应主体的方法。
响应处理程序和处理器
Response bodies有两种处理方式。 应用程序代码提供响应处理程序( HttpResponse.BodyHandler ), 一个是可以检查响应状态代码和头文件, 一个是返回一个HttpResponse.BodyProcessor以实际读取(或丢弃)正文并将其转换为一些有用的Java对象类型。 处理程序可以返回预定义的处理器类型之一或定制处理器, 如果正文被丢弃,则可以调用BodyProcessor.discard()并返回丢弃响应正文的处理器。 处理器和处理器的静态实现分别在BodyHandler和BodyProcessor中提供。 在所有情况下,提供的处理程序功能都是方便的实现, 它忽略了提供的状态代码和头文件,并返回相关的预定义的BodyProcessor 。
使用示例
- 示例1,BodyHandler
HttpResponse
resp = HttpRequest .create(URI.create("http://www.foo.com")) .GET() .response(BodyHandler.asFile(Paths.get("/tmp/f"))); } - 示例2,BodyProcessor。
HttpResponse
resp1 = HttpRequest .create(URI.create("http://www.foo.com")) .GET() .response( (status, headers) -> status == 200 ? BodyProcessor.asFile(Paths.get("/tmp/f")) : BodyProcessor.discard(Paths.get("/NULL"))); }
实战应用
这里是一个完整的示例应用,涵盖了HttpClient,httpRequest,HttpResponse等的使用。
package com.javanine.http;
import jdk.incubator.http.HttpClient; import jdk.incubator.http.HttpRequest; import jdk.incubator.http.HttpResponse; import jdk.incubator.http.MultiMapResult;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext; import javax.net.ssl.SSLParameters; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.*; import java.nio.file.Path; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.time.Duration; import java.util.Optional; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/** * Created by bgt on 2017/10/1. * Java9http示例 *
* VM 参数中添加模块支持 * --add-modules jdk.incubator.httpclient */ public class HttpDemo { // private static HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient(); private static HttpClient client = null;
static {
//这里是httpclient的配置
init();
}
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
// HttpDemo.HttpGet();
HttpDemo.HttpGet2();
}
public static void init(){
try {
Authenticator authenticator=new Authenticator() {
};
client= HttpClient.newBuilder()
.authenticator(authenticator)//配置authenticator
.sslContext(SSLContext.getDefault())//配置 sslContext
.sslParameters(new SSLParameters())//配置 sslParameters
.proxy(ProxySelector.getDefault())//配置 proxy
.executor(Executors.newCachedThreadPool())//配置 executor
.followRedirects(HttpClient.Redirect.ALWAYS)//配置 followRedirects
.cookieManager(new CookieManager())//配置 cookieManager
.version(HttpClient.Version.HTTP\_2)//配置 version
.build();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/\*\*
\* 普通get方式
\*
\*
\* 结果:{
"msg" : "未查询到用户,请认真检查账户或者是否登录",
"success" : false
}
响应码:200
\*/
public static void HttpGet() {
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest
//.newBuilder(URI.create("http://blog.csdn.net/u014042066"))
.newBuilder(URI.create("http://www.rqbao.com/lotteryAward/gettenrecordlist"))
.header("refer", "http://www.oschina.com")//携带的参数
.header("userId", "d3e750db32004972b0ae58f8129f50fc")
.timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2))//2秒过期
.GET()
.build();
getReponse(request);
}
public static void HttpGet2() {
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest
//.newBuilder(URI.create("http://blog.csdn.net/u014042066"))
.newBuilder(URI.create("http://www.rqbao.com/lotteryAward/gettenrecordlist"))
.header("refer", "http://www.oschina.com")//携带的参数
.header("userId", "d3e750db32004972b0ae58f8129f50fc")
.timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2))//2秒过期
.GET()
.build();
getAsyReponse2(request);
}
/\*\*
\* 文件上传
\*/
public static void HttpPost() {
try {
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest
.newBuilder(URI.create("http://blog.csdn.net/u014042066"))
.header("refer", "http://www.oschina.com")
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyProcessor.fromFile(Paths.get("/url.txt")))
.build();
getAsyReponse(request);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/\*\*
\* 携带参数
\*/
public static void HttpPost2() {
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest
.newBuilder(URI.create("http://blog.csdn.net/u014042066"))
.header("refer", "http://www.oschina.com")
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyProcessor.fromString("name=ricky,pwd=123456"))
.build();
getReponse(request);
}
/\*\*
\* 输出响应结果
\* @param request
\* @throws IOException
\* @throws InterruptedException
\*/
public static void getReponse(HttpRequest request) {
HttpResponse<String> response = null;
try {
if (client==null) {
init();
}
response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandler.asString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String result = response.body();
int code = response.statusCode();
if (code == 200) {
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
}
System.out.println("响应码:" + code);
}
/\*\*
\* 输出响应结果 带path形式
\* @param request
\* @throws IOException
\* @throws InterruptedException
\*/
public static void getReponsePath(HttpRequest request) {
HttpResponse<Path> response = null;
try {
client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandler.asFile(Paths.get("/url.text")));
Path body = response.body();
System.out.println(body);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/\*\*
\* 输出响应结果 带path形式的异步
\* @param request
\* @throws IOException
\* @throws InterruptedException
\*/
public static void getAsyReponsePath(HttpRequest request) {
CompletableFuture<Path> response = null;
client
.sendAsync(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandler.asFile(Paths.get("/url.text")))
.thenApply((response1) -> response1.body());
response.join();
}
/\*\*
\* 异步的输出响应结果
\* @param request
\* @throws IOException
\* @throws InterruptedException
\*/
public static void getAsyReponse(HttpRequest request) {
CompletableFuture<HttpResponse<String>> cf;
cf = client.sendAsync(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandler.asString());
HttpResponse<String> response = cf.join();
System.out.println(response.body());
}
/\*\*
\* 异步的输出响应结果
\* @param request
\* @throws IOException
\* @throws InterruptedException
\*/
public static void getAsyReponse2(HttpRequest request) {
MultiMapResult<String> ress;
ress = client.sendAsync(request, HttpResponse.MultiProcessor.asMap((req)-> Optional.of(
HttpResponse.BodyHandler.asString()
))).join();
ress.forEach((req,cf)->{
HttpResponse<String> resp=cf.join();
System.out.println("uri:"+resp.uri()+"---body:"+resp.body());
});
}
}
Java9的HttpClient提供了丰富的功能,这里只是做了个简单的入门与分享,不对之处还望指正。
相关文章
Java9之Shell入门
https://my.oschina.net/u/3048852/blog/1543044
Java9 Module解惑
https://my.oschina.net/u/3048852/blog/1544711
结语
作者: ricky
交流群:244930845