
为了让自己写的代码更优雅且高效,特意向大佬请教了这 10 条 JS 技巧
1. 数组分割
const listChunk = (list = [], chunkSize = 1) => {
const result = [];
const tmp = [...list];
if (!Array.isArray(list) || !Number.isInteger(chunkSize) || chunkSize <= 0) {
return result;
};
while (tmp.length) {
result.push(tmp.splice(0, chunkSize));
};
return result;
};
listChunk(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g']);
// [['a'], ['b'], ['c'], ['d'], ['e'], ['f'], ['g']]
listChunk(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'], 3);
// [['a', 'b', 'c'], ['d', 'e', 'f'], ['g']]
listChunk(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'], 0);
// []
listChunk(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'], -1);
// [] 2. 求数组元素交集
const listIntersection = (firstList, ...args) => {
if (!Array.isArray(firstList) || !args.length) {
return firstList;
}
return firstList.filter(item => args.every(list => list.includes(item)));
};
listIntersection([1, 2], [3, 4]);
// []
listIntersection([2, 2], [3, 4]);
// []
listIntersection([3, 2], [3, 4]);
// [3]
listIntersection([3, 4], [3, 4]);
// [3, 4] 3. 按下标重新组合数组
const zip = (firstList, ...args) => {
if (!Array.isArray(firstList) || !args.length) {
return firstList
};
return firstList.map((value, index) => {
const newArgs = args.map(arg => arg[index]).filter(arg => arg !== undefined);
const newList = [value, ...newArgs];
return newList;
});
};
zip(['a', 'b'], [1, 2], [true, false]);
// [['a', 1, true], ['b', 2, false]]
zip(['a', 'b', 'c'], [1, 2], [true, false]);
// [['a', 1, true], ['b', 2, false], ['c']] 4. 按下标组合数组为对象
const zipObject = (keys, values = {}) => {
const emptyObject = Object.create({});
if (!Array.isArray(keys)) {
return emptyObject;
};
return keys.reduce((acc, cur, index) => {
acc[cur] = values[index];
return acc;
}, emptyObject);
};
zipObject(['a', 'b'], [1, 2])
// { a: 1, b: 2 }
zipObject(['a', 'b'])
// { a: undefined, b: undefined } 5. 检查对象属性的值
const checkValue = (obj = {}, objRule = {}) => {
const isObject = obj => {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Object]';
};
if (!isObject(obj) || !isObject(objRule)) {
return false;
}
return Object.keys(objRule).every(key => objRule[key](obj[key]));
};
const object = { a: 1, b: 2 };
checkValue(object, {
b: n => n > 1,
})
// true
checkValue(object, {
b: n => n > 2,
})
// false 6. 获取对象属性
const get = (obj, path, defaultValue) => {
if (!path) {
return;
};
const pathGroup = Array.isArray(path) ? path : path.match(/([^[.\]])+/g);
return pathGroup.reduce((prevObj, curKey) => prevObj && prevObj[curKey], obj) || defaultValue;
};
const obj1 = { a: { b: 2 } }
const obj2 = { a: [{ bar: { c: 3 } }] }
get(obj1, 'a.b')
// 2
get(obj2, 'a[0].bar.c')
// 3
get(obj2, ['a', '0', 'bar', 'c'])
// 2
get(obj1, 'a.bar.c', 'default')
// default
get(obj1, 'a.bar.c', 'default')
// default 7. 将特殊符号转成字体符号
const escape = str => {
const isString = str => {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(str) === '[string Object]';
};
if (!isString(str)) {
return str;
}
return (str.replace(/&/g, '&')
.replace(/"/g, '"')
.replace(/'/g, ''')
.replace(/</g, '<')
.replace(/>/g, '>')
.replace(/\//g, '/')
.replace(/\\/g, '\')
.replace(/`/g, '`'));
}; 8. 利用注释创建一个事件监听器
class EventEmitter {
#eventTarget;
constructor(content = '') {
const comment = document.createComment(content);
document.documentElement.appendChild(comment);
this.#eventTarget = comment;
}
on(type, listener) {
this.#eventTarget.addEventListener(type, listener);
}
off(type, listener) {
this.#eventTarget.removeEventListener(type, listener);
}
once(type, listener) {
this.#eventTarget.addEventListener(type, listener, { once: true });
}
emit(type, detail) {
const dispatchEvent = new CustomEvent(type, { detail });
this.#eventTarget.dispatchEvent(dispatchEvent);
}
};
const emmiter = new EventEmitter();
emmiter.on('biy', () => {
console.log('hello world');
});
emmiter.emit('biu');
// hello world 9. 生成随机的字符串
const genRandomStr = (len = 1) => {
let result = '';
for (let i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
result += Math.random().toString(36).substr(2)
}
return result.substr(0, len);
}
genRandomStr(3)
// u2d
genRandomStr()
// y
genRandomStr(10)
// qdueun65jb 10. 判断是否是指定的哈希值
const isHash = (type = '', str = '') => {
const isString = str => {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(str) === '[string Object]';
};
if (!isString(type) || !isString(str)) {
return str;
};
const algorithms = {
md5: 32,
md4: 32,
sha1: 40,
sha256: 64,
sha384: 96,
sha512: 128,
ripemd128: 32,
ripemd160: 40,
tiger128: 32,
tiger160: 40,
tiger192: 48,
crc32: 8,
crc32b: 8,
};
const hash = new RegExp(`^[a-fA-F0-9]{${algorithms[type]}}$`);
return hash.test(str);
};
isHash('md5', 'd94f3f016ae679c3008de268209132f2');
// true
isHash('md5', 'q94375dj93458w34');
// false
isHash('sha1', '3ca25ae354e192b26879f651a51d92aa8a34d8d3');
// true
isHash('sha1', 'KYT0bf1c35032a71a14c2f719e5a14c1');
// false 前端面试题汇总
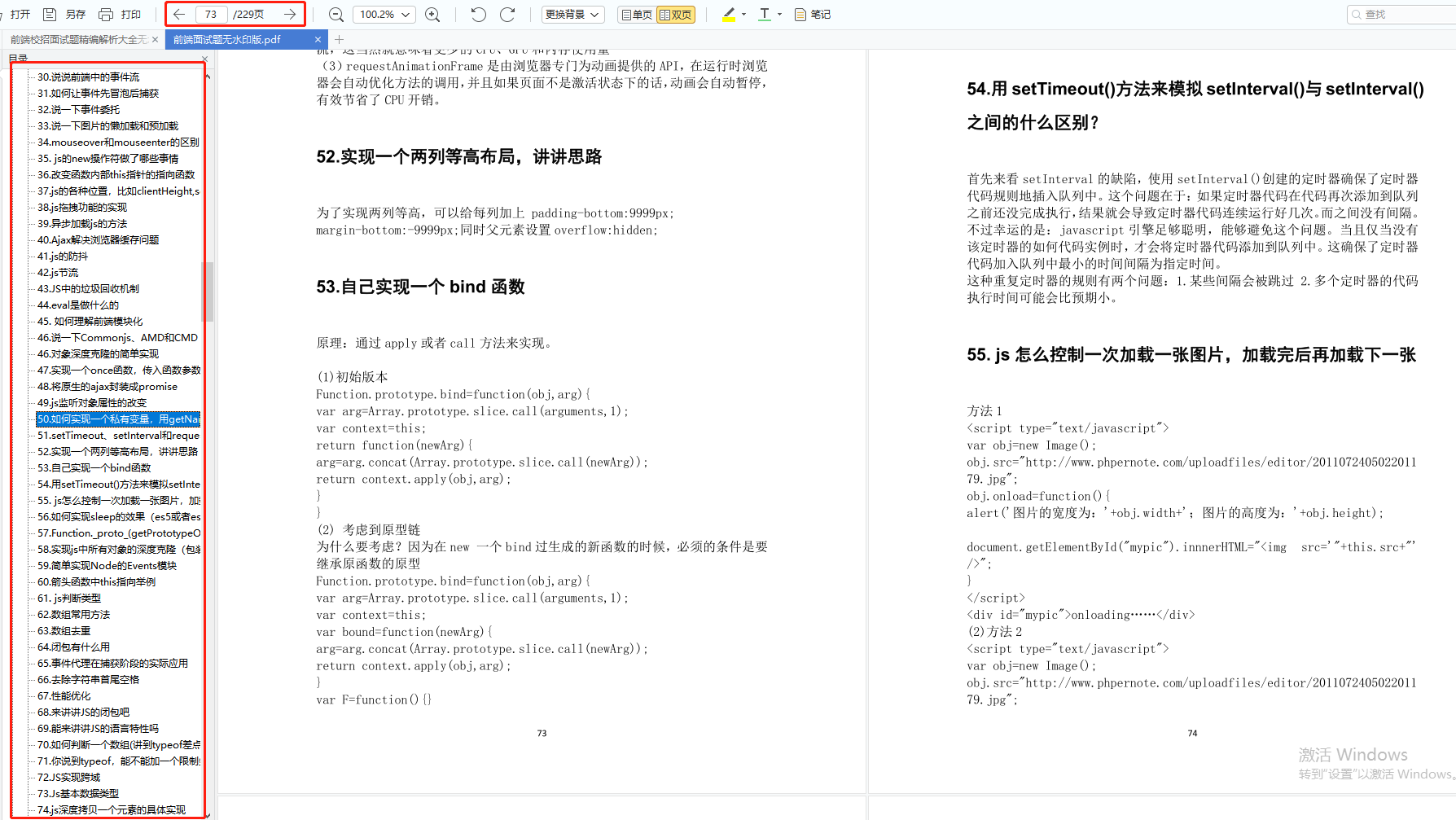
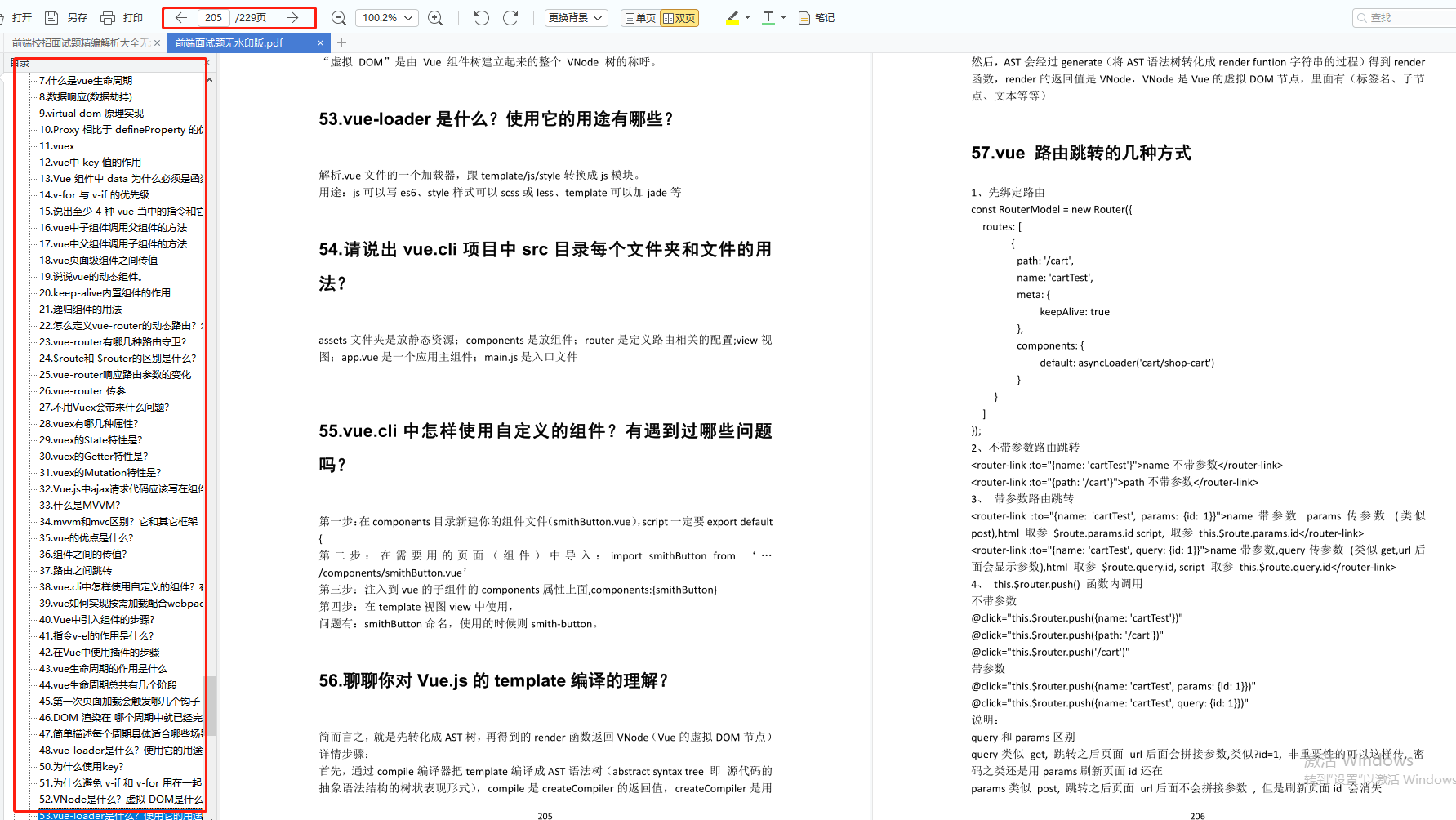
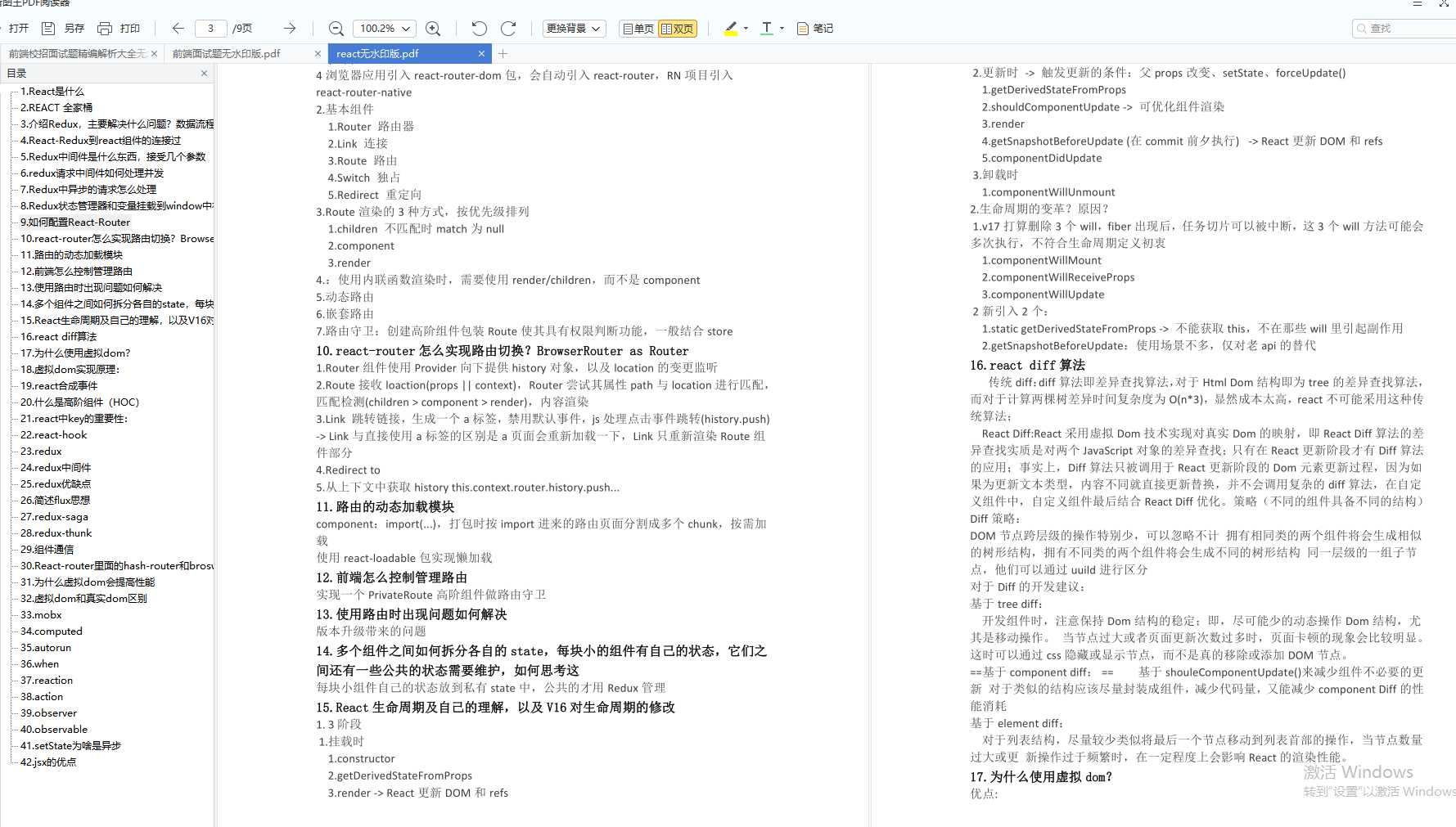
前端面试题是我面试过程中遇到的面试题,每一次面试后我都会复盘总结。我做了一个整理,并且在技术博客找到了专业的解答,大家可以参考下:
想学习前端web的朋友,和需要PDF文档的朋友都可以加入这边的交流裙,前面:938,中间:051,最后:673,裙里从学生到大佬都有,资源免费分享,不见不散哦!
本文转自 https://www.jianshu.com/p/5e0eac374657,如有侵权,请联系删除。













