最近想要学习MOM(消息中间件:Message Oriented Middleware),就从比较基础的activeMQ学起,rabbitMQ、zeroMQ、rocketMQ、Kafka等后续再去学习。
上面说activeMQ是一种消息中间件,可是为什么要使用activeMQ?
在没有使用JMS的时候,很多应用会出现同步通信(客户端发起请求后需要等待服务端返回结果才能继续执行)、客户端服务端耦合、单一点对点(P2P)通信的问题,JMS可以通过面向消息中间件的方式很好的解决了上面的问题。
JMS规范术语:
Provider/MessageProvider:生产者
Consumer/MessageConsumer:消费者
消息形式:
1、点对点(queue)
2、一对多(topic)
ConnectionFactory:连接工厂,JMS用它创建连接
Connnection:JMS Client到JMS Provider的连接
Destination:消息目的地,由Session创建
Session:会话,由Connection创建,实质上就是发送、接受消息的一个线程,因此生产者、消费者都是Session创建的
我这里安装的是Windows版本的,安装好了之后就是这样的目录
到bin目录下,启动activemq.bat
这样就启动成功了。
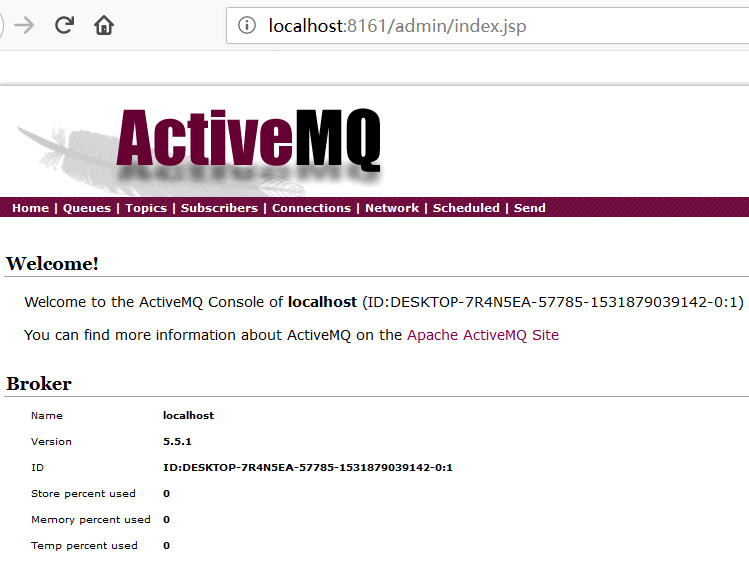
访问http://localhost:8161/admin/index.jsp可以看到管控台,如下图:
spring boot整合activeMQ:
pom.xml中引用
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId>
<artifactId>activemq-pool</artifactId>
<!-- <version>5.7.0</version> -->
</dependency>
在application.properties中配置activeMQ连接:
spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://localhost:61616
spring.activemq.in-memory=true
spring.activemq.pool.enabled=false
创建消息生产者:
/**
* @author huangzhang
* @description
* @date Created in 2018/7/16 18:57
*/
@Service("provider")
public class Provider {
@Autowired
private JmsMessagingTemplate jmsMessagingTemplate;
public void sendMessage(Destination destination, final String message){
jmsMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend(destination,message);
} //消费消费者返回的队列"return.queue"中的消息
@JmsListener(destination="return.queue")
public void consumerMessage(String string){
System.out.println("从return.queue队列收到的回复报文为:"+string);
}
}
创建第一个消费者:
/**
* @author huangzhang
* @description
* @date Created in 2018/7/16 19:31
*/
@Component
public class Consumer {
@JmsListener(destination = "mytest.queue")
public void receiveQueue(String text){
System.out.println("Consumer收到的报文为:"+text);
}
}
创建第二个消费者(这里不光消费了生产者插入队列中的message,而且将返回值插入到了"return.queue"队列中):
/**
* @author huangzhang
* @description
* @date Created in 2018/7/16 19:33
*/
@Component
public class Consumer1 {
@JmsListener(destination = "mytest.queue")
@SendTo("return.queue")
public String receiveQueue(String message){
System.out.println("Consumer1收到的报文为:"+message);
return "========return message "+message;
}
}
测试方法:
@Service
public class SpringbootJmsApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Provider provider;
public void contextLoads() throws InterruptedException {
Destination destination = new ActiveMQQueue("mytest.queue");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
provider.sendMessage(destination, "huangzhang "+i);
}
}
}
这里我在controller中调用了测试方法:
/**
* @author huangzhang
* @description
* @date Created in 2018/7/16 20:23
*/
@Controller
public class Test {
@Autowired
SpringbootJmsApplicationTests springbootJmsApplicationTests;
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String test01()throws Exception{
springbootJmsApplicationTests.contextLoads();
return "success!";
}
}
访问http://localhost:8080/对此demo进行测试

这里是执行结果,可以看出,两个消费者分别消费了生产者放入消息队列中的消息,并且Consumer1消费者将返回结果放入了队列中供生产者消费。
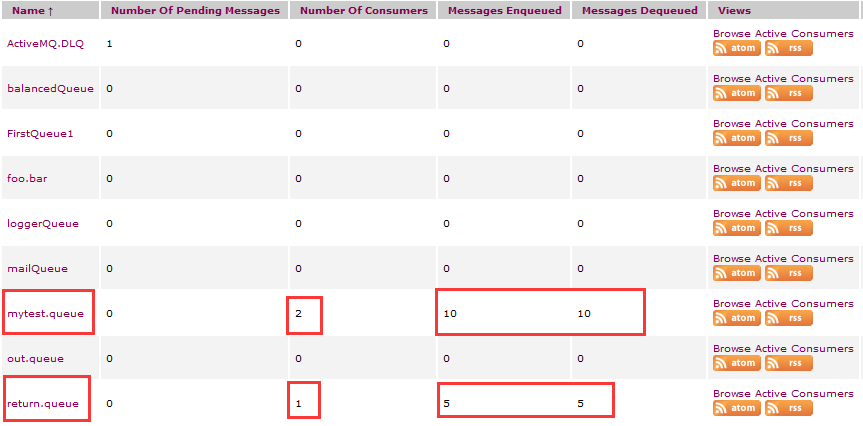
查看Queues
这里可以看出我们生产者循环往mytest.queue队列中写入10次,由两个消费者消费了这10次消息
consumer1消费了5次消息,并往返回队列return.queue中写入5次,由原生产者消费了者5次消息
到这里一个简单的spring boot整合activeMQ的一对一(queue)模式的demo就完成了(请多指正)。
下面我们对provider和consumer进行改造,实现多对多(topic)模式:
对test类进行修改,修改为以下代码:
@Service
public class SpringbootJmsApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Provider provider;
@Autowired
private TopicSender topicSender;
/*public void contextLoads() throws Exception {
Destination destination = new ActiveMQQueue("mytest.queue");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
provider.sendMessage(destination, "huangzhang "+i);
}
}*/
public void topicSend(){
Destination destination = new ActiveMQTopic("test.topic");
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++){
provider.sendMessage(destination, "topic"+i);
}
}
}
订阅者为:
/**
* @author huangzhang
* @description
* @date Created in 2018/7/16 19:31
*/
@Component
public class Consumer {
/*@JmsListener(destination = "mytest.queue")
public void receiveQueue(String text){
System.out.println("Consumer收到的报文为:"+text);
}*/
@JmsListener(destination = "test.topic")
public void receiveQueue1(String text){
System.out.println("Consumer收到的----topic----报文为:"+text);
}
}
两个订阅者修改方式一样。
然后像queue一样,通过controller调用test方法:
/**
* @author huangzhang
* @description
* @date Created in 2018/7/10 20:23
*/
@Controller
public class Test {
@Autowired
SpringbootJmsApplicationTests springbootJmsApplicationTests;
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String test01()throws Exception{
// springbootJmsApplicationTests.contextLoads();
springbootJmsApplicationTests.topicSend();
return "success!";
}
}
同样的启动项目之后调用http://localhost:8080/接口,控制台打印如下:

我们发现,这里consumer和consumer1两个订阅者都收到了10条订阅的"test.topic"消息,再次证明:
生产者发送一条消息到queue,只有一个消费者能收到;
发布者发送到topic的消息,只要订阅了topic的订阅者就会收到消息。















