DispatcherServlet源码分析
SpringMVC核心就是DispatcherServlet,所有得请求都会转发到DispatcherServlet,然后再通过DispatcherServlet执行具体得控制层(Handler)返回ModelAndView给客户端视图展示。
// 3. 将我们的DispatcherServlet 注入到 serlvet容器中 ServletRegistration.Dynamic dynamic = servletContext.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(app)); // 4.填写url路径映射 dynamic.addMapping("/");
DispatcherServlet其实就是一个Servlet类,无非就是包装一层,通过url能够映射找到我们得SpringMvc中定义得请求方法。
源代码分析:
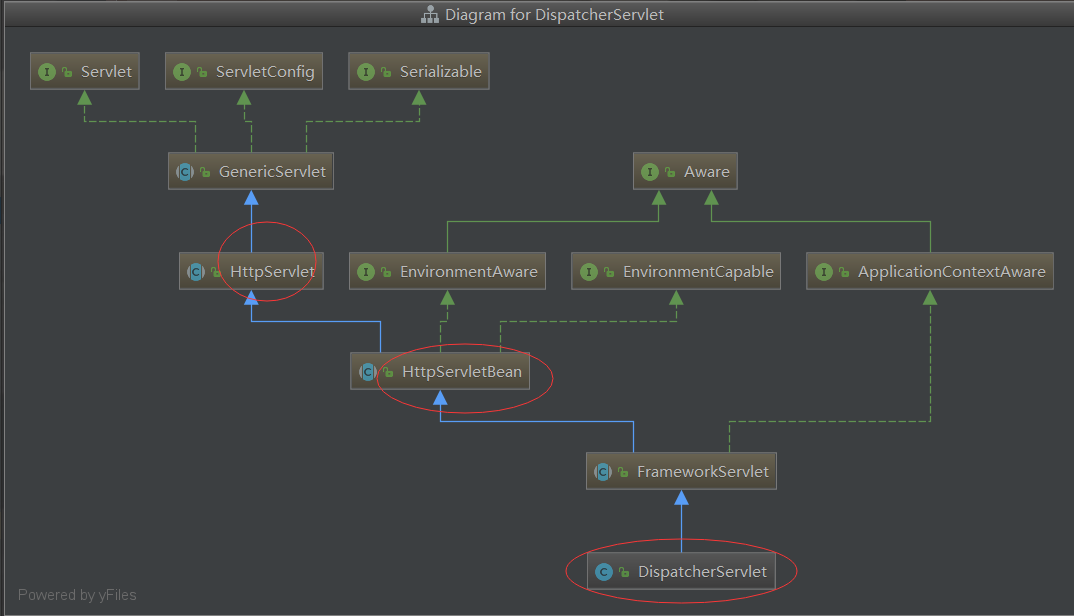
- 类的集成关系
DispatcherServlet继承FrameworkServlet继承HttpServlet
面向基本上思想 重写 先走父类 ,在走子类。
得出答案:先看HttpServlet在找到我们最后的子类
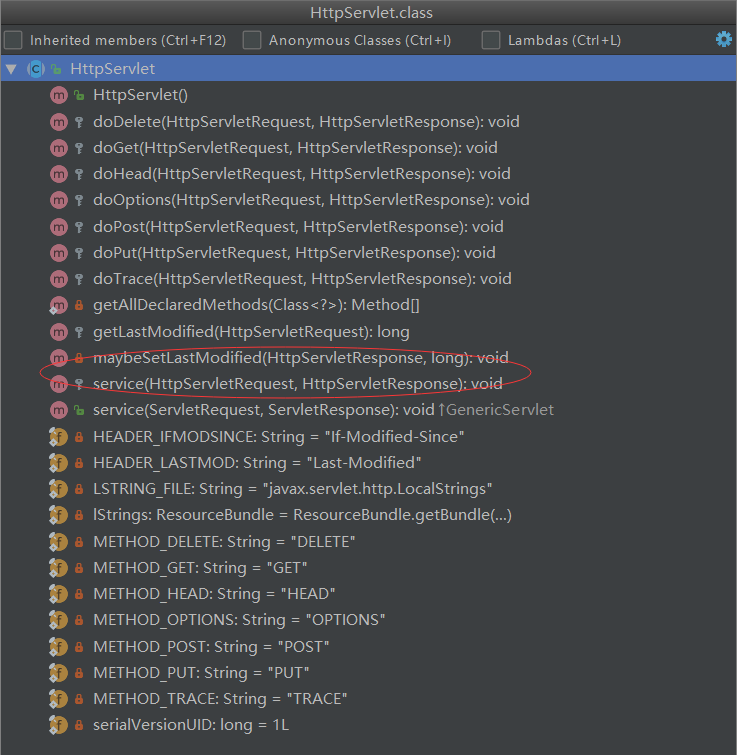
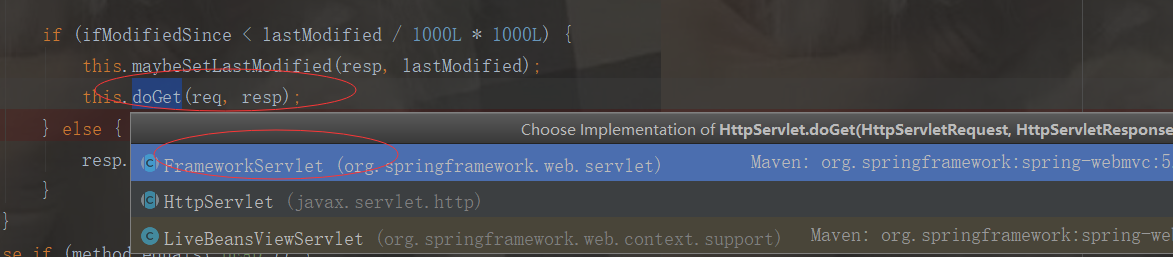
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { this.processRequest(request, response); }
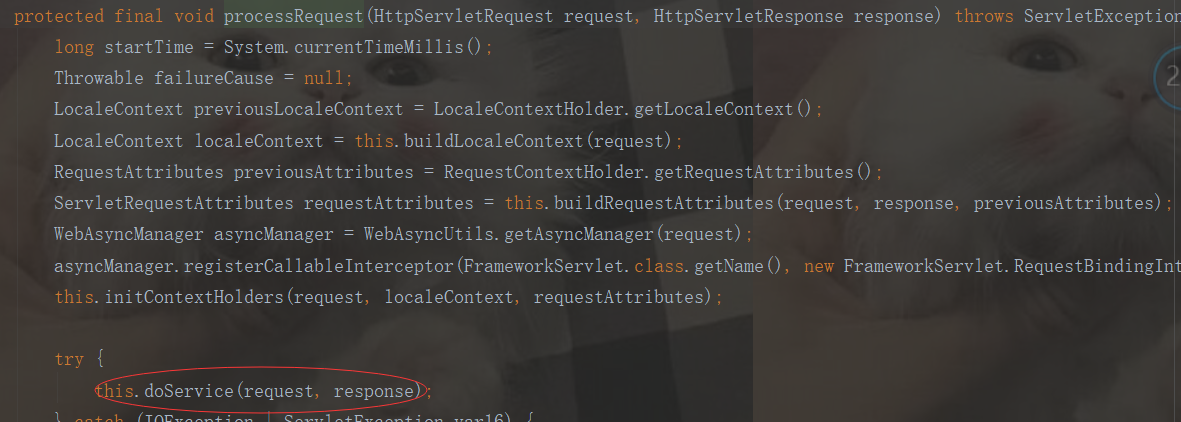
DispatcherServlet与Servlet关系
关系:DispatcherServlet继承FrameworkServlet继承HttpServlet
流程执行关系:
HttpServlet service方法 判断请求方法的类型
FrameworkServlet doService
DispatcherServlet doService
DispatcherServlet的初始化
在servlet初始化阶段会调用其init方法,所以我们首先要查看在DispatcherServlet中是否重写了init方法。我们在其父类HttpServletBean中找到该方法
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware { .... public final void init() throws ServletException { if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'"); } //解析init-param并封装至pvs中 PropertyValues pvs = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { try { //将当前的servlet类转换为一个BeanWrapper,从而能够以Spring的方式来对init-param的值进行注入 BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext()); //注册自定义属性编辑器,一旦遇到Resource类型的属性会使用ResourceEditor进行解析 bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment())); //空实现,留给子类覆盖 this.initBeanWrapper(bw); //属性注入 bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException var4) { if (this.logger.isErrorEnabled()) { this.logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'", var4); }
throw var4;
}
}
//留给子类扩展 this.initServletBean(); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); }
}
.... }
DispatcherServlet的初始化过程主要是通过将当前的Servlet类型实例转换为BeanWrapper类型实例,以便使用Spring中提供的注入功能进行对应属性的注入。
我们看下servletBean的初始化,HttpServletBean其父类FrameworkServlet覆盖了它的initServletBean函数,如下:
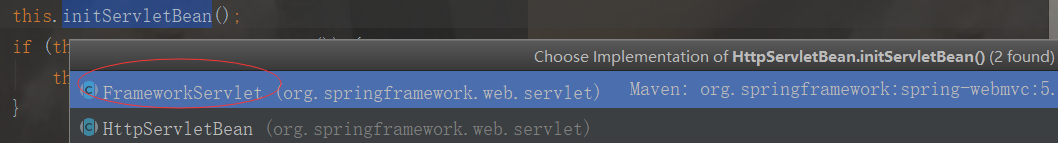
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { this.getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization started"); } //计时器,统计初始化的执行时间 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//关键的初始化逻辑委托给了这个方法 this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext(); //设计为子类覆盖 this.initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (RuntimeException | ServletException var5) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var5); throw var5; }
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
WebApplicationContext 的初始化
initWebApplicationContext函数主要工作就是创建或者刷新****WebApplicationContext 实例并对servlet功能所使用的变量进行初始化
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { //context实例在构造函数中被注入 wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } //刷新上下文环境 this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } }
if (wac == null) {
//根据contextAttribute属性加载webApplicationContext wac = this.findWebApplicationContext(); }
if (wac == null) {
wac = this.**createWebApplicationContext**(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
this.**onRefresh**(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = this.getServletContextAttributeName();
this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name \[" + attrName + "\]");
}
}
return wac;
}
刷新方法onRefresh
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { this.initStrategies(context); }
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context); //初始化上传文件解析器(或者是多部分请求解析器)
initLocaleResolver(context);//初始化本地化解析器
initThemeResolver(context);//初始化主题解析器
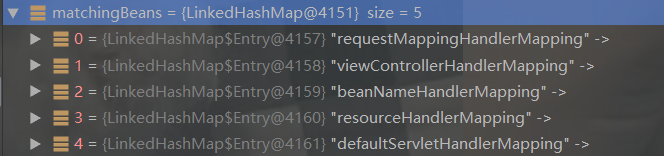
initHandlerMappings(context);//初始化处理器映射器
initHandlerAdapters(context);//初始化处理器适配器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);//初始化处理器异常解析器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);//初始化请求到视图名翻译器
initViewResolvers(context);//初始化视图解析器
initFlashMapManager(context);//初始化重定向数据管理器
}
DispatcherServlet的逻辑处理
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { ... try { try { ... //通过url路径地址去查找控制层类方法,如果没有找到的化,直接返回404 mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest); .... HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); .... if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; }
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
....
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
.... }
SpringMVC源码之定位Handler原理
private List
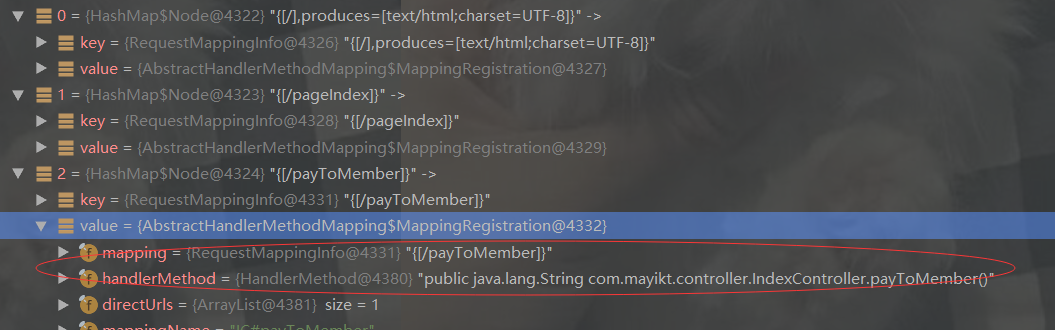
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
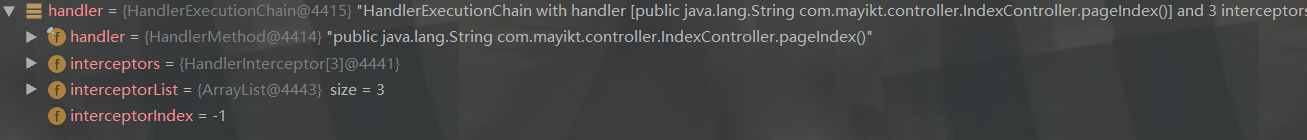
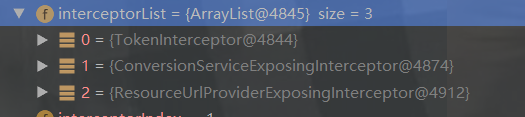
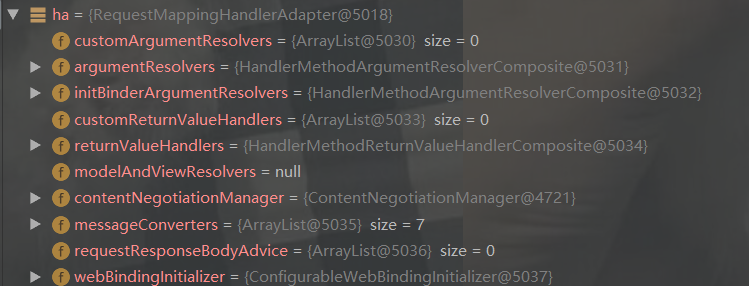
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; }
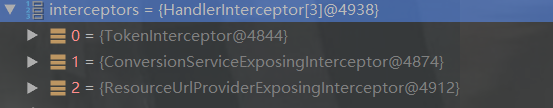
/** * 请求方法前置拦截,如果返回true 表示会执行到目标方法(请求方法) 如果返回false的情况下 则不会执行目标方法。 */ @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { String token = request.getParameter("token"); System.out.println(">>>>token<<<<:" + token); if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { response.setStatus(500); response.getWriter().print(" token is null"); return false; } // 执行我们的请求方法 return true; }
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
执行目标方法:
@RequestMapping("/pageIndex") public String pageIndex() { System.out.println(">>>pageIndex<<<<"); return "pageIndex"; }
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
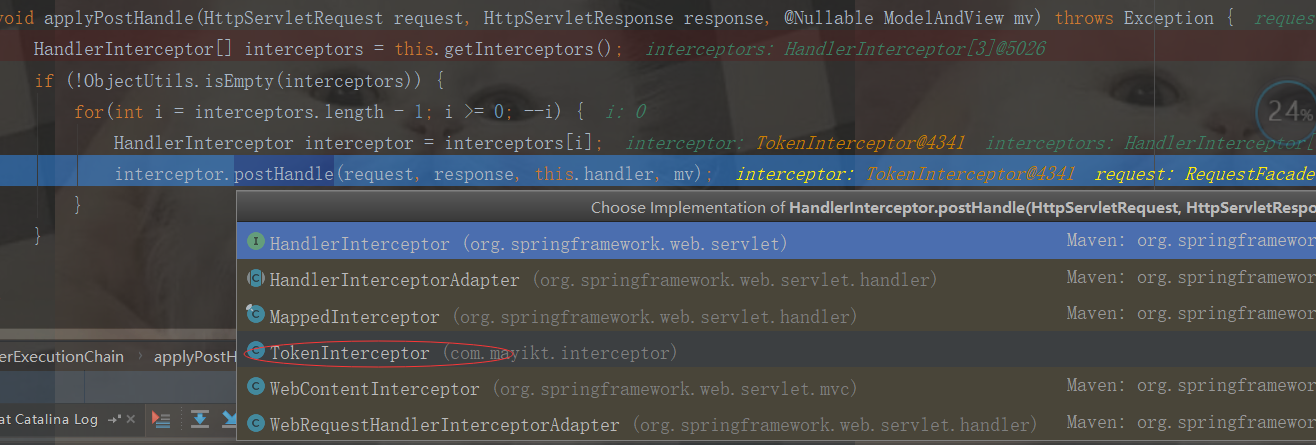
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("<<
DispatcherServlet源码流程分析
1.执行doDispatch
2.调用getHandler方法获取请求目标的方法 也就是 请求url映射路径对应的控制层具体的方法
handlerMappings的作用查找控制器位置,比如xml和注解方式。
3.调用getHandlerAdapter获取控制层适配器 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
4.执行拦截器前置方法 preHandle() 如果返回为true的话
5.执行实际请求目标方法 返回modeAndView对象
6.执行拦截器PostHandle()方法
7.设置渲染视图层内容
8.执行拦截器afterCompletion方
SpringMVC控制层容器初始化
- HttpServletBean init ()方法
- FrameworkServlet initServletBean方法→ initWebApplicationContext();
- DispatcherServlet onRefresh方法→ initStrategies()方法
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { this.initStrategies(context); }
当我们servlet容器初始化的时候初始化
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
本文参考
参考数据:Spring源码深度解析
蚂蚁课堂















