一:源码分析代码片段
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 基本mybatis环境
// 1.定义mybatis\_config文件地址
String resources = "mybatis\_config.xml";
// 2.获取InputStreamReaderIo流
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resources);
// 3.获取SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
// 4.获取Session
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 5.操作Mapper接口
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserEntity user = mapper.getUser(2);
System.out.println(user.getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
首先对步骤2进行分析
// 2.获取InputStreamReaderIo流
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resources);
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(String resource) throws IOException { InputStreamReader reader; if (charset == null) { reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource)); } else { reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource), charset); }
return reader;
}
通过上述代码可知:使用了门面模式:定义了Resource类,把复杂过程封装起来,方便用户使用,返回reader为InputStreamReader,指的是读取的mybatis_config.xml文件,断点调试结果如下:
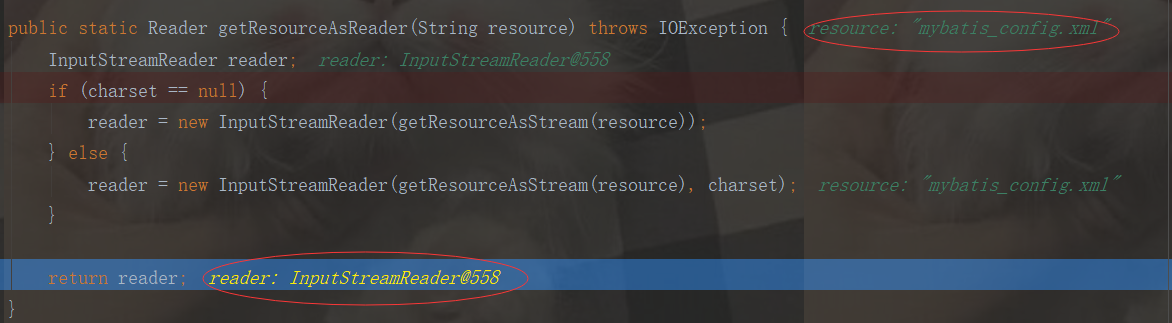
第三步源码分析
// 3.获取SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
进入SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()构造函数如下:
public SqlSessionFactoryBuilder() { }
可知,无参构造函数没用做任何事情,再进入build(reader)源码,reader参数为InputStream流
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) { return this.build((Reader)reader, (String)null, (Properties)null); }
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { SqlSessionFactory var5; try { XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties); var5 = this.build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception var14) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", var14); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException var13) {
;
}
}
return var5;
}
我们来分析下XMLConfigBuilder这个类是干嘛的,进入XMLConfigBuilder构造函数如下:
public XMLConfigBuilder(Reader reader, String environment, Properties props) { this(new XPathParser(reader, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props); }
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) { super(new Configuration()); this.localReflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory(); ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration"); this.configuration.setVariables(props); this.parsed = false; this.environment = environment; this.parser = parser; }
进入super()代码如下:
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) { this.configuration = configuration; this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry(); this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); }
通过上述代码可知:this.parsed = false;后面有用,这里先提下。返回原先执行处:var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
进入parser.parse()这个方法,代码如下:
public Configuration parse() { if (this.parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } else { this.parsed = true; this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return this.configuration; } }
由前面设置了this.parsed = false,可知this.parsed为false,就进入else分支,读者这个时候就有疑问了,为啥要设置this.parsed = false呢?
我们通过else分支可知,又设置了 this.parsed = true;说明再下一次再次进入parse方法的时候,this.parsed=true会直接抛出异常。
这里我们可以总结下:
为什么XMLConfigBuilder只能被使用一次呢?
答:因为我们的Configuration是一个全局的,所以只能被解析一次。
多次解析的话,会抛出:Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.异常,防止用户私自调用parse()方法再去重复解析,因为配置文件是全局的,不能多次解析。
进入else分支的下面这个代码中:
this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { this.propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); this.typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); this.pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); this.objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); this.objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); this.reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory")); this.settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings")); this.environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); this.databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); this.typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception var3) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + var3, var3); } }
我们先看看mybatis_config.xml配置文件的内容:
我们先进入下面这行代码:因为这个environments在我们配置文件中配置了,我们先分析它:
this.environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"))
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { if (this.environment == null) { this.environment = context.getStringAttribute("default"); } Iterator i$ = context.getChildren().iterator(); while(i$.hasNext()) { XNode child = (XNode)i$.next(); String id = child.getStringAttribute("id"); if (this.isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) { TransactionFactory txFactory = this.transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager")); DataSourceFactory dsFactory = this.dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource")); DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource(); Builder environmentBuilder = (new Builder(id)).transactionFactory(txFactory).dataSource(dataSource); this.configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build()); } } } }
通过断点调试environmentsElement()代码结果如下:
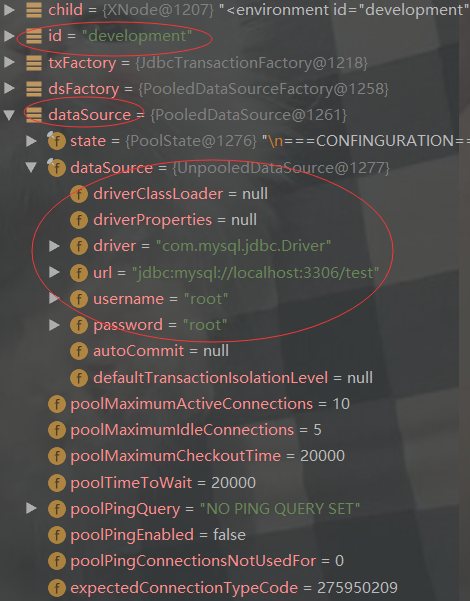
我们看下这段代码:
this.configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { this.environment = environment; }
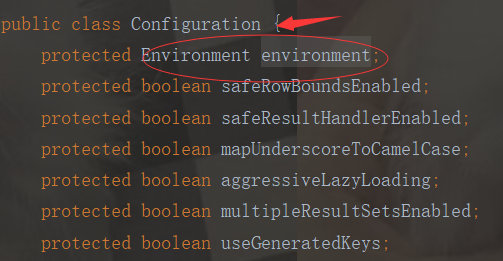
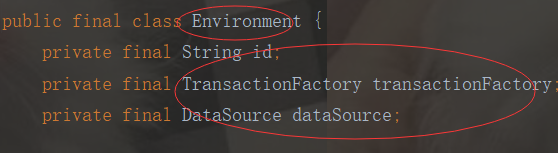
到这里我们就明白了:这里将解析的XML结点封装成Environment对象,再把Environment对象设置给Configuration对象中。也就是解析XML,再把XML转为Configuration实体类
到这里我们再来分析:mappers结点在配置文件中配置了,我们也来分析下,下面是mapper.xml配置文件的内容,看下是如何转化为实体对象保存起来的:
this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { Iterator i$ = parent.getChildren().iterator(); while(true) { while(i$.hasNext()) { XNode child = (XNode)i$.next(); String resource; if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { //注解方式配置扫包package resource = child.getStringAttribute("name"); this.configuration.addMappers(resource); } else { //resource 方式 resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url"); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class"); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser; InputStream inputStream; if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, this.configuration, resource, this.configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, this.configuration, url, this.configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else { if (resource != null || url != null || mapperClass == null) { throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one."); } Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); this.configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } } } return; } } }
通过上述代码可知,配置方式有两种:一种是注解形式扫包,第二种是resource方式
我们是resource方式的配置,所以进入else分支:
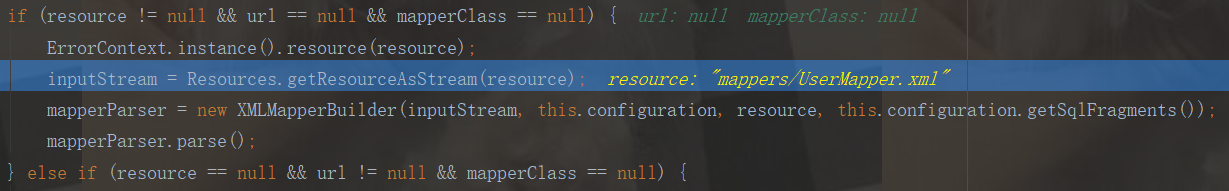
由上面断点分析可知,这里会读取mapper.xml配置文件的内容,转化为inputStream流,再解析mapper.xml配置文件
XMLMapperBuilder类的作用:解析mapper配置文件得到Configuration对象,我们看下XMLMapperBuilder怎么去解析mapper配置文件
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) { this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), configuration, resource, sqlFragments); }
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) { super(configuration); this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource); this.parser = parser; this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments; this.resource = resource; }
最终进入:
mapperParser.parse()
public void parse() { if (!this.configuration.isResourceLoaded(this.resource)) { this.configurationElement(this.parser.evalNode("/mapper")); this.configuration.addLoadedResource(this.resource); this.bindMapperForNamespace(); }
进入addLoadedResource()方法:
public void addLoadedResource(String resource) { this.loadedResources.add(resource); }
protected final Set
public Configuration() { this.loadedResources = new HashSet(); }
通过上述代码可知:loadedResources存放的都是mybatis映射的文件路径地址【mapper.xml】, 使用HashSet集合存放
存放进去之后,断点如下:
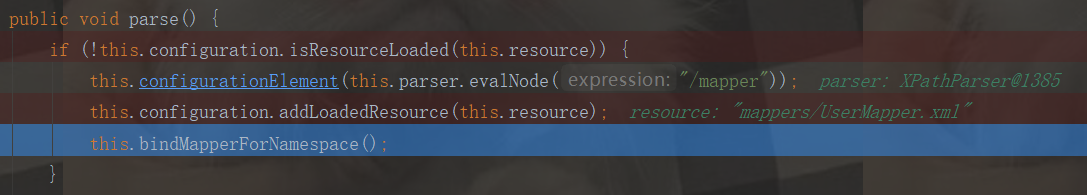
我们进入下面这个方法:
this.bindMapperForNamespace();
private void bindMapperForNamespace() { String namespace = this.builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(); //拿到mapper.xml里面配置的namespace,这里是com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper if (namespace != null) { Class boundType = null; try { boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace); //通过Java反射机制帮我去查找,这里得到interface com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper } catch (ClassNotFoundException var4) { ; } if (boundType != null && !this.configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {//判断mapper.xml配置文件是否注册过 this.configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace); this.configuration.addMapper(boundType); } } }
先看看addMapper方法:
this.configuration.addMapper(boundType);
public
public
this.knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
private final Map<Class, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap();
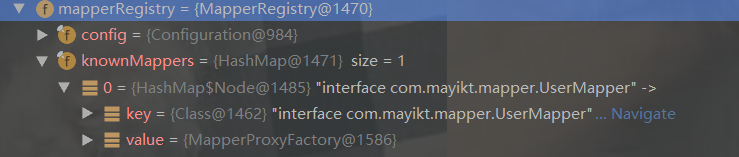
由上述代码可知:mapperRegistry作用是:存放dao层mapper接口,debug结果如下:
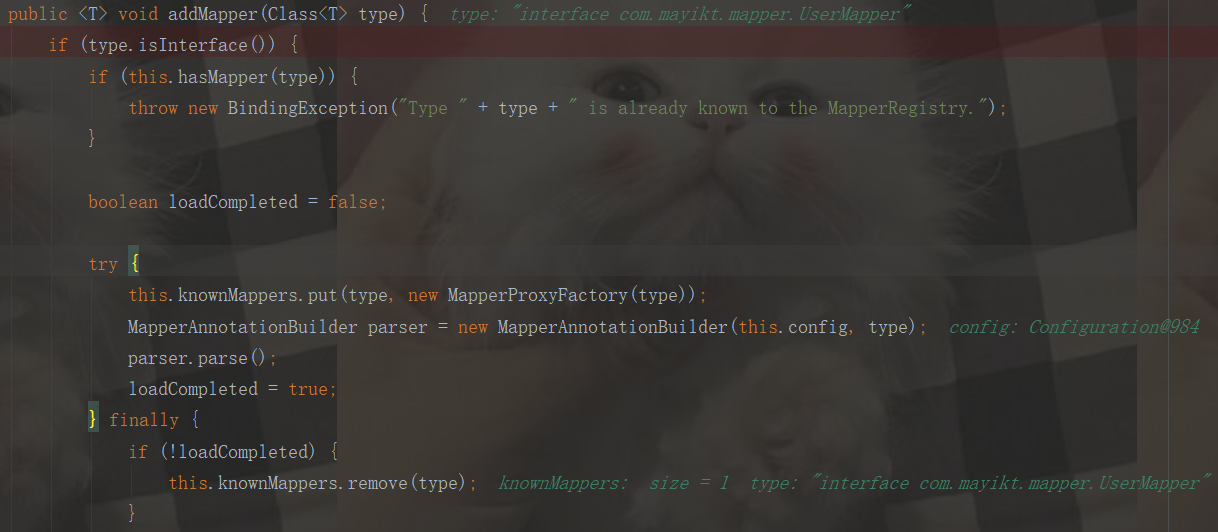
最后,我们来看看loadedResources里面的东西:存放的是userMapper的配置文件
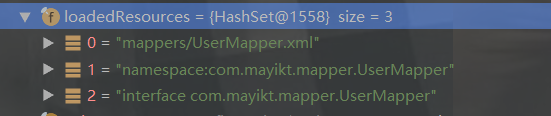
再看看mapperRegistery里面的东西:存放的是mapper接口
最后,我们回到开始的parse()方法,上述代码执行完this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration"))方法之后,返回configuration对象
public Configuration parse() { if (this.parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } else { this.parsed = true; this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return this.configuration; } }
到这里,我们就结束了源码分析,下面总结下大体流程:
总结:
获取本地InputStreamReader对象(mybatis配置文件)
调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
###再使用XMLConfigBuilder解析mybatis配置文件,装配到Configuration中。
将配置文件中的Mapper添加到Configuration mapperRegistry实现注册。
备注:mapperRegistry存放当前所有的mapper接口。
loadedResources里面的东西:存放的是userMapper的配置文件
本文参考














