Logstash数据处理工具
具有实时渠道能力的数据收集引擎,包含输入、过滤、输出模块,一般在过滤模块中做日志格式化的解析工作
日志信息-->logstsh-->json形式
mysql\ hbase\ ES-->logstsh(select * from user)-->ES
logstsh架构 比较耗费性能
搜集--->过滤--->处理
Grok:匹配需要收集的字段信息
Date:处理日期类型
Geoip:添加地理位置信息
Useragent:提取请求用户信息
input | 过滤组件(Grok正则匹配,)| -输出
ES("username")--->logstsh---ES
select * from user
kris1 smile alex
|
logstsh(input/filter)
input(kris1 event smile event alex event) queue队列
filter
input(kris1 event smile event alex event) queue队列
logstash安装
[root@localhost logstash]# tar -zxvf logstash-6.3.1.tar.gz
创建config目录目的-->自定义过滤文件和插件,保存配置文件信息
[elk@localhost logstash]$ mkdir config
[elk@localhost config]$ pwd
/home/elk/logstash/config
写这个小型配置/脚本;必须包含3部分;
①.2
按换行方式输入,输出以json的形式:
[elk@localhost config]$ vi test1.conf
input {
stdin {codec=>line}
}
output {
stdout {codec=>json}
}
heihei
{"message":"heihei","@timestamp":"2019-03-26T03:05:35.750Z","@version":"1","host":"localhost.localdomain"}
hello alex
{"message":"hello alex","@timestamp":"2019-03-26T03:06:11.283Z","@version":"1","host":"localhost.localdomain"}
③
Stdin
输入插件:可以管道输入,也可以从终端交互输入(前两个都是终端交互输入)
通用配置:
codec:类型为codec
type:类型为string自定义该事件类型,可用于后续判断
tags:类型为array,自定义事件的tag,可用于后续判断
add_field:类型为hash,为该事件添加字段
以管道方式输入
[elk@localhost config]$ echo "bar\nfoo" | ../logstash-6.3.1/bin/logstash -f test1.conf
{"@timestamp":"2019-03-25T12:22:43.534Z","host":"localhost.localdomain","message":"bar\\nfoo","@version":"1"}
④
输入输出,接收方式
以管道方式灌入数据
type是又添加一个字段,add_field是随机添加一个k v键值对;
[elk@localhost config]$ vi test2.conf
input{
stdin{
codec => "plain"
tags => ["test"]
type => "std"
add_field => {"key" => "value"}}
}
output{
stdout{
codec => "rubydebug"}
}
[elk@localhost config]$ ../logstash-6.3.1/bin/logstash -f ./test2.conf
Hello
{
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-27T00:42:18.166Z,
"@version" => "1",
"key" => "value",
"tags" => [
[0] "test"
],
"host" => "localhost.localdomain",
"type" => "std",
"message" => "Hello"
}
⑥ Elasticsearch 读取ES中的数据
哪个索引中有数据
从一个ES去同步到另外一个ES中就可以使用logstash去同步
[elk@localhost config]$ vi es.conf
input {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.1.101"
index => "kris"
query => '{"query": {"match_all": {} }}'
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
[elk@localhost config]$ ../logstash-6.3.1/bin/logstash -f ./es.conf
{
"@version" => "1",
"job" => "java senior engineer and java specialist",
"isMarried" => true,
"birth" => "1980-05-07",
"age" => 28,
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-25T13:15:27.762Z,
"username" => "alfred"
}
{
"@version" => "1",
"job" => "ruby engineer",
"isMarried" => false,
"birth" => "1986-08-07",
"age" => 23,
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-25T13:15:27.789Z,
"username" => "lee junior way"
}
{
"@version" => "1",
"job" => "java engineer",
"isMarried" => false,
"birth" => "1991-12-15",
"age" => 18,
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-25T13:15:27.790Z,
"username" => "alfred way"
}
{
"@version" => "1",
"job" => "java and ruby engineer",
"isMarried" => false,
"birth" => "1985-08-07",
"age" => 22,
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-25T13:15:27.790Z,
"username" => "lee"
}
logstsh filter
Filter是logstsh功能强大的原因,它可以对数据进行丰富的处理,比如解析数据、删除字段、类型转换等
date:日期解析
grok:正则匹配解析
dissect:分割符解析
mutate:对字段作处理,比如重命名、删除、替换等
json:按照json解析字段内容到指定字段中
geoip:增加地理位置数据
ruby:利用ruby代码来动态修改logstsh Event
[elk@localhost config]$ vi filter.conf
input {
stdin {codec => "json"}
}
filter {
date {
match => ["logdate","MM dd yyyy HH:mm:ss"]
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
[elk@localhost config]$ ../logstash-6.3.1/bin/logstash -f ./filter.conf
jing
[2019-03-25T23:51:09,341][WARN ][logstash.codecs.jsonlines] JSON parse error, original data now in message field {:error=>#<LogStash::Json::ParserError: Unrecognized token 'jing': was expecting ('true', 'false' or 'null')
at [Source: (String)"jing"; line: 1, column: 9]>, :data=>"jing"}
{
"host" => "localhost.localdomain",
"message" => "jing",
"@version" => "1",
"tags" => [
[0] "_jsonparsefailure"
],
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-26T03:51:09.375Z
}
Grok 正则匹配
93.180.71.3 - - [17/May/2015:08:05:32 +0000] "GET /downloads/product_1 HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)"
[0-9]+.[0-9]+.[0-9].[0-9](93.180.71.3)+ ? ? []...最终把它转换成(已经封装好的正则)
%{IPORHOST:clientip} %{USER:ident} %{USER:auth} \[%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}\] “%{WORD:verb} %{DATA:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion}” %{NUMBER:response:int} (?:-|%{NUMBER:bytes:int}) %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent}
形成json格式,message接收到的;clientip、ident、auth、timestamp等这些字段;
input接收hhttp7474端口
93.180.71.3 - - [17/May/2015:08:05:32 +0000] "GET /downloads/product_1 HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)"
93.180.71.3 - - [17/May/2015:08:05:23 +0000] "GET /downloads/product_1 HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Debian APT-HTTP/1.3 (0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)"
%{IPORHOST:clientip} %{USER:ident} %{USER:auth} \[%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}\] “%{WORD:verb} %{DATA:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion}” %{NUMBER:response:int} (?:-|%{NUMBER:bytes:int}) %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent}
[elk@localhost config]$vi grok.conf ##加\进行转义;
input {
http {port => 7474}
}
filter {
grok {
match => {
"message" => "%{IPORHOST:clientip} %{USER:ident} %{USER:auth} \[%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}\] \"%{WORD:verb} %{DATA:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion}\" %{NUMBER:response:int} (?:-|%{NUMBER:bytes:int}) %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent}"
}
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
[elk@localhost config]$ ../logstash-6.3.1/bin/logstash -f ./grok.conf
发送7474端口的GET请求:
http://192.168.1.101:7474/93.180.71.3%20-%20-%20[17/May/2015:08:05:32%20+0000]%20%22GET%20/downloads/product_1%20HTTP/1.1%22%20304%200%20%22-%22%20%22Debian%20APT-HTTP/1.3%20(0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)%22
{
"message" => "",
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-26T07:07:03.183Z,
"host" => "192.168.1.5",
"tags" => [
[0] "_grokparsefailure"
],
"@version" => "1",
"headers" => {
"http_host" => "192.168.1.101:7474",
"http_user_agent" => "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36",
"http_accept_language" => "zh-CN,zh;q=0.9",
"http_accept_encoding" => "gzip, deflate",
"http_version" => "HTTP/1.1",
"http_accept" => "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8",
"request_uri" => "/93.180.71.3%20-%20-%20[17/May/2015:08:05:32%20+0000]%20%22GET%20/downloads/product_1%20HTTP/1.1%22%20304%200%20%22-%22%20%22Debian%20APT-HTTP/1.3%20(0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)%22",
"http_connection" => "keep-alive",
"request_path" => "/93.180.71.3%20-%20-%20[17/May/2015:08:05:32%20+0000]%20%22GET%20/downloads/product_1%20HTTP/1.1%22%20304%200%20%22-%22%20%22Debian%20APT-HTTP/1.3%20(0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)%22",
"request_method" => "GET",
"http_upgrade_insecure_requests" => "1"
}
}
{
"message" => "",
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-26T07:07:03.403Z,
"host" => "192.168.1.5",
"tags" => [
[0] "_grokparsefailure"
],
"@version" => "1",
"headers" => {
"http_host" => "192.168.1.101:7474",
"http_user_agent" => "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36",
"http_referer" => "http://192.168.1.101:7474/93.180.71.3%20-%20-%20[17/May/2015:08:05:32%20+0000]%20%22GET%20/downloads/product_1%20HTTP/1.1%22%20304%200%20%22-%22%20%22Debian%20APT-HTTP/1.3%20(0.8.16~exp12ubuntu10.21)%22",
"http_accept_language" => "zh-CN,zh;q=0.9",
"http_accept_encoding" => "gzip, deflate",
"http_version" => "HTTP/1.1",
"http_accept" => "image/webp,image/apng,image/*,*/*;q=0.8",
"request_uri" => "/favicon.ico",
"http_connection" => "keep-alive",
"request_path" => "/favicon.ico",
"request_method" => "GET"
}
}
百度echart
https://echarts.baidu.com/echarts2/doc/example.html
数据可视化演示实战
l 需求:
收集Elasticserach集群的查询语句
分析查询语句的常用语句、响应时长等
l 方案
数据收集:Packetbeat+logstash
数据分析:Kibana+Elasticsearch
准备
l Production Cluster(生产环境)
1、Elasticsearch 192.168.14.13:9200
2、Kibana 192.168.14.15:5601
l Monitoring Cluster(监控环境)
1、Elasticsearch 192.168.14.16:8200
2、Kibana 192.168.14.16:8601
l Logstash\packetbeat
nginx -->log
↓
javaee logstash--->es-->kibana
1.tomcat-->web
2.nginx
3.logstash
4.es
5.kibana
101 102
es tomcat
kibana nginx
logstash
l 启动数据采集集群
启动ES: ./elasticsearch
./kibana #启动
l 启动数据分析集群
(1)启动ES
(2)启动logstash
安装tomcat,把java的web项目manager-test上传到webapps中;
[elk@localhost tomcat]$ ll
drwxrwxr-x. 9 elk elk 160 Mar 25 13:02 apache-tomcat-7.0.47
[elk@localhost tomcat]$ tar -zxvf /home/elk/soft/apache-tomcat-7.0.47.tar.gz -C ./tomcat/
[elk@localhost apache-tomcat-7.0.47]$ bin/startup.sh
Using CATALINA_BASE: /home/elk/tomcat/apache-tomcat-7.0.47
Using CATALINA_HOME: /home/elk/tomcat/apache-tomcat-7.0.47
Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /home/elk/tomcat/apache-tomcat-7.0.47/temp
Using JRE_HOME: /home/elk/jdk/jdk1.8.0_171/jre
Using CLASSPATH: /home/elk/tomcat/apache-tomcat-7.0.47/bin/bootstrap.jar:/home/elk/tomcat/apache-tomcat-7.0.47/bin/tomcat-juli.jar
http://192.168.1.102:8080/
[elk@localhost apache-tomcat-7.0.47]$ bin/shutdown.sh
http://192.168.1.102:8080/manager-test/tables.html
安装nginx
1、yum install gcc-c++ 安装nginx需要先将官网下载的源码进行编译,编译依赖gcc环境
2、yum install -y pcre pcre-devel PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expressions)是一个Perl库,包括 perl 兼容的正则表达式库。nginx的http模块使用pcre来解析正则表达式,所以需要在linux上安装pcre库。
注:pcre-devel是使用pcre开发的一个二次开发库。nginx也需要此库。
3、yum install -y zlib zlib-devel zlib库提供了很多种压缩和解压缩的方式,nginx使用zlib对http包的内容进行gzip,所以需要在linux上安装zlib库。
4、yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
OpenSSL 是一个强大的安全套接字层密码库,囊括主要的密码算法、常用的密钥和证书封装管理功能及SSL协议,并提供丰富的应用程序供测试或其它目的使用。
nginx不仅支持http协议,还支持https(即在ssl协议上传输http),所以需要在linux安装openssl库。
tar -zxvf /home/elk/soft/nginx-1.15.1.tar.gz -C ./nginx/
./configure --help查询详细参数
[root@localhost nginx-1.15.1]# ./configure \
> --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
> --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid \
> --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \
> --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \
> --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \
> --with-http_gzip_static_module \
> --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/client \
> --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/proxy \
> --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/fastcgi \
> --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/uwsgi \
> --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/scgi
**#注意:上边将临时文件目录指定为/var/temp/nginx,需要在/var下创建temp及nginx**目录
/var/log/nginx/access.log
编译安装
[root@localhost nginx-1.15.1]# make ##编译下让它执行
[root@localhost nginx-1.15.1]# make install
安装成功查看安装目录 :
[root@localhost nginx]# ll
total 4
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Mar 25 13:33 conf
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 40 Mar 25 13:33 html
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 19 Mar 25 13:33 sbin
[root@localhost nginx]# pwd 这个是nginc的实际目录
/usr/local/nginx
启动nginx
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
./nginx
[root@localhost conf]# rm -rf nginx.conf
[root@localhost conf]# cp /home/elk/file/project/nginx.conf ./ ##重写配置下nginx.conf文件;将配置好的复制过来
nginx.conf


#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] $http_host $request_method "$uri" "$query_string" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" $upstream_status $upstream_addr $request_time $upstream_response_time '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
upstream manager {
server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=10;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
proxy_pass http://manager/manager/index.html;
proxy_redirect off;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
View Code
修改下项目地址
[root@localhost conf]# vi nginx.conf
location / {
proxy_pass http://manager/manager-test/index.html;
proxy_redirect off;
}
启动:
[root@localhost conf]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx/conf
[root@localhost conf]# cd ../sbin/
[root@localhost sbin]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx/sbin
[root@localhost sbin]# ./ngin
http://192.168.1.102/
刷写网页就会生成日志信息
停止nginx
方式1,快速停止:
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
./nginx -s stop
此方式相当于先查出nginx进程id再使用kill命令强制杀掉进程。
方式2,完整停止(建议使用):
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
./nginx -s quit
此方式停止步骤是待nginx进程处理任务完毕进行停止。
重启nginx
方式1,先停止再启动(建议使用):
对nginx进行重启相当于先停止nginx再启动nginx,即先执行停止命令再执行启动命令。
如下:
./nginx -s quit
./nginx
方式2,重新加载配置文件:
当nginx的配置文件nginx.conf修改后,要想让配置生效需要重启nginx,使用-s reload不用先停止nginx再启动nginx即可将配置信息在nginx中生效,如下:
./nginx -s reload
测试
nginx安装成功,启动nginx,即可访问虚拟机上的nginx:
到这说明nginx上安装成功。
查询nginx进程:ps aux | grep nginx
主进程id,工作进程id
注意:执行./nginx启动nginx,这里可以-c指定加载的nginx配置文件,如下:
./nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
如果不指定-c,nginx在启动时默认加载conf/nginx.conf文件,此文件的地址也可以在编译安装nginx时指定./configure****的参数(--conf-path= 指向配置文件(nginx.conf****))
实时监控文件的变化
[root@localhost sbin]# cd /var/log/nginx/
[root@localhost nginx]# ls
access.log error.log
[root@localhost nginx]# tail -f access.log
logstash的安装配置
[elk@localhost config]$ vi nginx_logstash.conf 修改下路径
patterns_dir => "/home/elk/logstash/config/patterns/"
match => {
"message" => "%{NGINXACCESS}"
[elk@localhost config]$ ../logstash-6.3.1/bin/logstash -f ./nginx_logstash.conf
[elk@localhost config]$ pwd
/home/elk/logstash/config
[elk@localhost config]$ ll
total 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 elk elk 1090 Mar 25 13:56 nginx_logstash.conf
drwxrwxr-x. 2 elk elk 19 Mar 25 13:54 patterns
配置这两个文件即可;
[elk@localhost config]$ cat patterns/nginx
NGINXACCESS %{IPORHOST:clientip} %{HTTPDUSER:ident} %{USER:auth} \[%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}\] "(?:%{WORD:verb} %{NOTSPACE:request}(?: HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion})?|%{DATA:rawrequest})" %{NUMBER:response} (?:%{NUMBER:bytes}|-)
NGINXACCESSLOG %{COMMONAPACHELOG} %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent}
[elk@localhost config]$ vi nginx_logstash.conf
input {
file {
path => ["/var/log/nginx/access.log"]
type => "nginx_access"
#start_position => "beginning"
}
}
filter {
if [type] == "nginx_access" {
grok {
patterns_dir => "/home/elk/logstash/config/patterns/"
match => {
"message" => "%{NGINXACCESS}"
}
}
date {
match => ["timestamp","dd/MMM/YYY:HH:mm:ss Z"]
}
if [param] {
ruby {
init => "@kname = ['quote','url_args']"
code => "
new_event =
LogStash::Event.new(Hash[@kname.zip(event.get('param').split('?'))])
new_event.remove('@timestamp')
event.append(new_event)
"
}
}
if [url_args] {
ruby {
init => "@kname = ['key','value']"
code => "event.set('nested_args',event.get('url_args').split('&').cllect{|i| Hash[@kname.zip(i.split('='))]})"
remove_field => ["url_args","param","quote"]
}
}
mutate {
convert => ["response","integer"]
remove_field => "timestamp"
}
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.1.102:9200"]
index => "logstash-%{type}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
启动kibana:
[elk@localhost bin]$ ./kibana
一刷新网页就会产生log日志:
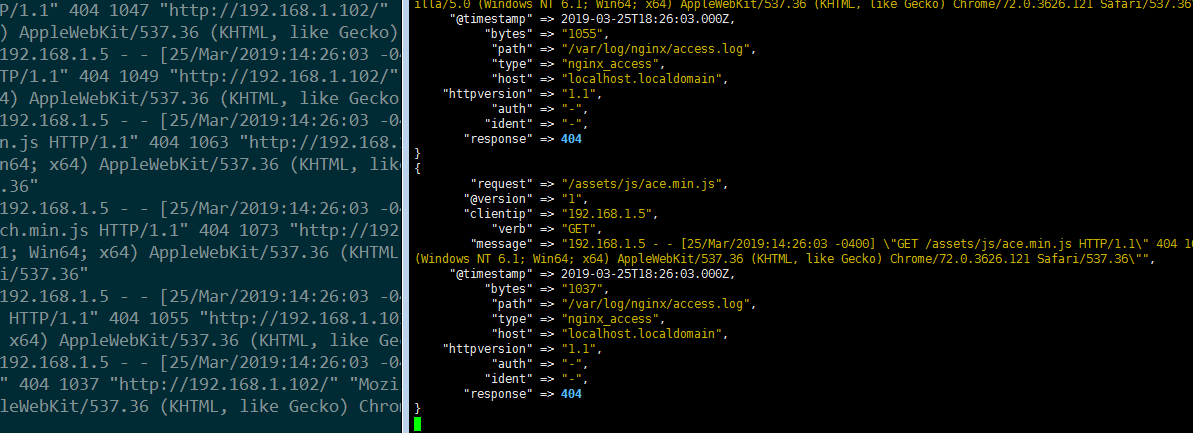
{
"request" => "/assets/js/ace.min.js",
"@version" => "1",
"clientip" => "192.168.1.5",
"verb" => "GET",
"message" => "192.168.1.5 - - [25/Mar/2019:14:01:58 -0400] \"GET /assets/js/ace.min.js HTTP/1.1\" 404 1037 \"http://192.168.1.102/\" \"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.121 Safari/537.36\"",
"@timestamp" => 2019-03-25T18:01:58.000Z,
"bytes" => "1037",
"path" => "/var/log/nginx/access.log",
"type" => "nginx_access",
"host" => "localhost.localdomain",
"httpversion" => "1.1",
"auth" => "-",
"ident" => "-",
"response" => 404
}
elasticsearch的索引是
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.1.101:9200"]
index => "logstash-%{type}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
查询下看到它会生成很多的log信息
GET logstash-nginx_access-2019.03.25/_search
log日志-->灌到ES中
图表展示: 创建logstash的信息
logstash-*
timestamp
创建索引
创建索引logstash-*
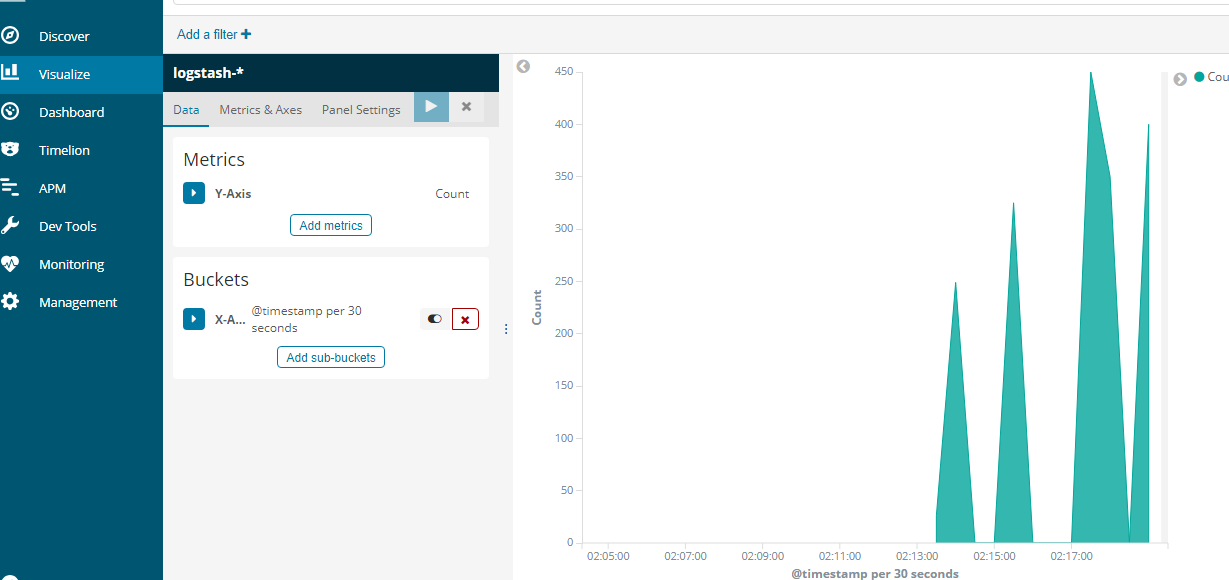
附录:防火墙配置
1、firewalld的基本使用
启动: systemctl start firewalld
关闭: systemctl stop firewalld
查看状态: systemctl status firewalld
开机禁用 : systemctl disable firewalld
开机启用 : systemctl enable firewalld
2.systemctl是CentOS7的服务管理工具中主要的工具,它融合之前service和chkconfig的功能于一体。
启动一个服务:systemctl start firewalld.service
关闭一个服务:systemctl stop firewalld.service
重启一个服务:systemctl restart firewalld.service
显示一个服务的状态:systemctl status firewalld.service
在开机时启用一个服务:systemctl enable firewalld.service
在开机时禁用一个服务:systemctl disable firewalld.service
查看服务是否开机启动:systemctl is-enabled firewalld.service
查看已启动的服务列表:systemctl list-unit-files|grep enabled
查看启动失败的服务列表:systemctl --failed
3.配置firewalld-cmd
查看版本: firewall-cmd --version
查看帮助: firewall-cmd --help
显示状态: firewall-cmd --state
查看所有打开的端口: firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
更新防火墙规则: firewall-cmd --reload
查看区域信息: firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
查看指定接口所属区域: firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=eth0
拒绝所有包:firewall-cmd --panic-on
取消拒绝状态: firewall-cmd --panic-off
查看是否拒绝: firewall-cmd --query-panic
4.那怎么开启一个端口呢
添加 firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent (--permanent永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效)
重新载入 firewall-cmd --reload
查看 firewall-cmd --zone= public --query-port=80/tcp
删除 firewall-cmd --zone= public --remove-port=80/tcp --permanent













