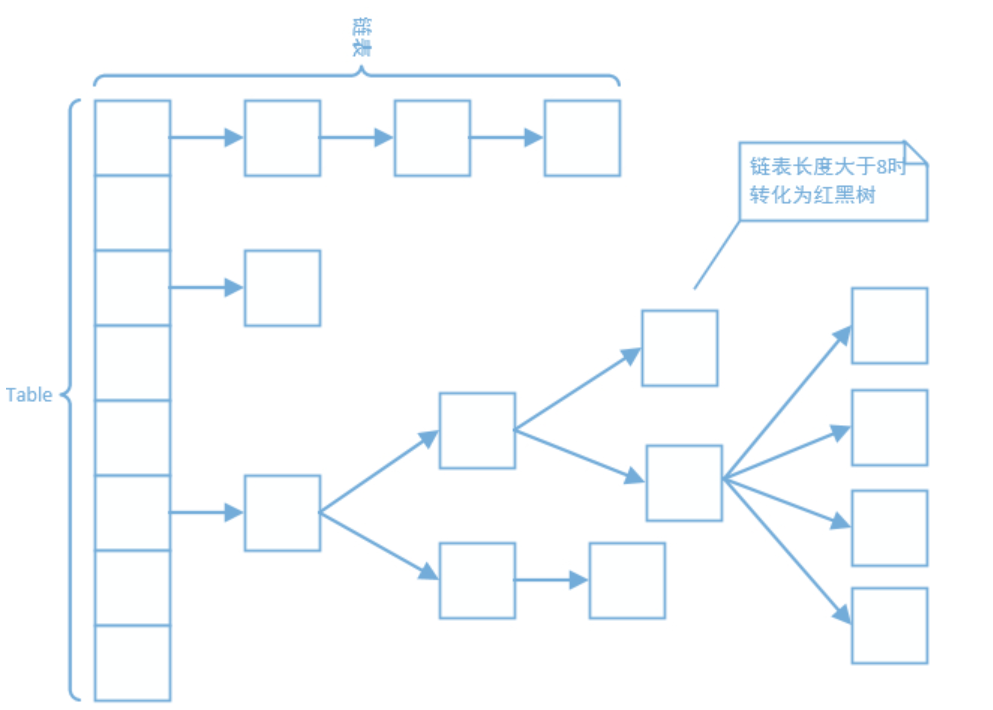
hashmap的数据结构,HashMap的数据结构是数组+链表+红黑树(红黑树since JDK1.8)。我们常把数组中的每一个节点称为一个桶。当向桶中添加一个键值对时,首先计算键值对中key的hash值,以此确定插入数组中的位置,但是可能存在同一hash值的元素已经被放在数组同一位置了,这种现象称为碰撞,这时按照尾插法(jdk1.7及以前为头插法)的方式添加key-value到同一hash值的元素的后面,链表就这样形成了。当链表长度超过8(TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)时,链表就转换为红黑树。
get方法
//首先将key散列一次,然后调用getNode方法去查找数据
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
//这是一个非常重要的方法 与定位桶的位置相关。hashmap的增删改查都需要先定位桶
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
} //第一步,取key的hashCode,第二步,key的hashCode高16位异或低16位,第三步,将第一步和第二部得到的结果进行取模运算
看到这里有个疑问,为什么要做异或运算?
设想一下,如果n很小,假设为16的话,那么n-1即为15(0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111),这样的值如果跟hashCode()直接做与操作,实际上只使用了哈希值的后4位。如果当哈希值的高位变化很大,低位变化很小,这样很容易造成碰撞,所以把高低位都参与到计算中,从而解决了这个问题,而且也不会有太大的开销。
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
//如果哈希表数组不为null并且数组长度大于0,并且((n - 1) & hash)对应的桶存在,哈希表中的定位桶使用的方法((n - 1) & hash)
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//如果桶中第一个node就匹配上了,并且key也匹配上了,那么返回这个node
if (first.hash == hash &&((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
//第一个node没有匹配上 那么在后续node上查找
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//如果节点是红黑树类型,那么调用红黑树的获取方法,否则变量链表 直到匹配上,否则返回null
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
put方法
//将key散列一次 然后使用putVal 执行put操作
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//如果哈希表数组为空或者数组的长度为0 将数组扩容一次
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 如果未碰撞 key对应的桶索引不存在,那么直接将数据加入到hash表中
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {//如果碰撞了
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果桶中第一个node的key与待插入的key匹配上了 记录该节点并赋值给e
if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)//如果第一个node未匹配,并且节点是红黑树类型,那么调用红黑树对应的插入方法插入数据
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {//如果第一个节点未匹配 并且不是红黑树结构,那么肯定是单向链表结构,下面要去链表中查找
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {//这里binCount代表遍历的次数
if ((e = p.next) == null) {//如果当前遍历到了最末尾节点,那么直接将数据加入到单向链表的末尾,并且判断链表是否需要转为红黑树 注意:此时e==null
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//在链表中查找是否有key是否有对应的node,如果有 那么终止循环
if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//如果key对应的节点不为null,那么返回将新增覆盖老值,并且返回老值
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
//访问回调函数
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
//桶结构变化了, 记录变化次数 并且判断是否需要扩容
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
//插入回调函数
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
//如果不是key覆盖的情况 那么返回null
return null;
}
resize 方法
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
//新建变量 用于保存老数组和老数组的长度和扩容前的临界值
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {//如果老容量>0
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {//如果老数组的长度大于等于最多容量,那么无法扩容
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//将扩容临界值修改为Integer的最大值
return oldTab;
}else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
//如果老容量的两倍小于最大容量,且老容量大于默认容量值,那么将新容量值设置为老容量值得两倍
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}else if (oldThr > 0)//如果老容量<=0 且老老临界值大于0,将老临界值设置为新容量
newCap = oldThr;
else { //如果老容量<=0,且 老临界值<=0 ,那么使用默认配置初始化新容量 新临界值。
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
//确定临界值的合法性
if (newThr == 0) {//由上面的判断可以发现 oldThr=0时 newThr才会=0
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
//设置新的临界值, 新的数组
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {//如果老数组不为空 将老数组元素复制到新的数组中
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {//遍历数组
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {//如果老桶不为空 使用e记录老桶
oldTab[j] = null;//将老桶置为空
if (e.next == null)// 如果桶中只有一个元素
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;//将老桶放入newTab中e.hash & (newCap - 1)的位置(这里为什么不使用newTab[j]呢?)
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)//如果是红黑树节点 使用红黑树的处理方法
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // 链表类型节点的数据复制
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}