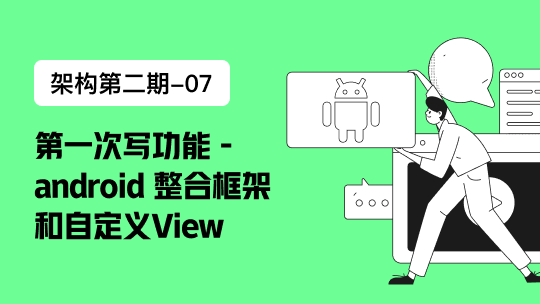
application.properties,用来配置一些可以手动修改而且不用编译的变量,这样的作用在于,打成war包或者jar包用于生产环境时,我们可以手动修改环境变量而不用再重新编译。
spring boo默认已经配置了很多环境变量,例如,tomcat的默认端口是8080,项目的contextpath是“/”等等(更多请看https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-external-config)
spring boot允许你自定义一个application.properties文件,然后放在以下的地方,来重写spring boot的环境变量或者定义你自己环境变量 1.当前目录的 “**/config”的子目录下 2. 当前目录下 3.** classpath根目录的“**/config**”包下 4. classpath的根目录下
其中1、2点适合在生产环境下,例如,打包成可执行的jar包 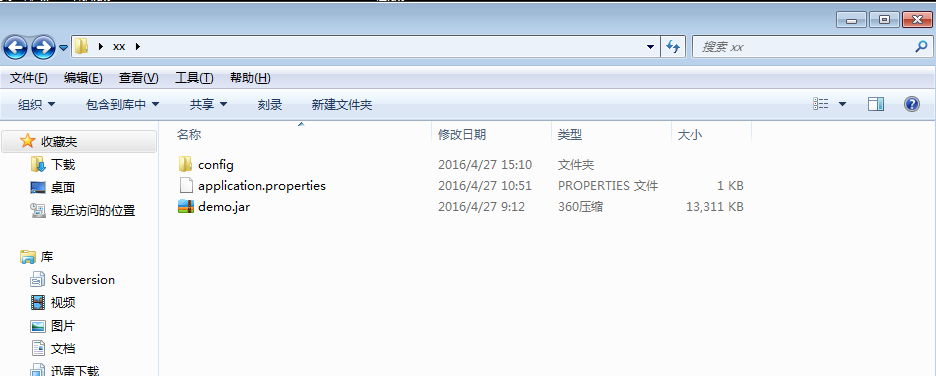
注意,“当前目录”是指demo.jar包的目录下,要使配置文件生效,在使用java -jar demo.jar的命令时,必须先路由到demo.jar包的路径下,再使用其命名 
另外,3、4点适合在开发环境下
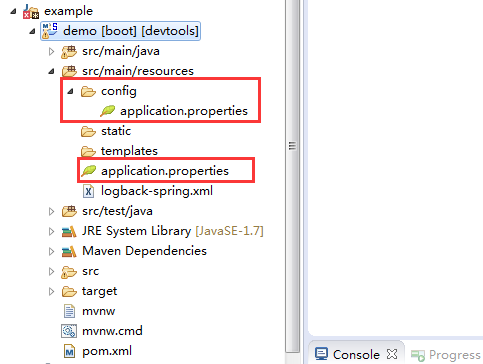
如果同时在四个地方都有配置文件,配置文件的优先级是从1到4。
使用配置文件之后,spring boot启动时,会自动把配置信息读取到spring容器中,并覆盖spring boot的默认配置,那么,我们怎么来读取和设置这些配置信息呢
1.通过命令行来重写和配置环境变量,优先级最高,例如可以通过下面的命令来重写spring boot 内嵌tomcat的服务端口,注意“=”俩边不要有空格
java -jar demo.jar --server.port=9000
2.通过**@value**注解来读取
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/task")
public class TaskController {
@Value("${connection.remoteAddress}") private String address;
@RequestMapping(value = {"/",""})
public String hellTask(@Value("${connection.username}")String name){
return "hello task !!";
}
}
自定义工具栏
@Component public class SystemConfig {
private static Properties props ; public SystemConfig(){ try { Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("/application.properties");// props = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 获取属性 * @param key * @return */ public static String getProperty(String key){ return props == null ? null : props.getProperty(key); } /** * 获取属性 * @param key 属性key * @param defaultValue 属性value * @return */ public static String getProperty(String key,String defaultValue){ return props == null ? null : props.getProperty(key, defaultValue); } /** * 获取properyies属性 * @return */ public static Properties getProperties(){ return props; }}
//用的话,就直接这样子 String value = SystemConfig.getProperty("key");