Author: xidianwangtao@gmail.com,Based on Kubernetes 1.9
摘要:Kubernetes StatefulSet在1.9版本中stable了,相信以后会有越老越多的企业会使用它来部署有状态应用,比如Mysql、Zookeeper、ElasticSearch、Redis等等。本文是对StatefulSet的源码分析,包括其Inner Structure、Sync的核心逻辑、Update的主要流程说明、完整的Code Logic Diagram及一些思考。
Inner Structure
下面是简单的StatefulSet Controller工作的内部结构图。 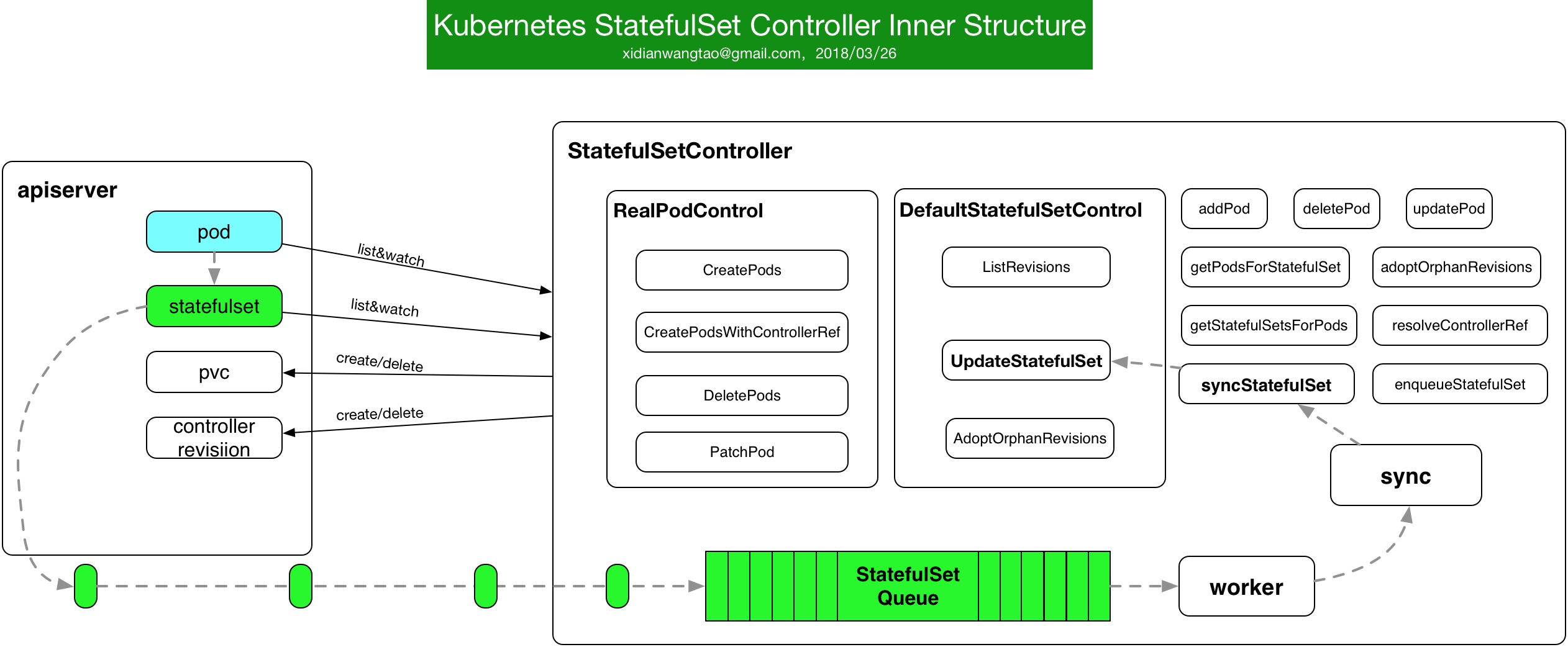
NewStatefulSetController
同其他Controller一样,StatefulSet Controller也是由ControllerManager初始化时负责启动。
// NewStatefulSetController creates a new statefulset controller.
func NewStatefulSetController(
podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer,
setInformer appsinformers.StatefulSetInformer,
pvcInformer coreinformers.PersistentVolumeClaimInformer,
revInformer appsinformers.ControllerRevisionInformer,
kubeClient clientset.Interface,
) *StatefulSetController {
...
ssc := &StatefulSetController{
kubeClient: kubeClient,
control: NewDefaultStatefulSetControl(
NewRealStatefulPodControl(
kubeClient,
setInformer.Lister(),
podInformer.Lister(),
pvcInformer.Lister(),
recorder),
NewRealStatefulSetStatusUpdater(kubeClient, setInformer.Lister()),
history.NewHistory(kubeClient, revInformer.Lister()),
),
pvcListerSynced: pvcInformer.Informer().HasSynced,
queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), "statefulset"),
podControl: controller.RealPodControl{KubeClient: kubeClient, Recorder: recorder},
revListerSynced: revInformer.Informer().HasSynced,
}
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
// lookup the statefulset and enqueue
AddFunc: ssc.addPod,
// lookup current and old statefulset if labels changed
UpdateFunc: ssc.updatePod,
// lookup statefulset accounting for deletion tombstones
DeleteFunc: ssc.deletePod,
})
ssc.podLister = podInformer.Lister()
ssc.podListerSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSynced
setInformer.Informer().AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: ssc.enqueueStatefulSet,
UpdateFunc: func(old, cur interface{}) {
oldPS := old.(*apps.StatefulSet)
curPS := cur.(*apps.StatefulSet)
if oldPS.Status.Replicas != curPS.Status.Replicas {
glog.V(4).Infof("Observed updated replica count for StatefulSet: %v, %d->%d", curPS.Name, oldPS.Status.Replicas, curPS.Status.Replicas)
}
ssc.enqueueStatefulSet(cur)
},
DeleteFunc: ssc.enqueueStatefulSet,
},
statefulSetResyncPeriod,
)
ssc.setLister = setInformer.Lister()
ssc.setListerSynced = setInformer.Informer().HasSynced
// TODO: Watch volumes
return ssc
}
很熟悉的代码风格,也是创建对应的eventBroadcaster,然后给对应的objectInformer注册对应的eventHandler:
- StatefulSetController主要ListWatch Pod和StatefulSet对象;
- Pod Informer注册了add/update/delete EventHandler,这三个EventHandler都会将Pod对应的StatefulSet加入到StatefulSet Queue中。
- StatefulSet Informer同样注册了add/update/event EventHandler,也都会将StatefulSet加入到StatefulSet Queue中。
- 目前StatefulSetController还未感知PVC Informer的EventHandler,这里继续按照PVC Controller全部处理。在StatefulSet Controller创建和删除Pod时,会调用apiserver创建和删除对应的PVC。
- RevisionController类似,在StatefulSet Controller Reconcile时会创建或者删除对应的Revision。
StatefulSetController sync
接下来,会进入StatefulSetController的worker(只有一个worker,也就是只一个go routine),worker会从StatefulSet Queue中pop out一个StatefulSet对象,然后执行sync进行Reconcile操作。
// sync syncs the given statefulset.
func (ssc *StatefulSetController) sync(key string) error {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
glog.V(4).Infof("Finished syncing statefulset %q (%v)", key, time.Now().Sub(startTime))
}()
namespace, name, err := cache.SplitMetaNamespaceKey(key)
if err != nil {
return err
}
set, err := ssc.setLister.StatefulSets(namespace).Get(name)
if errors.IsNotFound(err) {
glog.Infof("StatefulSet has been deleted %v", key)
return nil
}
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to retrieve StatefulSet %v from store: %v", key, err))
return err
}
selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(set.Spec.Selector)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("error converting StatefulSet %v selector: %v", key, err))
// This is a non-transient error, so don't retry.
return nil
}
if err := ssc.adoptOrphanRevisions(set); err != nil {
return err
}
pods, err := ssc.getPodsForStatefulSet(set, selector)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return ssc.syncStatefulSet(set, pods)
}
sync中根据setLabel匹配出所有revisions、然后检查这些revisions中是否有OwnerReference为空的,如果有,那说明存在Orphaned的Revisions。
注意:只要检查到有一个History Revision就会触发给所有的Resivions打上Patch:
{"metadata":{"ownerReferences":[{"apiVersion":"%s","kind":"%s","name":"%s","uid":"%s","controller":true,"blockOwnerDeletion":true}],"uid":"%s"}}调用getPodsForStatefulSet获取这个StatefulSet应该管理的Pods。
- 获取该StatefulSet对应Namesapce下所有的Pods;
- 执行ClaimPods操作:检查set和pod的Label是否匹配上,如果Label不匹配,那么需要release这个Pod,然后检查pod的name和StatefulSet name的格式是否能匹配上。对于都匹配上的,并且ControllerRef UID也相同的,则不需要处理。
- 如果Selector和ControllerRef都匹配不上,则执行ReleasePod操作,给Pod打Patch:
{“metadata":{"ownerReferences":[{"$patch":"delete","uid":"%s"}],"uid":"%s"}} - 对于Label和name格式能匹配上的,但是controllerRef为空的Pods,就执行AdoptPod,给Pod打上Patch:
{“metadata":{"ownerReferences":[{"apiVersion":"%s","kind":"%s","name":"%s","uid":"%s","controller":true,"blockOwnerDeletion":true}],"uid":"%s"}}
UpdateStatefulSet
syncStatefulSet的实现只是调用UpdateStatefulSet。
func (ssc *defaultStatefulSetControl) UpdateStatefulSet(set *apps.StatefulSet, pods []*v1.Pod) error {
// list all revisions and sort them
revisions, err := ssc.ListRevisions(set)
if err != nil {
return err
}
history.SortControllerRevisions(revisions)
// get the current, and update revisions
currentRevision, updateRevision, collisionCount, err := ssc.getStatefulSetRevisions(set, revisions)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// perform the main update function and get the status
status, err := ssc.updateStatefulSet(set, currentRevision, updateRevision, collisionCount, pods)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// update the set's status
err = ssc.updateStatefulSetStatus(set, status)
if err != nil {
return err
}
glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s pod status replicas=%d ready=%d current=%d updated=%d",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
status.Replicas,
status.ReadyReplicas,
status.CurrentReplicas,
status.UpdatedReplicas)
glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s revisions current=%s update=%s",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
status.CurrentRevision,
status.UpdateRevision)
// maintain the set's revision history limit
return ssc.truncateHistory(set, pods, revisions, currentRevision, updateRevision)
}
UpdateStatefulSet主要流程为:
- ListRevisions获取该StatefulSet的所有Revisions,并按照Revision从小到大进行排序。
- getStatefulSetRevisions获取currentRevison和UpdateRevision。
- 只有当RollingUpdate策略时Partition不为0时,才会有部分Pods是updateRevision。
- 其他情况,所有Pods都得维持currentRevision。
- updateStatefulSet是StatefulSet Controller的核心逻辑,负责创建、更新、删除Pods,使得声明式target得以维护:
- 使得target state始终有Spec.Replicas个Running And Ready的Pods。
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate,并且Partition为0,则保证所有Pods都对应Status.CurrentRevision。
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate,并且Partition不为0,则ordinal小于Partition的Pods保持Status.CurrentRevision,而ordinal大于等于Partition的Pods更新到Status.UpdateRevision。
- 如果更新策略是OnDelete,则只有删除Pods时才会触发对应Pods的更新,也就是说与Revisions不关联。
- truncateHistory维护History Revision个数不超过
.Spec.RevisionHistoryLimit。
updateStatefulSet
updateStatefulSet是整个StatefulSetController的核心。
func (ssc *defaultStatefulSetControl) updateStatefulSet(
set *apps.StatefulSet,
currentRevision *apps.ControllerRevision,
updateRevision *apps.ControllerRevision,
collisionCount int32,
pods []*v1.Pod) (*apps.StatefulSetStatus, error) {
// get the current and update revisions of the set.
currentSet, err := ApplyRevision(set, currentRevision)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
updateSet, err := ApplyRevision(set, updateRevision)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// set the generation, and revisions in the returned status
status := apps.StatefulSetStatus{}
status.ObservedGeneration = new(int64)
*status.ObservedGeneration = set.Generation
status.CurrentRevision = currentRevision.Name
status.UpdateRevision = updateRevision.Name
status.CollisionCount = new(int32)
*status.CollisionCount = collisionCount
replicaCount := int(*set.Spec.Replicas)
// slice that will contain all Pods such that 0 <= getOrdinal(pod) < set.Spec.Replicas
replicas := make([]*v1.Pod, replicaCount)
// slice that will contain all Pods such that set.Spec.Replicas <= getOrdinal(pod)
condemned := make([]*v1.Pod, 0, len(pods))
unhealthy := 0
firstUnhealthyOrdinal := math.MaxInt32
var firstUnhealthyPod *v1.Pod
// First we partition pods into two lists valid replicas and condemned Pods
for i := range pods {
status.Replicas++
// count the number of running and ready replicas
if isRunningAndReady(pods[i]) {
status.ReadyReplicas++
}
// count the number of current and update replicas
if isCreated(pods[i]) && !isTerminating(pods[i]) {
if getPodRevision(pods[i]) == currentRevision.Name {
status.CurrentReplicas++
} else if getPodRevision(pods[i]) == updateRevision.Name {
status.UpdatedReplicas++
}
}
if ord := getOrdinal(pods[i]); 0 <= ord && ord < replicaCount {
// if the ordinal of the pod is within the range of the current number of replicas,
// insert it at the indirection of its ordinal
replicas[ord] = pods[i]
} else if ord >= replicaCount {
// if the ordinal is greater than the number of replicas add it to the condemned list
condemned = append(condemned, pods[i])
}
// If the ordinal could not be parsed (ord < 0), ignore the Pod.
}
// for any empty indices in the sequence [0,set.Spec.Replicas) create a new Pod at the correct revision
for ord := 0; ord < replicaCount; ord++ {
if replicas[ord] == nil {
replicas[ord] = newVersionedStatefulSetPod(
currentSet,
updateSet,
currentRevision.Name,
updateRevision.Name, ord)
}
}
// sort the condemned Pods by their ordinals
sort.Sort(ascendingOrdinal(condemned))
// find the first unhealthy Pod
for i := range replicas {
if !isHealthy(replicas[i]) {
unhealthy++
if ord := getOrdinal(replicas[i]); ord < firstUnhealthyOrdinal {
firstUnhealthyOrdinal = ord
firstUnhealthyPod = replicas[i]
}
}
}
for i := range condemned {
if !isHealthy(condemned[i]) {
unhealthy++
if ord := getOrdinal(condemned[i]); ord < firstUnhealthyOrdinal {
firstUnhealthyOrdinal = ord
firstUnhealthyPod = condemned[i]
}
}
}
if unhealthy > 0 {
glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s has %d unhealthy Pods starting with %s",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
unhealthy,
firstUnhealthyPod.Name)
}
// If the StatefulSet is being deleted, don't do anything other than updating
// status.
if set.DeletionTimestamp != nil {
return &status, nil
}
monotonic := !allowsBurst(set)
// Examine each replica with respect to its ordinal
for i := range replicas {
// delete and recreate failed pods
if isFailed(replicas[i]) {
glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s is recreating failed Pod %s",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
replicas[i].Name)
if err := ssc.podControl.DeleteStatefulPod(set, replicas[i]); err != nil {
return &status, err
}
if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == currentRevision.Name {
status.CurrentReplicas--
} else if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == updateRevision.Name {
status.UpdatedReplicas--
}
status.Replicas--
replicas[i] = newVersionedStatefulSetPod(
currentSet,
updateSet,
currentRevision.Name,
updateRevision.Name,
i)
}
// If we find a Pod that has not been created we create the Pod
if !isCreated(replicas[i]) {
if err := ssc.podControl.CreateStatefulPod(set, replicas[i]); err != nil {
return &status, err
}
status.Replicas++
if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == currentRevision.Name {
status.CurrentReplicas++
} else if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == updateRevision.Name {
status.UpdatedReplicas++
}
// if the set does not allow bursting, return immediately
if monotonic {
return &status, nil
}
// pod created, no more work possible for this round
continue
}
// If we find a Pod that is currently terminating, we must wait until graceful deletion
// completes before we continue to make progress.
if isTerminating(replicas[i]) && monotonic {
glog.V(4).Infof(
"StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to Terminate",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
replicas[i].Name)
return &status, nil
}
// If we have a Pod that has been created but is not running and ready we can not make progress.
// We must ensure that all for each Pod, when we create it, all of its predecessors, with respect to its
// ordinal, are Running and Ready.
if !isRunningAndReady(replicas[i]) && monotonic {
glog.V(4).Infof(
"StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to be Running and Ready",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
replicas[i].Name)
return &status, nil
}
// Enforce the StatefulSet invariants
if identityMatches(set, replicas[i]) && storageMatches(set, replicas[i]) {
continue
}
// Make a deep copy so we don't mutate the shared cache
replica := replicas[i].DeepCopy()
if err := ssc.podControl.UpdateStatefulPod(updateSet, replica); err != nil {
return &status, err
}
}
// At this point, all of the current Replicas are Running and Ready, we can consider termination.
// We will wait for all predecessors to be Running and Ready prior to attempting a deletion.
// We will terminate Pods in a monotonically decreasing order over [len(pods),set.Spec.Replicas).
// Note that we do not resurrect Pods in this interval. Also not that scaling will take precedence over
// updates.
for target := len(condemned) - 1; target >= 0; target-- {
// wait for terminating pods to expire
if isTerminating(condemned[target]) {
glog.V(4).Infof(
"StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to Terminate prior to scale down",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
condemned[target].Name)
// block if we are in monotonic mode
if monotonic {
return &status, nil
}
continue
}
// if we are in monotonic mode and the condemned target is not the first unhealthy Pod block
if !isRunningAndReady(condemned[target]) && monotonic && condemned[target] != firstUnhealthyPod {
glog.V(4).Infof(
"StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to be Running and Ready prior to scale down",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
firstUnhealthyPod.Name)
return &status, nil
}
glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s terminating Pod %s for scale dowm",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
condemned[target].Name)
if err := ssc.podControl.DeleteStatefulPod(set, condemned[target]); err != nil {
return &status, err
}
if getPodRevision(condemned[target]) == currentRevision.Name {
status.CurrentReplicas--
} else if getPodRevision(condemned[target]) == updateRevision.Name {
status.UpdatedReplicas--
}
if monotonic {
return &status, nil
}
}
// for the OnDelete strategy we short circuit. Pods will be updated when they are manually deleted.
if set.Spec.UpdateStrategy.Type == apps.OnDeleteStatefulSetStrategyType {
return &status, nil
}
// we compute the minimum ordinal of the target sequence for a destructive update based on the strategy.
updateMin := 0
if set.Spec.UpdateStrategy.RollingUpdate != nil {
updateMin = int(*set.Spec.UpdateStrategy.RollingUpdate.Partition)
}
// we terminate the Pod with the largest ordinal that does not match the update revision.
for target := len(replicas) - 1; target >= updateMin; target-- {
// delete the Pod if it is not already terminating and does not match the update revision.
if getPodRevision(replicas[target]) != updateRevision.Name && !isTerminating(replicas[target]) {
glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s terminating Pod %s for update",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
replicas[target].Name)
err := ssc.podControl.DeleteStatefulPod(set, replicas[target])
status.CurrentReplicas--
return &status, err
}
// wait for unhealthy Pods on update
if !isHealthy(replicas[target]) {
glog.V(4).Infof(
"StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to update",
set.Namespace,
set.Name,
replicas[target].Name)
return &status, nil
}
}
return &status, nil
}
主要流程:
获取currentRevision和updateRevision对应的StatefulSet Object,并设置generation,currentRevision, updateRevision等信息到StatefulSet status。
将前面getPodsForStatefulSet获取到的pods分成两个slice:
- valid replicas slice: : 0 <= getOrdinal(pod) < set.Spec.Replicas
- condemned pods slice: set.Spec.Replicas <= getOrdinal(pod)
如果valid replicas中存在某些ordinal没有对应的Pod,则创建对应Revision的Pods Object,后面会检测到该Pod没有真实创建就会去创建对应的Pod实例:
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate且Partition为0或者ordinal < Partition,则使用currentRevision创建该Pod Object。
- 如果更新策略时RollingUpdate且Partition不为0且ordinal >= Partition,则使用updateRevision创建该Pod Object。
从valid repilcas和condemned pods两个slices中找出第一个unhealthy的Pod。(ordinal最小的unhealth pod)
healthy pods means:pods is running and ready, and not terminating.
对于正在删除(DeletionTimestamp非空)的StatefulSet,不做任何操作,直接返回当前status。
遍历valid replicas中pods,保证valid replicas中index在[0,spec.replicas)的pod都是Running And Ready的:
- 如果检测到某个pod Failed (pod.Status.Phase = Failed), 则删除这个Pod,并重新new这个pod object(注意revisions匹配)
- 如果这个pod还没有recreate,则Create it。
- 如果ParallelPodManagement = "OrderedReady”,则直接返回当前status。否则ParallelPodManagement = "Parallel”,则循环检测下一个。
- 如果pod正在删除并且ParallelPodManagement = "OrderedReady”,则返回status结束。
- 如果pod不是RunningAndReady状态,并且ParallelPodManagement = "OrderedReady”,则返回status结束。
- 检测该pod与statefulset的identity和storage是否匹配,如果有一个不匹配,则调用apiserver Update Stateful Pod进行updateIdentity和updateStorage(并创建对应的PVC),返回status,结束。
Pod is Running and Ready means:
pod.Status.Phase = Runnin,
pod.Status.Condition = Ready遍历condemned replicas中pods,index由大到小的顺序,确保这些pods最终都被删除:
- 如果这个Pod正在删除(DeletionTimestamp),并且Pod Management是OrderedReady,则进行Block住,返回status,流程结束。
- 如果是OrderedReady策略,Pod不是处于Running and Ready状态,且该pod不是first unhealthy pod,则返回status,流程结束。
- 其他情况,则删除该statefulset pod。
- 根据该pod的controller-revision-hash Label获取Revision,如果等于currentRevision,则更新status.CurrentReplicas;如果等于updateRevision,则更新status.UpdatedReplicas;
- 如果是OrderedReady策略,则返回status,流程结束。
OnDelete更新策略:删除Pod才会触发更新这个ordinal的更新 如果UpdateStrategy Type是OnDelete, 意味着只有当对应的Pods被手动删除后,才会触发Recreate,因此直接返回status,流程结束。
RollingUpdate更新策略:(Partition不设置就相当于0,意味着全部pods进行滚动更新) 如果UpdateStrategy Type是RollingUpdate, 根据RollingUpdate中
Partition配置得到updateMin作为update replicas index区间最小值,遍历valid replicas,index从最大值到updateMin递减的顺序:- 如果pod revision不是updateRevision,并且不是正在删除的,则删除这个pod,并更新status.CurrentReplicas,然后返回status,流程结束。
- 如果pod不是healthy的,那么将等待它变成healthy,因此这里就直接返回status,流程结束。
Identity Match
updateStatefulSet Reconcile中,会检查identity match的情况,具体包含哪些?
StatefulSetPodNameLabel = "statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name"
// identityMatches returns true if pod has a valid identity and network identity for a member of set.
func identityMatches(set *apps.StatefulSet, pod *v1.Pod) bool {
parent, ordinal := getParentNameAndOrdinal(pod)
return ordinal >= 0 &&
set.Name == parent &&
pod.Name == getPodName(set, ordinal) &&
pod.Namespace == set.Namespace &&
pod.Labels[apps.StatefulSetPodNameLabel] == pod.Name
}
- pod name和statefulset name内容匹配。
- namespace匹配。
- Pod的Label:
statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name与Pod name真实匹配。
Storage Match
updateStatefulSet Reconcile中,会检查Storage match的情况,具体怎么匹配的呢?
// storageMatches returns true if pod's Volumes cover the set of PersistentVolumeClaims
func storageMatches(set *apps.StatefulSet, pod *v1.Pod) bool {
ordinal := getOrdinal(pod)
if ordinal < 0 {
return false
}
volumes := make(map[string]v1.Volume, len(pod.Spec.Volumes))
for _, volume := range pod.Spec.Volumes {
volumes[volume.Name] = volume
}
for _, claim := range set.Spec.VolumeClaimTemplates {
volume, found := volumes[claim.Name]
if !found ||
volume.VolumeSource.PersistentVolumeClaim == nil ||
volume.VolumeSource.PersistentVolumeClaim.ClaimName !=
getPersistentVolumeClaimName(set, &claim, ordinal) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
Code Logic Diagram
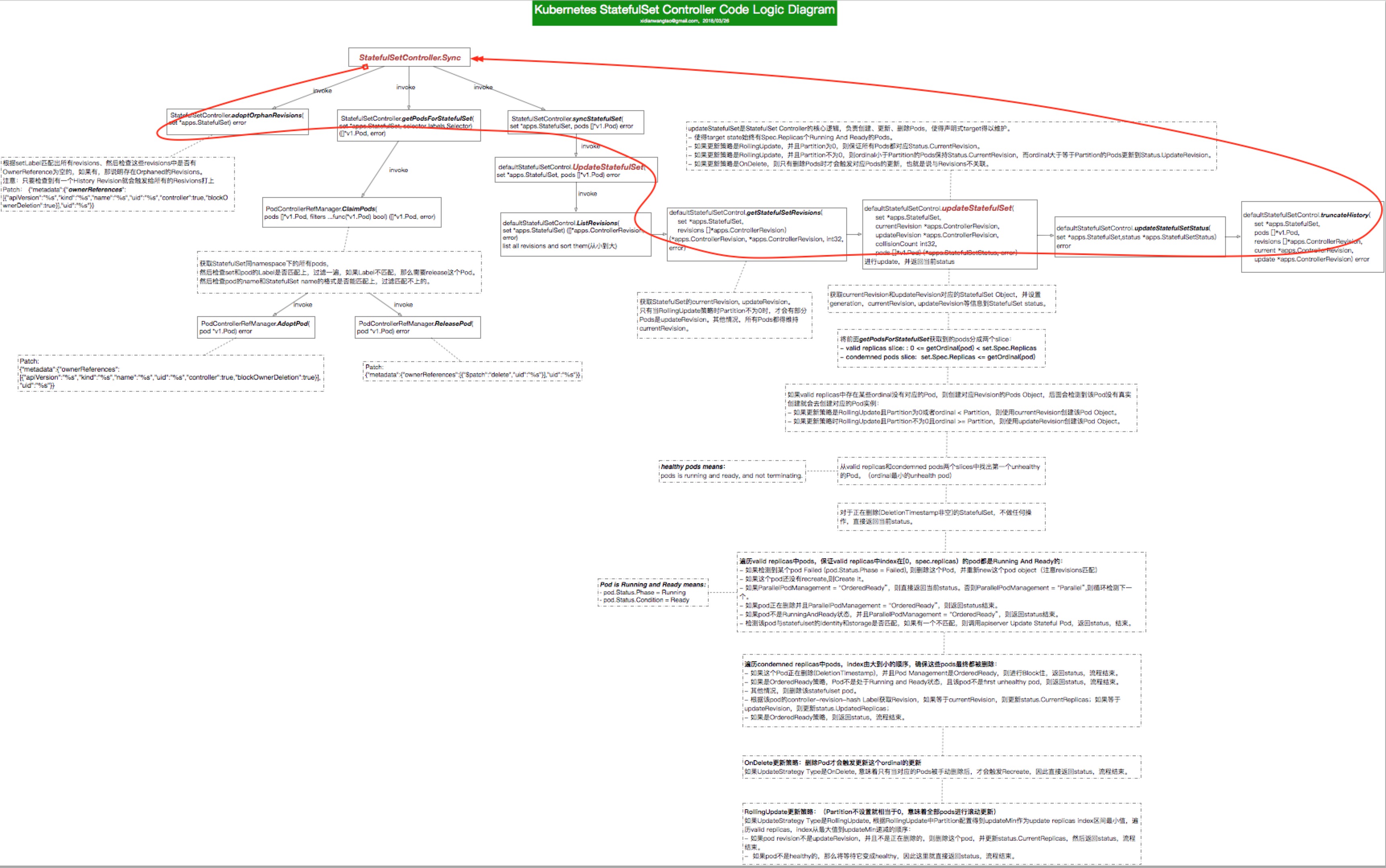
基于上述分析,下面是一个相对完整的StatefulSetController的代码逻辑图。 (不支持大于2MB的图片,所以不太清晰,不过基本在前面内容都提到了。)
思考
滚动更新过程中出现异常
在上一篇博文浅析Kubernetes StatefulSet中遗留了一个问题:StatefulSet滚动更新时,如果某个Pod更新失败,会怎么办呢?
通过上面源码分析中滚动更新部分的分析,我们知道:
- 如果UpdateStrategy Type是RollingUpdate, 根据RollingUpdate中
Partition(Partition不设置就相当于0,意味着全部pods进行滚动更新)配置得到updateMin作为update replicas index区间最小值,遍历valid replicas,index从最大值到updateMin递减的顺序:- 如果pod revision不是updateRevision,并且不是正在删除的,则删除这个pod,并更新status.CurrentReplicas,然后返回status,流程结束。
- 如果pod不是healthy的,那么将等待它变成healthy,因此这里就直接返回status,流程结束。
知道这一点后,就能回答这个问题了,答案很简单:
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate,则逐个滚动更新过程中,如果在更新某个ordinal replica时这个Pod一直无法达到Running and Ready状态,那么整个滚动更新流程将Block在这里。还没有更新的replicas将不会触发更新,已经更新成功的replicas就保持更新后的版本,并不存在什么自动回滚的机制。在下一次sync时,检测到这个Pod isFailed(pod.Status.Phase = Failed),会delete and recreate这个failed pod。
podManagementPolicy设置为Parallel时,体现在哪?
问题:podManagementPolicy: "Parallel"体现在什么时候呢?Scale的时候?RollingUpdate的时候?
- 在前面代码分析中updateStatefulSet中那段-"遍历valid replicas中pods,保证valid replicas中index在[0,spec.replicas)的pod都是Running And Ready的":如果发现某个ordinal replica应该创建但是还没被创建,则会触发create。如果podManagementPolicy设置为Parallel,则会继续
delete then create其他应该创建的replicas,而不会等待前面创建的replicas成为Running and Ready。 - 在前面代码分析中updateStatefulSet中那段-”遍历condemned replicas中pods,index由大到小的顺序,确保这些pods最终都被删除":podManagementPolicy设置为Parallel,如果发现某个ordinal replica正在删除,则继续删除其他应该删除的replicas,而不会等待之前删除的replica重建并成为Running and Ready状态。
因此Parallel体现在以下场景:
- 初始化部署StatefulSet时,并行create pods。
- 级联删除StatefulSet时,并行delete pods。
- Scale up时,并行create pods。
- Scale down时,并行delete pods。
而在滚动更新时,是不会受podManagementPolicy的配置影响的,都是按照逐个地、ordinal从大到小的的顺序,保证前者Running and Ready的原则,进行RollingUpdate。
如果更新策略是OnDelete呢?那情况就不同于RollingUpdate了,因为update的流程就体现在前面提到的两个阶段了,因此Parallel是会启作用的。













