1. 文件模式 (S_IFMT & mode) 测试文件类型的:比如 普通文件 目录文件 设备文件等,见后文stat fstat lstat测试例子。
2. 文件权限
先看一般情况下open函数创建的文件,测试代码如下:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h>
int main(void) { int fd = 0; fd = open("./file.txt",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0777); if (fd == -1) { perror("open"); } close(fd); }

执行后的结果可以看出,group组和其他组没有写权限,open函数中明明写的mode为0777,这是因为umask的作用,终端执行umask命令,可以看到结果为0022,屏蔽了group和other组的写权限,具体可以查阅umask的相关资料
如果我们需要使我们创建的文件指定我们的设定的权限,可以这么做,在线程中设定umask后在创建文件,此处设定umask并不改变系统的umask值
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h>
int main(void) { int fd = 0; if (umask(0000) == -1) { perror("umask"); } fd = open("./file.txt",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0777); if (fd == -1) { perror("open"); } close(fd); }
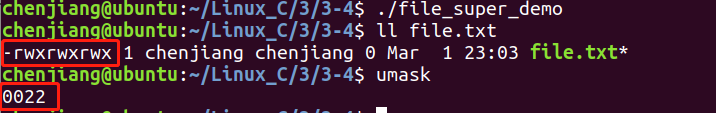
从测试结果可以看出,文件权限为所设定的权限,并且系统的umask值未修改,一般情况下shell中才会用umask,修改文件权限一般用chmod 或fchmod函数。
chmod或fchmod,二者区别 传入文件名和文件描述符
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h>
int main(void) { int fd = 0; #if 0
if (umask(0000) == -1) { perror("umask"); } #endif
fd = open("./file.txt",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0777); fchmod(fd,0777); if (fd == -1) { perror("open"); } close(fd); }
测试结果与umask一致。
chown fchown此处不再演示,与chmod一致。
- 获取文件的信息,以及测试文件类型
stat以及fstat用来获取文件的信息,结构体如下,可通过man 2 stat查看:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
};
下面例子获取了文件的状态,并判断文件是否是普通文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd = 0;
struct stat buf;
int status;
if (umask(0000) == -1)
{
perror("umask");
}
fd = open("./file.txt",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0777);
if (fd == -1)
{
perror("open");
}
fstat(fd,&buf);
if (status == -1)
{
perror("stat");
}
if (S_ISREG(fd) != -1)
{
printf("this is a regular file1!\n");
}
if (S_IFREG == (S_IFMT & (buf.st_mode)))
{
printf("this is a regular file2!\n");
}
close(fd);
}
用两种方法来测试文件的类型:S_ISREG(m)和bits flags定义:
S_IFMT 0170000 bit mask for the file type bit fields
S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket
S_IFLNK 0120000 symbolic link
S_IFREG 0100000 regular file
S_IFBLK 0060000 block device
S_IFDIR 0040000 directory
S_IFCHR 0020000 character device
S_IFIFO 0010000 FIFO
S_ISUID 0004000 set-user-ID bit
S_ISGID 0002000 set-group-ID bit (see below)
S_ISVTX 0001000 sticky bit (see below)
S_IRWXU 00700 mask for file owner permissions
S_IRUSR 00400 owner has read permission
S_IWUSR 00200 owner has write permission
S_IXUSR 00100 owner has execute permission
S_IRWXG 00070 mask for group permissions
S_IRGRP 00040 group has read permission
运行结果:
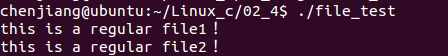
此外文件的时间操作(ctime atime mtime),重命名rename以及截断 truncate ,ftruncate ,access测试权限此处不再演示了。














