1.1 thymeleaf的基础知识介绍
1.1.1 标准表达式介绍
它们分为四类:
- 1.变量表达式
- 2. 选择表达式(星号表达式)
- 3. 消息表达式(井号表达式,资源表达式)通常做国际化
- 4.URL表达式
1.1.2 标准表达式详解
1.变量表达式
变量表达式用于访问容器上下文环境中的变量,功能和JSTL中的${}相同。比如我要在Controllar中用model.addAttribute向前端传入一个对象,那么前端如何接受呢? 以下是例子。
//向前端写入一个UL的对象和ID属性
@RequestMapping("/userPower")
public String userPower(@RequestParam("id") Integer id,Model model){
UserPower UL = us.selectUserByID(id);
model.addAttribute("ID","10081");
model.addAttribute("UL", UL);
return "userPower";
}
前端接收代码
<input th:text="${ID}" ></input >
<input th:if="${UL.Power} == 1" >管理员</input >
访问此页面,效果如下
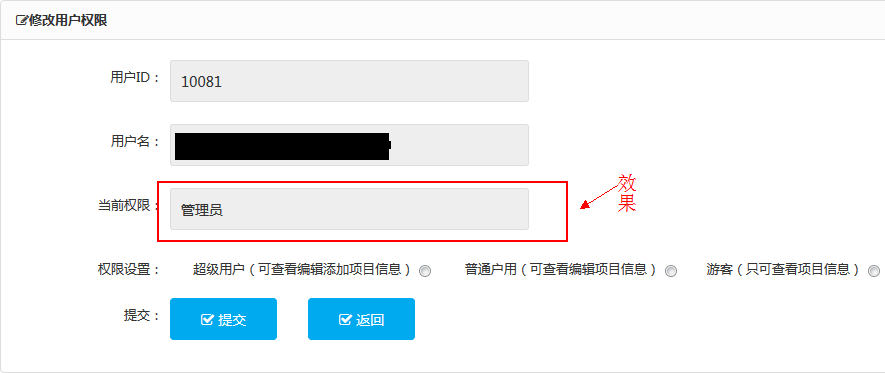
JAVA代码就不解释了,很简单。解释下HTML部分,th:text=" " 和 th:if=" " 是thymeleaf的一个属性,先不做解释。其$(ID),$(UL.Power)中的"UL"是Java代码中model传来的Key值,".Power"是UserPower对象中的一个属性。
2.星号表达式
择表达式(星号表达式)。只要是没有选择对象,选择表达式与变量表达式的语法是完全一样的。使用th:object对象属性来绑定对象。 代码如下。
//向前端写入一个UL的参数
@RequestMapping("/userPower")
public String userPower(@RequestParam("id") Integer id,Model model){
UserPower UL = us.selectUserByID(id);
model.addAttribute("UL", UL);
return "userPower";
}
前端接收代码
<div th:object=" ${UL}" >
<p>Name: <span th: text=" *{Name}" >张</span>. </p>
<p>LastName: <span th: text=" *{lastName}" >三</span>. </p>
<p>Address: <span th: text=" *{addr}" >北京</span>. </p>
</div>
Html解释:首先使用th:object来邦定后台传来的UserPower对象,然后使用*来代表这个对象,后面{}中的值是此对象中的属性。
3.消息表达式
消息表达式(井号表达式,资源表达式)。通常与th:text属性一起使用,指明声明了th:text的标签的文本是#{}中的key所对应的value,而标签内的文本将不会显示。就是说我们可以从.properties或yml文件中,用Key索引Value.
例子如下:HTML部分
<p th:text="#{home.language}" >This text will not be show! </p>
properties中我们自定义一个home.language的属性
home.language=这段文字将会被显示!!
访问页面,效果是英文不会被展示,展示的是属性文件中的中文。
4.URL表达式
超链接url表达式。
例如:
<script th:src="@{/static/js/jquery-2.4.min.js}"></script>
表达式简介到此为止,之后我会在写表达式在工作中使用,出现的一些问题,比如URL表达式如何代入参数,字符串的拼接等等。
1.1.3 thymeleaf属性的介绍
再说1.1.1的时候,出现不少如th:src、th:text等字眼,这些就是thymeleaf的属性,下面附属性,然后我会把常用的进行讲解。
th:action
th:each
th:field
th:href
th:id
th:if
th:include
th:fragment
th:object
th:src
th:replace
th:text
th:value
1、th:action
定义后台控制器的路径,类似

