在上一节JPA操作基础上修改
Cache缓存策略:使更少的操作数据库,更快的返回数据
1、引入cache依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.主要是修改UserSerViceImpl服务层实现类
@Service
@Transactional //事务
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#id")
public User findUserById(Integer id) {
System.out.println("查询用户查询数据库");
return userRepository.getOne(id);
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "userListPage" , key = "#pageable") //key值可视化,每页的key值是不同的
public Page<User> findUserListPage(Pageable pageable) {
System.out.println("分页查询数据库");
return userRepository.findAll(pageable);
}
@Override
//@CacheEvict(value = "users",key = "#id") //清空缓存中以users和key值缓存策略缓存的对象
@CacheEvict(value = "userListPage",allEntries = true) //清空所有缓存中以users缓存策略缓存的对象
public void saveUser(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
}
/*
注解Caching可以混合几个注解
*/
@Override
@Caching(evict = {@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "user",key = "#user.id"),
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "user2" ,key = "user2.id")})
public void updateUser(User user) {
}
}
3.测试TsetController类
@Controller
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/getUserById")
public @ResponseBody User getUserById(){
System.out.println(userService.findUserById(1527));
System.out.println(userService.findUserById(1527));
System.out.println(userService.findUserById(1528));
return userService.findUserById(1527);
}
}
4.对启动类添加缓存注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching //对缓存做配置
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
5.进行测试:
运行结果:
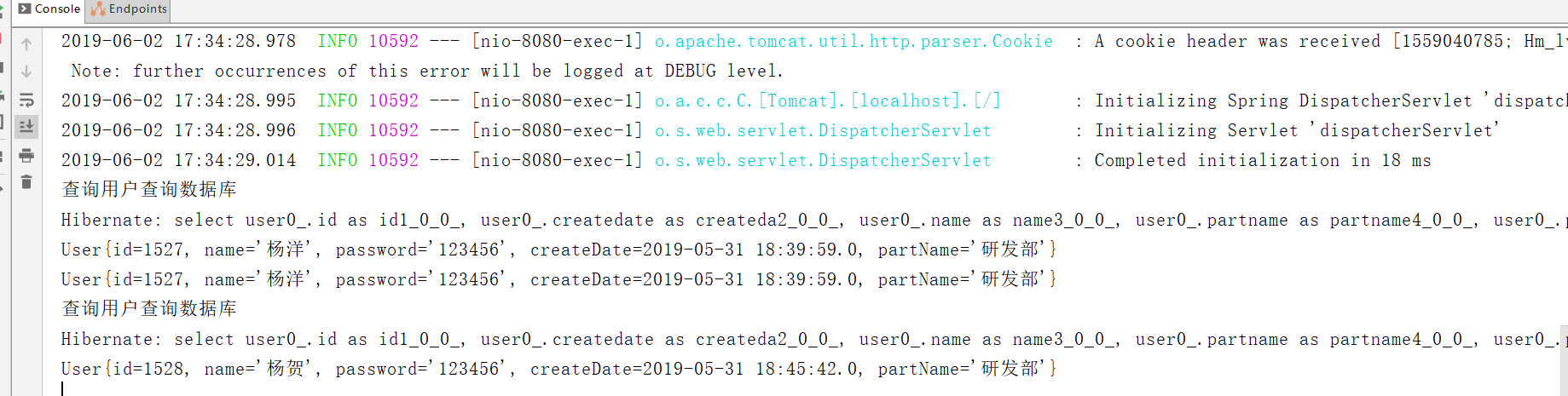
第二次查询数据库是因为id不同没有这个缓存,会去查询数据库的













