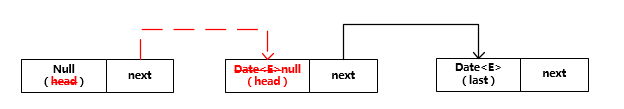
##基本概念
LinkedBlockingQueue 是一个用链表实现的有界阻塞队列。
LinkedBlockingQueue 按照先进先出的原则对元素进行排序。
LinkedBlockingQueue 采用了双锁、双条件队列来提高读写效率。
##内部构造
LinkedBlockingQueue 内部维护着一个单向链表,且链表头节点的值永远为空。如下图所示:
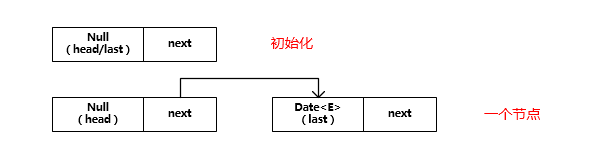
下面来看它的构成:
Node ,节点
static class Node
{ E item; Node next; Node(E x) { item = x; } } 构造函数
private transient Node
head; private transient Node last; private final int capacity; public LinkedBlockingQueue() { // 该队列是有界的,若不指定容量,默认为最大值 this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); }
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) { if (capacity <= 0){ // 抛出异常... } this.capacity = capacity; last = head = new Node
(null); }
##双锁机制
由于采用了双锁机制,因此它的出队、入队操作可以同时进行,从而提高效率。
// 用于入队操作
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
// 用于出队操作
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
由于出入队可以同时进行,因此必须避免冲突问题。
同一元素操作冲突:由于 LinkedBlockingQueue 采用了 FIFO(先进先出)的原则,实际上是双端操作,不会存在冲突。并且在其内部定义了两个变量:head、last。
// 出队修改头节点 private transient Node
head; // 入队修改尾节点 private transient Node
last; 元素数量操作冲突:因为入队数量要+1,出队数量要-1,因此需要保证它的可见性,这里采用了这里采用原子类来实现:
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
##入队操作
offer,该操作成功返回 true,失败返回 false。
public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null){ // 抛出异常... } // 判断元素的个数是否超过容量4 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; if (count.get() == capacity){ return false; } int c = -1; Node
node = new Node(e); // 加锁 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; putLock.lock(); try { // 再次判断,存在等待获取锁期间,其他线程执行入队操作。 if (count.get() < capacity) { // 入队操作 enqueue(node); // 注意:数量+1,返回的旧值 c = count.getAndIncrement(); if (c + 1 < capacity){ // 队列未满,唤醒因为队列满而阻塞的线程 notFull.signal(); } } } finally { putLock.unlock(); } // 为 0 表示之前队列是空的,唤醒出队时因为空队列而进入 notEmpty 条件等待队列的线程 if (c == 0){ signalNotEmpty(); } return c >= 0; } put,该操作成功返回 true,失败则进入阻塞。
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null){ // 抛出异常... } int c = -1; Node<E> node = new Node(e); final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; final AtomicInteger count = this.count; putLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { // 满队列,进入条件等待队列,线程阻塞 while (count.get() == capacity) { notFull.await(); } // 关键-> 入队操作 enqueue(node); c = count.getAndIncrement(); if (c + 1 < capacity){ notFull.signal(); } } finally { putLock.unlock(); } if (c == 0){ signalNotEmpty(); }}
关键
private void enqueue(Node
node) { last = last.next = node; } private void signalNotEmpty() { final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lock(); try { notEmpty.signal(); } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } }
入队操作的过程如下所示:
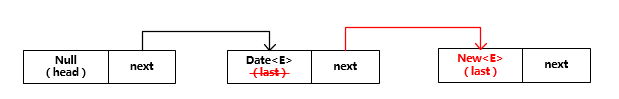
##出队操作
poll,成功返回被移除的元素,失败返回 null。
public E poll() { final AtomicInteger count = this.count; if (count.get() == 0){ return null; } E x = null; int c = -1; // 加锁 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lock(); try { if (count.get() > 0) { // 关键 -> 出队 x = dequeue(); c = count.getAndDecrement(); if (c > 1){ notEmpty.signal(); } } } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } // 表示出队前满队列,唤醒因入队时满队列而进入 notFull 条件等待队列的线程。 if (c == capacity){ signalNotFull(); } return x; }
take,成功返回被移除的元素,失败则线程阻塞。
public E take() throws InterruptedException { E x; int c = -1; final AtomicInteger count = this.count; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { // 空队列,进入条件等待队列,线程阻塞 while (count.get() == 0) { notEmpty.await(); } x = dequeue(); c = count.getAndDecrement(); if (c > 1){ notEmpty.signal(); }
} finally { takeLock.unlock(); } if (c == capacity){ signalNotFull(); } return x; }关键
private E dequeue() { // 头节点、以及它的后继节点 Node
h = head; Node first = h.next; // 等于 h.next = null,即断开后指针 h.next = h; // 设置新的头节点 head = first; E x = first.item; // 将节点的值置空 first.item = null; return x; } private void signalNotFull() { final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; putLock.lock(); try { notFull.signal(); } finally { putLock.unlock(); } }
出队过程如下图所示: