Http协议的重要性相信不用我多说了,HttpClient相比传统JDK自带的URLConnection,增加了易用性和灵活性(具体区别,日后我们再讨论),它不仅是客户端发送Http请求变得容易,而且也方便了开发人员测试接口(基于Http协议的),即提高了开发的效率,也方便提高代码的健壮性。因此熟练掌握HttpClient是很重要的必修内容,掌握HttpClient后,相信对于Http协议的了解会更加深入。
一、简介
HttpClient是Apache Jakarta Common下的子项目,用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持HTTP协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支持HTTP协议最新的版本和建议。HttpClient已经应用在很多的项目中,比如Apache Jakarta上很著名的另外两个开源项目Cactus和HTMLUnit都使用了HttpClient。
下载地址: http://hc.apache.org/downloads.cgi
二、特性
1. 基于标准、纯净的java语言。实现了Http1.0和Http1.1
2. 以可扩展的面向对象的结构实现了Http全部的方法(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS, and TRACE)。
3. 支持HTTPS协议。
4. 通过Http代理建立透明的连接。
5. 利用CONNECT方法通过Http代理建立隧道的https连接。
6. Basic, Digest, NTLMv1, NTLMv2, NTLM2 Session, SNPNEGO/Kerberos认证方案。
7. 插件式的自定义认证方案。
8. 便携可靠的套接字工厂使它更容易的使用第三方解决方案。
9. 连接管理器支持多线程应用。支持设置最大连接数,同时支持设置每个主机的最大连接数,发现并关闭过期的连接。
10. 自动处理Set-Cookie中的Cookie。
11. 插件式的自定义Cookie策略。
12. Request的输出流可以避免流中内容直接缓冲到socket服务器。
13. Response的输入流可以有效的从socket服务器直接读取相应内容。
14. 在http1.0和http1.1中利用KeepAlive保持持久连接。
15. 直接获取服务器发送的response code和 headers。
16. 设置连接超时的能力。
17. 实验性的支持http1.1 response caching。
18. 源代码基于Apache License 可免费获取。
三、使用方法
使用HttpClient发送请求、接收响应很简单,一般需要如下几步即可。
1. 创建HttpClient对象。
2. 创建请求方法的实例,并指定请求URL。如果需要发送GET请求,创建HttpGet对象;如果需要发送POST请求,创建HttpPost对象。
3. 如果需要发送请求参数,可调用HttpGet、HttpPost共同的setParams(HetpParams params)方法来添加请求参数;对于HttpPost对象而言,也可调用setEntity(HttpEntity entity)方法来设置请求参数。
4. 调用HttpClient对象的execute(HttpUriRequest request)发送请求,该方法返回一个HttpResponse。
5. 调用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可获取服务器的响应头;调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可获取HttpEntity对象,该对象包装了服务器的响应内容。程序可通过该对象获取服务器的响应内容。
6. 释放连接。无论执行方法是否成功,都必须释放连接
四、实例
[java] view plain copy
package com.test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.KeyManagementException;
import java.security.KeyStore;
import java.security.KeyStoreException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.ParseException;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLContexts;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.TrustSelfSignedStrategy;
import org.apache.http.entity.ContentType;
import org.apache.http.entity.mime.MultipartEntityBuilder;
import org.apache.http.entity.mime.content.FileBody;
import org.apache.http.entity.mime.content.StringBody;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
public class HttpClientTest {
public void jUnitTest() {
get();
}
/**
* HttpClient连接SSL
*/
public void ssl() {
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = null;
try {
KeyStore trustStore = KeyStore.getInstance(KeyStore.getDefaultType());
FileInputStream instream = new FileInputStream(new File("d:\\tomcat.keystore"));
try {
// 加载keyStore d:\\tomcat.keystore
trustStore.load(instream, "123456".toCharArray());
} catch (CertificateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
instream.close();
} catch (Exception ignore) {
}
}
// 相信自己的CA和所有自签名的证书
SSLContext sslcontext = SSLContexts.custom().loadTrustMaterial(trustStore, new TrustSelfSignedStrategy()).build();
// 只允许使用TLSv1协议
SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslsf = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslcontext, new String[] { "TLSv1" }, null,
SSLConnectionSocketFactory.BROWSER_COMPATIBLE_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER);
httpclient = HttpClients.custom().setSSLSocketFactory(sslsf).build();
// 创建http请求(get方式)
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("https://localhost:8443/myDemo/Ajax/serivceJ.action");
System.out.println("executing request" + httpget.getRequestLine());
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
try {
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
if (entity != null) {
System.out.println("Response content length: " + entity.getContentLength());
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(entity));
EntityUtils.consume(entity);
}
} finally {
response.close();
}
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeyManagementException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeyStoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (httpclient != null) {
try {
httpclient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* post方式提交表单(模拟用户登录请求)
*/
public void postForm() {
// 创建默认的httpClient实例.
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
// 创建httppost
HttpPost httppost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/myDemo/Ajax/serivceJ.action");
// 创建参数队列
List
formparams = new ArrayList (); formparams.add(new BasicNameValuePair("username", "admin"));
formparams.add(new BasicNameValuePair("password", "123456"));
UrlEncodedFormEntity uefEntity;
try {
uefEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(formparams, "UTF-8");
httppost.setEntity(uefEntity);
System.out.println("executing request " + httppost.getURI());
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httppost);
try {
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Response content: " + EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTF-8"));
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
}
} finally {
response.close();
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭连接,释放资源
try {
httpclient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 发送 post请求访问本地应用并根据传递参数不同返回不同结果
*/
public void post() {
// 创建默认的httpClient实例.
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
// 创建httppost
HttpPost httppost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/myDemo/Ajax/serivceJ.action");
// 创建参数队列
List
formparams = new ArrayList (); formparams.add(new BasicNameValuePair("type", "house"));
UrlEncodedFormEntity uefEntity;
try {
uefEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(formparams, "UTF-8");
httppost.setEntity(uefEntity);
System.out.println("executing request " + httppost.getURI());
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httppost);
try {
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Response content: " + EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTF-8"));
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
}
} finally {
response.close();
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭连接,释放资源
try {
httpclient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 发送 get请求
*/
public void get() {
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
try {
// 创建httpget.
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://www.baidu.com/");
System.out.println("executing request " + httpget.getURI());
// 执行get请求.
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
try {
// 获取响应实体
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
// 打印响应状态
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
if (entity != null) {
// 打印响应内容长度
System.out.println("Response content length: " + entity.getContentLength());
// 打印响应内容
System.out.println("Response content: " + EntityUtils.toString(entity));
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
} finally {
response.close();
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭连接,释放资源
try {
httpclient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 上传文件
*/
public void upload() {
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
try {
HttpPost httppost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/myDemo/Ajax/serivceFile.action");
FileBody bin = new FileBody(new File("F:\\image\\sendpix0.jpg"));
StringBody comment = new StringBody("A binary file of some kind", ContentType.TEXT_PLAIN);
HttpEntity reqEntity = MultipartEntityBuilder.create().addPart("bin", bin).addPart("comment", comment).build();
httppost.setEntity(reqEntity);
System.out.println("executing request " + httppost.getRequestLine());
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httppost);
try {
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
HttpEntity resEntity = response.getEntity();
if (resEntity != null) {
System.out.println("Response content length: " + resEntity.getContentLength());
}
EntityUtils.consume(resEntity);
} finally {
response.close();
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
httpclient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
本实例是采用HttpClient4.3最新版本。该版本与之前的代码写法风格相差较大,大家多留意下。
HttpClient简介
HTTP 协议可能是现在 Internet 上使用得最多、最重要的协议了,越来越多的 Java 应用程序需要直接通过 HTTP 协议来访问网络资源。虽然在 JDK 的 java.net 包中已经提供了访问 HTTP 协议的基本功能,但是对于大部分应用程序来说,JDK 库本身提供的功能还不够丰富和灵活。HttpClient 是 Apache Jakarta Common 下的子项目,用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持 HTTP 协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支持 HTTP 协议最新的版本和建议。HttpClient 已经应用在很多的项目中,比如 Apache Jakarta 上很著名的另外两个开源项目 Cactus 和 HTMLUnit 都使用了 HttpClient。更多信息请关注http://hc.apache.org/
HttpClient 功能介绍
以下列出的是 HttpClient 提供的主要的功能,要知道更多详细的功能可以参见 HttpClient 的主页。
实现了所有 HTTP 的方法(GET,POST,PUT,HEAD 等)
支持自动转向
支持 HTTPS 协议
支持代理服务器等
**应用HttpClient来对付各种顽固的WEB服务器
**转自:http://blog.csdn.net/ambitiontan/archive/2006/01/06/572171.aspx
一般的情况下我们都是使用IE或者Navigator浏览器来访问一个WEB服务器,用来浏览页面查看信息或者提交一些数据等等。所访问的这些页面有的仅仅是一些普通的页面,有的需要用户登录后方可使用,或者需要认证以及是一些通过加密方式传输,例如HTTPS。目前我们使用的浏览器处理这些情况都不会构成问题。不过你可能在某些时候需要通过程序来访问这样的一些页面,比如从别人的网页中“偷”一些数据;利用某些站点提供的页面来完成某种功能,例如说我们想知道某个手机号码的归属地而我们自己又没有这样的数据,因此只好借助其他公司已有的网站来完成这个功能,这个时候我们需要向网页提交手机号码并从返回的页面中解析出我们想要的数据来。如果对方仅仅是一个很简单的页面,那我们的程序会很简单,本文也就没有必要大张旗鼓的在这里浪费口舌。但是考虑到一些服务授权的问题,很多公司提供的页面往往并不是可以通过一个简单的URL就可以访问的,而必须经过注册然后登录后方可使用提供服务的页面,这个时候就涉及到COOKIE问题的处理。我们知道目前流行的动态网页技术例如ASP、JSP无不是通过COOKIE来处理会话信息的。为了使我们的程序能使用别人所提供的服务页面,就要求程序首先登录后再访问服务页面,这过程就需要自行处理cookie,想想当你用java.net.HttpURLConnection来完成这些功能时是多么恐怖的事情啊!况且这仅仅是我们所说的顽固的WEB服务器中的一个很常见的“顽固”!再有如通过HTTP来上传文件呢?不需要头疼,这些问题有了“它”就很容易解决了!
我们不可能列举所有可能的顽固,我们会针对几种最常见的问题进行处理。当然了,正如前面说到的,如果我们自己使用java.net.HttpURLConnection来搞定这些问题是很恐怖的事情,因此在开始之前我们先要介绍一下一个开放源码的项目,这个项目就是Apache开源组织中的httpclient,它隶属于Jakarta的commons项目,目前的版本是2.0RC2。commons下本来已经有一个net的子项目,但是又把httpclient单独提出来,可见http服务器的访问绝非易事。
Commons-httpclient项目就是专门设计来简化HTTP客户端与服务器进行各种通讯编程。通过它可以让原来很头疼的事情现在轻松的解决,例如你不再管是HTTP或者HTTPS的通讯方式,告诉它你想使用HTTPS方式,剩下的事情交给httpclient替你完成。本文会针对我们在编写HTTP客户端程序时经常碰到的几个问题进行分别介绍如何使用httpclient来解决它们,为了让读者更快的熟悉这个项目我们最开始先给出一个简单的例子来读取一个网页的内容,然后循序渐进解决掉前进中的所有问题。
1. 读取网页(HTTP/HTTPS)内容
下面是我们给出的一个简单的例子用来访问某个页面
/** *最简单的HTTP客户端,用来演示通过GET或者POST方式访问某个页面 *@authorLiudong */
public class SimpleClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { HttpClient client = new HttpClient(); // 设置代理服务器地址和端口 //client.getHostConfiguration().setProxy("proxy_host_addr",proxy_port); // 使用 GET 方法 ,如果服务器需要通过 HTTPS 连接,那只需要将下面 URL 中的 http 换成 https
HttpMethod method=new GetMethod("http://java.sun.com"); //使用POST方法 //HttpMethod method = new PostMethod("http://java.sun.com");
client.executeMethod(method); //打印服务器返回的状态
System.out.println(method.getStatusLine()); //打印返回的信息
System.out.println(method.getResponseBodyAsString()); //释放连接
method.releaseConnection(); } }
在这个例子中首先创建一个HTTP客户端(HttpClient)的实例,然后选择提交的方法是GET或者POST,最后在HttpClient实例上执行提交的方法,最后从所选择的提交方法中读取服务器反馈回来的结果。这就是使用HttpClient的基本流程。其实用一行代码也就可以搞定整个请求的过程,非常的简单!
2、使用POST方式提交数据(httpClient3)
httpclient使用了单独的一个HttpMethod子类来处理文件的上传,这个类就是MultipartPostMethod,该类已经封装了文件上传的细节,我们要做的仅仅是告诉它我们要上传文件的全路径即可,下面这里将给出关于两种模拟上传方式的代码
第一种:模拟上传url文件(该方式也适合做普通post请求):
/** * 上传url文件到指定URL * @param fileUrl 上传图片url * @param postUrl 上传路径及参数,注意有些中文参数需要使用预先编码 eg : URLEncoder.encode(appName, "UTF-8") * @return * @throws IOException */
public static String doUploadFile(String postUrl) throws IOException { if(StringUtils.isEmpty(postUrl)) return null; String response = ""; PostMethod postMethod = new PostMethod(postUrl); try { HttpClient client = new HttpClient(); client.getHttpConnectionManager().getParams() .setConnectionTimeout(50000);// 设置连接时间
int status = client.executeMethod(postMethod); if (status == HttpStatus.SC_OK) { InputStream inputStream = postMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( inputStream)); StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); String str = ""; while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { stringBuffer.append(str); } response = stringBuffer.toString(); } else { response = "fail"; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 释放连接
postMethod.releaseConnection(); } return response; }
第二种:模拟文件上传到指定位置
/** * 上传文件到指定URL * @param file * @param url * @return * @throws IOException */
public static String doUploadFile(File file, String url) throws IOException { String response = ""; if (!file.exists()) { return "file not exists"; } PostMethod postMethod = new PostMethod(url); try { //---------------------------------------------- // FilePart:用来上传文件的类,file即要上传的文件
FilePart fp = new FilePart("file", file); Part[] parts = { fp }; // 对于MIME类型的请求,httpclient建议全用MulitPartRequestEntity进行包装
MultipartRequestEntity mre = new MultipartRequestEntity(parts, postMethod.getParams()); postMethod.setRequestEntity(mre); //---------------------------------------------
HttpClient client = new HttpClient(); client.getHttpConnectionManager().getParams() .setConnectionTimeout(50000);// 由于要上传的文件可能比较大 , 因此在此设置最大的连接超时时间
int status = client.executeMethod(postMethod); if (status == HttpStatus.SC_OK) { InputStream inputStream = postMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( inputStream)); StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); String str = ""; while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { stringBuffer.append(str); } response = stringBuffer.toString(); } else { response = "fail"; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 释放连接
postMethod.releaseConnection(); } return response; }
3. 处理页面重定向
在JSP/Servlet编程中response.sendRedirect方法就是使用HTTP协议中的重定向机制。它与JSP中的<jsp:forward …>的区别在于后者是在服务器中实现页面的跳转,也就是说应用容器加载了所要跳转的页面的内容并返回给客户端;而前者是返回一个状态码,这些状态码的可能值见下表,然后客户端读取需要跳转到的页面的URL并重新加载新的页面。就是这样一个过程,所以我们编程的时候就要通过HttpMethod.getStatusCode()方法判断返回值是否为下表中的某个值来判断是否需要跳转。如果已经确认需要进行页面跳转了,那么可以通过读取HTTP头中的location属性来获取新的地址。
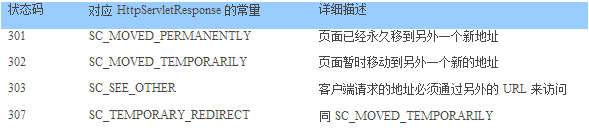
下面的代码片段演示如何处理页面的重定向
client.executeMethod(post); System.out.println(post.getStatusLine().toString()); post.releaseConnection(); // 检查是否重定向
int statuscode = post.getStatusCode(); if ((statuscode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY) || (statuscode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY) || (statuscode ==HttpStatus.SC_SEE_OTHER) || (statuscode == HttpStatus.SC_TEMPORARY_REDIRECT)) { // 读取新的 URL 地址
Header header=post.getResponseHeader("location"); if (header!=null){ Stringnewuri=header.getValue(); if((newuri==null)||(newuri.equals(""))) newuri="/"; GetMethodredirect=newGetMethod(newuri); client.executeMethod(redirect); System.out.println("Redirect:"+redirect.getStatusLine().toString()); redirect.releaseConnection(); }else System.out.println("Invalid redirect"); }
我们可以自行编写两个JSP页面,其中一个页面用response.sendRedirect方法重定向到另外一个页面用来测试上面的例子。
4. 模拟登录开心网
本小节应该说是HTTP客户端编程中最常碰见的问题,很多网站的内容都只是对注册用户可见的,这种情况下就必须要求使用正确的用户名和口令登录成功后,方可浏览到想要的页面。因为HTTP协议是无状态的,也就是连接的有效期只限于当前请求,请求内容结束后连接就关闭了。在这种情况下为了保存用户的登录信息必须使用到Cookie机制。以JSP/Servlet为例,当浏览器请求一个JSP或者是Servlet的页面时,应用服务器会返回一个参数,名为jsessionid(因不同应用服务器而异),值是一个较长的唯一字符串的Cookie,这个字符串值也就是当前访问该站点的会话标识。浏览器在每访问该站点的其他页面时候都要带上jsessionid这样的Cookie信息,应用服务器根据读取这个会话标识来获取对应的会话信息。
对于需要用户登录的网站,一般在用户登录成功后会将用户资料保存在服务器的会话中,这样当访问到其他的页面时候,应用服务器根据浏览器送上的Cookie中读取当前请求对应的会话标识以获得对应的会话信息,然后就可以判断用户资料是否存在于会话信息中,如果存在则允许访问页面,否则跳转到登录页面中要求用户输入帐号和口令进行登录。这就是一般使用JSP开发网站在处理用户登录的比较通用的方法。
这样一来,对于HTTP的客户端来讲,如果要访问一个受保护的页面时就必须模拟浏览器所做的工作,首先就是请求登录页面,然后读取Cookie值;再次请求登录页面并加入登录页所需的每个参数;最后就是请求最终所需的页面。当然在除第一次请求外其他的请求都需要附带上Cookie信息以便服务器能判断当前请求是否已经通过验证。说了这么多,可是如果你使用httpclient的话,你甚至连一行代码都无需增加,你只需要先传递登录信息执行登录过程,然后直接访问想要的页面,跟访问一个普通的页面没有任何区别,因为类HttpClient已经帮你做了所有该做的事情了,太棒了!下面的例子实现了模拟登陆开心网并向自己好友发送消息的功能。
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.Cookie; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.Header; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpStatus; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.NameValuePair; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.cookie.CookiePolicy; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.GetMethod; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.PostMethod; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpClientParams; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpMethodParams; class Login { public static String loginurl = "https://security.kaixin001.com/login/login_post.php"; static Cookie[] cookies = {}; static HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient(); static String email = "xxx@qq.com";//你的email
static String psw = "xxx";//你的密码 // 消息发送的action
String url = "http://www.kaixin001.com/home/"; public static void getUrlContent() throws Exception { HttpClientParams httparams = new HttpClientParams(); httparams.setSoTimeout(30000); httpClient.setParams(httparams); httpClient.getHostConfiguration().setHost("www.kaixin001.com", 80); httpClient.getParams().setParameter( HttpMethodParams.HTTP_CONTENT_CHARSET, "UTF-8"); PostMethod login = new PostMethod(loginurl); login.addRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8"); NameValuePair Email = new NameValuePair("loginemail", email);// 邮箱
NameValuePair password = new NameValuePair("password", psw);// 密码 // NameValuePair code = new NameValuePair( "code" // ,"????");//有时候需要验证码,暂时未解决
NameValuePair[] data = { Email, password }; login.setRequestBody(data); httpClient.executeMethod(login); int statuscode = login.getStatusCode(); System.out.println(statuscode + "-----------"); String result = login.getResponseBodyAsString(); System.out.println(result+"++++++++++++"); cookies = httpClient.getState().getCookies(); System.out.println("==========Cookies============"); int i = 0; for (Cookie c : cookies) { System.out.println(++i + ": " + c); } httpClient.getState().addCookies(cookies); // 当state为301或者302说明登陆页面跳转了,登陆成功了
if ((statuscode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY) || (statuscode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY) || (statuscode == HttpStatus.SC_SEE_OTHER) || (statuscode == HttpStatus.SC_TEMPORARY_REDIRECT)) { // 读取新的 URL 地址
Header header = login.getResponseHeader("location"); // 释放连接
login.releaseConnection(); System.out.println("获取到跳转header>>>" + header); if (header != null) { String newuri = header.getValue(); if ((newuri == null) || (newuri.equals(""))) newuri = "/"; GetMethod redirect = new GetMethod(newuri); // //////////// redirect.setRequestHeader("Cookie", cookies.toString()); httpClient.executeMethod(redirect); System.out.println("Redirect:"
+ redirect.getStatusLine().toString()); redirect.releaseConnection(); } else System.out.println("Invalid redirect"); } else { // 用户名和密码没有被提交,当登陆多次后需要验证码的时候会出现这种未提交情况
System.out.println("用户没登陆"); System.exit(1); } } public static void sendMsg() throws Exception { // 登录后发消息
System.out.println("*************发消息***********"); String posturl = "http://www.kaixin001.com/msg/post.php"; PostMethod poster = new PostMethod(posturl); poster.addRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8"); poster.setRequestHeader("Cookie", cookies.toString()); NameValuePair uids = new NameValuePair("uids", "89600585");// 发送的好友对象的id,此处换成你的好友id
NameValuePair content = new NameValuePair("content", "你好啊!");// 需要发送的信息的内容
NameValuePair liteeditor_0 = new NameValuePair("liteeditor_0", "你好啊!");// 需要发送的信息的内容
NameValuePair texttype = new NameValuePair("texttype", "plain"); NameValuePair send_separate = new NameValuePair("send_separate", "0"); NameValuePair service = new NameValuePair("service", "0"); NameValuePair[] msg = { uids, content, texttype, send_separate, service,liteeditor_0 }; poster.setRequestBody(msg); httpClient.executeMethod(poster); String result = poster.getResponseBodyAsString(); System.out.println(result+"++++++++++++"); //System.out.println(StreamOut(result, "iso8859-1"));
int statuscode = poster.getStatusCode(); System.out.println(statuscode + "-----------"); if(statuscode == 301 || statuscode == 302){ // 读取新的 URL 地址
Header header = poster.getResponseHeader("location"); System.out.println("获取到跳转header>>>" + header); if (header != null) { String newuri = header.getValue(); if ((newuri == null) || (newuri.equals(""))) newuri = "/"; GetMethod redirect = new GetMethod(newuri); // //////////// redirect.setRequestHeader("Cookie", cookies.toString()); httpClient.executeMethod(redirect); System.out.println("Redirect:"
+ redirect.getStatusLine().toString()); redirect.releaseConnection(); } else System.out.println("Invalid redirect"); } poster.releaseConnection(); } public static String StreamOut(InputStream txtis, String code) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(txtis, code)); String tempbf; StringBuffer html = new StringBuffer(100); while ((tempbf = br.readLine()) != null) { html.append(tempbf + "\n"); } return html.toString(); } }
5. 提交XML格式参数
提交XML格式的参数很简单,仅仅是一个提交时候的ContentType问题,下面的例子演示从文件文件中读取XML信息并提交给服务器的过程,该过程可以用来测试Web服务。
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.EntityEnclosingMethod; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.PostMethod; /** *用来演示提交XML格式数据的例子 */
public class PostXMLClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { File input = new File(“test.xml”); PostMethod post = new PostMethod(“http://localhost:8080/httpclient/xml.jsp”); // 设置请求的内容直接从文件中读取
post.setRequestBody( new FileInputStream(input)); if (input.length() < Integer.MAX_VALUE) post.setRequestContentLength(input.length()); else post.setRequestContentLength(EntityEnclosingMethod.CONTENT_LENGTH_CHUNKED); // 指定请求内容的类型
post.setRequestHeader( "Content-type" , "text/xml; charset=GBK" ); HttpClient httpclient = new HttpClient(); int result = httpclient.executeMethod(post); System.out.println( "Response status code: " + result); System.out.println( "Response body: " ); System.out.println(post.getResponseBodyAsString()); post.releaseConnection(); } }
6. 访问启用认证的页面
我们经常会碰到这样的页面,当访问它的时候会弹出一个浏览器的对话框要求输入用户名和密码后方可,这种用户认证的方式不同于我们在前面介绍的基于表单的用户身份验证。这是HTTP的认证策略,httpclient支持三种认证方式包括:基本、摘要以及NTLM认证。其中基本认证最简单、通用但也最不安全;摘要认证是在HTTP 1.1中加入的认证方式,而NTLM则是微软公司定义的而不是通用的规范,最新版本的NTLM是比摘要认证还要安全的一种方式。
下面例子是从httpclient的CVS服务器中下载的,它简单演示如何访问一个认证保护的页面:
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.UsernamePasswordCredentials; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.GetMethod; public class BasicAuthenticationExample { public BasicAuthenticationExample() { } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { HttpClient client = new HttpClient(); client.getState().setCredentials( "www.verisign.com" , "realm" , new UsernamePasswordCredentials( "username" , "password" ) ); GetMethod get = new GetMethod( "https://www.verisign.com/products/index.html" ); get.setDoAuthentication( true ); int status = client.executeMethod( get ); System.out.println(status+ "\n" + get.getResponseBodyAsString()); get.releaseConnection(); } }
7. 多线程模式下使用
多线程同时访问httpclient,例如同时从一个站点上下载多个文件。对于同一个HttpConnection同一个时间只能有一个线程访问,为了保证多线程工作环境下不产生冲突,httpclient使用了一个多线程连接管理器的类:MultiThreadedHttpConnectionManager,要使用这个类很简单,只需要在构造HttpClient实例的时候传入即可,代码如下:
MultiThreadedHttpConnectionManager connectionManager = new MultiThreadedHttpConnectionManager();
HttpClient client = new HttpClient(connectionManager);
以后尽管访问client实例即可。
httpClient完整封装
HttpInvoke.java:封装了HttpClient调度的必要参数设置,以及post,get等常用方法
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.*; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.auth.AuthScope; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.PostMethod; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.GetMethod; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.net.SocketTimeoutException; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; public class HttpInvoker { private Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HttpInvoker.class); private static HttpInvoker httpInvoker = new HttpInvoker(); private HttpClient client = null; private String charset = "gbk"; private int timeout = 10000; private boolean useProxy = false; private String proxyHost = null; private int proxyPort; private String proxyUsername = null; private String proxyPassword = null; private boolean initialized = false; public static HttpInvoker getInstance() { return httpInvoker; } private HttpInvoker() { client = new HttpClient(new MultiThreadedHttpConnectionManager()); client.getParams().setParameter("http.protocol.content-charset", "gbk"); client.getParams().setContentCharset("gbk"); client.getParams().setSoTimeout(timeout); } public HttpInvoker(String charset, int timeout, boolean useProxy, String proxyHost, int proxyPort, String proxyUsername, String proxyPassword) { client = new HttpClient(new MultiThreadedHttpConnectionManager()); if(charset != null && !charset.trim().equals("")) { this.charset = charset; } if(timeout > 0) { this.timeout = timeout; } client.getParams().setParameter("http.protocol.content-charset", charset); client.getParams().setContentCharset(charset); client.getParams().setSoTimeout(timeout); if(useProxy && proxyHost != null &&
!proxyHost.trim().equals("") && proxyPort > 0) { HostConfiguration hc = new HostConfiguration(); hc.setProxy(proxyHost, proxyPort); client.setHostConfiguration(hc); if (proxyUsername != null && !proxyUsername.trim().equals("") && proxyPassword != null && !proxyPassword.trim().equals("")) { client.getState().setProxyCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials(proxyUsername, proxyPassword)); } } initialized = true; logger.debug("HttpInvoker初始化完成"); } public synchronized void init() { if(charset != null && !charset.trim().equals("")) { client.getParams().setParameter("http.protocol.content-charset", charset); client.getParams().setContentCharset(charset); } if(timeout > 0) { client.getParams().setSoTimeout(timeout); } if(useProxy && proxyHost != null &&
!proxyHost.trim().equals("") && proxyPort > 0) { HostConfiguration hc = new HostConfiguration(); hc.setProxy(proxyHost, proxyPort); client.setHostConfiguration(hc); if (proxyUsername != null && !proxyUsername.trim().equals("") && proxyPassword != null && !proxyPassword.trim().equals("")) { client.getState().setProxyCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials(proxyUsername, proxyPassword)); } } initialized = true; logger.debug("HttpInvoker初始化完成"); } public String invoke(String url) throws Exception { return invoke(url, null, false); } public String invoke(String url, Map params, boolean isPost) throws Exception { logger.debug("HTTP调用[" + (isPost?"POST":"GET") + "][" + url + "][" + params + "]"); HttpMethod httpMethod = null; String result = ""; try { if(isPost && params != null && params.size() > 0) { Iterator paramKeys = params.keySet().iterator(); httpMethod = new PostMethod(url); NameValuePair[] form = new NameValuePair[params.size()]; int formIndex = 0; while(paramKeys.hasNext()) { String key = (String)paramKeys.next(); Object value = params.get(key); if(value != null && value instanceof String && !value.equals("")) { form[formIndex] = new NameValuePair(key, (String)value); formIndex++; } else if(value != null && value instanceof String[] && ((String[])value).length > 0) { NameValuePair[] tempForm =
new NameValuePair[form.length + ((String[])value).length - 1]; for(int i=0; i<formIndex; i++) { tempForm[i] = form[i]; } form = tempForm; for(String v : (String[])value) { form[formIndex] = new NameValuePair(key, (String)v); formIndex++; } } } ((PostMethod)httpMethod).setRequestBody(form); } else { if(params != null && params.size() > 0) { Iterator paramKeys = params.keySet().iterator(); StringBuffer getUrl = new StringBuffer(url.trim()); if(url.trim().indexOf("?") > -1) { if(url.trim().indexOf("?") < url.trim().length()-1 && url.trim().indexOf("&") < url.trim().length()-1) { getUrl.append("&"); } } else { getUrl.append("?"); } while(paramKeys.hasNext()) { String key = (String)paramKeys.next(); Object value = params.get(key); if(value != null && value instanceof String && !value.equals("")) { getUrl.append(key).append("=").append(value).append("&"); } else if(value != null && value instanceof String[] && ((String[])value).length > 0) { for(String v : (String[])value) { getUrl.append(key).append("=").append(v).append("&"); } } } if(getUrl.lastIndexOf("&") == getUrl.length()-1) { httpMethod = new GetMethod(getUrl.substring(0, getUrl.length()-1)); } else { httpMethod = new GetMethod(getUrl.toString()); } } else { httpMethod = new GetMethod(url); } } client.executeMethod(httpMethod); // result = httpMethod.getResponseBodyAsString();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( httpMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream(),"ISO-8859-1")); String line = null; String html = null; while((line = reader.readLine()) != null){ if(html == null) { html = ""; } else { html += "\r\n"; } html += line; } if(html != null) { result = new String(html.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), charset); } } catch (SocketTimeoutException e) { logger.error("连接超时[" + url + "]"); throw e; } catch (java.net.ConnectException e) { logger.error("连接失败[" + url + "]"); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("连接时出现异常[" + url + "]"); throw e; } finally { if (httpMethod != null) { try { httpMethod.releaseConnection(); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("释放网络连接失败[" + url + "]"); throw e; } } } return result; } public void setCharset(String charset) { this.charset = charset; } public void setTimeout(int timeout) { this.timeout = timeout; } public void setProxyHost(String proxyHost) { this.proxyHost = proxyHost; } public void setProxyPort(int proxyPort) { this.proxyPort = proxyPort; } public void setProxyUsername(String proxyUsername) { this.proxyUsername = proxyUsername; } public void setProxyPassword(String proxyPassword) { this.proxyPassword = proxyPassword; } public void setUseProxy(boolean useProxy) { this.useProxy = useProxy; } public synchronized boolean isInitialized() { return initialized; } }
http访问网络的代理ip和端口,还有使用用户及密码都可以在Spring容器中注入进来:
<bean id="httpInvoker" class="HttpInvoker">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="gbk" /><!--useProxy-->
<constructor-arg type="int" value="10000" /><!--useProxy-->
<constructor-arg type="boolean" value="true" /><!--useProxy-->
<!--代理地址 -->
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="192.168.1.1" />
<constructor-arg type="int" value="8080" />
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="" /><!--用户名-->
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="" /><!--密码-->
</bean>
使用方式:post
Map<String,String> params = new HashMap<String,String>(); params.put("check", check); String result = httpInvoker.invoke( "someURL", params, true);
使用方式:get
String content = httpInvoker.invoke(url);
参考资料:
httpclient首页: http://jakarta.apache.org/commons/httpclient/
关于NTLM是如何工作: http://davenport.sourceforge.net/ntlm.html
--------------------------------------------
HttpClient入门
http://blog.csdn.net/ambitiontan/archive/2006/01/07/572644.aspx
Jakarta Commons HttpClient 学习笔记
http://blog.csdn.net/cxl34/archive/2005/01/19/259051.aspx
Cookies,SSL,httpclient的多线程处理,HTTP方法
http://blog.csdn.net/bjbs_270/archive/2004/11/05/168233.aspx
















