目录
一、I/O复用模型回顾二、创建选择器 1.Pipe函数 2.Poll函数三、注册Channel到Selector四、Select返回就绪事件集合
一、I/O复用模型回顾
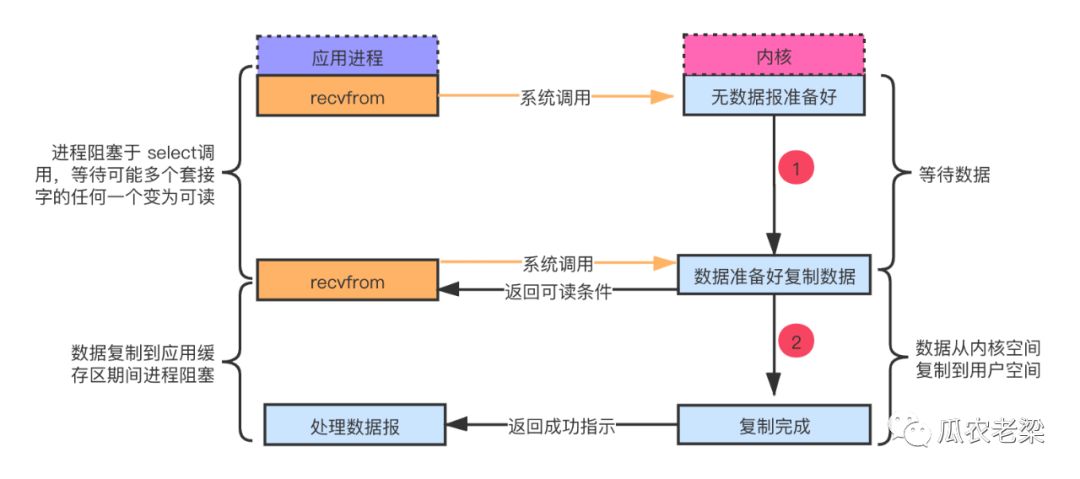
备注:I/O复用可以调用select/poll阻塞在这两个系统调用中的某一个上,而不是阻塞在真正的I/O系统调用上。图示中应用进程阻塞于select调用,等待数据报套接字变为可读,当select返回套接字可读这一条件时,调用recvfrom把所读数据复制到应用进程缓冲区。特点:select等待多个描述符就绪;即图示中第1步可以等待多个文件描述符。
二、创建选择器
通过Selector.open()创建选择器。
Selector selector = Selector.open();
以Linux中使用PollSelectorImpl跟踪实现过程。
PollSelectorImpl(SelectorProvider sp) { super(sp, 1, 1); // Native调用pipe()函数返回两个文件描述符 long pipeFds = IOUtil.makePipe(false); // @1 // 文件描述符fd0只读数据 fd0 = (int) (pipeFds >>> 32); // 文件描述符fd1只写数据 fd1 = (int) pipeFds; // pollfd结构类型数组 pollWrapper = new PollArrayWrapper(INIT_CAP); // @2 pollWrapper.initInterrupt(fd0, fd1); channelArray = new SelectionKeyImpl[INIT_CAP];}
long pipeFds = IOUtil.makePipe(false);staticnativelongmakePipe(boolean blocking);//IOUtil.c#Java_sun_nio_ch_IOUtil_makePipe()pipe(fd)
1.Pipe函数
IOUtil.makePipe本地方法调用IOUtil.c#Java_sun_nio_ch_IOUtil_makePipe()->pipe(fd).
原型函数
intpipe(int fildes[2]);
函数描述
The pipe() function creates a data pipe and places two file descriptors, one each into the arguments fildes[0] and fildes[1], that refer to the open file descriptions for the read and write ends of the pipe, respectively. Their integer values will be the two lowest available at the time of the pipe() call. The O_NONBLOCK and FD_CLOEXEC flags will be clear on both descriptors. NOTE: these flags can, however, be set by the fcntl() function.Data can be written to the file descriptor fildes[1] and read from file descriptor fildes[0]. A read on the file descriptor fildes[0] will access data written to the file descriptor fildes[1] on a first-in-first-out basis. File descriptor fildes[0] is open for reading only. File descriptor fildes[1] is open for writing only.
备注:pipe()创建数据通道成功会将一对打开的文件描述符填充到参数fildes;文件描述符fildes[1]只能写数据;文件描述符fildes[0]只能读数据;写入fildes[1]的数据可以通过fildes[0]读取。
2.Poll函数
原型函数
intpoll(struct pollfd fds[], nfds_t nfds, int timeout)
函数说明
The poll() function is used to enable an application to multiplex I/O over a set of descriptors. For each member of the array pointed to by fds, poll() will examine the given descriptor for the event(s) specified. nfds is the number of pollfd structures in the fds array. The poll() function will determine which descriptors can read or write data, or whether certain events have occured on the descriptors within the timeout period.
参数说明 fds
structpollfd { int fd; /* Descriptor */ short events; /* Requested events */ short revents; /* Returned events */ };
(Input) Specifies an array of descriptors to be examined and the events of interest for each descriptor.
nfds
pollfd 结构体数组元素个数。
返回值
发生错误时,poll函数的返回值为-1;若定时器到时没有任何描述符就绪,则返回0;否则返回就绪描述符的个数,即:revents成员值非0的描述符个数。
备注:Poll函数第一个参数指向pollfd结构数组;pollfd用于检测给定描述符fd的条件;要检测的条件由events指定,revents返回该描述符的状态。Poll函数功能:允许进程指示内核等待事件中的任何一个发生,并只在有一个或多个事件发生或经历一段特定事件后才唤醒它。例如:集合中{1,4,5}中任何描述符准备好读时,告知内核返回;PollArrayWrapper为了封装pollfd结构数组。
三、注册Channel到Selector
// 示例代码serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8089));serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);// JDK代码publicfinal SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att) throws ClosedChannelException{ synchronized (regLock) { // 通道需开启状态 if (!isOpen()) throw new ClosedChannelException(); // 操作合法性校验 if ((ops & ~validOps()) != 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); // 通道需非阻塞 if (blocking) throw new IllegalBlockingModeException(); SelectionKey k = findKey(sel); if (k != null) { // 注册操作并转换Poll Native支持的事件 k.interestOps(ops); k.attach(att); } if (k == null) { // New registration synchronized (keyLock) { if (!isOpen()) throw new ClosedChannelException(); // 注册channel到selector并返回选择SelectionKey k = ((AbstractSelector)sel).register(this, ops, att); addKey(k); } } return k; }}
备注:注册操作建立通道与选择器的注册关系,通过SelectionKeyImpl来建立;并把感兴趣的操作注册到PollArrayWrapper的EventOps中;即对应原型函数的pollfd结构体events中。
四、Select返回就绪事件集合
// 示例代码int n = selector.select();// JDK代码protectedintdoSelect(long timeout) throws IOException { ... pollWrapper.poll(totalChannels, 0, timeout); ... int numKeysUpdated = updateSelectedKeys(); ...}// JDK代码protectedintupdateSelectedKeys() {int numKeysUpdated = 0;for (int i=channelOffset; i<totalChannels; i++) { // 获取通道就绪操作类型(可读、可写、错误等) int rOps = pollWrapper.getReventOps(i); ... // 将ReventOps就绪的操作类型转换到SelectionKeyImpl if (sk.channel.translateAndSetReadyOps(rOps, sk)) { numKeysUpdated++; } ...}return numKeysUpdated;}
备注:selector.select()调用Native函数poll;将返回的就绪操作注册到选择键中,方便后续操作。
五、本文总结
多路复用主要依靠Native函数Pipe函数和Poll函数(本文Poll函数为例);在Java实现中主要过程为:通过SelectionKeyImpl建立选择器与通道的关系;通过PollArrayWrapper封装Poll函数的pollfd结构体数组;将感兴趣的操作注册到pollfd的events中;将pollf中revents返回就绪的事件转换到选择键SelectionKeyImpl中。通过遍历就绪事件集合进行读写操作。
六、系列文章
「瓜农老梁 学习同行」

本文分享自微信公众号 - 瓜农老梁(gh_01130ae30a83)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。











