
封装、继承、多态、抽象四大特征

多态:一个对象的多种状态,是从继承来的;
软件的可读性和可维护性是密切相关的;

多个age 会造成一定理解上的困难;
所以,带一个this;
这样比较好理解了,this是属于一个对象的;

this----"我的"---代词;
this 是属于一个具体的对象的,而不是属于一个类的;
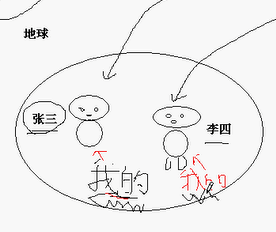
JAVA虚拟机给每个对象分配一个虚拟机,代表当前对象
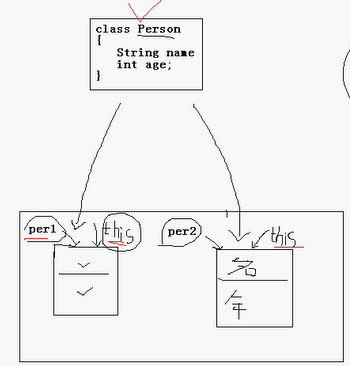

dog引用的名存放在P1里面,但是内存放在dog1
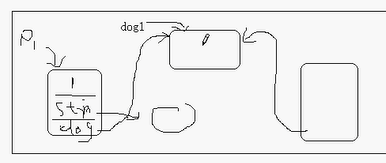
this是不能在外面去使用的;
只能 在类定义的 时候去使用;
构造方法(构造函数)就是用来初始化成员变量的;
类变量和类方法:
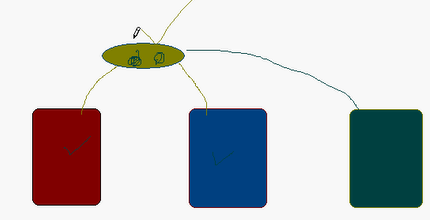
如果有公共的空间;可以共同的操作;
static int total = 0;

如果加了static,编译器可以准确的理解到total
是属于大家的,而不是属于某个小孩子的;
ch1,ch2,ch3都可访问到 静态变量total;
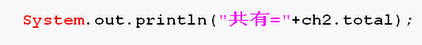
或者直接用类名也可以访问到静态变量total:

java****面向对象编程(2)--this
一个问题?
请大家看一段代码:(Demo112.java)
*****重点*:this是属于一个对象,不属于类的。
java虚拟机会给每个对象分配this,代表当前对象。坦白的讲,要明白this不是件容易的事
注意事项:this不能在类定义的外部使用,只能在类定义的方法中使用
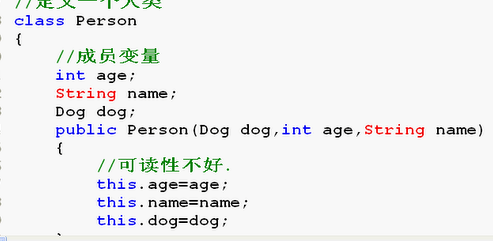
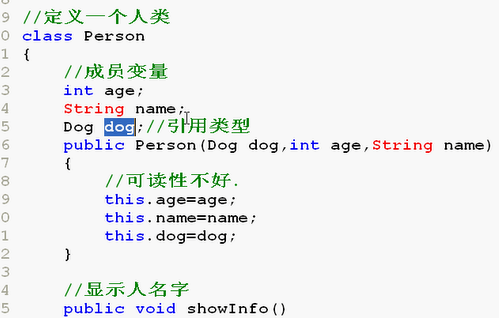
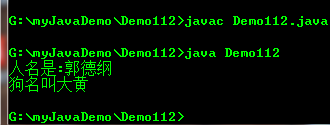
/* this的必要性 */ public class Demo112{ public static void main(String []args){ Dog dog1=new Dog(2,"大黄"); Person p1=new Person(dog1,23,"郭德纲"); Person p2=new Person(dog1,24,"刘谦"); p1.showInfo(); p1.dog.showInfo(); } } //定义一个人类 class Person{ //成员变量 int age; String name; Dog dog;//引用类型 public Person(Dog dog,int age,String name){ //可读性不好 //age=age; //name=name; this.age=age; //this.age指this代词指定是成员变量age this.name=name; //this.name指this代词指定是成员变量name this.dog=dog; } //显示人名字 public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("人名是:"+this.name); } } class Dog{ int age; String name; public Dog(int age,String name){ this.age=age; this.name=name; } //显示狗名 public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("狗名叫"+this.name); } }
this.age=age; this.name=name;
x
1
/*
2
this的必要性
3
*/
4
public class Demo112{
5
public static void main(String []args){
6
Dog dog1=new Dog(2,"大黄");
7
Person p1=new Person(dog1,23,"郭德纲");
8
Person p2=new Person(dog1,24,"刘谦");
9
p1.showInfo();
10
p1.dog.showInfo();
11
}
12
}
13
//定义一个人类
14
class Person{
15
//成员变量
16
int age;
17
String name;
18
Dog dog;//引用类型
19
public Person(Dog dog,int age,String name){
20
//可读性不好
21
//age=age;
22
//name=name;
23
this.age=age; //this.age指this代词指定是成员变量age
24
this.name=name; //this.name指this代词指定是成员变量name
25
this.dog=dog;
26
}
27
//显示人名字
28
public void showInfo(){
29
System.out.println("人名是:"+this.name);
30
}
31
}
32
33
class Dog{
34
int age;
35
String name;
36
public Dog(int age,String name){
37
this.age=age;
38
this.name=name;
39
}
40
//显示狗名
41
public void showInfo(){
42
System.out.println("狗名叫"+this.name);
43
}
44
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
类变量--提出问题?
提出问题的主要目的就是让大家思考解决之道。
public class Demo113{ public static void main(String []args){ /* int total=0; Child ch1=new Child(3,"妞妞"); ch1.joinGame(); total++; Child ch2=new Child(4,"小小"); ch2.joinGame(); total++; */ Child ch1=new Child(3,"妞妞"); ch1.joinGame(); Child ch2=new Child(4,"小小"); ch2.joinGame(); Child ch3=new Child(5,"大大"); ch3.joinGame(); System.out.println("共有="+Child.total); } } //定义小孩类 class Child{ int age; String name; //static公共函数,total是静态变量,因此它可以被任何一个对象访问 static int total=0; public Child(int age,String name){ this.age=age; this.name=name; } public void joinGame(){ total++; System.out.println("有一个小孩加入了"); } }
1
public class Demo113{
2
public static void main(String []args){
3
/* int total=0;
4
Child ch1=new Child(3,"妞妞");
5
ch1.joinGame();
6
total++;
7
Child ch2=new Child(4,"小小");
8
ch2.joinGame();
9
total++;
10
*/
11
Child ch1=new Child(3,"妞妞");
12
ch1.joinGame();
13
Child ch2=new Child(4,"小小");
14
ch2.joinGame();
15
Child ch3=new Child(5,"大大");
16
ch3.joinGame();
17
System.out.println("共有="+Child.total);
18
}
19
}
20
//定义小孩类
21
class Child{
22
int age;
23
String name;
24
//static公共函数,total是静态变量,因此它可以被任何一个对象访问
25
static int total=0;
26
public Child(int age,String name){
27
this.age=age;
28
this.name=name;
29
}
30
public void joinGame(){
31
total++;
32
System.out.println("有一个小孩加入了");
33
}
34
}
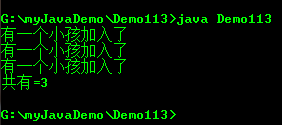
ch1/ch2/ch3 的输出结果都是3; 共享static静态变量的内存;










