public interface FzkRepository extends MongoRepository<Fzk, String> {
Fzk findByName(String name);
}
@RestControllerpublic class TestController {
@Autowired
private FzkRepository fzkReposiroty;
}
为什么一个接口,没有实现类就能被注入?
首先如果想使用MongoRepository,一定会在配置中加入@EnableMongoRepositories,就从EnableMongoRepositories开始
@Import(MongoRepositoriesRegistrar.class)
跟踪进入RepositoryBeanDefinitionRegistrarSupport
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
....
AnnotationRepositoryConfigurationSource configurationSource = new AnnotationRepositoryConfigurationSource(annotationMetadata, getAnnotation(), resourceLoader, environment, registry);
if (annotationMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(getAnnotation().getName()) == null) {
return;
}
RepositoryConfigurationExtension extension = getExtension();
RepositoryConfigurationUtils.exposeRegistration(extension, registry, configurationSource);
RepositoryConfigurationDelegate delegate = new RepositoryConfigurationDelegate(configurationSource, resourceLoader,
environment);
delegate.registerRepositoriesIn(registry, extension);
}
没什么可说的,只有使用了EnableMongoRepositories才会继续进行,注册bean交给了RepositoryConfigurationDelegate 来进行。继续进入RepositoryConfigurationDelegate.registerRepositoriesIn方法
1 public List
扫描实现了MongoRepository的接口并生成RepositoryConfigurationSource的逻辑在RepositoryConfigurationExtensionSupport.getRepositoryConfigurations方法中
public <T extends RepositoryConfigurationSource> Collection<RepositoryConfiguration<T>> getRepositoryConfigurations(
T configSource, ResourceLoader loader, boolean strictMatchesOnly) {
....
Set<RepositoryConfiguration<T>> result = new HashSet<RepositoryConfiguration<T>>();
for (BeanDefinition candidate : configSource.getCandidates(loader)) {
RepositoryConfiguration<T> configuration = getRepositoryConfiguration(candidate, configSource);
if (!strictMatchesOnly || configSource.usesExplicitFilters()) {
result.add(configuration);
continue;
}
Class<?> repositoryInterface = loadRepositoryInterface(configuration, loader);
if (repositoryInterface == null || isStrictRepositoryCandidate(repositoryInterface)) {
result.add(configuration);
}
}
return result;
}
继续跟踪RepositoryConfigurationSourceSupport.getCandidates
public Collection<BeanDefinition> getCandidates(ResourceLoader loader) {
RepositoryComponentProvider scanner = new RepositoryComponentProvider(getIncludeFilters(), registry);
scanner.setConsiderNestedRepositoryInterfaces(shouldConsiderNestedRepositories());
scanner.setEnvironment(environment);
scanner.setResourceLoader(loader);
for (TypeFilter filter : getExcludeFilters()) {
scanner.addExcludeFilter(filter);
}
Set<BeanDefinition> result = new HashSet<BeanDefinition>();
for (String basePackage : getBasePackages()) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidate = scanner.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
result.addAll(candidate);
}
return result;
}
RepositoryComponentProvider.findCandidateComponents,先由父类ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider处理
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinition>();
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + (basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
......for (Resource resource : resources) {
......
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
......
}
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) { //1
if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
return false;
}
}
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) { //2 if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { return isConditionMatch(metadataReader); } } return false; }
private boolean isConditionMatch(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
if (this.conditionEvaluator == null) {
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(getRegistry(), getEnvironment(), getResourceLoader());
}
return !this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata());
}
判断条件,1.如果是注解了NoRepositoryBean就不处理,2.判断了是Repository后,继续判断是否有@Condition。找到了所有复合条件的类后,组成RepositoryConfiguration后,继续跟踪RepositoryConfigurationDelegate.registerRepositoriesIn,组成BeanDefinitionBuilder,构件出MongoRepositoryFactoryBean。
public class MongoRepositoryFactoryBean<T extends Repository<S, ID>, S, ID extends Serializable>
extends RepositoryFactoryBeanSupport<T, S, ID>
public abstract class RepositoryFactoryBeanSupport<T extends Repository<S, ID>, S, ID extends Serializable>
implements InitializingBean, RepositoryFactoryInformation<S, ID>, FactoryBean<T>, BeanClassLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware
MongoRepositoryFactoryBean间接实现InitializingBean,因此他会实现afterPropertiesSet方法
在AbstractApplicationContext -> refresh() -> finishBeanFactoryInitialization()阶段,实例化bean时进行实例化。
这个例子里,TestController注入了FzkRepository ,实例化TestController时发现需要注入FzkRepository 会先实例化FzkRepository。
在DefaultListableBeanFactory的preInstantiateSingletons()时
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
......
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}......
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
......
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
......
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}......
return (T) bean;
}
多次调用进入AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean。
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
......
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}......
}
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
......
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
......
}
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
......
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
...... }
上面说了由BeanDefinitionBuilder构件出MongoRepositoryFactoryBean,而MongoRepositoryFactoryBean实现了InitializingBean,这里进入到了MongoRepositoryFactoryBean.afterPropertiesSet
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
super.afterPropertiesSet();
Assert.notNull(operations, "MongoTemplate must not be null!");
if (!mappingContextConfigured) {
setMappingContext(operations.getConverter().getMappingContext());
}
}
进入到父累RepositoryFactoryBeanSupport.afterPropertiesSet
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.factory = createRepositoryFactory();
......
if (publisher != null) {
this.factory.addRepositoryProxyPostProcessor(new EventPublishingRepositoryProxyPostProcessor(publisher));
}
this.repositoryMetadata = this.factory.getRepositoryMetadata(repositoryInterface);
if (!lazyInit) {
initAndReturn();
}
}
private T initAndReturn() {
......
if (this.repository == null) {
this.repository = this.factory.getRepository(repositoryInterface, customImplementation);
}
return this.repository;
}
这里的factory是MongoRepositoryFactory,接下来,才是创建代理的部分
public <T> T getRepository(Class<T> repositoryInterface, Object customImplementation) {
......
// Create proxy
ProxyFactory result = new ProxyFactory();
result.setTarget(target);
result.setInterfaces(new Class[] { repositoryInterface, Repository.class });
......
result.addAdvice(new QueryExecutorMethodInterceptor(information, customImplementation, target, projectionFactory));
return (T) result.getProxy(classLoader);
}
第一重点是ProxyFactory,这里target是SimpleMongoRepository,repositoryInterface是FzkRepository(自己的接口)。
另一个重点是增加了一个切入点QueryExecutorMethodInterceptor。看看QueryExecutorMethodInterceptor
public QueryExecutorMethodInterceptor(RepositoryInformation repositoryInformation, Object customImplementation,
Object target, ProjectionFactory projectionFactory) {
......
this.resultHandler = new QueryExecutionResultHandler();
this.repositoryInformation = repositoryInformation;
this.customImplementation = customImplementation;
this.target = target;
QueryLookupStrategy lookupStrategy = getQueryLookupStrategy(queryLookupStrategyKey,
RepositoryFactorySupport.this.evaluationContextProvider);
lookupStrategy = lookupStrategy == null ? getQueryLookupStrategy(queryLookupStrategyKey) : lookupStrategy;
Iterable<Method> queryMethods = repositoryInformation.getQueryMethods();
......
for (Method method : queryMethods) {
RepositoryQuery query = lookupStrategy.resolveQuery(method, repositoryInformation, projectionFactory,
namedQueries);
invokeListeners(query);
queries.put(method, query);
}
}
首先他是一个MethodInterceptor,一个有个invoke方法,这个方法之后在说。现在先看构造器里干了什么。
首先构件一个MongoRepositoryFactory$MongoQueryLookupStrategy类型的lookupStrategy 。处理jpa写法的方法就是由它来处理,这里的例子是findByName方法。继续跟踪,看看是怎么将findByName解析成{"name" : ***}的。写了这么多,终于快到终点了。继续看,进入到MongoQueryLookupStrategy.resolveQuery
public RepositoryQuery resolveQuery(Method method, RepositoryMetadata metadata, ProjectionFactory factory,
NamedQueries namedQueries) {
MongoQueryMethod queryMethod = new MongoQueryMethod(method, metadata, factory, mappingContext);
String namedQueryName = queryMethod.getNamedQueryName();
if (namedQueries.hasQuery(namedQueryName)) {
String namedQuery = namedQueries.getQuery(namedQueryName);
return new StringBasedMongoQuery(namedQuery, queryMethod, operations, EXPRESSION_PARSER,
evaluationContextProvider);
} else if (queryMethod.hasAnnotatedQuery()) {
return new StringBasedMongoQuery(queryMethod, operations, EXPRESSION_PARSER, evaluationContextProvider);
} else {
return new PartTreeMongoQuery(queryMethod, operations);
}
}
这里,无@Query注解,进入PartTreeMongoQuery分支
public PartTreeMongoQuery(MongoQueryMethod method, MongoOperations mongoOperations) {
super(method, mongoOperations);
this.processor = method.getResultProcessor();
this.tree = new PartTree(method.getName(), processor.getReturnedType().getDomainType());
this.isGeoNearQuery = method.isGeoNearQuery();
this.context = mongoOperations.getConverter().getMappingContext();
}
public class PartTree {
private static final String KEYWORD_TEMPLATE = "(%s)(?=(\\p{Lu}|\\P{InBASIC_LATIN}))";
private static final String QUERY_PATTERN = "find|read|get|query|stream";
private static final String COUNT_PATTERN = "count";
private static final String EXISTS_PATTERN = "exists";
private static final String DELETE_PATTERN = "delete|remove";
private static final Pattern PREFIX_TEMPLATE = Pattern.compile( //
"^(" + QUERY_PATTERN + "|" + COUNT_PATTERN + "|" + EXISTS_PATTERN + "|" + DELETE_PATTERN + ")((\\p{Lu}.*?))??By");
public PartTree(String source, Class<?> domainClass) {
......
Matcher matcher = PREFIX_TEMPLATE.matcher(source);
if (!matcher.find()) {
this.subject = new Subject(null);
this.predicate = new Predicate(source, domainClass);
} else {
this.subject = new Subject(matcher.group(0));
this.predicate = new Predicate(source.substring(matcher.group().length()), domainClass);
}
}
}
最终生成的query,已经将name(key)解析出来了。
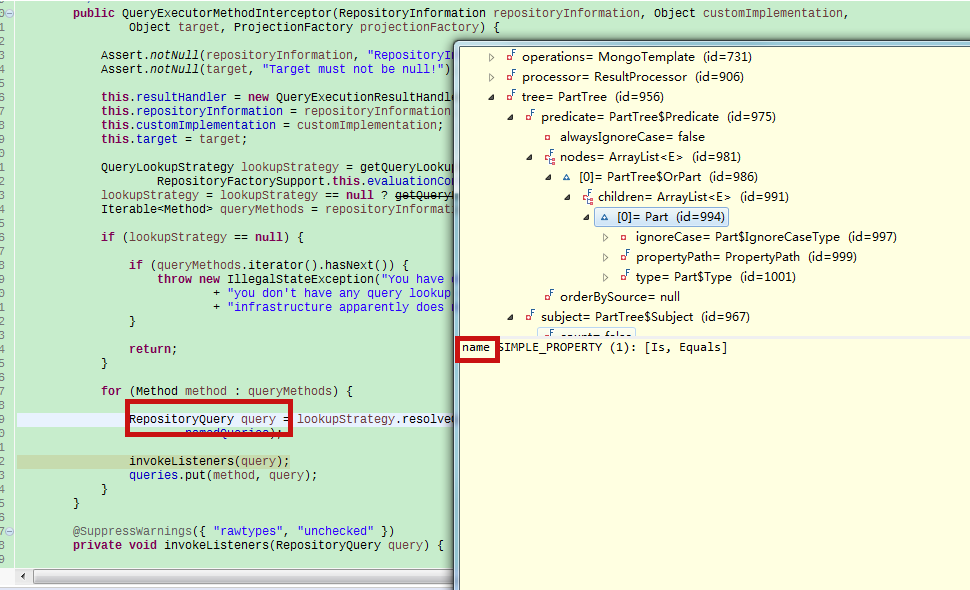
至此,终于解析完,怎么创建的代理,怎么根据方法名来解析sql。最后就是使用点
上面说了,使用时,会调用QueryExecutorMethodInterceptor.invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object result = doInvoke(invocation);
return resultHandler.postProcessInvocationResult(result, invocation.getMethod());
}
private Object doInvoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
Object[] arguments = invocation.getArguments();
if (isCustomMethodInvocation(invocation)) {
Method actualMethod = repositoryInformation.getTargetClassMethod(method);
return executeMethodOn(customImplementation, actualMethod, arguments);
}
if (hasQueryFor(method)) {
return queries.get(method).execute(arguments);
}
// Lookup actual method as it might be redeclared in the interface
// and we have to use the repository instance nevertheless
Method actualMethod = repositoryInformation.getTargetClassMethod(method);
return executeMethodOn(target, actualMethod, arguments);
}
queries.get(method)得到PartTreeMongoQuery
public Object execute(Object[] parameters) {
MongoParameterAccessor accessor = new MongoParametersParameterAccessor(method, parameters);
Query query = createQuery(new ConvertingParameterAccessor(operations.getConverter(), accessor));
applyQueryMetaAttributesWhenPresent(query);
ResultProcessor processor = method.getResultProcessor().withDynamicProjection(accessor);
String collection = method.getEntityInformation().getCollectionName();
MongoQueryExecution execution = getExecution(query, accessor,
new ResultProcessingConverter(processor, operations, instantiators));
return execution.execute(query, processor.getReturnedType().getDomainType(), collection);
}
构件出Query得到结果返回













