关注 Vue中文社区 ,回复“ 加群 ”
加入我们一起学习,天天进步

作者:小锁君少 | 来源:掘金
前言
之前使用过 Vue 开发后台、中台项目,也做过移动端 H5,弄过一点小的前端架构。每做一个项目都会收获了不一样的经验和理解。下面我把这些点点滴滴的经验总结下来,做一个系列的文章分享和阶段性的总结。
常规操作,先点赞后观看哦!你的点赞是我创作的动力之一!
概览
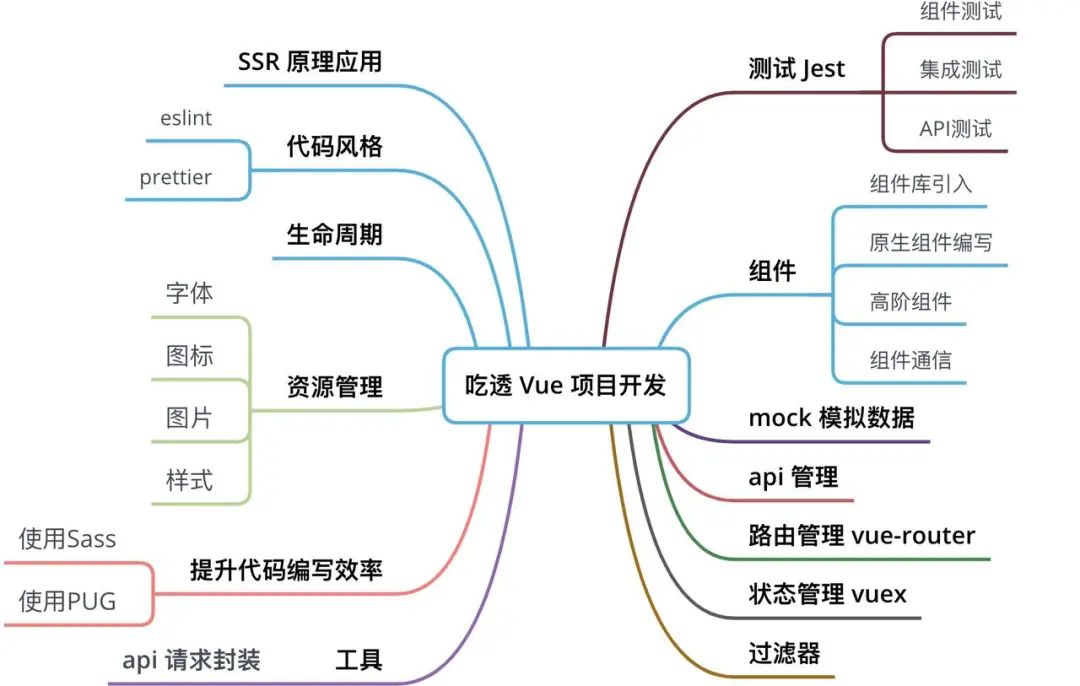
问题
我将从 16 个方面来论述 vue 开发过程中的一些技巧和原理。当然由于篇幅有限,先论述前 8 个问题,下节将完成全系列内容。
本篇文章将围绕下列问题进行论述:
如何规范你的 git 提交,并自动生成并提交日志?
如何配置和使用 Sass 和 PUG 提升你的编码效率?
如何处理你的代码风格问题,以及如何使用 perttier 与 eslint 解决效率风格两难问题?
如何管理页面的路由,如何编写异步路由?
如何编写组件,引入组件库?
如何管理你的资源,如何引入图标,样式?
如何封装你的 axios,管理你的api?
如何使用 mock 模拟你的数据,实现真正意义的前后端分离?
实践
实践之前:我希望你有如下准备,或者知识储备。
了解
npm/yarn/git/sass/pug/vue/vuex/vue-router/axios/mock/ssr/jest的使用和原理。当然上面知识不了解也没关系哈哈哈,文章中会提到大致用法和作用。
如何规范 git 提交
代码提交记录是一个很好的代码修改日志。规范的代码提交记录,不管在平时代码开发维护过程中,还是在定位 bug 或者回退版本来说都是极为重要。
原理
两种做法:
自己手动规范 git 的提交原则或者团队统一制定。这个靠自觉,好习惯养成之后就没问题来
使用插件规范,比如下面这种
为了规范提交,我使用了如下插件:
commitizen
conventional-changelog
cz-conventional-changelog
conventional-changelog-cli
解决方案
安装系列插件依赖
`yarn add -D commitizen conventional-changelog cz-conventional-changelog`
安装依赖时,要注意是否是生产环境需要的。显然
commitizen只在开发环境中使用。-D只在dev环境使用
配置依赖路径
在 package.json 中添加配置
`{`
`//...`
` "config": {`
` "commitizen": {`
` "path": "./node_modules/cz-conventional-changelog"`
` }`
` }`
`}`
在命令行中输入
`git add -A`
`git-cz`
出现了交互输入方式,规范你的 commit 输入格式
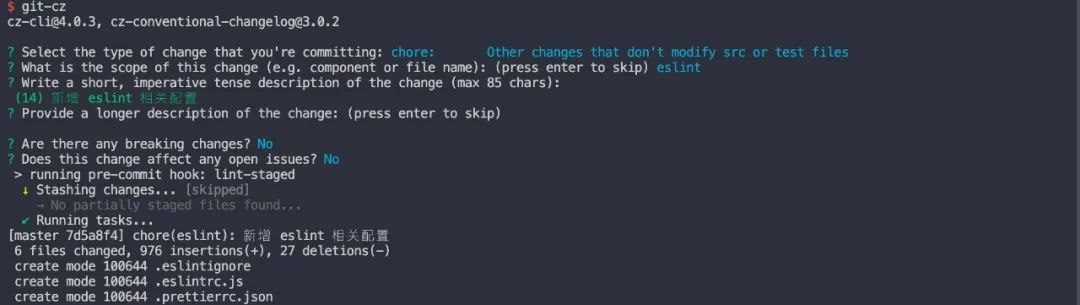
生成 CHANGELOG
`npm i -g conventional-changelog-cli`
增加一个npm 命令,快速生成日志
`"genlog": "conventional-changelog -p angular -i .github/CHANGELOG.md -s"`
使用 yarn命令生成日志
`yarn genlog`
自动生成的log
`# 0.1.0 (2019-12-27)`
`## Features`
`* **git:** 增加commitizen工具规范提交 ([58e3937](https://github.com/suoyuesmile/suo-design-pro/commit/58e39370aa838fd99312f73b37d092ffadc85990))`
如何管理代码风格
较统一的代码风格利于阅读,也利于协作。
原理与解决方案
使用 eslint 约束基本风格和语法,使用 prettier 自动格式化你的代码。
实践
安装 eslint 依赖
`{`
` "eslint": "^5.16.0",`
` "eslint-config-standard": "^6.2.1",`
` "eslint-friendly-formatter": "^2.0.7",`
` "eslint-loader": "^2.1.2",`
` "eslint-plugin-html": "^2.0.1",`
` "eslint-plugin-promise": "^3.5.0",`
` "eslint-plugin-standard": "^2.3.1",`
` "eslint-plugin-vue": "^5.0.0"`
`}`
使用两个插件,一个 plugin:vue/essential,一个是 standard。 vue/essential 为了在 vue 里面也可以生效。另一个是 standard。standard 标准文档
使用 recommend 也可以,采用推荐 lint,更加轻量化
`module.exports = {`
` root: true,`
` env: {`
` node: true`
` },`
` extends: ['plugin:vue/essential', 'standard'],`
` rules: {`
` quotes: ['error', 'single'],`
` indent: ['error', 2, { MemberExpression: 'off' }],`
` 'arrow-parens': 0,`
` 'no-loop-func': 2,`
` 'space-before-function-paren': ['error', 'never'],`
` indent: ['error', 2, { SwitchCase: 1 }]`
` },`
` parserOptions: {`
` parser: require.resolve('babel-eslint'),`
` ecmaVersion: 2018,`
` sourceType: 'module'`
` }`
`}`
可以自定义 rules 的规则
rules 的规则 { 规则名:[是否关闭/规则等级,配置的值,只对部分配置] }
indent: ['error', 2, { SwitchCase: 1 }]兼容 prettier,prettier 会将代码格式化成 eslint 报错的情况。规则等级:0 关闭 1 警告 2 报错
使用 prettier
配置 prettier 文件
`{`
` "printWidth": 150,`
` "singleQuote": true,`
` "trailingComma": "none",`
` "semi": false,`
` "tabWidth": 2,`
` "useTabs": false,`
` "bracketSpacing": true,`
` "jsxBracketSameLine": false,`
` "arrowParens": "always",`
` "proseWrap": "preserve",`
` "overrides": [`
` {`
` "files": ["*.json", ".eslintrc", ".tslintrc", ".prettierrc", ".tern-project"],`
` "options": {`
` "parser": "json",`
` "tabWidth": 2`
` }`
` },`
` {`
` "files": "*.{css,sass,scss,less}",`
` "options": {`
` "parser": "css",`
` "tabWidth": 2`
` }`
` },`
` {`
` "files": "*.ts",`
` "options": {`
` "parser": "typescript"`
` }`
` },`
` {`
` "files": "*.vue",`
` "options": {`
` "parser": "vue"`
` }`
` },`
` {`
` "files": "*.md",`
` "options": {`
` "parser": "markdown"`
` }`
` }`
` ]`
`}`
开启 vscode 自动格式化
`{`
` // prettier`
` "prettier.singleQuote": true,`
` "prettier.semi": false,`
` "prettier.tabWidth": 2,`
` "[javascript]": {`
` "editor.formatOnSave": true,`
` "editor.defaultFormatter": "esbenp.prettier-vscode"`
` }`
`}`
如何提升编码效率
原理与解决方案
我主要从 3 个方面来做一些编码效率上的改进
升级你的 vue-cli 减少 webpack 配置的成本
使用 sass,利用里面函数、mixins、变量提升 css 文件的复用
使用 pug,减少 html 的代码编写量
实践
vue-cli3+、vue-cli4+相比于vue-cli2+最大的改变就是将约定俗称的配置,全部公共化了,也就是做了一次二次封装。这样的好处在于,我们不必要在繁多的配置代码中寻找需要的配置。
简单新建一个配置入口就能操作我们大多数想要的功能。在 root 目录下新建一个 vue.config.js 文件,作为我们 webpack 的配置文件。
初始化 vue 配置
`const autoprefixer = require('autoprefixer')`
`module.exports = {`
` publicPath: process.env === 'production' ? '' : '/',`
` outputDir: 'dist',`
` assetsDir: 'static',`
` filenameHashing: true,`
` lintOnSave: true,`
` runtimeCompiler: false,`
` transpileDependencies: [/\/node_modules\/vue-echarts\//, /\/node_modules\/resize-detector\//],`
` productionSourceMap: false`
`}`
简单的配置完成后,我们引入一个 sass 工具用于编写 sass文件
用法见 sass 参考资料!
使用 Sass
安装与使用
`yarn add -D sass sass-loader`
如何处理样式
在 assets 目录中建立一个 styles 文件专门来存放样式文件,新增入口 index.scss文件,便于 JavaScript 引入,增加 utils.scss、reset.scss、varibles 文件。
这些样式工具都是为了提升我们
scss开发效率,具有畅快的开发体验!
使用 varibles 变量文件
为了提升我们代码的可读性,复用性。使用 sass 变量必不可少。
还有一点就是利于全局修改样式,如果需要更换皮肤这个功能,我们只需要更改全局的主题色,即可更换主题,那样更加方便。
`// 主题色`
`$color-red: #ff3333;`
`$color-purple: #ff33a9;`
`$color-orange: #ff8833;`
`$color-blue: #3377ff;`
`// 文字色`
`$color-black: #000;`
`$color-dark: #333;`
`$color-deep: #555;`
`$color-pl: #999999;`
`$color-weak: #B3B3B3;`
`$color-white: #fff;`
`// 背景色`
`$bg-bar: #F9F9F9;`
`$bg-page: #F3F3F3;`
`$bg-page-light: #F9F9F9;`
使用变量之后,sass 文件不会直接生效,至少在 vue 文件 里面是访问不到的。需要在 vue.config.js 里面增加如下配置。
`module.exports = {`
` // ...`
` css: {`
` sourceMap: true,`
` loaderOptions: {`
` sass: {`
`` prependData: ` ``
` @import "@/assets/styles/variable.scss";`
`` ` ``
` }`
` }`
` }`
`}`
覆盖默认样式
常规操作, 引入 reset.scss 将默认样式覆盖掉
`/* http://meyerweb.com/eric/tools/css/reset/`
` v2.0 | 20110126`
` License: none (public domain)`
`*/`
`html, body, div, span, applet, object, iframe,`
`h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, p, blockquote, pre,`
`a, abbr, acronym, address, big, cite, code,`
`del, dfn, em, img, ins, kbd, q, s, samp,`
`small, strike, strong, sub, sup, tt, var,`
`b, u, i, center,`
`dl, dt, dd, ol, ul, li,`
`fieldset, form, label, legend,`
`table, caption, tbody, tfoot, thead, tr, th, td,`
`article, aside, canvas, details, embed,`
`figure, figcaption, footer, header, hgroup,`
`menu, nav, output, ruby, section, summary,`
`time, mark, audio, video {`
` margin: 0;`
` padding: 0;`
` border: 0;`
` font-size: 100%;`
` font: inherit;`
` vertical-align: baseline;`
`}`
`/* HTML5 display-role reset for older browsers */`
`article, aside, details, figcaption, figure,`
`footer, header, hgroup, menu, nav, section {`
` display: block;`
`}`
`body {`
` line-height: 1;`
`}`
`ol, ul {`
` list-style: none;`
`}`
`blockquote, q {`
` quotes: none;`
`}`
`blockquote:before, blockquote:after,`
`q:before, q:after {`
` content: '';`
` content: none;`
`}`
`table {`
` border-collapse: collapse;`
` border-spacing: 0;`
`}`
`html, body {`
` width: 100%;`
` height: 100%;`
` overflow: auto;`
` margin: 0;`
` scroll-behavior: smooth;`
` -webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch;`
`}`
使用样式工具集
有时候我们发现,光是引入变量还不够,变量工具只能允许我们在 css 类文件中使用。假如我想着模版中直接使用样式,有没有更快的方案呢?
当然有的,我们可以自定义一个常用的样式工具集。设置一些背景颜色、字体颜色、盒子模型中的常规操作。
要是有设计规范更好哦,我也是常常向设计师提出要求,一定要制定出一套产品的设计规范。
`// utils 工具`
`// 颜色`
`.bg-red {background-color: $color-red!important;}`
`.bg-purple {background-color: $color-purple!important;}`
`.bg-orange {background-color: $color-orange!important;}`
`.bg-blue {background-color: $color-blue!important;}`
`.color-red {color: $color-red!important;}`
`.color-purple {color: $color-purple!important;}`
`.color-orange {color: $color-orange!important;}`
`.color-blue {color: $color-blue!important;}`
`.text-black {color: #000;}`
`.text-dark {color: #333;}`
`.text-deep {color: #555;}`
`.text-weak {color: #B3B3B3;}`
`.text-white {color: #fff;}`
`// 字体`
`.f10 {font-size: 10px;}`
`.f12 {font-size: 12px;}`
`.f14 {font-size: 14px;}`
`.f15 {font-size: 15px;}`
`.f17 {font-size: 17px;}`
`.f20 {font-size: 20px;}`
`.f24 {font-size: 24px;}`
`// 文字对齐`
`.tl {text-align: left;}`
`.tc {text-align: center;}`
`.tr {text-align: right;}`
`// 浮动与清除浮动`
`.fl {float: left;}`
`.fr {float: right;}`
`.fix {*zoom: 1;}`
`.fix:after{display:table; content:''; clear:both;}`
`// 显示`
`.dn{display:none;}`
`.di{display:inline;}`
`.db{display:block;}`
`.dib{display:inline-block;}`
`.dt{display:table;}`
`div.dib{*display:inline; *zoom:1;}`
`.vm {vertical-align: middle;}`
`.vib {display:inline-block; vertical-align: middle;}`
`// 定位`
`.pr {position: relative;}`
`.pa {position: absolute;}`
`.pf {position: fixed;}`
`// 盒子模型`
`.ml4 {margin-left: 4px;}`
`.mr4 {margin-right: 4px;}`
`.mt4 {margin-top: 4px;}`
`.mb4 {margin-bottom: 4px;}`
`.ml8 {margin-left: 8px;}`
`.mr8 {margin-right: 8px;}`
`.mt8 {margin-top: 8px;}`
`.mb8 {margin-bottom: 8px;}`
`.ml12 {margin-left: 12px;}`
`.mr12 {margin-right: 12px;}`
`.mt12 {margin-top: 12px;}`
`.mb12 {margin-bottom: 12px;}`
`.ml16 {margin-left: 16px;}`
`.mr16 {margin-right: 16px;}`
`.mt16 {margin-top: 16px;}`
`.mb16 {margin-bottom: 16px;}`
`.ml20 {margin-left: 20px;}`
`.mr20 {margin-right: 20px;}`
`.mt20 {margin-top: 20px;}`
`.mb20 {margin-bottom: 20px;}`
`.ml24 {margin-left: 24px;}`
`.mr24 {margin-right: 24px;}`
`.mt24 {margin-top: 24px;}`
`.mb24 {margin-bottom: 24px;}`
`.ml10 {margin-left: 10px;}`
`.mr10 {margin-right: 10px;}`
`.mt10 {margin-top: 10px;}`
`.mb10 {margin-bottom: 10px;}`
`.ml15 {margin-left: 15px;}`
`.mr15 {margin-right: 15px;}`
`.mt15 {margin-top: 15px;}`
`.mb15 {margin-bottom: 15px;}`
`// 按钮禁用`
`.disabled{outline:0 none; cursor:default!important; opacity:.4; filter:alpha(opacity=40); -ms-pointer-events:none; pointer-events:none;}`
增加样式入口文件
最后一步,新建一个入口文件,将样式工具类全部导入进来,供主程序引入。
`// index.scss 文件`
`// @import './varibles.scss'`
`@import './reset.scss';`
`@import './utils.scss';`
varibles.scss vue 配置中引入,这里无需引入
在 main.js 中直接引入 index.scss
`import'@/assets/styles/index.scss'`
vue 中写样式要注意哪些方面,有哪些技巧呢?
避免全局污染
在页面中写 css/scss 加上 scoped, scoped 的功能就是使页面的样式是局部的,不让影响其他页面的样式。
bem 规范
我们大多数人时候会遇到问题, 样式嵌套太多了怎么命名
BEM是块(block)、元素(element)、修饰符(modifier)的简写,由 Yandex 团队提出的一种前端 CSS 命名方法论。
名字太长易读性太差
`.cardbox {`
` .cardbox-card {`
` .cardbox-card-wrapper`
` .cardbox-card-wrapper-header {`
` .cardbox-card-wrapper-header-title {`
` // ...`
` }`
` }`
` .cardbox-card-wrapper-body{`
` .cardbox-card-item {`
` .cardbox-card-item-title {`
` // ...`
` }`
` }`
` }`
` }`
` }`
`}`
bem 使用方式
block-name__element-name--color
区分块,子元素,修饰元素
块,页面中独立的单元
子元素,块里面的儿子
card__item使用__连接子元素长命名使用 - 连接
修饰(易变的)
card__item--warning使用--
我们使用 bem 改造样式
`.cardbox {`
` &__header {`
` &__title {`
` //...`
` }`
` }`
` &__body {`
` &__item {`
` &__title {`
` //...`
` }`
` }`
` }`
`}`
bem 一般推荐子元素嵌套尽量在2-3层以内
但是我们发现样式子元素嵌套有点多,使用了两重子元素嵌套。
大致原理是 尝试分离父子元素的关系,把卡片本身当作一个块看待。
下面来试着去减少嵌套:
`.cardbox {`
` &__header {`
` &__title {`
` //...`
` }`
` }`
` &__body {`
` .card {`
` &__title {`
` //...`
` }`
` }`
` }`
`}`
现在编写样式效率提高也更加规范了,那么编写 HTML 也是有很多累赘的代码。
比如大多数标签都是前开后闭的。通过 pug 我们可以省略很多字符的敲打,下面我们谈谈如何使用 pug 编写模版。
当然喜欢哪种 HTML 编写风格见人见智啦,我自己更加倾向 pug,那种缩进和简洁的表达,有种在写 scss 的感觉。
如何使用 pug
类似 sass,首先安装 pug 和 pug 的 loader
`yarn add -D pug pug-html-loader pug-plain-loader`
完成配置
`module.exports = {`
`// ...`
` chainWebpack: (config) => {`
` config.module`
` .rule('pug')`
` .test(/\.pug$/)`
` .use('pug-html-loader')`
` .loader('pug-html-loader')`
` .end()`
` }`
`}`
编写 pug 代码
使用 scss 工具与 pug 完美搭配,少写很多代码
`// 登陆`
`<template lang="pug">`
` .login`
` h1.login__title.ml15 注册/登陆`
` .login__form.mt15.ml15`
` van-field.login__form__input(placeholder="输入手机号" v-model="phone")`
` .login__form__protocol.mt15`
` .login__form__protocol__tips.dib.text-weak 注册或登录即表示同意`
` .login__form__protocol__name.dib.color-orange 《用户协议》`
` app-button.mt15(size="large"`
` theme="orange"`
` :disabled="phone.length !== 11"`
` @click="handleSubmit"`
` ) 下一步`
`</template>`
我们已经引入了样式,接下来我将谈谈其他资源的引入
如何管理你的资源
原理与解决方案
我暂时把资源分为下面几种
字体
ICON
图片
样式

把他们各自新建一个目录,都放在 assets 目录下面分门别类,供其他地方调用。使用 alias 更好重命名,使之更便捷的访问到。
增加 vue.config.js 配置 ,设置 assets别名
`const path = require('path')`
`function resolve(dir) {`
` return path.join(__dirname, dir)`
`}`
`module.exports = {`
` //...`
` chainWebpack: (config) => {`
` config.resolve.alias.set('@', resolve('src')).set('@assets', resolve('src/assets'))`
` }`
`}`
ICON
引入 iconfont
- iconfont 阿里图标项目中下载,将整个项目图标包一起下载下来

- 引入 iconfont 样式 需要下面四个文件
iconfont.eoticonfont.ttficonfont.wofficonfont.woff2
项目中引入 iconfont 让
icon组件化<template><i class="iconfont" v-on="$listeners" :class="name"></i></template><script>export default {props: {name: String}}</script><style lang="scss" scoped>.iconfont {font-size: 16px;color: $color-icon;}</style>
引入图片作为 ICON
让图片组件化,我们再来写一个 img 组件
`<template lang="pug">`
` img(`
`` :src="require(`@/assets/images/${name}.png`)"``
` v-bind="$attrs"`
` v-on="$listeners"`
` :style="{'width': width ? width + 'px' : size + 'px', 'height': height ? height + 'px' : size + 'px' }")`
`</template>`
`<script>`
`export default {`
` name: 'app-img',`
` props: {`
` name: {`
` type: String,`
` default: ''`
` },`
` size: {`
` type: Number,`
` default: 16`
` },`
` width: {`
` type: Number,`
` default: 0`
` },`
` height: {`
` type: Number,`
` default: 0`
` }`
` }`
`}`
`</script>`
如何管理你的路由
原理与解决方案
使用 vue-router,使用 import() 生成异步路由,只有在访问时候才会加载模块。
为什么使用 import() 会异步加载模块?
MDN:在您希望按照一定的条件或者按需加载模块的时候,动态import() 是非常有用的。而静态型的 import 是初始化加载依赖项的最优选择,使用静态 import 更容易从代码静态分析工具和 tree shaking 中受益。
说白了就是起到一个 按需加载的目的。现在大多数实现的按需加载,基本都是依赖 import() 这个方法。
安装 vue-router
`yarn add vue-router`
安装完 router,在编写 router 先创建页面
新建一个空页面
src 目录下新增 views 目录存放页面文件。创建 index 目录和 home 页面
`<template lang="pug">`
` .home 首页`
`</template>`
`<script>`
`export default {`
`}`
`</script>`
`<style lang="scss" scoped>`
`</style>`
编写路由
`const routes = [`
` {`
` // 首页`
` path: '/',`
` name: 'index',`
` redirect: '/home',`
` component: App,`
` children: [`
` {`
` // 首页`
` path: 'home',`
` name: 'home',`
` // 路由懒加载`
` component: () =>`
` import(`
` /* webpackChunkName: "index" */'../views/index/home.vue'`
` )`
` }`
` ]`
` }`
`]`
`Vue.use(VueRouter)`
`const router = new VueRouter({`
` mode: 'history',`
` routes: routes,`
` base: process.env.BASE_URL,`
` props: true`
`})`
`exportdefault router`
为了消除 # 显得路径更加好看简洁,我们采用 history 模式,但是 history 模式有个问题就是,异步路由没有缓存在页面中,第一次进入页面会找不到
在 vue.config.js 中增加配置,开发环境可以访问到,恢复正常
`module.exports = {`
`// ...`
` devServer: {`
` historyApiFallback: true`
` }`
`}`
关于路由还有很多可以研究到地方,可以自行研究哦!
组件化开发
原理与解决方案
一般来说,我们根据组件的复用度,分给基础(公共)组件和业务组件。
为了节省时间,快速开发,这里基础组件大部分引用开源组件。当然不能直接就用哦。
一般要进行二次封装,也就是高阶组件开发。
通过修改和覆盖当前组件的样式来达到修改样式的作用。
通过拦截事件来更改js的逻辑。
下面我们先引入 vant 组件
实践
引入 vant
`yarn add vant`
对基础组件进行二次封装和改造
下面 7 步来写好一个公共组件
新建一个
components目录来存放基础组件基础组件命名为
app-xxx或appXxx,新建一个app-button目录,新建index.vue根据设计稿设计和编写组件
编写组件之前首先要设计组件,根据组件的不变性和可变性原则编写。不变性是组件的核心,可变性根据参数对组件对相关部分进行调节,实现可选择的功能。
实现组件
<template lang="pug">div.dibvan-button.btn(@click="$emit('click')":class="getClass" v-bind="$attrs":style="{'width': size === 'large' ? '345px': '', 'backgroundColor': getBgColor, borderColor: getBgColor, color: getBgColor}")slot</template><script>import { Button } from 'vant'import Vue from 'vue'import { getColor } from '@/utils'Vue.use(Button)export default {name: 'app-button',props: {type: {type: String,default: 'primary'},theme: {type: String,default: 'blue'},size: {type: String,default: ''}},computed: {getClass() {if (!this.type) {return ''}return `app-btn--${this.type}`},getBgColor() {if (!this.theme) {return ''}return getColor(this.theme)}}}</script><style lang="scss" scoped>.app-btn {::v-deep &--primary {padding: 8px 30px;height: 40px;border-radius: 4px;font-size: 15px;font-weight: 400;line-height: 19px;color: white!important;}::v-deep &--minor {padding: 5px 10px;height: 26px;border-radius: 14px;font-size: 12px;font-weight: 400;line-height: 16px;background-color: #fff!important;}::v-deep &--rect {padding: 5px px;height: 49px;font-size: 14px;color: white!important;}}</style>
::v-deep 样式深覆盖,scoped 情况下覆盖组件样式,不改变其样式
- 写好基础组件 README,为什么要写文档呢?如果多人开发同一个项目,基础组件会被其他人引用。方便其他人使用,所以要写文档。
一句话言:只要可能被其他人用的公共方法和组件,注释或文档是很重要的,对自己的代码负责哈。
其他用法参照 vant
- 全局引用,基础组件许多页面都会用到,将其设置成全局组件,其他地方就不必再引用了哦。
新建一个文件 global 存放全局组件注册,在 main.js 引入
`import Vue from'vue'`
`import appButton from'@/components/app-button'`
`Vue.component('app-button', appButton)`
- 写好
demo,即使暂时不写单元测试,也要写好一个demo,使之能正常的运行
添加 demo 页面和路由
`<template lang="pug">`
` div(class="base")`
` // 按钮组件`
` app-button.mt4(theme="blue") 确认支付`
` app-button(theme="orange") 确认支付`
` app-button(theme="purple") 确认支付`
` app-button.mt4(theme="red") 确认支付`
` app-button(theme="grey") 确认支付`
` app-button.mt4(theme="blue" size="large") 修改地址`
` app-button.mt4(theme="orange" size="large") 修改地址`
` app-button.mt4(theme="purple" size="large") 修改地址`
` app-button.mt4(theme="red" size="large") 修改地址`
` app-button.mt4(theme="grey" size="large") 修改地址`
` app-button.mt4(theme="blue" type="minor") 确认收货`
` app-button(theme="orange" type="minor") 确认收货`
` app-button(theme="purple" type="minor") 确认收货`
` app-button(theme="red" type="minor") 修改地址`
` app-button(theme="grey" type="minor") 修改地址`
` app-button.mt4(theme="blue" type="rect") 确认收货`
` app-button(theme="orange" type="rect") 确认收货`
` app-button(theme="purple" type="rect") 确认收货`
` app-button(theme="red" type="rect") 修改地址`
` app-button(theme="grey" type="rect") 修改地址`
`</template>`
`<script>`
`export default {`
`}`
`</script>`
`<style lang="scss">`
`</style>`
实现效果
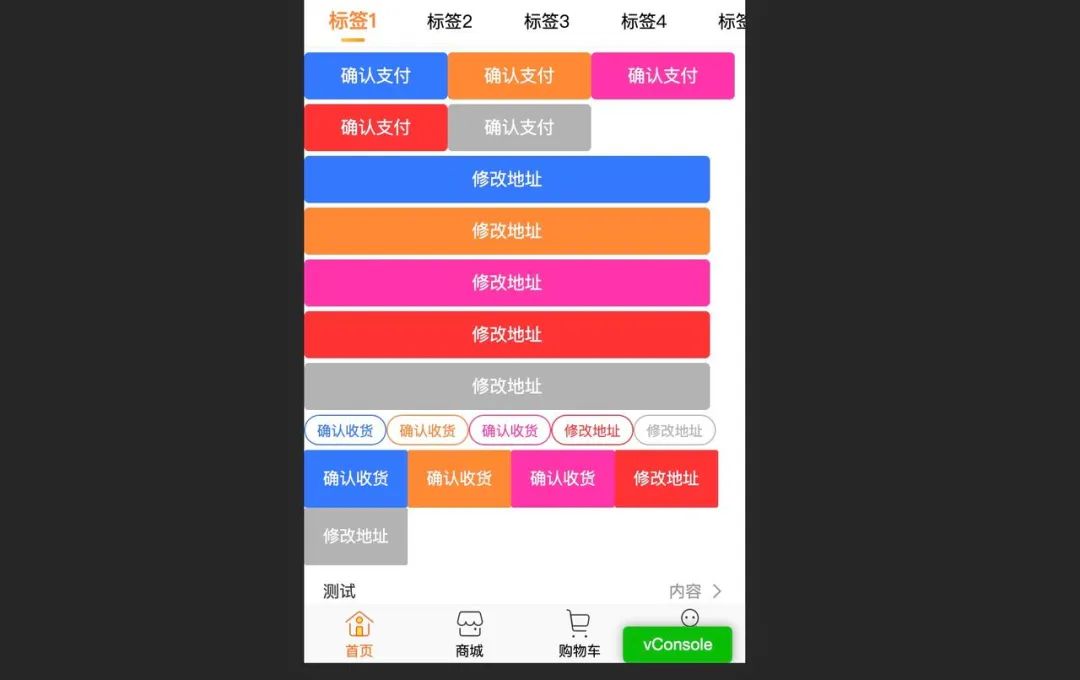
如何封装请求
原理与解决方案
基本上就是对 axios 的封装,封装主要有两个目的。
修改一些基础的配置:请求地址,超时,其他的杂七杂八的
统一操作:统一处理错误,统一处理请求参数和格式,响应参数和格式。统一处理 message,统一拦截挂载等等。
网上已经有很多类似的文章了, 我这里给出我常用的封装方案。
实践
根据不同环境设置请求地址
`// .env-default.js 文件`
`// 不同环境访问不同的路径`
`const api = {`
` develop: 'http://xxxx:8080',`
` mock: 'http://xxxx',`
` feature: 'http://xxxx',`
` test: 'http://xxxx',`
` production: 'http://xxxx'`
`}`
`exportconst baseURL = api[process.env.NODE_ENV || 'dev']`
因为每个人开发环境,mock环境不一定相同,这个文件建议 gitignore忽略掉。模版可以写在 readme 文档中,启动项目时加入文件。
新建一个 utils 工具
我们现在将 axios 封装成我们自己需要的配置,然后定义四个常用的请求方法供调用
`// utils/http.js 文件`
`import axios from'axios'`
`import { baseURL } from'../../.env-defalut.js'`
`// axios 配置`
`const defaultBaseUrl = 'http://localhost:8080/'`
`// 默认超时时间`
`axios.defaults.timeout = 15000`
`// 数据接口域名统一配置.env`
`axios.defaults.baseURL = baseURL || defaultBaseUrl`
`// http request 拦截器`
`axios.interceptors.request.use(`
` (config) => {`
` config.headers = {`
` }`
` return config`
` },`
` (err) => {`
` returnPromise.reject(err)`
` }`
`)`
`// http response 拦截器`
`axios.interceptors.response.use(`
` (response) => {`
` return response`
` },`
` (error) => {`
` const data = error.response.data`
` returnPromise.reject(data || error)`
` }`
`)`
`exportdefault axios`
`/**`
` * fetch 请求方法`
` * @param {*} url`
` * @param {*} params`
` */`
`exportfunction fetch(url, params = {}) {`
` returnnewPromise((resolve, reject) => {`
` axios`
` .get(url, {`
` params: params`
` })`
` .then((response) => {`
` resolve(response.data)`
` })`
` .catch((err) => {`
` reject(err)`
` })`
` })`
`}`
`/**`
` * post 请求方法,发送数据格式 json`
` * @param {*} url`
` * @param {*} data`
` */`
`exportfunction post(`
` url,`
` data = {},`
` config = {`
` transformRequest: [`
` function(fData, headers) {`
` headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json'`
` returnJSON.stringify(fData)`
` }`
` ]`
` }`
`) {`
` returnnewPromise((resolve, reject) => {`
` axios.post(url, data, config).then(`
` (response) => {`
` resolve(response.data)`
` },`
` (err) => {`
` reject(err)`
` }`
` )`
` })`
`}`
`/**`
` * patch 请求方法,发送数据格式 json`
` * @param {*} url`
` * @param {*} data`
` */`
`exportfunction patch(url, data = {}) {`
` returnnewPromise((resolve, reject) => {`
` axios`
` .patch(url, data, {`
` transformRequest: [`
` function(fData, headers) {`
` headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json'`
` returnJSON.stringify(fData)`
` }`
` ]`
` })`
` .then(`
` (response) => {`
` resolve(response.data)`
` },`
` (err) => {`
` reject(err)`
` }`
` )`
` })`
`}`
`exportfunction del(url, data) {`
` returnnewPromise((resolve, reject) => {`
` axios.delete(url, { data }).then(`
` (response) => {`
` resolve(response.data)`
` },`
` (err) => {`
` reject(err)`
` }`
` )`
` })`
`}`
如何管理 api
原理
首先要制定一个 api 的原则 我的原则一般是这些:
干净纯粹
尽量不要处理数据
独立单一不要互相依赖
好处在于:不在 api 里面处理数据,api里面的接口和接口文档上一样。避免别人引用我的api,还要去看代码,只需要看文档就好了。
例子:想象这样一种情况,别人引用了我的 api,突然发现响应数据不对。首先它排查到页面数据没更改。看了api文档,数据也没问题,最后发现我在写 api 的时候进行了处理,这个 api 呢又不能改动,改了影响我自己的模块。只能它在重新写一个api,这样显得很繁杂了,不够干净优雅。
`import { fetch, post } from'@/utils/http'`
`// 用户登陆`
`exportconst login = data => post('/user/login', data)`
`// 获取用户信息`
`exportconst getUserInfo = (data) => fetch('/api/user/info', data)`
如果需要处理数据,要么使用一个中间工具处理,要么在页面里面处理。当然还是实际问题实际分析。
如何使用mock模拟数据
原理与解决方案
一般就是两种方案,一是模拟后端,使用远程在线 JSON 服务器。另外一种搭建本地 JSON 或者 使用现成的 Node 服务器拦截请求。
这两种方式各有千秋,没有优劣之分,适合就是最好的。
远程在线mock
我用过的远程在线 mock
apizza:好用,功能齐全,喜欢他的文件展开目录
api,免费版只支持 2 个人共同编辑swagger:开源免费,
api管理太凌乱,rap/rap2:开源免费,可以搭建本地
api,需要自己搭建
使用远程 mock的优点:
不需要在项目内部增加
mock功能更加全面完善
可以在接口文档基础上
mock,与接口文档放在一起查看更加方便。
缺点:需要自己另外搭建服务器,只支持静态的 mock,不能与单元测试结合使用
本地JSON mock
使用
webpack内部 mock 配置devServer: {// 接口未实现情况下,使用mockbefore: require('./mock')}
基本原理:主要是使用 node 读取文件,转换成 JSON 格式,使用 mock.js 模拟数据,最后 webpack 拦截请求生成 json响应数据
`const Mock = require('mockjs')`
`module.exports = (app) => {`
` function getJsonFile (filePath) {`
` var json = fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(__dirname, filePath), 'utf-8')`
` returnJSON.parse(json)`
` },`
` const returnMock = (datafile, res, req) => {`
` setTimeout(() => {`
` var json`
` if (/\.json$/.test(datafile)) {`
` // json文件暴露的是mock的模板`
` json = getJsonFile(datafile)`
` } elseif (/\.js$/.test(datafile)) {`
` json = require(datafile)(req.query)`
` }`
` res.json(Mock.mock(json))`
` }, 500)`
` }`
`}`
- 使用
json-server搭建 主要分为下面几步
npm安装json-server编写
npm脚本命令,引入mock配置文件编写
mock路由匹配规则
比较简单这里不详细描述了!
本地的缺点在于需要
前端需要根据
api文档写mock数据格式功能没有远程
mock那么完善,支持restful需要去研究下也是需要配置相关
mock工具
优点在于
不用查看编辑
api文档在代码中就可以更改和查看
mock数据支持使用
JavaScipt动态处mock,可以与单元测试结合使用
总结
本篇文章耗费作者一个多星期的业余时间,存手工敲打 6000+字,同时收集,整理之前很多技巧和边写作边 思考和 总结。如果能对你有帮助,便是它最大的价值。都看到这里还不 点赞,太过不去啦!😄
由于技术水平有限,文章中如有错误地方,请在评论区指出,感谢!
文中大多数代码将在 suo-design-pro 中更新
项目有时间会尽量完善
写实践总结性文章真的很耗费时间。如何文章中有帮到你的地方 分享下呗,让更多人看到!
下节内容预告
如何编写原生组件,以及组件编写的思考与原则?
如何使用vuex 以及它的应用场景和原理
如何使用过滤器,编写自己的过滤器
如何使用 Jest 测试你的代码?TDD 与 BDD 的比较
往期

转发在看就是最大的支持❤️
本文分享自微信公众号 - Vue中文社区(vue_fe)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。














