1、新建rabbitmq-springboot项目
1.1pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>cn.tedu</groupId>
<artifactId>rabbitmq-springboot</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>rabbitmq-springboot</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.amqp</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rabbit-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
1.2 application.yml
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.64.140
username: admin
password: admin
1.3 主程序
删除自动创建的主程序
我们为每种模式创建一个包,在每个包中创建各自的主程序,单独测试.
2、简单模式
2.1 主程序
Spring提供的Queue类,是队列的封装对象,它封装了队列的参数信息.
RabbitMQ的自动配置类,会发现这些Queue实例,并在RabbitMQ服务器中定义这些队列.
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m1;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Queue helloworldQueue() {
/**
* 封装队列的信息
* 自动配置类(RabbitAutoConfiguration)会自动发现Queue实例,
* 并自动在RabbtiMq中定义队列
*
* return new Queue("helloworld"); - 默认为true,是持久队列
* return new Queue("helloworld", false); - false,非持久队列
*/
return new Queue("helloworld", false);
}
}
2.2 生产者
AmqpTemplate是rabbitmq客户端API的一个封装工具,提供了简便的方法来执行消息操作.
AmqpTemplate由自动配置类自动创建
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m1;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Sender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate at;
public void send() {
// 这里向 helloworld 队列发送消息
at.convertAndSend("helloworld", "Hello world!"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("消息已发送");
}
}
2.3 消费者
通过@RabbitListener从指定的队列接收消息
使用@RebbitHandler注解的方法来处理消息
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m1;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "helloworld")
public class Receiver {
@RabbitHandler //指定处理消息的方法
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者收到:"+msg);
}
}
还有另一种方法:
@Component
public class Receiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "helloworld")
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("收到: "+msg);
}
}
且,@RabbitListener 注解中也可以直接定义队列:
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(name = "helloworld",durable = "false"))
2.4 测试类
在存放测试代码的目录中,创建测试类
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m1;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class Test1 {
@Autowired
Sender sender;
@Test
void test1() throws Exception {
sender.send();
System.out.println("[按回车结束]");
new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
}
}
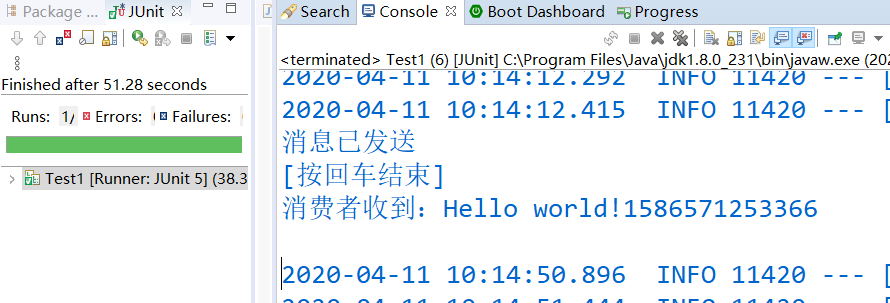
结果显示:
3、工作模式
3.1 主程序
在主程序中创建名为task_queue的持久队列
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m2;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Queue taskQueue() {
// 这个构造方法创建的队列参数为: 持久,非排他,非自动删除
return new Queue("task_queue");
}
}
3.2 生产者
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m2;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Sender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate at;
public void send() {
while(true) {
System.out.println("输入:");
String msg = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
at.convertAndSend("task_queue", msg);
}
}
}
spring boot封装的 rabbitmq api 中, 发送的消息默认是持久化消息.
如果希望发送非持久化消息, 需要在发送消息时做以下设置:
使用 MessagePostProcessor 前置处理器参数
从消息中获取消息的属性对象
在属性中把 DeliveryMode 设置为非持久化
//如果需要设置消息为非持久化,可以取得消息的属性对象,修改它的deliveryMode属性 t.convertAndSend("task_queue", (Object) msg, new MessagePostProcessor() { @Override public Message postProcessMessage(Message message) throws AmqpException { MessageProperties props = message.getMessageProperties(); props.setDeliveryMode(MessageDeliveryMode.NON_PERSISTENT); return message; } });
3.3消费者
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m2;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Receiver {
@RabbitListener(queues="task_queue")
public void receive1(String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver1 - 收到: "+msg);
for (int i = 0; i < msg.length(); i++) {
if (msg.charAt(i) == '.') {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
System.out.println("\nreceive1 处理结束");
}
@RabbitListener(queues="task_queue")
public void receive2(String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver2 - 收到: "+msg);
for (int i = 0; i < msg.length(); i++) {
if (msg.charAt(i) == '.') {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
System.out.println("\nreceive2 处理结束");
}
}
3.4 测试类
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m2;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class Test1 {
@Autowired
Sender sender;
@Test
void test1() throws Exception {
sender.send();
}
}
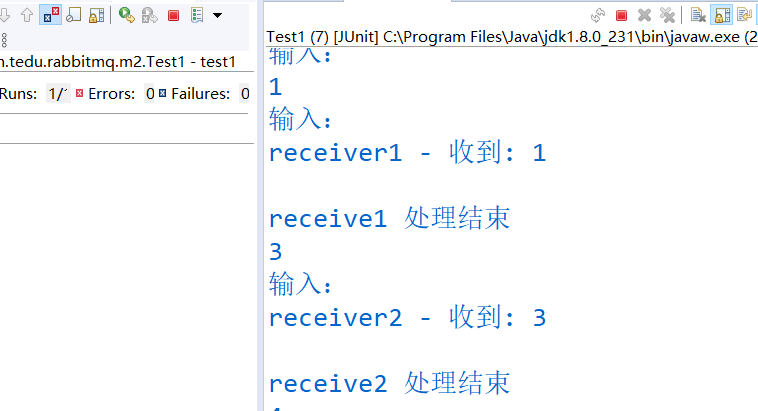
显示效果:
3.5 Ack模式
在 spring boot 中提供了三种确认模式:
- NONE - 使用rabbitmq的自动确认
- ** AUTO** - 使用rabbitmq的手动确认, springboot会自动发送确认回执 (默认)
- MANUAL - 使用rabbitmq的手动确认, 且必须手动执行确认操作
默认的 AUTO 模式中, 处理消息的方法抛出异常, 则表示消息没有被正确处理, 该消息会被重新发送.
设置ack模式 (如若是auto这步可以忽略)
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
# acknowledgeMode: NONE # rabbitmq的自动确认
acknowledgeMode: AUTO # rabbitmq的手动确认, springboot会自动发送确认回执 (默认)
# acknowledgeMode: MANUAL # rabbitmq的手动确认, springboot不发送回执, 必须自己编码发送回执
手动执行确认
如果设置为 MANUAL 模式,必须手动执行确认操作
@RabbitListener(queues="task_queue")
public void receive1(String s, Channel c, @Header(name=AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver1 - 收到: "+s);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '.') {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
// 手动发送确认回执
c.basicAck(tag, false);
}
抓取数量
工作模式中, 为了合理地分发数据, 需要将 Qos 设置成 1, 每次只接收一条消息, 处理完成后才接收下一条消息.
spring boot 中是通过 prefetch 属性进行设置, 改属性的默认值是** 250**.
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1 # qos=1, 默认250
auto - 显示效果
输入:
receiver2 - 收到: 4
receive2 处理结束
2..........
输入:
receiver1 - 收到: 2..........
3.
输入:
receiver2 - 收到: 3.
4
receive2 处理结束
...
3
输入:
receiver2 - 收到: 3
receive2 处理结束
2
输入:
receiver2 - 收到: 2
receive2 处理结束
3
输入:
receiver2 - 收到: 3
receive2 处理结束
receive1 处理结束
4、发布和订阅模式
4.1 主程序
创建 FanoutExcnahge 实例, 封装 fanout 类型交换机定义信息.
spring boot 的自动配置类会自动发现交换机实例, 并在 RabbitMQ 服务器中定义该交换机.
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m3;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("logs");
}
}
4.2 生产者
生产者向指定的交换机 logs 发送数据.
不需要指定队列名或路由键, 即使指定也无效, 因为 fanout 交换机会向所有绑定的队列发送数据, 而不是有选择的发送.
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m3;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Publisher {
@Autowired
AmqpTemplate t;
public void send() {
while (true) {
System.out.print("输入:");
String s = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
// 指定向 logs 交换机发送, 不指定队列名或路由键
t.convertAndSend("logs","",s);
}
}
}
4.3 消费者
消费者需要执行以下操作:
- 定义随机队列(随机命名,非持久,排他,自动删除)
- 定义交换机(可以省略, 已在主程序中定义)
- 将队列绑定到交换机
spring boot 通过注解完成以上操作:
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( //这里进行绑定设置
value = @Queue, //这里定义随机队列,默认属性: 随机命名,非持久,排他,自动删除
exchange = @Exchange(name = "logs", declare = "false") //指定 logs 交换机,因为主程序中已经定义,这里不进行定义
))
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m3;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Subscriber {
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(name = "logs", declare = "false")))
public void receive1(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver1 - 收到: "+s);
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(name = "logs", declare = "false")))
public void receive2(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver2 - 收到: "+s);
}
}
4.4 测试类
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m3;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class PublishSubscribeTests {
@Autowired
Publisher publisher;
@Test
void test1() throws Exception {
publisher.send();
}
}
5、路由模式
与发布和订阅模式代码类似, 只是做以下三点调整:
- 使用 direct 交换机
- 队列和交换机绑定时, 设置绑定键
- 发送消息时, 指定路由键
5.1 主程序
主程序中使用 DirectExcnahge 对象封装交换机信息, spring boot 自动配置类会自动发现这个对象, 并在 RabbitMQ 服务器上定义这个交换机.
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m4;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("direct_logs");
}
}
5.2 生产者
生产者向指定的交换机发送消息, 并指定路由键.
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m4;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class RouteSender {
@Autowired
AmqpTemplate t;
public void send() {
while (true) {
System.out.print("输入消息:");
String s = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
System.out.print("输入路由键:");
String key = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
// 第二个参数指定路由键
t.convertAndSend("direct_logs",key,s);
}
}
}
5.3 消费者
消费者通过注解来定义随机队列, 绑定到交换机, 并指定绑定键:
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( // 这里做绑定设置
value = @Queue, // 定义队列, 随机命名,非持久,排他,自动删除
exchange = @Exchange(name = "direct_logs", declare = "false"), // 指定绑定的交换机,主程序中已经定义过队列,这里不进行定义
key = {"error","info","warning"} // 设置绑定键
))
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m4;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class RouteReceiver {
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue,exchange = @Exchange(name = "direct_logs", declare = "false"),key = {"error"}))
public void receive1(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver1 - 收到: "+s);
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(name = "direct_logs", declare = "false"),key = {"error","info","warning"}))
public void receive2(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver2 - 收到: "+s);
}
}
5.4 测试类
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m4;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class RouteTests {
@Autowired
RouteSender sender;
@Test
void test1() throws Exception {
sender.send();
}
}
6、主题模式
主题模式不过是具有特殊规则的路由模式, 代码与路由模式基本相同, 只做如下调整:
- 使用 topic 交换机
- 使用特殊的绑定键和路由键规则
6.1 主程序
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m5;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
@Bean
public TopicExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new TopicExchange("topic_logs");
}
}
6.2 生产者
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m5;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TopicSender {
@Autowired
AmqpTemplate t;
public void send() {
while (true) {
System.out.print("输入消息:");
String s = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
System.out.print("输入路由键:");
String key = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
t.convertAndSend("topic_logs",key,s);
}
}
}
消费者
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m5;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TopicReceiver {
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue,exchange = @Exchange(name = "topic_logs", declare = "false"),key = {"*.orange.*"}))
public void receive1(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver1 - 收到: "+s);
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(name = "topic_logs", declare = "false"),key = {"*.*.rabbit","lazy.#"}))
public void receive2(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receiver2 - 收到: "+s);
}
}
6.4 测试类
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m5;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class TopicTests {
@Autowired
TopicSender sender;
@Test
void test1() throws Exception {
sender.send();
}
}
7、RPC异步调用
7.1 主程序
主程序中定义两个队列
发送调用信息的队列: rpc_queue
返回结果的队列: 随机命名
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m6;
import java.util.UUID;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args); } @Bean public Queue sendQueue() { return new Queue("rpc_queue",false); } @Bean public Queue rndQueue() { return new Queue(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), false); }}
7.2 服务端
从rpc_queue接收调用数据, 执行运算求斐波那契数,并返回计算结果. @Rabbitlistener注解对于具有返回值的方法:
会自动获取
replyTo属性自动获取
correlationId属性向 replyTo 属性指定的队列发送计算结果, 并携带
correlationId属性package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m6;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component public class RpcServer { @RabbitListener(queues = "rpc_queue") public long getFbnq(int n) { return f(n); } private long f(int n) { if (n==1 || n==2) { return 1; } return f(n-1) + f(n-2); } }
7.3 客户端
使用 SPEL 表达式获取随机队列名: "#{rndQueue.name}"
发送调用数据时, 携带随机队列名和correlationId
从随机队列接收调用结果, 并获取correlationId
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m6;
import java.util.UUID;
import org.springframework.amqp.AmqpException;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessagePostProcessor;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageProperties;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.AmqpHeaders;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Header;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class RpcClient {
@Autowired
AmqpTemplate t;
@Value("#{rndQueue.name}")
String rndQueue;
public void send(int n) {
// 发送调用信息时, 通过前置消息处理器, 对消息属性进行设置, 添加返回队列名和关联id
t.convertAndSend("rpc_queue", (Object)n, new MessagePostProcessor() {
@Override
public Message postProcessMessage(Message message) throws AmqpException {
MessageProperties p = message.getMessageProperties();
p.setReplyTo(rndQueue);
p.setCorrelationId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
return message;
}
});
}
//从随机队列接收计算结果
@RabbitListener(queues = "#{rndQueue.name}")
public void receive(long r, @Header(name=AmqpHeaders.CORRELATION_ID) String correlationId) {
System.out.println("\n\n"+correlationId+" - 收到: "+r);
}
}
7.4 测试类
package cn.tedu.rabbitmq.m6;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class TopicTests {
@Autowired
RpcClient client;
@Test
void test1() throws Exception {
while (true) {
System.out.print("求第几个斐波那契数: ");
int n = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
client.send(n);
}
}
}
六种工作模式的整合springboot就此结束!!!







