1. Install
1.1 编译前Lib安装
备注:因为Centos安装的最小版本 所以缺的基础Lib有点多 。。这里应该是全的了
yum -y install gcc.x86_64 gcc-plugin-devel.x86_64 pcre-devel.x86_64 pcre-static.x86_64 pcre.x86_64 openssl-devel.x86_64 openssl-static.x86_64 openssl.x86_64 libxml2-static.x86_64 libxml2.x86_64 libxml2-devel.x86_64 libxslt-devel.x86_64 libxslt.x86_64 gd-devel.x86_64 gd.x86_64 GeoIP-devel.x86_64 GeoIP.x86_64
1.2 编译安装
1.2.1 configure
1.2.1.1 可用参数
- --prefix=PATH: 设定nginx的安装目录
- --user=name: 设定nginx worker process 以什么用户权限运行,可以用过nginx.conf修改
- --group=name:设定nginx worker process 以什么用户组权限运行,可以用过nginx.conf修改
- --with-threads :nginx是否使用线程池
- --with-file-aio :设定在Linux上是否使用AIO
1.2.1.2 常用但不默认构建module表
- --with-http_ssl_module https模块,默认不构建,需要OpenSSL库支持
- --with-http_realip_module real_ip模块保证后端服务器的HttpRequestHeader中的IP为客户端实际IP,默认不构建;
- --with-http_gunzip_module 对被gzip压缩的响应进行解压适应无法解压的客户端,默认不构建
- --with-http_gzip_static_module 向客户端发送以gzip压缩过的文件,默认不构建
- --with-http_slice_module 将http大请求划分成几个小请求,默认不构建
- --with-debug 支持debug日志,默认不构建
- --with-stream 支持四层的负载均衡,默认不构建
1.2.1.3 一个常用configure样例
./configure --prefix=/opt/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with_stream
2. Begin Usage
2.1 nginx 启动相关命令
- ./nginx 启动nginx
- ./nignx -s stop — 快速关闭,即使有正在处理的请求直接关系连接
- ./nignx -s quit — 优雅的关闭,不接受处理新请求;
- ./nignx -s reload — 重新载入配置
- ./nignx -s reopen — 重新打开日志输出
- ./nginx -t 检测磁盘上的配置文是否合法
2.2 配置文件文件及解释
2.2.1 基本结构
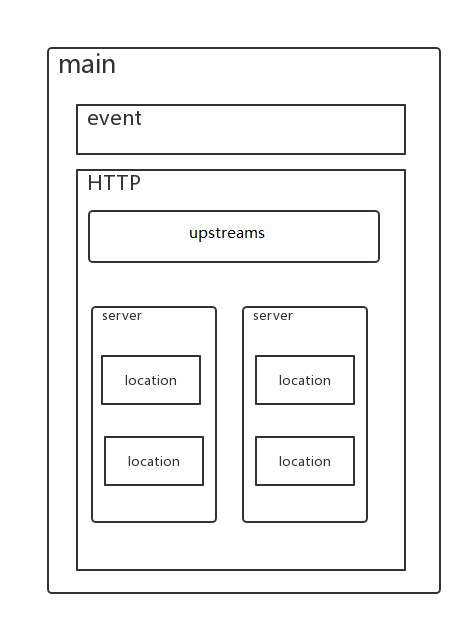
2.2.2 基础配置解释
user nginx nginx; # 需要创建一个nginx 用户及nginx用户组,禁止登陆
worker_processes 8; # 一般和CPU的核心数量一致即可,假定8个;
# worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000 00010000 00100000 01000000 10000000;
# worker_cpu_affinity 仅linux系列支持,8核8位,4核心4位(0001 0010 0100 1000);设定进程的和CPU核心的绑定关系,可以见减少进程在CPU核心间调度产生的L123缓存的调度,从而提升效能
error_log logs/error.log info; # 设定nginx的日志位置及日志等级
pid logs/nginx.pid; # 设定 nginx master进程Id文件
worker_rlimit_nofile 65536; # 设定每个worker进程最大句柄数,linux `ulimit -n 65536` 修改
events {
use epoll; # 使用的IO模型,select、poll、epoll; Linux 可用的就这三个,默认epoll;
worker_connections 65536; #设定每个worker process 可以处理的连接数,不能超过上面的worker_rlimit_nofile值
}
http {
include mime.types; # 引入文件 mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream; # 默认的mime type为 application/octet-stream
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"' ; # 设定日志格式
access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on; # 设定 nginx 是否使用 sendfile 函数输出文件,对于下载服务时请关闭;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
upstream backend { # 负载均衡模块,一个后端服务器组;像 upstream,server等等相关的东西都可以另起文件,然后include 进来;
server 192.168.1.11 weight = 5;
server 192.168.1.12 weight = 2;
server 192.168.1.10 backup;
}
server { #可以有多个不同的server(name、IP、端口不完全一致就可以)
listen 127.0.0.1:80; # 监听的IP和端口,端口省略就是协议默认端口,IP省略就监听全部的IP
server_name localhost; # server的name,就是域名;支持通配符比如*.aruforce.site;支持正则 `~`开头
# nginx 收到请求时:会先匹配IP和端口,如果有多个server匹配,则继续匹配req_header_Host 与server_name
# 如果还是有多server_name 匹配:
# 首选 正常的域名 的server
# 次选 *开头的通配符域名 的server
# 再次 *结尾的通配符域名 的server
# 最后 选第一个出现的正则表达式域名 的server
# 如果不存在匹配的域名则转发到默认的server(一般就是第一个)
charset utf-8; #设定响应头
access_log logs/80-localhost.access.log main;
# 错误页设置
error_page 404 /404.html; # 当http 404时返回/404.html
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # 当http 50x时返回/50x.html
# 静态文件
location / {
root html; #root是指从本地文件目录查找,结尾不允许有/,如果一个req的URI匹配到,将访问文件系统的html$URI的文件,而URI starts with '/';
index index.html index.htm;
}
location =/app/index.html{ # 精确匹配,访问http://localhost/app/index.html时,会访问html/app/index.html
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# 下面的 2 和 3 区别
location ^~ /app/{ # 访问http://localhost/app/index2.html时,会访问./app/index2.html;即使是有开头的^~但由于不是最长匹配,那么会进行正则型的匹配
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /app/index2.html{ # 访问http://localhost/app/index2.html时,因为没有^~开头,尽管是最长匹配项,但仍旧会进行正则项的匹配,所以会访问./app/index2.html;如果 开头有^~则会访问html2/app/index2.html
root html2; #
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ /app/{ #正则型匹配
root ./; # './'是指nignx的目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
location = /50x.html { # 精确匹配
root html;
}
location /app2{ # prefix型访问http://localhost/app2 时,会被nginx 回复301 重定向到 http://localhost/app2/;如果代理的是app2这个文件,请在前面加上`=`
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#代理功能
location /nexus/{ #proxy1
proxy_pass http://localhost:8081;
# proxy_pass 的uri要不要以`/`结尾:
# 结尾是`/`的,nginx会把原请求的URI截断掉locationURI的部分然后拼接上proxy_pass的URI;
# 结尾不是`/`的 就是proxy_pass_uri+req_uri;
}
# location /nexus/{ #proxy2
# proxy_pass http://localhost:8081/nexus/; # 这条配置和上面的是一个效果;
# }
# 这里以浏览器访问http://localhost/nexus/index.html为例说明:
# proxy1的配置 相当浏览器访问http://localhost:8081+/nexus/index.thml
# proxy2的配置 相当于浏览器访问 http://localhost:8081/nexus/ + index.html;
}
# 一个 HTTPS服务器
server {
listen 443 ssl; #
server_name www.aruforce.site *.aruforce.site;
ssl_certificate cert.pem; # 证书
ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # 签名
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
3. location的语法及匹配规则
3.1 语法
location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri{
#config
}
3.1.1 前缀
- location的写法分为两个大类prefix型 和 正则表达式型;
- prefix型 必须以
/开头(最佳实践,不写也行,nginx默认会加上); - 正则表达式行型 开头必须有
~(表示区分大小写的正则)或者~*(表示不区分大小写的正则); =代表精确匹配,只配合prefix型使用;^~这个表示为最佳匹配,不再匹配正则型;
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000013267839;要么这个文档有点不太对要么是我对这个文档理解错误了. 关于^~的解释还有匹配执行流程;
按照我对这个文档的内容理解,以上面的配置在访问
http://localhost/app/index2.html应该是访问html/app/index2.html文件才对(location ^~ /app/生效),但是实际上是./app/index2.html(location ~ /app/生效了);
3.1.2 prefix型的uri结尾的/
- 有
/的,req会被正常处理 - 没有
/的,nginx 会响应301(永久重定向),重定向的URI = $req.uri+ / - 如果要代理具体的URI ,请使用
=精确匹配;
3.2 大体匹配流程(规则)
- nginx 首先会把req的URI正常化(解码[%xx],解路径[.或者..],尽可能压缩相邻重复的
/后再开始匹配; - nginx会先查找 prefix型location进行匹配(从上到下),如果匹配项以
=开头的location则直接使用,否则继续向下匹配,从所有的prefix型匹配项中选择前缀最长A作为备用,如果A 以^~开头,会直接使用A,否则继续检查正则型,; - nginx从正则型的location从上往下进行匹配,若不存在匹配项,则使用
A,否则使用第一个正则匹配项B;
3.3 例子
location = / {
[ configuration A ]
}
location / {
[ configuration B ]
}
location /documents/ {
[ configuration C ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
[ configuration D ]
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
[ configuration E ]
}
- 当req URI 为
/时,使用A; - 当req URI 为
/index.html时,使用B - 当req URI 为
/documents/index.html时,使用C - 当req URI为
/images/a.jpg时,使用D; - 当req URI 为
/docments/a.jpg时,使用 E;
4. http_core 提供的常用的变量(per request at runtime)(echo $*** 可以输出取到的值到日志文件,windows版本不支持echo)
参数
解释
$arg_name
获取请求行中name对应的值,比如http://localhost/index.html?token=123,$arg_token就是123
$args-$query_string
获取请求行参数,对于/index.html?token=123&sign=321=>token=123&sign=321,同$query_string
$bytes_sent
发送响应的字节数
$connection
connecttion的序号
$content_type
request header 里面的Content-Type的值
$cookie_name
请求中cookies 里面的name key对应的value,和$arg_name有点类似
$document_root
当前request的root或者alias指令对应的值
$uri-$document_uri
request header里面的URI. 不带请求参数,类似于/nexus/index.html
$host
请求行的host参数值->请求头的Host值-> server_name指令的value
$request_method
获取请求方法,GET、POST、HEAD、OPTIONS、PUT等等
$http_name
request header 里面的name对应的值,比如 $http_user_agent
$https
返回当前链接是否是使用SSL,是返回on,否则返回空串
$is_args
返回当前链接请求行是否参数,是返回?,否则返回空串
$scheme
使用的协议, 比如http或者是https,比如rewrite ^(.+)$ $scheme://example.com$1 redirect
$connection_requests
当前conenction发送的请求的数量
$content_length
request header 里面的Content-lenght的值
$binary_remote_addr
获取客户端IP的二进制表示
$body_bytes_sent
发送响应的字节数,不包括response header
$remote_addr
获取Client的IP
$remote_port
获取Client的port
$proxy_protocol_addr
返回走代理协议的客户端在代理协议头的地址,在listen指令后必须加上 proxy_protocol参数
$proxy_protocol_port
返回走代理协议的客户端在代理协议头的端口,在listen指令后必须加上 proxy_protocol参数
5. http_rewrite 模块
5.1 用途
rewrite 模块主要用来修改每个request的URI;server 及location context可以多次使用;提供了if,break,return,rewrite,set几个指令;
5.2 执行流程
- nginx 接收到了请求,确认使用那个server context
- server context 内的 rewrite模块的指令按出现的顺序执行;
- 新的URI(如果有重写的话)用来确定要使用的location context,该context 的指令执行按顺序执行;
- 如果URI被改写了,则重新确认location context继续执行;(location 更改的最大次数为10次)
5.3 指令 及用法
5.3.1 if
if (condition) { # 注意if和 ( 之间有个空格
}
用法
说明事项
样例
if($xxx)
取值型
if ( $cookie_bind) { return 403 ;} 如cookie里面带bind参数直接403禁止访问
if ($xxx = xxx)orif ($xxx != xxx)
等于或者不等于
if ($arg_token = "") {return 403;} 如果请求参数不带token 也会被禁止访问
if ($xxx ~ regx) or if ($xxx ~* regx)
正则型
`if($user_agent ~*(baidu
if (-d|-f|-e|-x)
根据文件夹或者文件是否存在或者可执行做操作
if (-!d /var/www/static){return 404;} 如果不目录存在直接反404
5.3.2 break
停止处理当前上下文内的rewrite模块的指令集,如果在location 上下文内,则跳过继续执行其他模块的指令;
5.3.3 return
停止处理当前请求,返回一个http状态码给客户端;
301、302、303、307、308:还可以追加一个重定向的URL 比如
return 302 $scheme://$host:$server_post/login.html
444 :这个不是标准的状态码,nginx 会断开和客户端的链接
5.3.4 rewrite
rewrite regex replacement [flag];
- regex:匹配请求URI的正则表达式,如果表示包含
}或者:那么表达式需要用""或者''包起来 - repalcement:用于替换的新URL:如果repalcement 以
http://或者https://或者$scheme开头 nginx 用 replacement 发起重定向;重定向时会加上原来的请求参数,如果不需要可以在repalcement末尾加上?阻止; - flag:
取值
解释
last
停止处理当前的上下文的rewrite模块指令,并重新查找一个新的location contex
break
停止处理当前的上下文的rewrite模块指令,继续当前location的其他处理指令
redirect
发起临时重定向302, 要求repalcement 不以http://或者 https:// 或者 $scheme 开头
permanent
发起永久重定向301
5.3.5 rewrite_log
是否开启rewrite 模块处理的日志(level=notice),on |off ; 开启的话会输出到error_log里面
6. 负载均衡
6.1 http层负载均衡及Health check
http {
upstream backend { # http 后端服务器组;需要处在 http context 内
least_conn;
# 未指定均衡算法 则使用Round Robin 随机转发
# least_conn:优先向当前连接数最小的服务器转发
# ip-hash; # 根据客户端的ip进行取模后转发,能保证同一个IP的被转发到一个服务器(目的是session共享)
# hash $request_uri ;# 通用Hash,根据请求的某个参数来Hash
server 192.168.1.11 weight = 5 fail_timeout=30s max_fail = 10 slow_start=30s;
# 如果仅一个服务器后面这些参数会被忽略
# weight(权重):接受5/7的请求;
# health_ckeck(服务状态检查):如果30S内有10次失败,则这个服务器会被标记为不可用
# slow_start:服务刚启动时处理请求可能比较慢(比如缓存是边运行边加载的情况下),可能会被流量直接打死,可以设置slow_start 这段时间后,流量才会逐步上升到响应的权重
server 192.168.1.12 weight = 2; #接受 接受2/7的请求
server 192.168.1.10 backup; # 备机当前面两个不可用时会把请求转发到这里
}
server{
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
}
6.2 TCP|UDP 负载均衡( ./configure --with-stream 模块) 及healthCheck
# 4层TCP负载均衡,均衡的是connection,也就说不用担心一个ClientSocket的数据被负载到不同的机器去
# 在nginx.conf 引入启动后(main context);mysql 连接 127.0.0.1:9000(当然是可行的)
# 原本打算是试下UDP DNS的,但是手头没Linux环境所以...
stream { # 必须出现在main context,意思是说和http event等一个级别
server{
listen 127.0.0.1:9090;
proxy_pass mysql;
}
upstream mysql{ #TCP负载均衡服务器组
hash $remote_addr consistent; #
server 127.0.0.1:3306 weight=5 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s slow_start=30s;
server 192.168.1.101:3306 ;
}
# DNS 服务
#server{
# listen 127.0.0.1:53;
# proxy_pass remote_dns;
#}
#upstream remote_dns{ #TCP 负载均衡服务器组
# hash $remote_addr consistent; #
# server 192.168.1.1:53 ; # dns server
# server 192.168.0.1:53; # dns server
#}
}













