0. 入门demo
此代码是
OpenFeign的示例代码,获取一个Github仓库的所有贡献者,创建一个issue。 建议由此开始DEBUG调试阅读源码interface GitHub { @RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors") List
contributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo); @RequestLine("POST /repos/{owner}/{repo}/issues") void createIssue(Issue issue, @Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo);
}
public static class Contributor { String login; int contributions; }
public static class Issue { String title; String body; List
assignees; int milestone; List labels; } public class MyApp { public static void main(String... args) { GitHub github = Feign.builder() .decoder(new GsonDecoder()) .target(GitHub.class, "https://api.github.com"); // Fetch and print a list of the contributors to this library. List
contributors = github.contributors("OpenFeign", "feign"); for (Contributor contributor : contributors) { System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")"); } } }
Feign.build 注入依赖配置项
public Feign build() {
SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory synchronousMethodHandlerFactory =
new SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory(client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger,
logLevel, decode404, closeAfterDecode, propagationPolicy);
ParseHandlersByName handlersByName =
new ParseHandlersByName(contract, options, encoder, decoder, queryMapEncoder,
errorDecoder, synchronousMethodHandlerFactory);
return new ReflectiveFeign(handlersByName, invocationHandlerFactory, queryMapEncoder);
}
调用JDK动态代理生成接口代理类
动态代理生成接口对象
public class ReflectiveFeign extends Feign {
@Override
public <t> T newInstance(Target<t> target) {
//使用Contract解析接口类上的方法和注解,转换单独MethodHandler处理
Map<string, methodhandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
// 使用DK动态代理为接口生成代理对象,实际业务逻辑交给 InvocationHandler 处理,其实就是调用 MethodHandler
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<!--?-->[]{target.type()}, handler);
return proxy;
}
}
解析接口方法注解信息
- 如何解析上文 Demo 中
Github.contributors方法的注解信息呢。Feign中提供一个Contract解析协议,有如下实现。
默认支持解析逻辑
class Default extends Contract.BaseContract {
protected void processAnnotationOnMethod(MethodMetadata data, Annotation methodAnnotation, Method method) {
Class<!--? extends Annotation--> annotationType = methodAnnotation.annotationType();
if (annotationType == RequestLine.class) {
//@RequestLine 注解处理逻辑
} else if (annotationType == Body.class) {
//@Body 注解处理逻辑
} else if (annotationType == Headers.class) {
//@Headers 注解处理逻辑
}
}
protected boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data, Annotation[] annotations, int paramIndex) {
boolean isHttpAnnotation = false;
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class<!--? extends Annotation--> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (annotationType == Param.class) {
Param paramAnnotation = (Param) annotation;
//@Param 注解处理逻辑
} else if (annotationType == QueryMap.class) {
//@QueryMap 注解处理逻辑
} else if (annotationType == HeaderMap.class) {
//@HeaderMap 注解处理逻辑
}
}
return isHttpAnnotation;
}
}
原生的常用注解
Annotation
Interface Target
@RequestLine
Method
@Param
Parameter
@Headers
Method, Type
@QueryMap
Parameter
@HeaderMap
Parameter
@Body
Method
Spring MVC 扩展注解
SpringMvcContract 为
spring-cloud-open-feign的扩展支持SpringMVC注解,现feign版本也已支持public class SpringMvcContract {
// 处理类上的 @RequestMapping @Override protected void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<!--?--> clz) { if (clz.getInterfaces().length == 0) { RequestMapping classAnnotation = findMergedAnnotation(clz, RequestMapping.class); } } // 处理 @RequestMapping 注解,当然也支持衍生注解 @GetMapping @PostMapping 等处理 @Override protected void processAnnotationOnMethod(MethodMetadata data, Annotation methodAnnotation, Method method) { if (!RequestMapping.class.isInstance(methodAnnotation) && !methodAnnotation .annotationType().isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) { return; } RequestMapping methodMapping = findMergedAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class); // 获取请求方法 RequestMethod[] methods = methodMapping.method(); // produce处理 parseProduces(data, method, methodMapping); // consumes处理 parseConsumes(data, method, methodMapping); // headers头处理 parseHeaders(data, method, methodMapping); data.indexToExpander(new LinkedHashMap<integer, param.expander>()); } // 处理 请求参数 SpringMVC 原生注解 @Override protected boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data, Annotation[] annotations, int paramIndex) { Param.Expander expander = this.convertingExpanderFactory .getExpander(typeDescriptor); if (expander != null) { data.indexToExpander().put(paramIndex, expander); } return isHttpAnnotation; }}
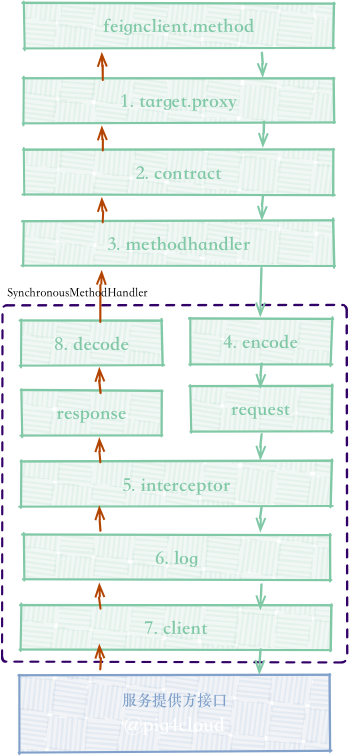
MethodHandler 请求处理逻辑
MethodHandler 路由
如上图, 根据不同的请求方法路由到不同的 MethodHandler 实现
final class SynchronousMethodHandler implements MethodHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {
// 获取请求模板
RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv);
// 参数处理
Options options = findOptions(argv);
// 默认的重试器
Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone();
while (true) {
try {
// 执行请求拦截器
Request request = targetRequest(template);
// 输出请求报文
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRequest(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, request);
}
Response response = client.execute(request, options);
// 根据返回的状态码 ,做 Decode 处理
...
return response;
} catch (RetryableException e) {
// 执行重试的相关逻辑
}
}
}
}
根据不同参数构建请求模板
- 表单提交 、还是直接body 提交
执行请求拦截器生成最终Request
// 获取全部的请求拦截器,一个个执行
Request targetRequest(RequestTemplate template) {
for (RequestInterceptor interceptor : requestInterceptors) {
interceptor.apply(template);
}
return target.apply(template);
}
请求日志处理
日志输出级别,配置
public enum Level { /** * 不输出 / NONE, /* * 只记录输出Http 方法、URL、状态码、执行时间 / BASIC, /* * 输出请求头 和 Http 方法、URL、状态码、执行时间 / HEADERS, /* * 输出请求头、报文体 和 Http 方法、URL、状态码、执行时间 */ FULL }
Client 执行最终的Requst 请求
默认default 处理
通过JDK 的
java.net包 实现,没请求都会创建连接实现。可以配置成HttpClient或者OKHttp的高性能实现class Default implements Client {
private final SSLSocketFactory sslContextFactory; private final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier; @Override public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException { HttpURLConnection connection = convertAndSend(request, options); return convertResponse(connection, request); }」
Spring Cloud 的负载均衡处理
// Spring Cloud 的Client 实现
public class FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient {
@Override
public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException {
// 例如请求: http://pig-auth-server/token/info
final URI originalUri = URI.create(request.url());
// 截取到serviceId: pig-auth-server
String serviceId = originalUri.getHost();
// 调用 loadBalancer API 获取到可以的服务实例
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancerClient.choose(serviceId);
// 构建真实的请求URL http://172.17.0.110:8763/token/info
String reconstructedUrl = loadBalancerClient.reconstructURI(instance, originalUri)
.toString();
// 创建请求 并执行
Request newRequest = Request.create(request.httpMethod(), reconstructedUrl,
request.headers(), request.requestBody());
return delegate.execute(newRequest, options);
}
}
返回报文Decoder 处理
默认处理
class Default implements Encoder {
@Override public void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) { if (bodyType == String.class) { template.body(object.toString()); } else if (bodyType == byte[].class) { template.body((byte[]) object, null); } else if (object != null) { throw new EncodeException( format("%s is not a type supported by this encoder.", object.getClass())); } }}
若是返回报文报错处理
public static class Default implements ErrorDecoder {
private final RetryAfterDecoder retryAfterDecoder = new RetryAfterDecoder(); @Override public Exception decode(String methodKey, Response response) { FeignException exception = errorStatus(methodKey, response); Date retryAfter = retryAfterDecoder.apply(firstOrNull(response.headers(), RETRY_AFTER)); if (retryAfter != null) { return new RetryableException( response.status(), exception.getMessage(), response.request().httpMethod(), exception, retryAfter, response.request()); } return exception; } private <t> T firstOrNull(Map<string, collection<t>> map, String key) { if (map.containsKey(key) && !map.get(key).isEmpty()) { return map.get(key).iterator().next(); } return null; }} }
注入 自定义的 ErrorDecoder 比较常用。
以上内容为 OpenFeign 的请求处理流程,下面为扩展内容 spring-cloud-open-feign 是如何初始化及其运行的呢?
【扩展】 Spring Cloud OpenFeign
EnableFeignClients 解析
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableFeignClients {
}
- 当我们在 Main 方法,加上
@EnableFeignClients注解,则开启了spring-cloud-open-feign的相关功能。 Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)导入FeignClientsRegistrar,扫描@FeignClient注入到容器
FeignClientsRegistrar
class FeignClientsRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 扫描配置注解中配置范围内的 @FeignClient
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
// 注入IOC 容器
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
}
}
//feignclient <--> bean 构造
private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map<string, object> attributes) {
String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName();
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
validate(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("url", getUrl(attributes));
definition.addPropertyValue("path", getPath(attributes));
String name = getName(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("name", name);
String contextId = getContextId(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("contextId", contextId);
definition.addPropertyValue("type", className);
definition.addPropertyValue("decode404", attributes.get("decode404"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallback", attributes.get("fallback"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallbackFactory", attributes.get("fallbackFactory"));
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
...
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className,
new String[] { alias });
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry);
}
}
默认情况
public class FeignAutoConfiguration {
// 未引入 feign-hystrix 模块,则还是注入 DefaultTargeter
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign")
protected static class DefaultFeignTargeterConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public Targeter feignTargeter() {
return new DefaultTargeter();
}
}
}
未引入 feign-hystrix 则还是上文的流程就同最初的流程一致 , 我们在调用 feignclient.method 会触发动态代理,执行 MethodHandler 的逻辑
HystrixFeign
- 首先,引入了
HystrixFeign,是不是意味逻辑变得更了呢
最初 0. 入门Demo Feign.builder(),就变成了 HystrixFeign.builder()
public final class HystrixFeign {
public static Builder builder() {
return new Builder();
}
public static final class Builder extends Feign.Builder {
// 注入 HystrixInvocationHandler 的实现
Feign build(final FallbackFactory<!--?--> nullableFallbackFactory) {
super.invocationHandlerFactory(new InvocationHandlerFactory() {
@Override
public InvocationHandler create(Target target,
Map<method, methodhandler> dispatch) {
return new HystrixInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, setterFactory,
nullableFallbackFactory);
}
});
super.contract(new HystrixDelegatingContract(contract));
return super.build();
}
}
}
注入
HystrixInvocationHandler的实现,使用HystrixCommand 包装,最终还是使用methodhandler 去调用最终的接口final class HystrixInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
@Override public Object invoke(final Object proxy, final Method method, final Object[] args) throws Throwable { // 使用HystrixCommand 包装 HystrixCommand<object> hystrixCommand = new HystrixCommand<object>(setterMethodMap.get(method)) { @Override protected Object run() throws Exception { try { // 调用 methodhandler 处理最终的请求 return HystrixInvocationHandler.this.dispatch.get(method).invoke(args); } catch (Exception e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable t) { throw (Error) t; } } }; return hystrixCommand.execute(); }}
SentinelFeign
先看类注释
like {@link HystrixFeign.Builder},"借鉴" HystrixFeign/**
- {@link Feign.Builder} like {@link HystrixFeign.Builder}.
*/ public final class SentinelFeign { }
注入
SentinelInvocationHandler的实现,使用Sentinel包装,最终还是使用methodhandler 去调用最终的接口public class SentinelInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { @Override public Object invoke(final Object proxy, final Method method, final Object[] args) throws Throwable { // 使用sentinel 包装请求 try { ContextUtil.enter(resourceName); entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, EntryType.OUT, 1, args); result = methodHandler.invoke(args); } catch (Throwable ex) { // fallback 逻辑 } finally { ContextUtil.exit(); } return result; } }
总结时序图
后续计划
欢迎关注我,后边更新 Ribbon、Hystrix、Sentinel、Nacos 等组件源码图文解析。 > 项目推荐: Spring Cloud 、Spring Security OAuth2的RBAC权限管理系统 欢迎关注 </method,></string,></string,></integer,></string,>













