[toc]
一、简介
简介部分参考博文
https://www.cnblogs.com/hanyifeng/p/6728151.html
supervisor与launchd,daemontools,runit等程序有着相同的功能,与某些程序不同的是,它并不作为“id 为 1的进程”而替代init。相反,它用于控制应用程序,像启动其它程序一样,通俗理解就是,把Supervisor服务管理的进程程序,它们作为supervisor的子进程来运行,而supervisor是父进程。supervisor来监控管理子进程的启动关闭和异常退出后的自动启动。
1、Supervisor与系统自带init 进程管理比较
方便:有些编译运行的程序,在安装完成后,需要为他们编写启动停止管理脚本,写入和维护可能很痛苦,而且进程在异常崩溃结束时,许多程序都不会正确重新启动的。Supervisord启动管理的程序进程是作为其子进程来运行的,并且可以配置为在进程崩溃停止时自动重新启动它们。
准确:在Unix上的进程通常很难获得准确的up/down状态。Pidfiles经常说谎。Supervisord将进程作为子进程启动,所以它总是知道其子进程的正确的up/down状态,可以方便的对这些数据进行查询
进程分组:进程支持分组启动和停止,也支持启动顺序,即‘优先级’,supervisor允许为进程分配优先级,并允许用户通过supervisorctl客户端发出命令,如“全部启动”和”重新启动所有“,它们以预先分配的优先级顺序启动。还可以将进程分为”进程组“,一组逻辑关联的进程可以作为一个单元停止或启动。
2、Supervisor的特点
简单:supervisor通过简单的INI风格的配置文件进行配置管理,易于学习,并提供了许多每个进程选项,如重新启动失败的进程和日志的自动切割。
集中:supervisor提供一个start、stop和监控进程的地方,进程可以单独或分组进行控制。可以通过supervisor的本地或远程命令行管理和web管理(一般为了安全,web通常需要禁用)
高效:supervisor通过fork/exec启动子进程,子进程需要前台运行,操作系统进程终止时去通知supervisor,而不像一些我们需要写脚本去定期轮询PID文件来重新启动失败的进程。
可扩展:supervisor有一个简单的事件(event)通知协议,还有一个用于控制的XML-RPC接口,可以用Python开发人员来扩展构建。
兼容:supervisor由Python编写,在除Windows操作系统以外基本都支持,如linux,Mac OS x,solaris,FreeBSD系统
3、Supervisor的组建构成
Supervisord:supervisor服务器的进程名是supervisord。它主要负责在自己的调用中启动子程序,响应客户端的命令,重新启动崩溃或退出的进程,记录其子进程stdout和stderr的输出,以及生成和处理对应于子进程生命周期中的”event“
服务器进程使用的配置文件,通常路径存放在/etc/supervisord.confa中。此配置文件是INI格式的配置文件。
supervisorctl:supervisor命令行的客户端名称是supervisorctl。它为supervisord提供了一个类似于shell的交互界面。使用supervisorctl,用户可以查看不同的supervisord进程列表,获取控制子进程的状态,如停止和启动子进程
web服务器:一个可以通过Web界面来查看和控制进程的状态,默认监听在9001上。
二、安装和配置
本次测试环境
主机名
ip
系统
auto
10.0.0.6/24
Centos 7.5
1、安装
[root@auto ~]# yum install supervisor -y
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
epel/x86_64/metalink | 8.4 kB 00:00:00
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* epel: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.aliyun.com
base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00
docker-ce-edge | 3.5 kB 00:00:00
docker-ce-stable | 3.5 kB 00:00:00
epel | 3.2 kB 00:00:00
extras | 3.4 kB 00:00:00
nginx | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
updates | 3.4 kB 00:00:00
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package supervisor.noarch 0:3.1.4-1.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
=============================================================================================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
=============================================================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
supervisor noarch 3.1.4-1.el7 epel 446 k
Transaction Summary
=============================================================================================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package
Total download size: 446 k
Installed size: 2.2 M
Downloading packages:
supervisor-3.1.4-1.el7.noarch.rpm | 446 kB 00:00:01
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : supervisor-3.1.4-1.el7.noarch 1/1
Verifying : supervisor-3.1.4-1.el7.noarch 1/1
Installed:
supervisor.noarch 0:3.1.4-1.el7
Complete!
#生成配置文件
[root@auto ~]# echo_supervisord_conf>/etc/supervisord.conf
[root@auto ~]# cat /etc/supervisord.conf
; Sample supervisor config file.
;
; For more information on the config file, please see:
; http://supervisord.org/configuration.html
;
; Notes:
; - Shell expansion ("~" or "$HOME") is not supported. Environment
; variables can be expanded using this syntax: "%(ENV_HOME)s".
; - Comments must have a leading space: "a=b ;comment" not "a=b;comment".
[unix_http_server]
file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; (socket 文件的路径)
;chmod=0700 ; socket 文件权限 (default 0700)
;chown=nobody:nogroup ; socket 文件属主:属组
;username=user ; (启动http的用户 (open server))
;password=123 ; (默认的密码 (open server))
;[inet_http_server] ; 默认禁用tcp监听的http 服务
;port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; (指定监听在本机ip地址和端口)
;username=user ; (默认启动http服务的用户)
;password=123 ; (默认的密码)
[supervisord]
logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ; (主日志文件的存放位置,默认在程序的工作启动目录)
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; (主日志文件的最大值,之后进行切割;默认 50MB)
logfile_backups=10 ; (主日志文件备份的数目;默认 10)
loglevel=info ; (日志级别;默认是info; 其它: debug,warn,trace)
pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ; (supervisord 运行时的pidfile路径;默认 supervisord.pid)
nodaemon=false ; (如果为true,程序就以前台运行;默认是 false)
minfds=1024 ; (min. 启动有效的文件描述符数目;默认 1024)
minprocs=200 ; (min. 有效进程描述符;默认 200)
;umask=022 ; (进程文件创建的默认权限;默认 022)
;user=chrism ; (默认是当前启动的用户)
;identifier=supervisor ; (supervisord 标识符, 默认是'supervisor')
;directory=/tmp ; (默认启动时间不会切换)
;nocleanup=true ; (在启动时不清理临时文件;默认值为false)
;childlogdir=/tmp ; ('AUTO' 子进程日志目录, 默认 $TEMP)
;environment=KEY="value" ; (增加一个环境变量键值对:key=”value“)
;strip_ansi=false ; (在log日志里去掉ansi转义编码; 默认是 false)
; 下面的部分选项必须保留在RPC的配置文件中
; (supervisorctl/web 接口) 使用以下配置来管理
; added by defining them in separate rpcinterface: sections
[rpcinterface:supervisor]
supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface
[supervisorctl]
serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket
;serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; use an http:// url to specify an inet socket
;username=chris ; should be same as http_username if set
;password=123 ; should be same as http_password if set
;prompt=mysupervisor ; cmd line prompt (default "supervisor")
;history_file=~/.sc_history ; use readline history if available
; 以下是被管理的示例程序显示所有可能用到的配置。
; 创建一个或“多个”程序: 要遵循以下的键值对规则。
; supervisor.
;[program:theprogramname]
;command=/bin/cat ; 程序的启动命令 (使用绝对路径)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name 表示 (默认是 %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; 启动时的进程数 (默认 1)
;directory=/tmp ; 执行时切换到的目录 (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=999 ; 相对启动优先级(default 999)
;autostart=true ; 是否跟随supervisord程序启动该监控程序 (default: true)
;startsecs=1 ; # 在设定时间内,程序必须保持运行 (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; 当启动失败时尝试的最大次数(default 3)
;autorestart=unexpected ; 如果退出后,什么状态退出的去重启,默认非意外的(def: unexpected)
;exitcodes=0,2 ; 'expected' 符合退出代码之后去重启 (default 0,2)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; 用于杀死进程的信号 (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; 最大等待秒数 SIGKILL (default 10)
;stopasgroup=false ; 发送停止信号到Unix进程组 (default false)
;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL UNIX进程组 (def false)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=true ; 是否开启程序标准错误输出的重定向 (default false)
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; 标准输出路径; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; 文件最大大小 # 日志文件进行切割 (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # 日志文件备份数目 (default 10)
;stdout_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; ‘捕获模式’中的字节数 (default 0)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; 在标准输出写入文件时发出事件 (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; 标准错误输出, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; 文件最大大小 # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (default 10)
;stderr_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;environment=A="1",B="2" ; 添加进程环境变量 (def no adds)
;serverurl=AUTO ; 覆盖serverurl计算 (childutils)
;下面是event事件部分所有可能设置的值,大部分同上面一样。
; eventlistener subsection values, create one or more 'real'
; eventlistener: sections to be able to handle event notifications
; sent by supervisor.
;[eventlistener:theeventlistenername]
;command=/bin/eventlistener ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1)
;events=EVENT ; event notif. types to subscribe to (req'd)
;buffer_size=10 ; event buffer queue size (default 10)
;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=-1 ; the relative start priority (default -1)
;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true)
;startsecs=1 ; # of secs prog must stay up to be running (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures when starting (default 3)
;autorestart=unexpected ; autorestart if exited after running (def: unexpected)
;exitcodes=0,2 ; 'expected' exit codes used with autorestart (default 0,2)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false)
;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=false ; redirect_stderr=true is not allowed for eventlisteners
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (default 10)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (default 10)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;environment=A="1",B="2" ; process environment additions
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils)
; The below sample group section shows all possible group values,
; create one or more 'real' group: sections to create "heterogeneous"
; process groups.
;[group:thegroupname]
;programs=progname1,progname2 ; 这里的progname1,progname2就是定义的监控管理程序的名字,如[program:x]这里就是x
;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999)
; 下面的 [include] 选项只能包含一个files 设置,功能是定义supervisor管理程序的配置文件,可以单独的移除去,和主配置文件分开,方便。
; setting can list multiple files (separated by whitespace or
; newlines). It can also contain wildcards. The filenames are
; interpreted as relative to this file. Included files *cannot*
; include files themselves.
;[include]
;files = relative/directory/*.ini ;定义管理监控程序的配置文件的路径
2、管理supervisor
1)supervisord -c /etc/supervisor.conf 服务端启动
上面命令会让supervisor在后台运行,后续管理命令直接在bash界面执行
supervisorctl status #查看状态
supervisorctl stop usercenter #停止子进程
supervisorctl start usercenter #开启子进程
supervisorctl restart usercenter #重启子进程
supervisorctl reread #读取有更新(增加)的配置文件,不会启动新添加的程序
supervisorctl update #重启配置文件修改过的程序
2)supervisorctl -c /etc/supervisor.conf 客户端启动
这个命令会进入 supervisorctl 的 shell 界面,然后可以执行不同的命令了:
> status # 查看程序状态
> stop tomcat # 关闭 tomcat 程序
> start tomcat # 启动 tomcat 程序
> restart tomcat # 重启 tomcat 程序
> reread # 读取有更新(增加)的配置文件,不会启动新添加的程序
> update # 重启配置文件修改过的程序
> exit # 退出
3)web界面
后续演示
2、配置supervisor管理nginx进程
#修改配置文件
[root@auto supervisord.d]# vim supervisor.conf
[include]
files = /etc/supervisord.d/*.conf
#(此处类似nginx的include conf.d/*.conf)
注意!!!supervisor不能管理daemon进程,nginx 是daemon进程,如果要管理,需要在nginx.conf配置文件的http标签外增加 daemon off; 此处只是测试适用。
# 修改nginx配置
[root@auto super]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
daemon off;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
.......
配置supervisor管理nginx的配置文件
[root@auto supervisord.d]# pwd
/etc/supervisord.d
[root@auto supervisord.d]# cat nginx_test.conf
[program:nginx]
command=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
stdout_logfile=/tmp/nginx.log
stderr_logfile=/tmp/nginx_err.log
autostart=true
autorestart=true
startsecs=10
stopwaitsecs=50 #这里最好配置
priority=1
运行supervisor并查看状态
#运行前查看nginx进程
[root@auto etc]# ps -ef|grep nginx
root 3311 1991 0 17:21 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#运行supervisor
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl status
nginx STARTING
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl status
nginx RUNNING pid 3342, uptime 0:01:36
#验证nginx进程
[root@auto supervisord.d]# !ps
ps -ef|grep nginx
root 3342 3302 0 17:23 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 3343 3342 0 17:23 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 3360 1991 0 17:25 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#nginx开启成功
3、配置supervisor管理mysql进程
配置文件无需修改 只需要在/etc/supervisord.d/内增加管理mysq的配置文件。与nginx的类似
[root@auto supervisord.d]# vim mysql.conf
[program:mysql]
command=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data --plugin-dir=/usr/local/mysql/lib/plugin --user=mysql --log-error=/usr/local/mysql/data/auto.err --pid-file=/usr/local/mysql/data/auto.pid --port=3306
stdout_logfile=/tmp/mysql.log
stderr_logfile=/tmp/mysql_err.log
autostart=true
autorestart=true
startsecs=10
stopwaitsecs=50
priority=3
适用supervisorctl客户端命令平滑增加mysql管理
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl reread
mysql: available
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl update
mysql: added process group
#验证
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl status
mysql RUNNING pid 3512, uptime 0:00:15
nginx RUNNING pid 3342, uptime 0:07:55
4、配置supervisor管理php进程
配置文件无需修改 只需要在/etc/supervisord.d/内增加管理php的配置文件。与nginx的类似,由于php的daemon进程,需要在配置文件php-fpm.conf内进行修改
[root@auto super]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
;daemonize = yes ;默认配置
daemonize = no
#配置supervisor管理php配置文件
[root@auto supervisord.d]# vim php.conf
[program:php]
command=/usr/local/php/sbin/php-fpm
stdout_logfile=/tmp/php.log
stderr_logfile=/tmp/php_err.log
autostart=true
autorestart=true
startsecs=20
stopwaitsecs=30
priority=2
适用supervisorctl客户端命令平滑增加php管理
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl reread
php: available
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl update
php: added process group
#验证
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl status
mysql RUNNING pid 3512, uptime 0:04:41
nginx RUNNING pid 3342, uptime 0:12:21
php RUNNING pid 3658, uptime 0:00:21
5、web界面管理supervisor进程
修改配置文件
[root@auto supervisord.d]# vim /etc/supervisor.conf
#下面是修改部分
[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default
port=10.0.0.6:9001 ; (ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface)
username=admin ; (default is no username (open server))
password=admin123 ; (default is no password (open server))
保存后平滑启动
[root@auto supervisord.d]# supervisorctl update
打开浏览器 登陆http://10.0.0.6:9001,根据配置文件内的username和password登陆管理
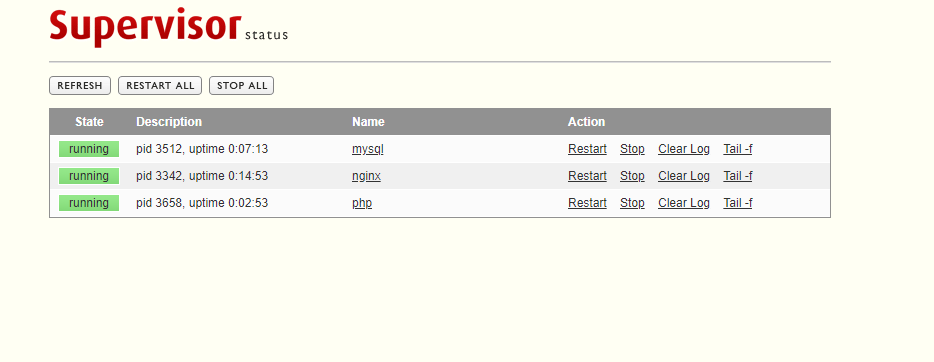
该界面可以对supervisor管理的所有进程进行管理 关闭 重启 等 ,也能查看相应的运行时间和启动失败日志等信息。
6、测试
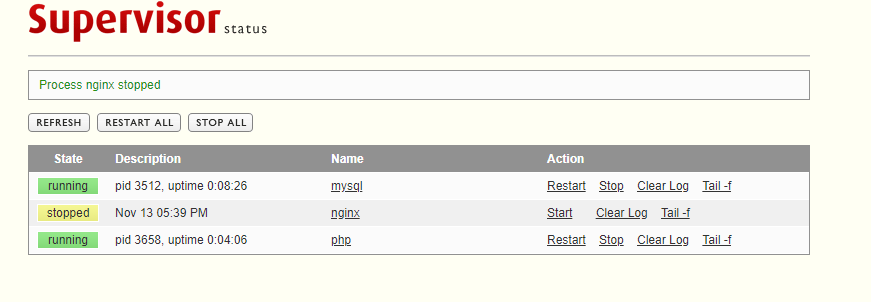
1)测试1
尝试web关闭nginx 返回auto主机进行查看
[root@auto supervisord.d]# ps -ef|grep nginx
root 3679 1991 0 17:39 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#发现nginx已经关闭
2)测试2
尝试手动停止nginx进程,观察supervisor是否会对nginx进程重启
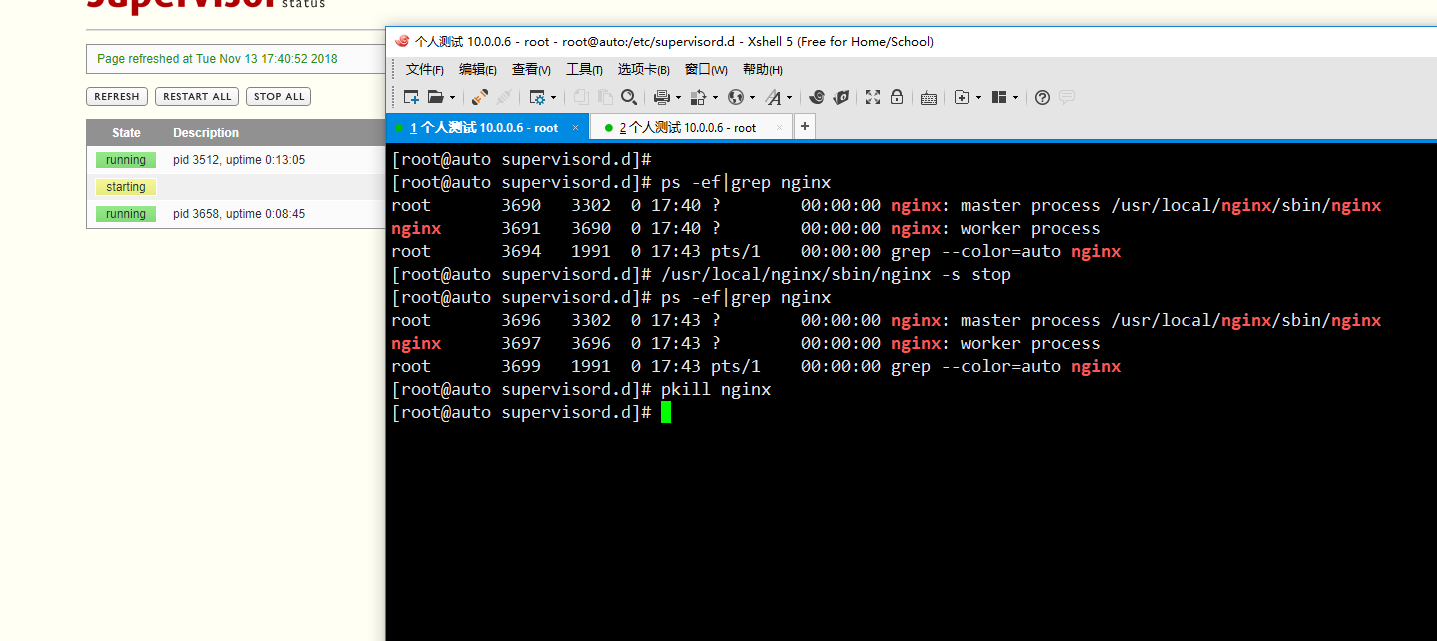
测试结果可知,无论是正常关闭nginx还是pkill强制关闭nginx,supervisor都会重新启动,验证成功
三、总结
supervisor在生产中还是比较实用的,可以管理很大一部分服务,对于本身就是daemon运行的程序,实际意义不是很大(个人理解),对于服务启动速度,测试结果是和配置文件内的startsecs有关,从手动执行 supervisorctl start nginx命令开始,大约过了startsecs配置的时间,才会真正的更新是否开启状态,其实真正的服务启动情况和具体服务有关,这个时间可以根据实际情况处理。至于stopwaitsecs的适用我还没真正掌握,测试时候如果不配置该时间,服务会无法启动,个人暂时理解为执行start的时候会在stopwaitsecs时间内对服务进行检测,如果在该时间内还没启动,则视为失败,后续继续测试验证。














