一、使用I/O操作文件
关键步骤:
- 使用File类操作文件或目录属性
- 使用FileInputStream类读文本文件
- 使用FileOutputStram类写文本文件
- 使用BufferedReader类和FileReader类读文本文件
- 使用BufferedWriter类和FileWriter类读文本文件
- 使用DataInputStream类读二进制文件
- 使用DataOutputStream类写二进制文件
- 重定向标准I/O
1.使用File类操作文件或目录属性
java.io包提供了一些接口和类,对文件进行基本操作,包括对文件和目录属性的操作、对文件读写的操作等。
File即可以表示文件,也可以表示目录,在程序中一个File对象可以代表一个文件或目录。
- File类的构造方法
- File(String pathname) :用指定的文件路径构造文件
- File(String dir,String subpath):在指定的目录下创建指定文件名的文件,dir指定目录路径,subpath指定文件名
- File(File parent,String subpath):根据一个文件对象和一个文件构造文件对象,parent指定目录文件,subpath指定文件名
- File类常用方法
方法名
说明
创建:
createNewFile()
在指定位置创建一个空文件,成功就返回true,如果已存在就不创建,然后返回false。
mkdir()
在指定位置创建一个单级文件夹。它的路径名有当前File对象指定
mkdirs()
在指定位置创建一个多级文件夹,即包括父目录的目录
renameTo(File dest)
如果目标文件与源文件是在同一个路径下,那么renameTo的作用是重命名, 如果目标文件与源文件不是在同一个路径下,那么renameTo的作用就是剪切,而且还不能操作文件夹。
删除:
delete()
删除文件或者一个空文件夹,不能删除非空文件夹,马上删除文件,返回一个布尔值。
deleteOnExit()
jvm退出时删除文件或者文件夹,用于删除临时文件,无返回值。
判断:
exists()
文件或文件夹是否存在。
isFile()
是否是一个文件,如果不存在,则始终为false。
isDirectory()
是否是一个目录,如果不存在,则始终为false。
isHidden()
是否是一个隐藏的文件或是否是隐藏的目录。
isAbsolute()
测试此抽象路径名是否为绝对路径名。
获取:
getName()
获取文件或文件夹的名称,不包含上级路径。
getAbsolutePath()
获取文件的绝对路径,与文件是否存在没关系
length()
获取文件的大小(字节数),如果文件不存在则返回0L,如果是文件夹也返回0L。
getParent()
返回此抽象路径名父目录的路径名字符串;如果此路径名没有指定父目录,则返回null
lastModified()
获取最后一次被修改的时间。
文件夹相关:
static File[] listRoots()
列出所有的根目录(Window中就是所有系统的盘符)
list()
返回目录下的文件或者目录名,包含隐藏文件。对于文件这样操作会返回null。
listFiles()
返回目录下的文件或者目录对象(File类实例),包含隐藏文件。对于文件这样操作会返回null。
list(FilenameFilter filter)
返回指定当前目录中符合过滤条件的子文件或子目录。对于文件这样操作会返回null。
listFiles(FilenameFilter filter)
返回指定当前目录中符合过滤条件的子文件或子目录。对于文件这样操作会返回null。
package cn.IO;
import java.io.*;
public class FileMethods {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileMethods fm=new FileMethods();
File file=new File("D:\\javaWork\\IoTest.txt");
fm.create(file);
fm.showFileInfo(file);
//fm.delete(file);
}
/**
* 创建文件的方法
* @param file 文件对象
*/
public void create(File file){
if(!file.exists()){
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件已创建!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 删除文件
* @param file 文件对象
*/
public void delete(File file){
if(file.exists()){
file.delete();
System.out.println("文件已删除!");
}
}
/**
* 显示文件信息
* @param file 文件对象
*/
public void showFileInfo(File file){
if(file.exists()){ //判断文件是否存在
if(file.isFile()){ //如果是文件
System.out.println("名称:" + file .getName());
System.out.println("相对路径: " + file.getPath());
System.out.println("绝对路径: " + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件大小:" + file.length()+ " 字节");
System.out.println("最后修改日期:"+file.lastModified());
}
if(file.isDirectory()){
System.out.println("此文件是目录");
}
}else
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
}

2.Java的流
读文件是把文件中的数据读取到内存中,写文件是把呢村中的数据写到文件中,他们都是通过流来读写的。
流是指一连串流动的字符,是以先进先出的方式发送和接受数据的通道,如图:
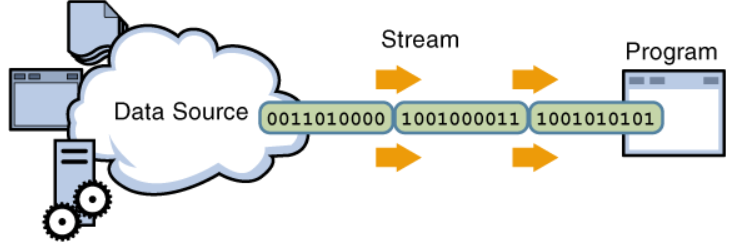
流分为输入输出流,是相对于计算机内存来说的,输出流主要由OutInputStream和Writer作为基类,而输入流则主要由InputStream和Reader作为基类。
分类:表中带下划线的是抽象类,不能创建对象。粗体部分是节点流,其他就是常用的处理流。
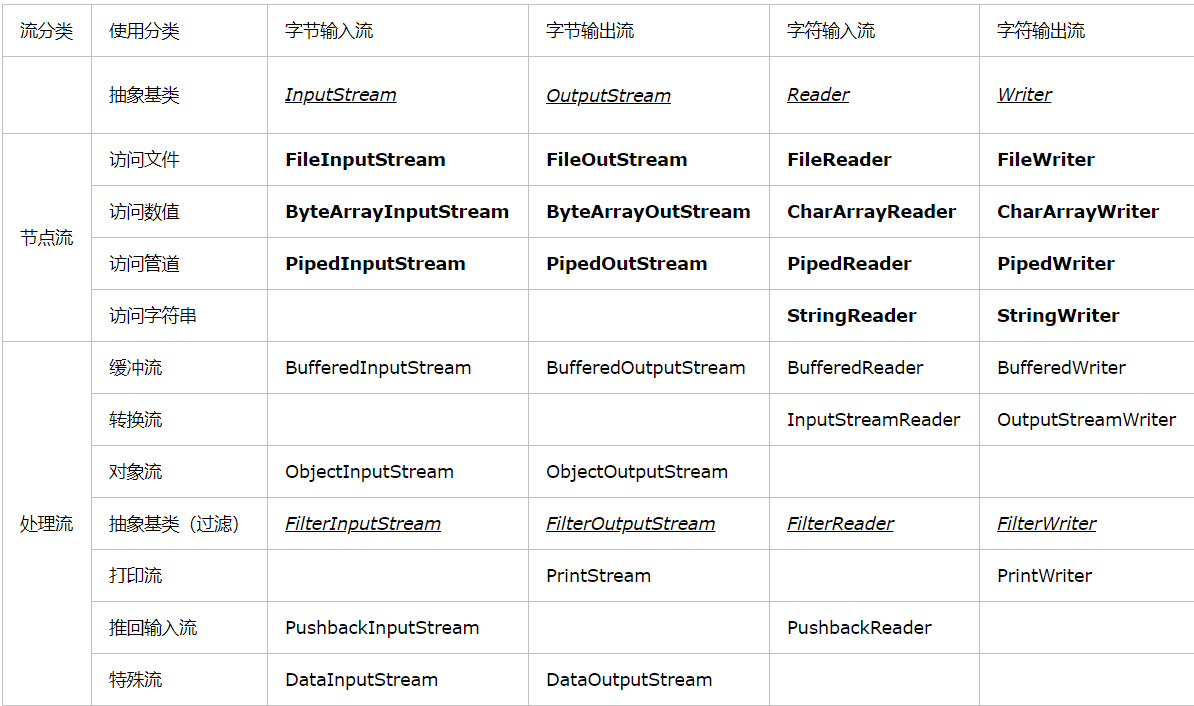
- 字节流时8为通用字节流,基本单位是字节;字符流是16位Unicode字符流,基本单位是Unicode字符(适用于处理字符串和文本)。
- Java IO是采用的是装饰模式,即采用处理流来包装节点流的方式,来达到代码通用性。
- 处理流和节点流的区分方法,节点流在新建时需要一个数据源(文件、网络)作为参数,而处理流需要一个节点流作为参数。
- 处理流的作用就是提高代码通用性,编写代码的便捷性,提高性能。
- 节点流都是对应抽象基类的实现类,它们都实现了抽象基类的基础读写方法。其中read()方法如果返回-1,代表已经读到数据源末尾。
** 3.用InputStream类和OutputStream类(字节流)读写文本文件**
字节流类是从抽象类InputStream和OutputStream派生出来的一系列类.这类流以字节为基本处理单位.InputStream 和 OutputStream类除了可以用来处理二进制文件的数据之外,也可以用来处理文本文件。
方法名
说明
InputStream类的常用方法:
public abstract int read() thows IOException
方法返回一个0至255之间的整数或-1, -1代表遇到了流的结束,其它对应读入的字节
public int read(byte[]b) thows IOException
方法将字节读入参数给定的缓冲区字节数组,返回值是实际读入的字节数或-1(遇到了流结束)
public int read(byte[]b, int i, int b) thows IOException
方法的后两个参数分别给出读入的起始位置和读入的最大字节数
public int available()
返回当前流对象中还没有被读取的字节数量.也就是获得流中数据的长度
public long skip(long n)
跳过当前流对象中的n个字节,而实际跳过的字节数量则以返回值的方式返回
public boolean markSupported()
判断流是否支持标记(mark),标记可以方便的回到原来读过的位置
public void close()
关闭当前流对象,并释放该流对象占用的资源
public void mark(int i)
为流中当前的位置设置标志,使得以后可以从该位置继续读取
public void reset()
使流读取的位置回到设定标记的位置
OutputStream类的常用方法:
public void write(int b) throws IOException
向流的末尾写入一个字节的数据
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException
将数组b中的数据依次写入当前的流对象中
public void wirte(byte[]b, int i, int n)
将数组中从开始下标(包含),后续长度的数据依次写入到流对象中
public void close()
关闭当前流对象,并释放该流对象占用的资源
public void flush()
将当前流对象中的缓冲数据强制输出出去.使用该方法可以实现立即输出
**使用FileInputStream字节流都文本文件
★构造方法:
**(1) FileInputStream(File f)
以指定名字的文件对象f为数据源建立文件输入流.如果f存在的话但是它应是一个文件路径,如果是目录则会抛出IOException,但是如果是这个目录不存在的时候则会抛出:FileNotFoundException
(2) FileInputStream(String name)
以名为name的文件为数据源建立文件输入流.
(3) FileInputStream(FileDescriptor f)
根据文件描述符对象f为输入端建立一个文件输入流.
package cn.IO; import java.io.*; public class FileInputStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args){ FileInputStream fis=null; //创建流对象 try { //IoTest.txt可先先手动写入一些数据 fis=new FileInputStream("d:\\javaWork\\IoTest.txt"); int data; System.out.println("可读取的字节数:"+fis.available()); System.out.print("文件内容为:"); //循环读数据 read()方法是从输入流读取1个8位的字节,把它转化为0-255之间的整数返回。将返回的整数转换为字符 while((data=fis.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)data); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { //关闭流对象 fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }注意:read()方法返回整数,如果读取的是字符串,需要进行强制类型转换;流对象使用完毕后需关闭
******使用FileOutputStream字节流写文本文件
★构造方法
1)FileOutputStream(File f)
2)FileOutputStream(File f, boolean b)
3)FileOutputStream(String f)
package cn.IO; import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args){ FileOutputStream fos=null; try { fos=new FileOutputStream("d:\javaWork\IoTest.txt",false); String str="好好学习Java"; byte[] words=str.getBytes("UTF-8"); fos.write(words,0,words.length); System.out.println("hello文件已更新"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("文件更新时出错!"); e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { if(fos!=null){ fos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
使用FileOutputStream要注意: 1) 在创建FileOutputStream实例时,如果相应文件不存在,则会自动创建一个空文件;
2)如果参数file或name表示的文件路径尽管存在,但是代表一个文件目录,则此时会抛出FileNotFoundException异常;
3)默认情况下,像文件写数据时将覆盖原有的内容
4. 使用字符流BufferedReader、FileReader和BufferedWriter、FileWriter读写文本文件
使用字符流BufferedReader、FileReader读文本文件
★BufferedReader构造方法有:
1)BufferedReader(Reader in)
2)BufferedReader(Reader in, int bufSize)
★FileReader**构造方法:
1)FileReader(File file);
2)FileReader(FileDescriptor e );
3)FileReader(String filename);
BufferedReader、FileReader两个类都是Reader抽象类的子类,使用了缓冲区,提高了读文本文件的效率。
Reader类是个抽象类,该类的所有方法在错误条件下都会抛出IOException异常,常用方法如下:方法名
说明
Reader类是个抽象类,该类的所有方法在错误条件下都会抛出IOException异常:
abstract void close()
关闭输入源
void mark(int numChars)
放置一个标记到输入源的当前点
boolean markSupported()
如果这个流支持mark/reset方法,将返回true
int read()
读取单个字符
int read(char[] buf)
读字符读入到字符数组
abstract int read(char[] buf, int offset, int numChars)
将字符读入数组的某一部分
boolean ready()
如果下一个输入请求不必等待,返回true,否则返回false
void reset()
重置输入指针到前面设置的标记
long skip(long numChars)
跳过n个字符输入,返回实际跳过的字符数
Writer类也是个抽象类:
abstract void close()
关闭输出流
abstract void flush()
确定输出状态以便清空任何缓存
void write(int ch)
写入单个字符
void write(char[] buf)
写入字符数组
abstract void write(char[] buf, int offset, int numChars)
写入字符数组的一部分
void write(String str)
写入字符串
void write(String str, int offset, int numChars)
写入字符串的一部分
补充:read()方法是按字节读取,只判断有没有读取到数据,不管内容的,所以换行符也会被读出来;
而BufferedReader引用.**readLine()**是按行读取的,即从当前位置一直读取数据,直到遇到换行符,然后去掉换行符,返回读取到的数据
实例:package cn.IO; import java.io.*; public class BufferedReaderTest { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { FileReader fr=null; BufferedReader br=null; try { //创建一个FileReader对象 fr=new FileReader("d:\\javaWork\\hello.txt"); //创建一个BufferedReader 对象 br=new BufferedReader(fr); //读取一行数据 String line=null; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(line); } }catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("文件不存在!"); }finally{ try { //关闭 流 if(br!=null) br.close(); if(fr!=null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }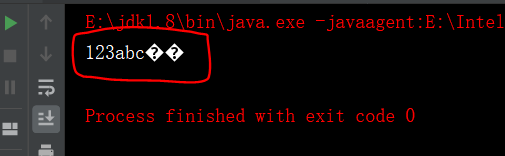
注意:读取文件时,出现中文乱码,由于文件是txt格式,编码格式默认为ANSI格式,即GBK,所以需要转为utf-8:
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File("文件路径")), "utf-8"); package cn.IO; import java.io.*; /* * 当hello.txt编码格式是ANSI时,程序可以正常读取数据,(InputStreamReader fr=new InputStreamReader(fis,"gbk"); ); * 当hello.txt编码格式改为UTF-8时,代码改为InputStreamReader fr=new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8"); 时才可以正常读取数据。 * */ public class BufferedReaderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { InputStreamReader fr = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\javaWork\\hello.txt"); // 指定编码格式 fr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf-8"); br = new BufferedReader(fr); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } } catch (IOException e) { try { br.close(); fr.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } }但是对于一些特殊符号如空格等以及输出中文时出现乱码,这里引用一个转码类,将源文件解析后转成utf-8,再读取数据:
package cn.IO; import java.io.*;//转码类 public class getCharset { public static String get_charset(File file) { String charset = "GBK"; byte[] first3Bytes = new byte[3];//首先3个字节 try { boolean checked = false; BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(file)); bis.mark(0); int read = bis.read(first3Bytes, 0, 3); if (read == -1) return charset; if (first3Bytes[0] == (byte) 0xFF && first3Bytes[1] == (byte) 0xFE) { charset = "UTF-16LE"; checked = true; } else if (first3Bytes[0] == (byte) 0xFE && first3Bytes[1] == (byte) 0xFF) { charset = "UTF-16BE"; checked = true; } else if (first3Bytes[0] == (byte) 0xEF && first3Bytes[1] == (byte) 0xBB && first3Bytes[2] == (byte) 0xBF) { charset = "UTF-8"; checked = true; } bis.reset(); if (!checked) { // int len = 0; int loc = 0; while ((read = bis.read()) != -1) { loc++; if (read >= 0xF0) break; if (0x80 <= read && read <= 0xBF) // 单独出现BF以下的,也算是GBK break; if (0xC0 <= read && read <= 0xDF) { read = bis.read(); if (0x80 <= read && read <= 0xBF) // 双字节 (0xC0 - 0xDF) // (0x80 // - 0xBF),也可能在GB编码内 continue; else break; } else if (0xE0 <= read && read <= 0xEF) {// 也有可能出错,但是几率较小 read = bis.read(); if (0x80 <= read && read <= 0xBF) { read = bis.read(); if (0x80 <= read && read <= 0xBF) { charset = "UTF-8"; break; } else break; } else break; } } } bis.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return charset; } } package cn.IO; import java.io.*; //1、导入相关包 public class BufferedReaderTest { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //FileReader fr=null; BufferedReader br=null; try { //获取文件编码格式 File dir = new File("d:\\javaWork\\hello.txt");//指定路径 String charset=getCharset.get_charset(dir); if (charset == "GBK") { //2、InputStreamReader是转换流 InputStreamReader reader_GBK = new InputStreamReader( new FileInputStream(dir), "gb2312"); //3、创建一个BufferedReader流对象 br = new BufferedReader(reader_GBK); } if (charset == "UTF-8") { InputStreamReader reader_UTF = new InputStreamReader( new FileInputStream(dir), "UTF-8"); //3、创建一个BufferedReader流对象 br = new BufferedReader(reader_UTF); } //4、使用readLine()读取一行数据 String line=null; while((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } //System.out.println(new String(s.getBytes("utf-8"),"utf-8"));*/ }catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("文件不存在!"); }finally{ try { //5、关闭 流 if(br!=null) br.close(); //if(fr!=null) //fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }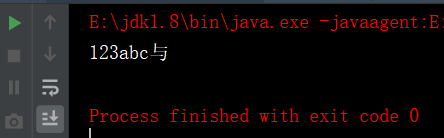
*使用字符流BufferedWriter、FileWriter写文本文件*****
BufferedWriter和FileWriter类继承自Writer类,他们是用来将数据写入到缓冲区里。使用过程与使用BufferedReader、FileReader类过程相似。不同的是,缓冲区内的数据最后必须要用flush()方法将缓冲区清空,也就是将缓冲区中的数据全部写到文件内。
★BufferedWriter构造方法有:
1)BufferedWriter(Writer out)
2)BufferedWriter(Writer out, int bufSize)
★FileWriter构造方法有:
1)FileWrite(File filePath)
2)FileWrite(File f, boolean append)
3)FileWrite(FileDescriptor e)
4)FileWrite(String filename)
5)FileWrite(String filename,boolean append)
package cn.IO;
//1、引入相关的类
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter fw=null;
BufferedWriter bw=null;
FileReader fr=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
try {
//2、创建一个FileWriter 对象
fw=new FileWriter("d:\\javaWork\\hello.txt");
//3、创建一个BufferedWriter 对象
bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
//4、用write()方法写文本文件
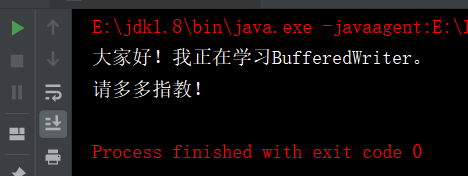
bw.write("大家好!");
bw.write("我正在学习BufferedWriter。");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("请多多指教!");
bw.newLine();
//5、调用flush()方法刷新缓冲区
bw.flush();
//6、读取文件内容
//获取文件编码格式
File dir = new File("d:\\javaWork\\hello.txt");//指定路径
String charset=getCharset.get_charset(dir);
if (charset.equals("GBK")) {
//InputStreamReader是转换流
InputStreamReader reader_GBK = new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream(dir), "gb2312");
//创建一个BufferedReader流对象
br = new BufferedReader(reader_GBK);
}
if (charset.equals("UTF-8")) {
InputStreamReader reader_UTF = new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream(dir), "UTF-8");
//创建一个BufferedReader流对象
br = new BufferedReader(reader_UTF);
}
//使用readLine()读取一行数据
String line=null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.println("文件不存在!");
}finally{
try{
if(fw!=null)
fw.close();
if(br!=null)
br.close();
if(fr!=null)
fr.close();
}catch(IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5. 读写二进制文件
1.使用DtaInputStream、DataOutputStream字节流读写二进制文件 这两个流属于过滤流,常以其它流如InputStream或OutputStream作为它们的输入或输出,例如:
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\a.txt");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\a.txt");
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
DateInputStream和DataOutputStream的输入和输出几乎是对应的,每种基本数据类型的读写方法可以从其后缀名字识别.例如:
readInt(),writeInt() // 读写一个int值
readBoolean(),writeBoolean() // 读写一个布尔值
readChar(),writeChar() // 读写一个字符
readDouble(),writeDouble() // 读写一个双精度浮点值
readFloat(),writeFloat() // 读写一个单精度浮点值
writeChars() // 写一个字符串,但没有直接读字符串的方法
readUTF(),writeUTF() //读写才用UTF-8字符集编码的字符串
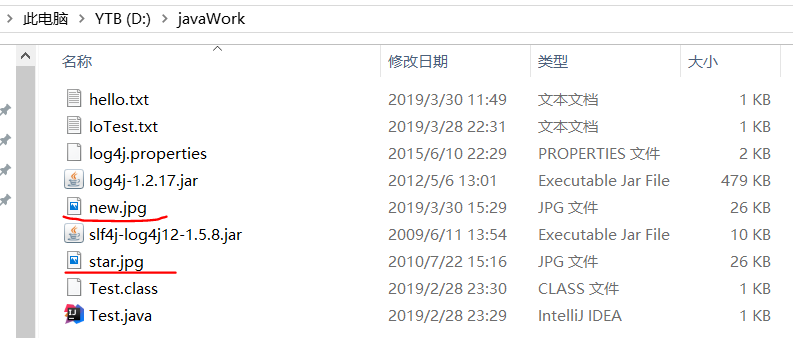
package cn.IO; import java.io.*; //二进制文件的读写 public class ReadAndWriteBinaryFile { public static void main(String[] args){ DataInputStream dis=null; DataOutputStream dos=null; FileInputStream fis=null; FileOutputStream fos=null; try { //创建输入流对象 fis=new FileInputStream("d:\javaWork\star.jpg"); dis=new DataInputStream(fis); //创建输出流对象 fos=new FileOutputStream("d:\javaWork\new.jpg"); dos=new DataOutputStream(fos); //读取文件并写入文件 int temp; while((temp=dis.read())!=-1){ dos.write(temp); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { if(dis!=null){ dis.close(); } if(dos!=null){ dos.close(); } if(fis!=null){ fis.close(); } if(fos!=null){ fos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
6. 重定向标准I/O
前面介绍的十几个常用的流对象,用于对文件进行操作。还有2个流:System.in和System.out,它是Java提供的两个标准输入/输出流,主要用于键盘接受数据以及向屏幕输出数据。
- System.in常用方法:
- int read() 此方法从键盘接受一个字节的数据,返回值是该字符的ASCII码
- int read(byte[] buf) 此方法从键盘接受多个字节的数据,保存至buf中,返回值是接受字节数据的个数,非ASCII码
- System.out常用方法:
- print() 向屏幕输入数据,不换行,参数可以是Java的任意数据类型
- println() 向屏幕输入数据,换行,参数可以是Java的任意数据类型
有些时候使用标准I/O读写文件会很方便,如何实现呢?首先需要重定向标准I/O,就是讲标准I/O重新定向到其他的I/O设备,例如将输出设备定位到文件。
System类提供了3个重定向标准I/O的方法,如下表:
方法名
说明
static void setErr(PrintStream err)
重定向标准错误输出流
static void setIn(InputStream in)
重定向标准输r入流
static void setOut(OutputStream out)
重定向标准输出流
实例:
package cn.IO;
import java.io.*;
/*
* 重定向输入输出流
*/
public class PrintStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
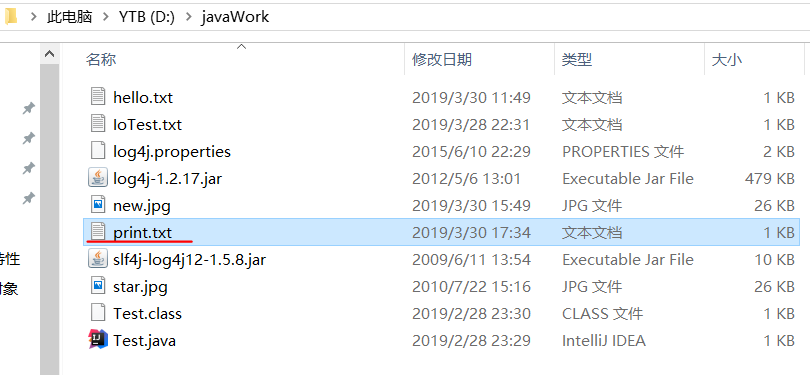
File file = new File("d:\\javaWork\\print.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
PrintStream printStream = null;
try{
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
//创建PrintStream输出流
printStream = new PrintStream(fileOutputStream);
//将标准输出流重定向到文件
System.setOut(printStream);
//向文件中输出内容
System.out.println("我的测试,重定向到print文件!");
}catch(FileNotFoundException fi){
fi.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(printStream!=null){
printStream.close();
}
try{
if(fileOutputStream!=null){
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}catch (IOException ioe){
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}

7.IO 的一般使用原则:
1)按数据来源(去向)分:
1 、是文件: FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, ( 字节流 )FileReader, FileWriter( 字符 )
2 、是 byte[] : ByteArrayInputStream, ByteArrayOutputStream( 字节流 )
3 、是 Char[]: CharArrayReader, CharArrayWriter( 字符流 )
4 、是 String: StringBufferInputStream, StringBufferOuputStream ( 字节流 )StringReader, StringWriter( 字符流 )
5 、网络数据流: InputStream, OutputStream,( 字节流 ) Reader, Writer( 字符流 )
2)按是否格式化输出分:
1 、要格式化输出: PrintStream, PrintWriter
3)按是否要缓冲分:
1 、要缓冲: BufferedInputStream, BufferedOutputStream,( 字节流 ) BufferedReader, BufferedWriter( 字符流 )
4)按数据格式分:
1 、二进制格式(只要不能确定是纯文本的,比如图片、音频、视频) : InputStream, OutputStream 及其所有带 Stream 结尾的子类
2 、纯文本格式(含纯英文与汉字或其他编码方式); Reader, Writer 及其所有带 Reader, Writer 的子类
5)按输入输出分:
1 、输入: Reader, InputStream 类型的子类
2 、输出: Writer, OutputStream 类型的子类
6)特殊需要:
1 、从 Stream 到 Reader,Writer 的转换类: InputStreamReader, OutputStreamWriter
2 、对象输入输出: ObjectInputStream, ObjectOutputStream
3 、进程间通信: PipeInputStream, PipeOutputStream, PipeReader, PipeWriter
4 、合并输入: SequenceInputStream
5 、更特殊的需要: PushbackInputStream, PushbackReader, LineNumberInputStream, LineNumberReader













