Redis从入门到放弃系列(五) ZSet
本文例子基于:5.0.4 ZSet是Redis中一种比较复杂的数据结构,当存储大小在128之内且member得长度在64以下,其实现为zipList,超过为SkipList
忽然发现,到现在第五篇文章,还没有讲到zipList,然而前面例如Hash,List的篇章都涉及到了zipList的,后面会单独写一篇zipList的实现的~立Flag 请期待 【Redis从入门到放弃系列(外传) ZipList】
言归正传,首先让我们来看一下该如何在redis里面使用ZSet类型
//将一个或多个元素及其分数加入到有序集合里面
ZADD key [NX|XX] [CH] [INCR] score member [score member ...]
代码示例:
//添加元素
>zadd store 1000 xiaoming 2000 xiaoqiang 3000 xiaoyue
(integer) 3
//返回指定区间内的有序集合列表
> zrange store 0 -1 withscores
1) "xiaoming"
2) "1000"
3) "xiaoqiang"
4) "2000"
5) "xiaoyue"
6) "3000"
//返回有序集合的数量
>zcard store
(integer) 3
//查看处于1000到2000的存款的人数
>zcount store 1000 2000
(integer) 2
//查询处于1000到2000的存款的人群
> ZRANGEBYSCORE store 1000 2000
1) "xiaoming"
2) "xiaoqiang"
//根据member查看当前排名
>zrank store xiaoming
(integer) 0
至此,redis zset的用法先告一段落.
源码解析
按照惯例,先来一波zset的数据结构
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;
double score;
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
unsigned long length;
int level;
} zskiplist;
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
SkipList编码的有序集合底层是使用一个命为zset的结构体构成的,该结构体拥有两种数据类型,dict跟zskiplist。zskiplist按照score从小到大保存所有集合元素,dict则保存着member到score的映射关系,两个数据结构共用着相同元素的ele和score的内存。 zskiplist是一个双向链表,这是为了方便倒序方式获取一个范围内的元素。 关于跳跃链表的讲解请参考漫画算法:什么是跳跃表?
当我们在使用zadd key member的时候,redis是如何实现的呢?让我们来看一下源码:
/* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already
* exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership
* of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL];
int i, level;
serverAssert(!isnan(score));
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
/* we assume the element is not already inside, since we allow duplicated
* scores, reinserting the same element should never happen since the
* caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table if the element is
* already inside or not. */
level = zslRandomLevel();
if (level > zsl->level) {
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {
rank[i] = 0;
update[i] = zsl->header;
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
zsl->level = level;
}
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele);
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;
}
/* increment span for untouched levels */
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];
if (x->level[0].forward)
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
zsl->length++;
return x;
}
上面的流程我们用一张图来表示,如下所示: 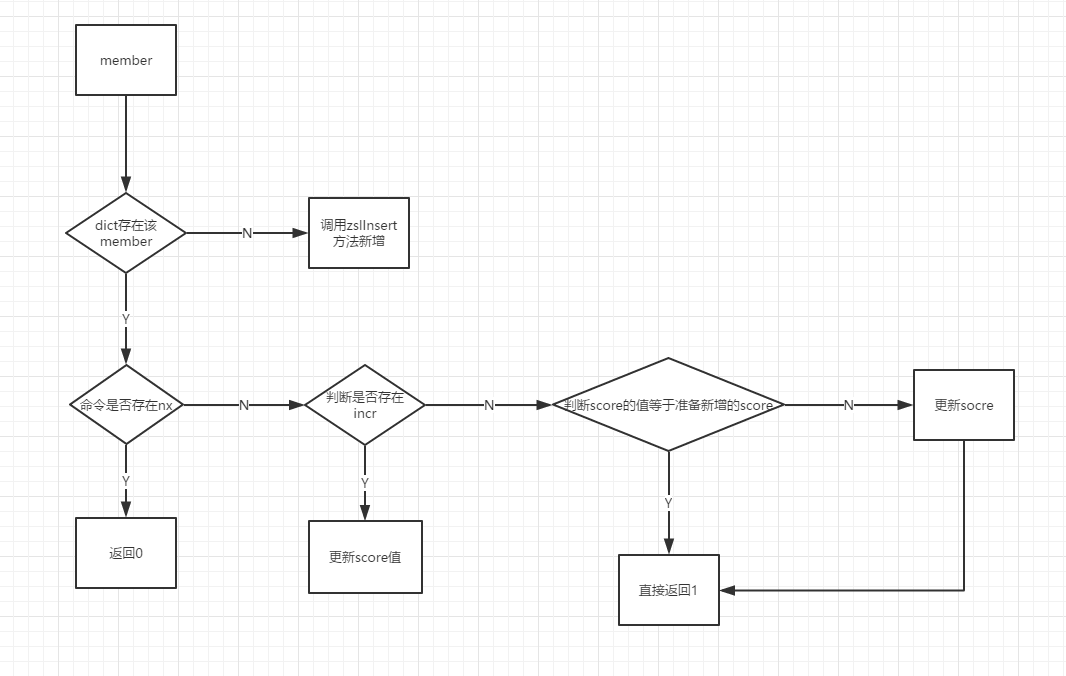
当我们在使用zrank key member的时候,zset是怎么实现的呢?让我们一起来看一下源码
long zsetRank(robj *zobj, sds ele, int reverse) {
unsigned long llen;
unsigned long rank;
llen = zsetLength(zobj);
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
//忽略掉 zipList查找过程
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplist *zsl = zs->zsl;
dictEntry *de;
double score;
de = dictFind(zs->dict,ele);
if (de != NULL) {
score = *(double*)dictGetVal(de);
rank = zslGetRank(zsl,score,ele);
/* Existing elements always have a rank. */
serverAssert(rank != 0);
if (reverse)
return llen-rank;
else
return rank-1;
} else {
return -1;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
}
}
/* Find the rank for an element by both score and key.
* Returns 0 when the element cannot be found, rank otherwise.
* Note that the rank is 1-based due to the span of zsl->header to the
* first element. */
unsigned long zslGetRank(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long rank = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) <= 0))) {
rank += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* x might be equal to zsl->header, so test if obj is non-NULL */
if (x->ele && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {
return rank;
}
}
return 0;
}
其实查找的时候跟上面插入流程是有很多地方享受的,获取用户的排名是通过累加的span。
应用场景
1.排行榜
2.存储社交关系
3.滑动窗口应用









