类型的检测——向上转型 向下转型
向上转型:父类对象的引用指向子类对象,向下转型:向上转型的基础上再次指向子类的对象
1.向上转型


package text5;
public class Father {
public void say(){
System.out.println("father say()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father son=new Son();
son.say();
}
}
class Son extends Father{
public void say(){
System.out.println("son say()");
}
}
View Code
有时候使用向上转型会丢掉子类特有的方法,


package text5;
public class Father {
public void say(){
System.out.println("father say()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father son=new Son();
son.sayMe();
}
}
class Son extends Father{
public void say(){
System.out.println("son say()");
}
public void sayMe(){
System.out.println("son sayMe");
}
}
View Code
2.向下转型(强转)注意强转的方法


package text5;
public class Father {
public void say() {
System.out.println("father say()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 向上转型
Father son = new Son();
son.say();
// 向下转型
Son son2 = (Son) son;
son2.sayMe();
}
}
class Son extends Father {
public void say() {
System.out.println("son say()");
}
public void sayMe() {
System.out.println("son sayMe");
}
}
View Code
动态绑定;


package text5;
public class Father {
public void say() {
System.out.println("father say()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 向上转型
Father son = new Son();
son.say();
}
}
class Son extends Father {
public void say() {
System.out.println("son say()");
}
public void sayMe() {
System.out.println("son sayMe");
}
}
View Code
静态绑定;!!!!


package text5;
public class Father {
private String name = "father";
public static void say() {
System.out.println("father say()");
}
public void say1() {
System.out.println("father say1()");
}
/// 主运行程序
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 向上转型
Father son = new Son();
System.out.println(son.name);
son.say1();
son.say();
Son f = (Son) son;
f.say();
f.say1();
}
}
class Son extends Father {
String name = "Son";
public static void say() {
System.out.println("son say()");
}
public void say1() {
System.out.println("son say1");
}
}
View Code
1.使用多态实现主人给宠物喂食:
2.使用多态实现主人领养宠物并与宠物玩耍
3.使用多态计算汽车租赁总租金
4.使用多态完善汽车租赁系统计价
父亲不能调用儿子的方法,需要强制转换
A.实现主人给宠物喂食:
Pet:


package Animal2;
public abstract class Pet {
private String name;
private int health;
private int love;
public Pet() {
}
public Pet(String name, int health, int love) {
this.name = name;
this.health = health;
this.love = love;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("宠物的自白:");
System.out.print("我的名字叫" + getName() + ",健康值是" + getHealth() + ",和主人的亲密度是" + getLove());
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getHealth() {
return health;
}
public void setHealth(int health) {
// 设置默认
if (health < 0 || health > 100)
health = 60;
this.health = health;
}
public int getLove() {
return love;
}
public void setLove(int love) {
if (love < 0 || love > 100)
love = 60;
this.love = love;
}
public abstract void eat();
}
View Code
Dog


package Animal2;
public class Dog extends Pet {
private String strain;
public Dog(String name, int health, int love) {
super(name, health, love);
// this.strain = strain;
}
public Dog(String name, int health, int love, String strain) {
super(name, health, love);
this.strain = strain;
}
// 接飞盘
public void getFrise() {
System.out.println("接飞盘啊");
}
public Dog() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("宠物的自白");
System.out.println("我的名字叫" + this.getName() + ",健康值是" + this.getHealth() + "和主人的亲密度是" + this.getLove()
+ ",我是一只酷酷的" + strain);
}
public String getStrain() {
return strain;
}
public void setStrain(int strain) {
if(strain==1){
this.strain = "拉布拉多";
}else this.strain="博美";
}
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(getHealth()==100){
System.out.println("狗狗已经饱了,不需要吃东西了。");
}else {
System.out.println("带狗狗去吃骨头......");
setHealth(getHealth() + 3);
System.out.println("狗狗的健康值为:"+getHealth());
}
}
}
View Code
Penguin


package Animal2;
public class Penguin extends Pet {
String sex;
public Penguin(String name, int health, int love, String sex) {
super(name, health, love);
this.sex = sex;
}
public Penguin(String name, int health, int love) {
super(name, health, love);
// this.sex=sex;
}
public Penguin() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public void swim() {
System.out.println("会游泳啊");
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("宠物的自白");
System.out.println(
"我的名字叫" + this.getName() + ",健康值是" + this.getHealth() + "和主人的亲密度是" + this.getLove() + ",性别是" + sex);
}
public void setSex(int sex) {
if (sex == 1) {
this.sex = "Q仔";
return;
}
this.sex = "Q妹";
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (getHealth() == 100) {
System.out.println("企鹅已经饱了,不需要吃东西了。");
} else {
System.out.println("带企鹅去吃骨头......");
setHealth(getHealth() + 5);
System.out.println("qie的健康值为:" + getHealth());
}
}
}
View Code
Master:


package Animal2;
//主人与宠物玩
public class Master {
public void play(Pet pet) {
if (pet instanceof Dog) {
Dog dog = (Dog) pet;
dog.getFrise();
} else if (pet instanceof Penguin) {
Penguin pen = (Penguin) pet;
pen.swim();
}
}
// 喂食物
public void feed(Pet pet) {
if (pet instanceof Dog) {
Dog dog = (Dog) pet;
dog.eat();
} else if (pet instanceof Penguin) {
Penguin penguin = (Penguin) pet;
penguin.eat();
}
}
}
View Code
Test:


package Animal2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Master master=new Master();
Pet dog=new Dog();
dog.setName("黑比");
dog.setLove(68);
dog.setHealth(0);
((Dog) dog).setStrain(1);//儿子的调用强转
master.feed(dog);
dog.print();
System.out.println("*********************");
Pet penguin=new Penguin();
penguin.setName("QQ");
penguin.setHealth(100);
penguin.setLove(76);
((Penguin) penguin).setSex(1);//儿子的调用
penguin.print();
}
}
View Code
B.使用多态实现汽车总租金
首先定义一个机动车抽象类,
Vehicle:


package Car;
/**
* 汽车抽象类
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public abstract class Vehicle {
private String no;
private String brand;
// 有参构造
public Vehicle(String no, String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
this.no = no;
}
// 抽象方法,计算汽车租赁价格
public abstract int cale(int days);
// 自动获取的方法
public String getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(String no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
}
View Code
Bus;


package Car;
public class Bus extends Vehicle {
private int seat;// 座位数
// 构造不要忘了
public Bus(String no, String brand, int seat) {
super(no, brand);// 自动
this.seat = seat;
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public int cale(int days) {
if (seat < 16)
return days * 800;
else
return days * 1500;
}
public int getSeat() {
return seat;
}
public void setSeat(int seat) {
this.seat = seat;
}
}
View Code
Car:


package Car;
/**
* 轿车类
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Car extends Vehicle {
private String type;// 汽车型号
public Car(String no, String brand, String type) {
super(no, brand);
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public int cale(int days) {
if ("1".equals(type)) {// 代表550i
return days * 500;
} else if ("2".equals(type)) {
return days * 600;
} else
return 300 * days;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
View Code
Truck:


package Car;
/**
* 计算总的租价
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public final class Truck extends Vehicle {
int ton;// 吨位
public Truck(String no, String brand, int ton) {
super(no, brand);
this.ton = ton;
}
@Override
public int cale(int days) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return days * ton;
}
}
View Code
Customer:


package Car;
public class Customer {
private String id;
private String name;
public Customer(String id,String name){
this.name=name;
this.id=id;
}
public int calcTotalRent(Vehicle motos[],int days){
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<motos.length;i++)
sum+=motos[i].cale(days);
return sum;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
View Code
Test:


package Car;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int days;// 租赁天数
int totalRent;// 总租赁费用
Vehicle motos[] = new Vehicle[5];
motos[0] = new Car("宝马x5", "豫DX56432", "1");
motos[1] = new Car("宝马x6", "豫DX51112", "2");
motos[2] = new Car("金龙", "豫DX99832", "3");
motos[3] = new Bus("别克林荫大道", "豫DX99832", 34);
motos[4] = new Truck("比亚迪", "豫DX99832", 8);
// 控制台输入
// 1、客户租赁的多辆汽车信息及租赁天数
Customer customer = new Customer("1", "万方");
// 2、计算总租赁费用
System.out.println("总租金为:" + customer.calcTotalRent(motos, 5));
}
}
View Code
案例一:
Animal:


package text2;
public class Animal {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void cry(){
System.out.println("不知道怎么叫");
}
}
View Code
Cat:


package text2;
public class Cat extends Animal{
public void cry(){
System.out.println("喵喵叫");
}
}
View Code
Dog;


package text2;
public class Dog extends Animal{
public void cry(){
System.out.println("汪汪叫");
}
}
View Code
Test:


package text2;
public class Tset {
public static void main(String[] args){
Cat cat=new Cat();
cat.cry();
Dog dog=new Dog();
dog.cry();
Animal an=new Cat();
an.cry();
an=new Dog();
an.cry();
}
}
View Code
案例二;
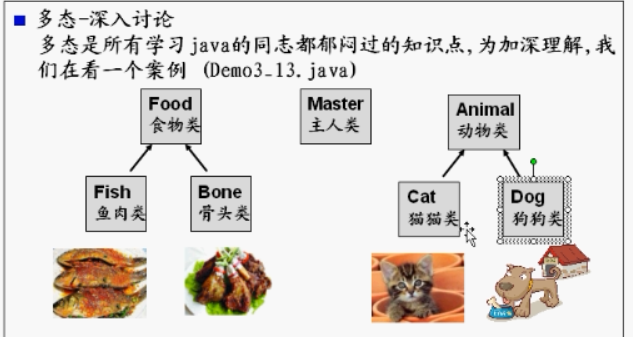
Animal:


package text2;
public class Animal {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void cry(){
System.out.println("不知道怎么叫");
}
public void eat(){
}
}
View Code
Cat;


package text2;
public class Cat extends Animal{
public void cry(){
System.out.println("喵喵叫");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("猫喜欢吃鱼");
}
}
View Code
Dog:


package text2;
public class Dog extends Animal{
public void cry(){
System.out.println("汪汪叫");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("狗喜欢吃骨头");
}
}
View Code
Food;


package text2;
public class Food {
String name;
public void showname(){
}
}
View Code
Fish:
Bone;


package text2;
public class Bone extends Food{
public void showname(){
System.out.println("我是骨头");
}
}
View Code
MAster:


package text2;
public class Master {
//给动物喂食物
public void feed(Animal an,Food f)//灵活
{
an.eat();
f.showname();
}
}
View Code
Test;


package text2;
public class Tset {
public static void main(String[] args){
Master master=new Master();
master.feed(new Dog(), new Bone());
}
}
View Code